Android Studio 3.0 (October 2017)
Android Studio 3.0.0 is a major release that includes a variety of new features and improvements.
macOS users: If you are updating an older version of Android Studio, you may encounter an update error dialog that says "Some conflicts were found in the installation area". Simply ignore this error and click Cancel to resume the installation.
3.0.1 (November 2017)
This is a minor update to Android Studio 3.0 that includes general bug fixes and performance improvements.
Android Plugin for Gradle 3.0.0
The new Android plugin for Gradle includes a variety of improvements and new features, but it primarily improves build performance for projects that have a large number of modules. When using the new plugin with these large projects, you should experience the following:
- Faster build configuration times due to new delayed dependency resolution.
- Variant-aware dependency resolution for only the projects and variants you are building.
- Faster incremental build times when applying simple changes to code or resources.
Note: These improvements required significant changes that break some of the plugin's behaviors, DSL, and APIs. Upgrading to version 3.0.0 might require changes to your build files and Gradle plugins.
This version also includes the following:
- Support for Android 8.0.
- Support for building separate APKs based on language resources.
- Support for Java 8 libraries and Java 8 language features (without the Jack compiler).
- Support for Android Test Support Library 1.0 (Android Test Utility and Android Test Orchestrator).
- Improved ndk-build and cmake build speeds.
- Improved Gradle sync speed.
- AAPT2 is now enabled by default.
- Using
ndkCompileis now more restricted. You should instead migrate to using either CMake or ndk-build to compile native code that you want to package into your APK. To learn more, read Migrate from ndkcompile.
For more information about what's changed, see the Android Plugin for Gradle release notes.
If you're ready to upgrade to the new plugin, see Migrate to Android Plugin for Gradle 3.0.0.
Kotlin support
As announced at Google I/O 2017, the Kotlin programming language is now officially supported on Android. So with this release, Android Studio includes Kotlin language support for Android development.
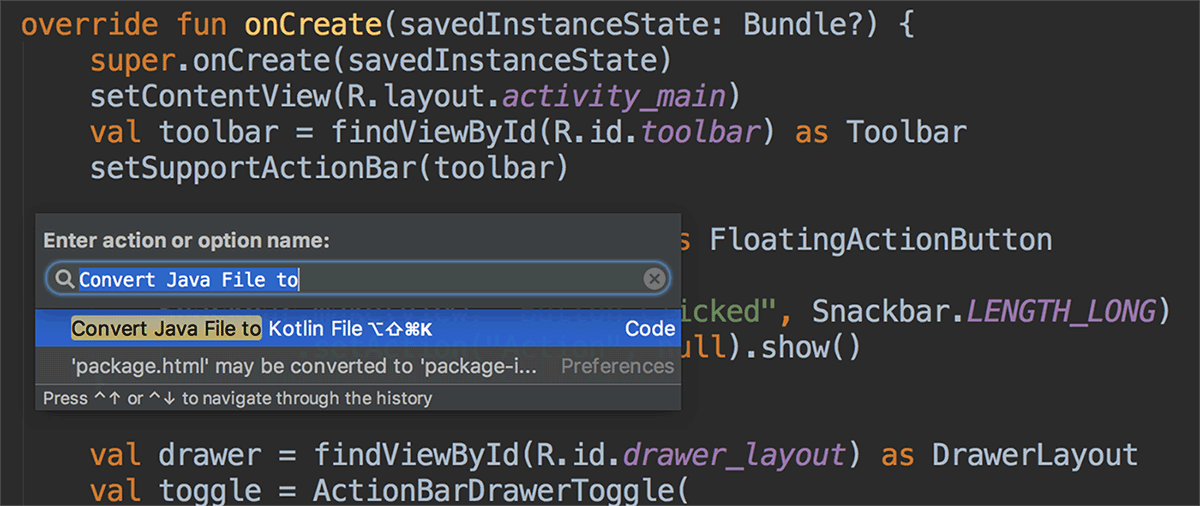
You can incorporate Kotlin into your project by converting a Java file to Kotlin (click Code > Convert Java File to Kotlin File) or by creating a new Kotlin- enabled project using the New Project wizard.
To get started, read how to add Kotlin to your project.
Java 8 language features support
You can now use certain Java 8 language features and consume libraries built with Java 8. Jack is no longer required, and you should first disable Jack to use the improved Java 8 support built into the default toolchain.
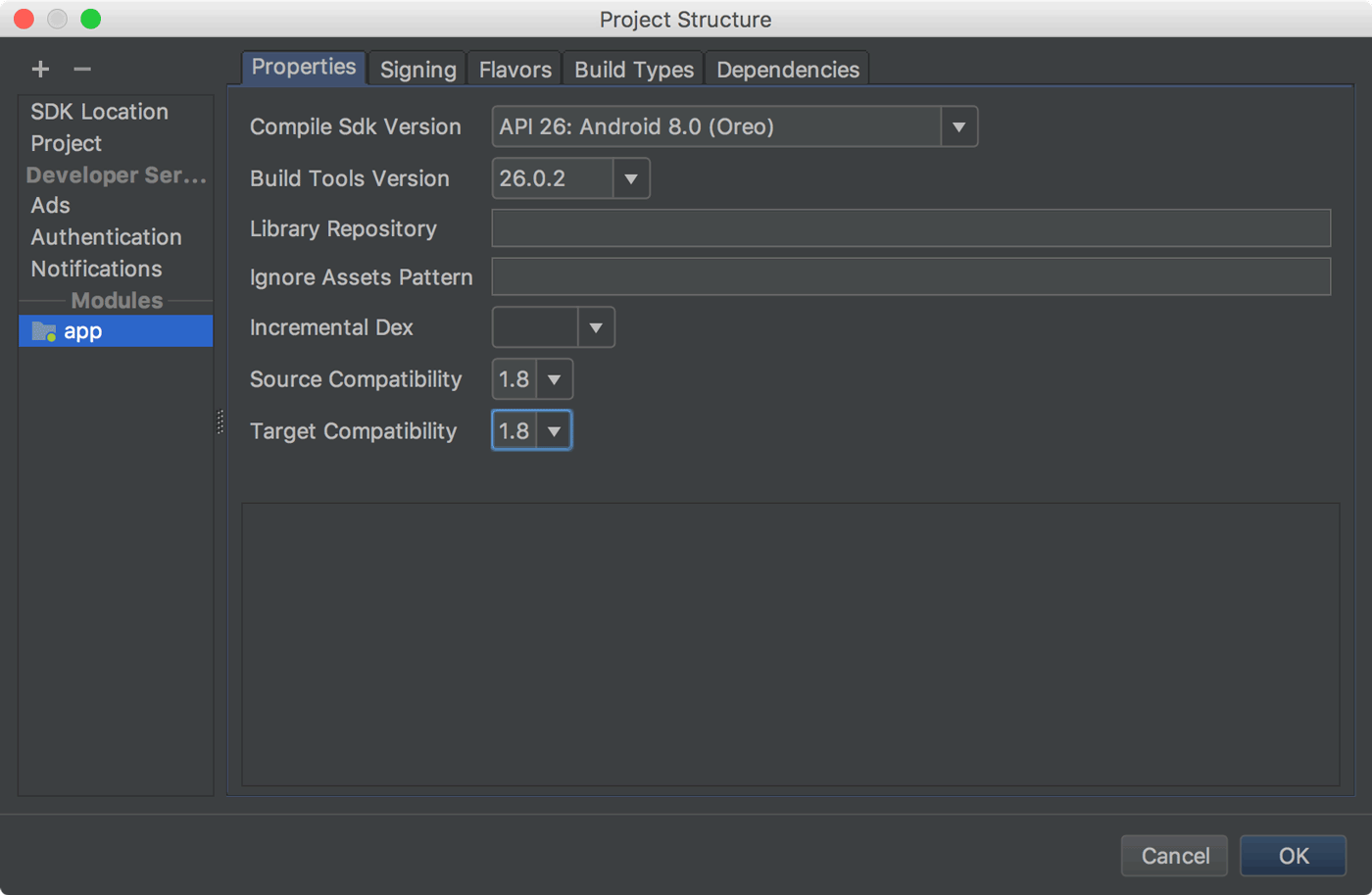
To update your project to support the new Java 8 language toolchain, update the Source Compatibility and Target Compatibility to 1.8 in the Project Structure dialog (click File > Project Structure). To learn more, read how to use Java 8 language features.
Android Profiler
The new Android Profiler replaces the Android Monitor tool and provides a new suite of tools to measure your app's CPU, memory, and network usage in realtime. You can perform sample-based method tracing to time your code execution, capture heap dumps, view memory allocations, and inspect the details of network-transmitted files.
To open, click View > Tool Windows > Android Profiler (or click Android Profiler in the toolbar).
The event timeline at the top of the window shows touch events, key presses, and activity changes so you have more context to understand other performance events in the timeline.
Note: The Logcat view also moved to a separate window (it was previously inside Android Monitor, which was removed).
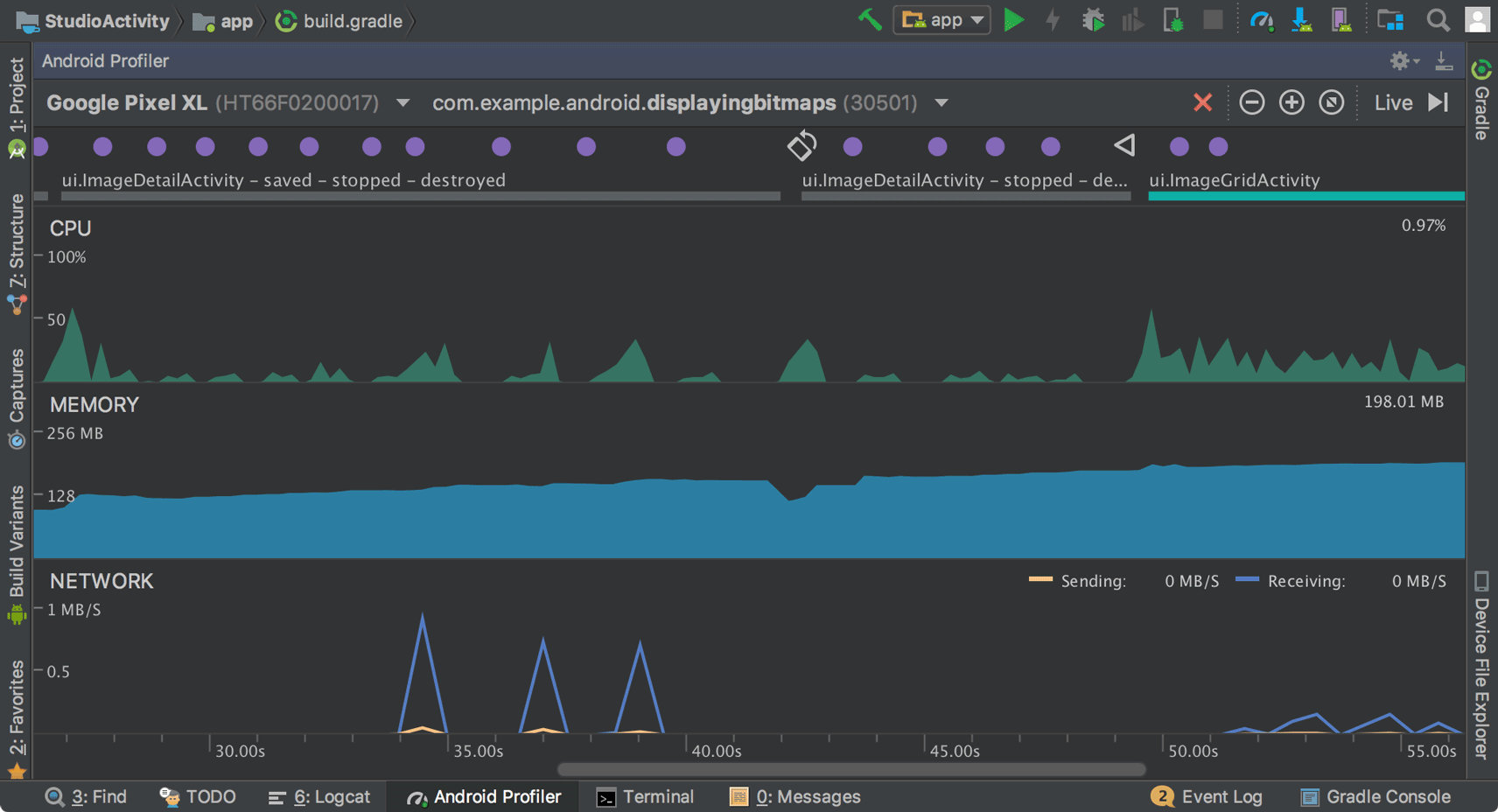
From the Android Profiler's overview timeline, click on the CPU, MEMORY, or NETWORK timelines to access the corresponding profiler tools.
CPU Profiler
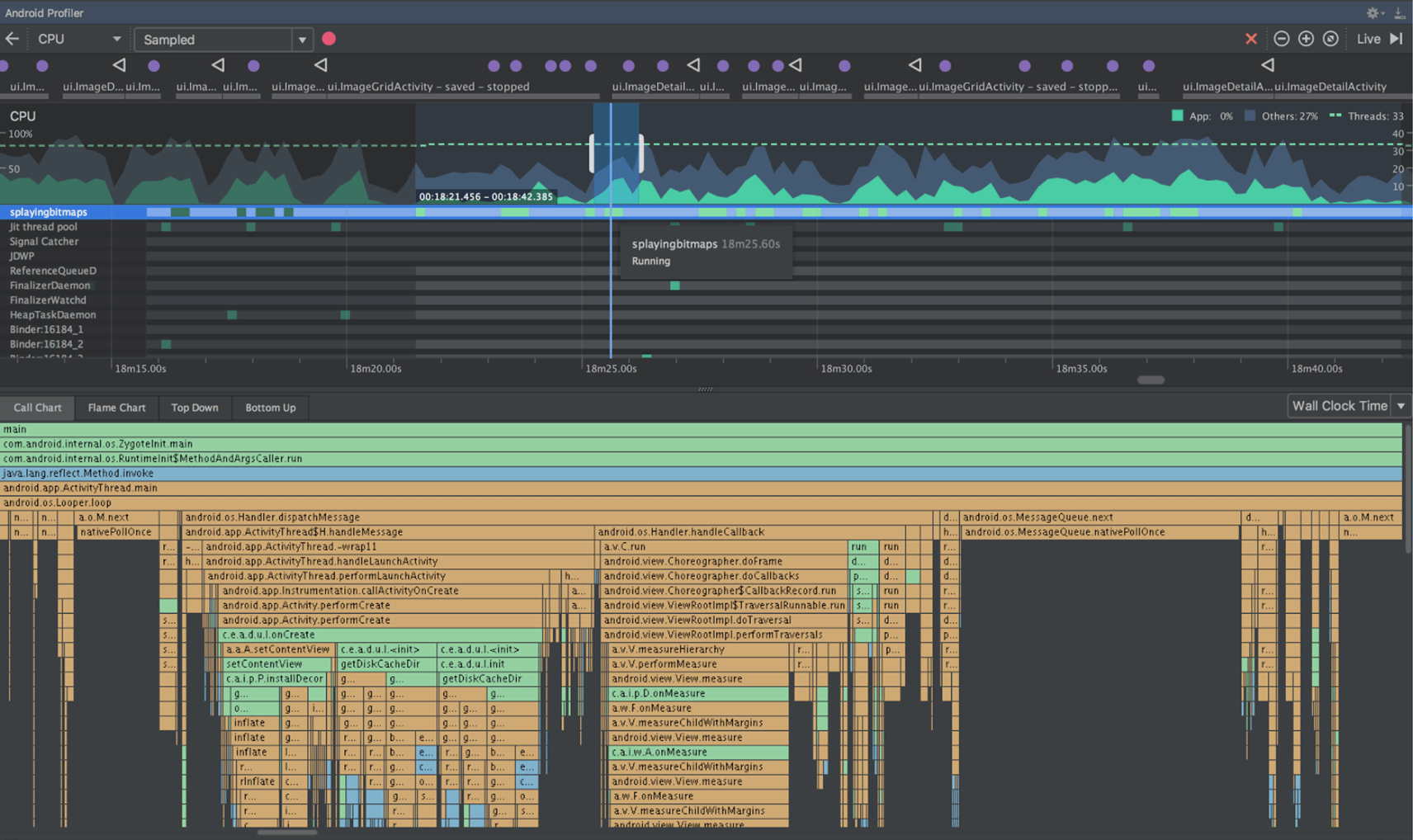
The CPU Profiler helps you analyze the CPU thread usage of your app by triggering a sample or instrumented CPU trace. Then, you can troubleshoot CPU performance issues using a variety of data views and filters.
For more information, see the CPU Profiler guide.
Memory Profiler
The Memory Profiler helps you identify memory leaks and memory churn that can lead to stutter, freezes, and even app crashes. It shows a realtime graph of your app's memory use, lets you capture a heap dump, force garbage collections, and track memory allocations.
For more information, see the Memory Profiler guide.
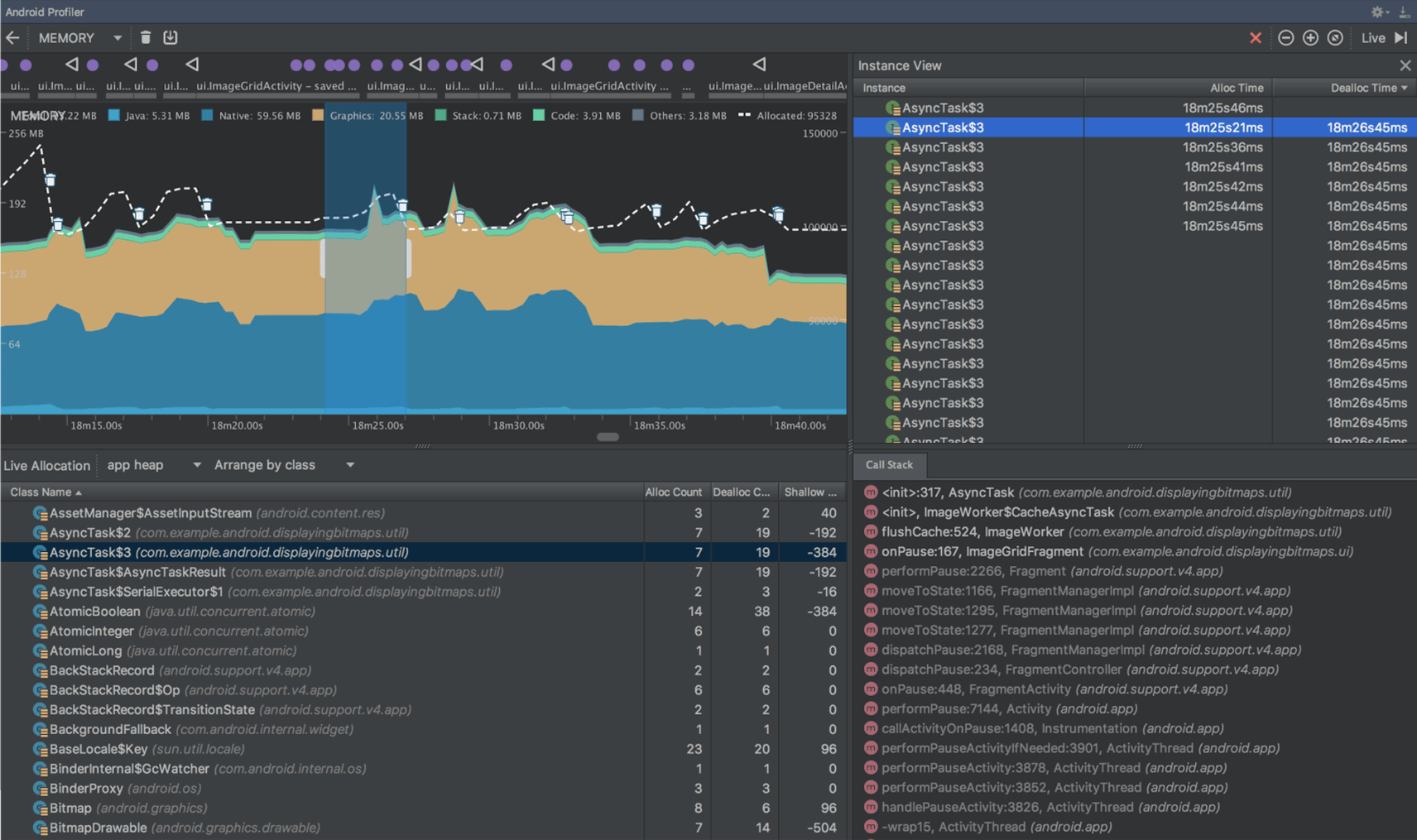
Network Profiler
The Network Profiler allows you to monitor the network activity of your app, inspect the payload of each of your network requests, and link back to the code that generated the network request.
For more information, see the Network Profiler guide.
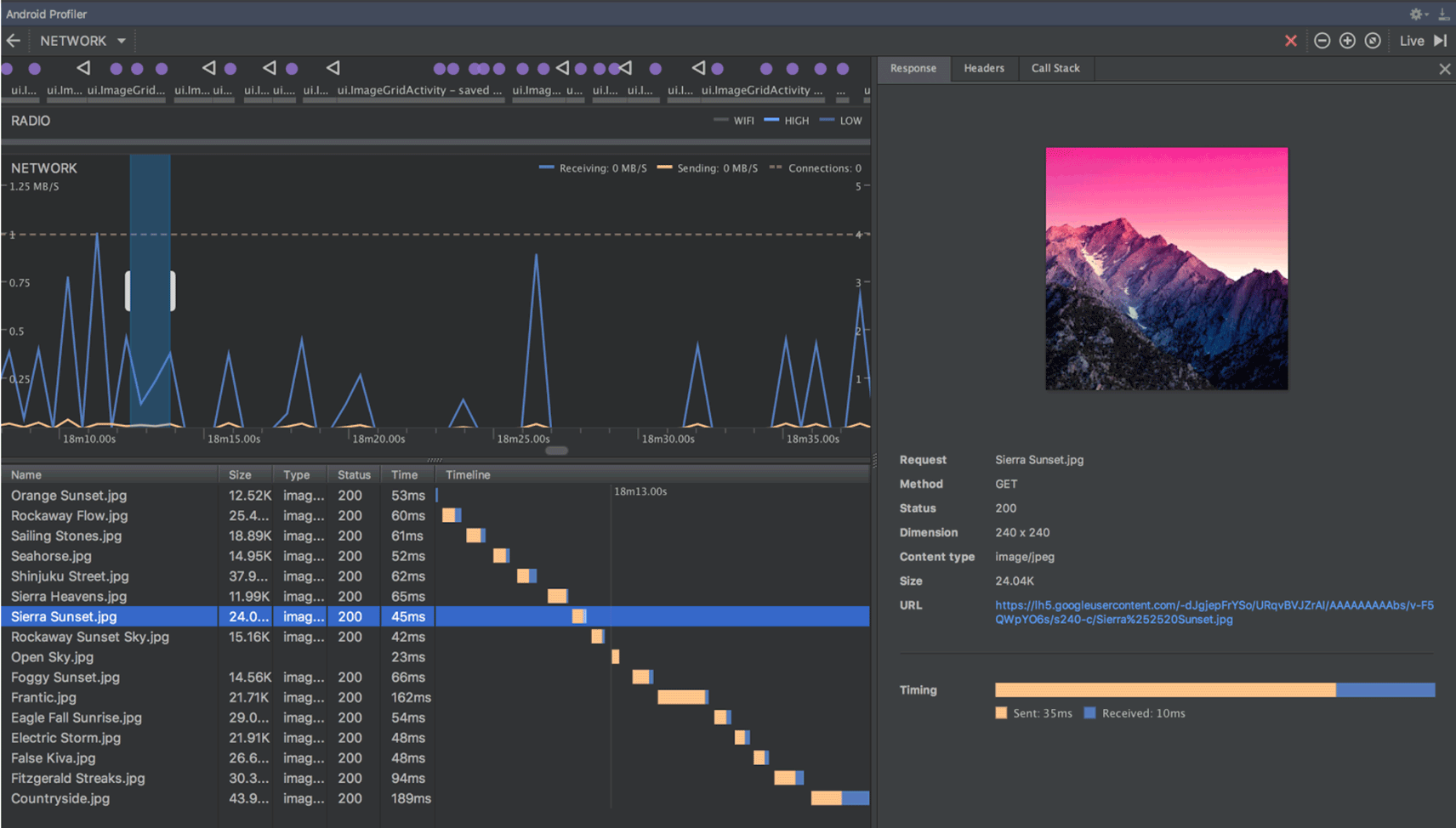
APK profiling and debugging
Android Studio now allows you to profile and debug any APK without having to build it from an Android Studio project—as long as the APK is built to enable debugging and you have access to the debug symbols and source files.
To get started, click Profile or debug APK from the Android Studio Welcome screen. Or, if you already have a project open, click File > Profile or debug APK from the menu bar. This displays the unpacked APK files, but it does not decompile the code. So, to properly add breakpoints and view stack traces, you need to attach Java source files and native debug symbols.
For more information, see Profile and Debug Pre-built APKs.
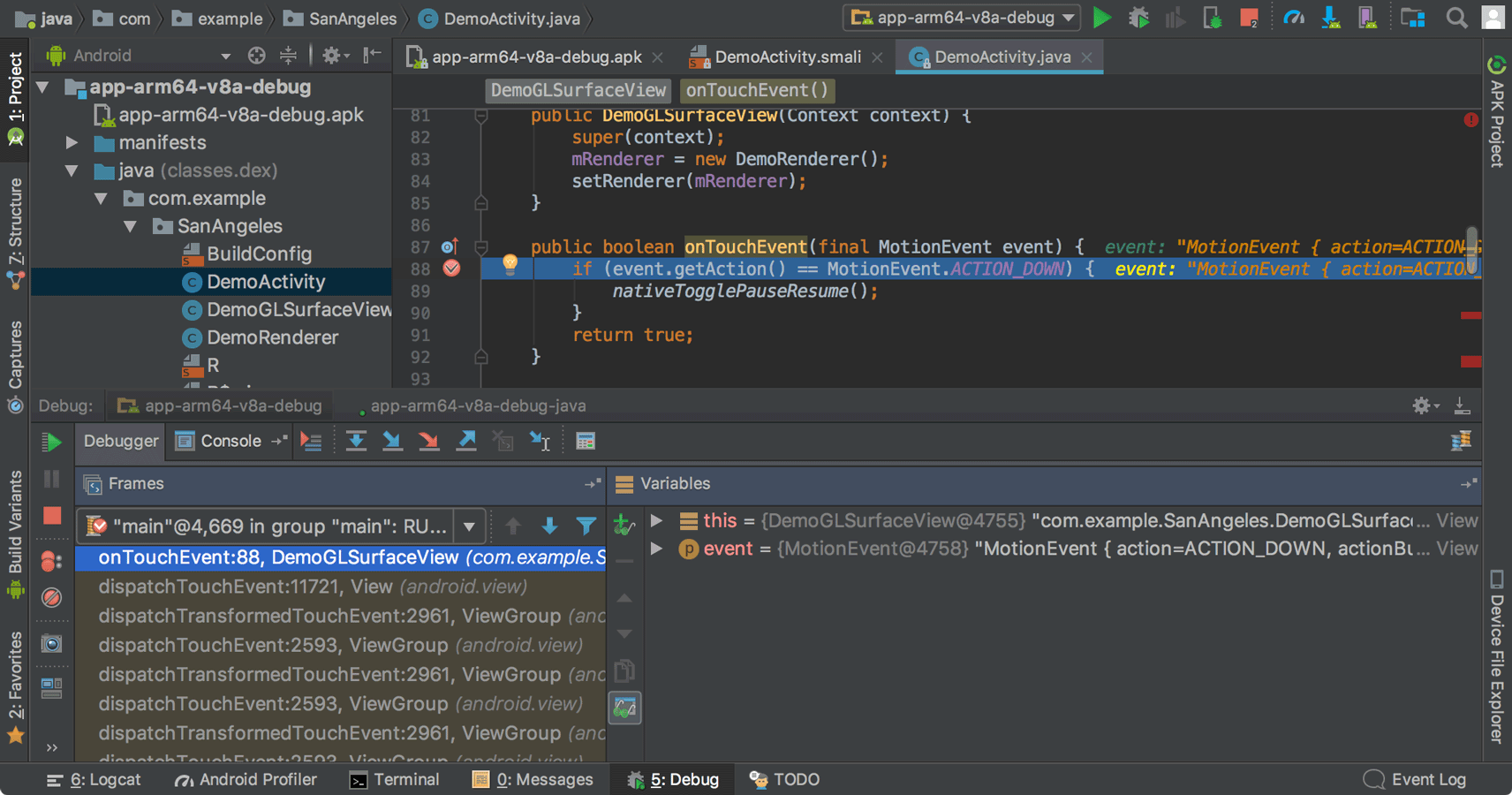
Device File Explorer
The new Device File Explorer allows you to inspect your connected device's filesystem, and transfer files between the device and your computer. This replaces the filesystem tool available in DDMS.
To open, click View > Tool Windows > Device File Explorer.
For more information, see the Device File Explorer guide.
Instant Apps support
New support for Android Instant Apps allows you to create Instant Apps in your project using two new module types: Instant App modules and Feature modules (these require that you install the Instant Apps Development SDK).
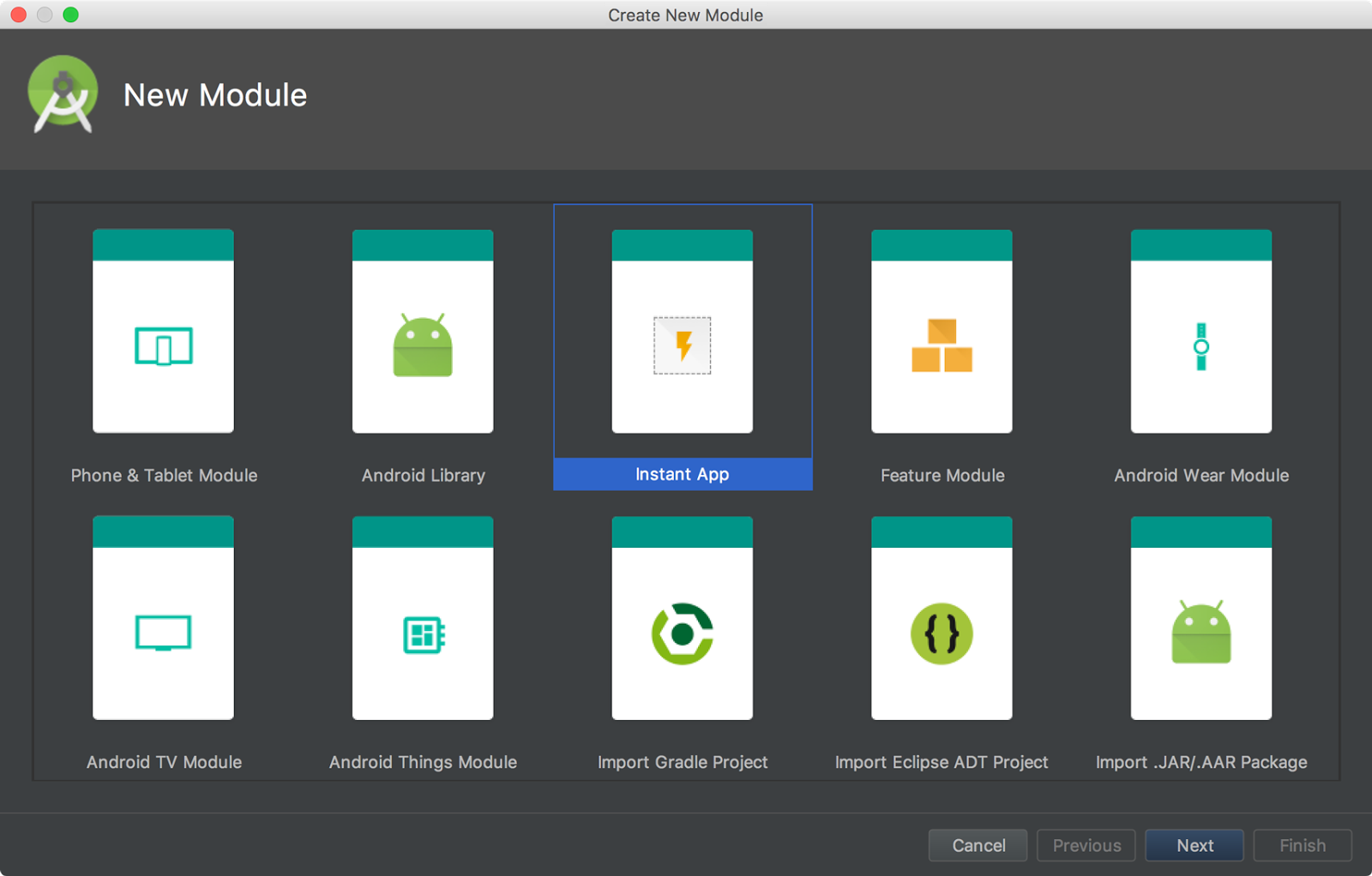
Android Studio also includes a new modularize refactoring action to help you add support for Instant Apps in an existing project. For example, if you want to refactor your project to place some classes in an Instant App feature module, select the classes in the Project window and click Refactor > Modularize. In the dialog that appears, select the module where the classes should go and click OK.
And when you're ready to test your Instant App, you can build and run your Instant App module on a connected device by specifying the Instant App's URL within the run configuration launch options: Select Run > Edit Configurations, select your Instant App module, and then set the URL under Launch Options.
For more information, see Android Instant Apps.
Android Things modules
New Android Things templates in the New Project and New Module wizards to help you start developing for Android-powered IOT devices.
For more information, see how to create an Android Things project.
Adaptive Icons wizard
Image Asset Studio now supports vector drawables and allows you to create adaptive launcher icons for Android 8.0 while simultaneously creating traditional icons ("Legacy" icons) for older devices.
To start, right-click on the res folder in your project, and then click New > Image Asset. In the Asset Studio window, select Launcher Icons (Adaptive and Legacy) as the icon type.
Note: You must set compileSdkVersion to 26 or higher to use adaptive launcher
icons.
For more information, read about Adaptive Icons.
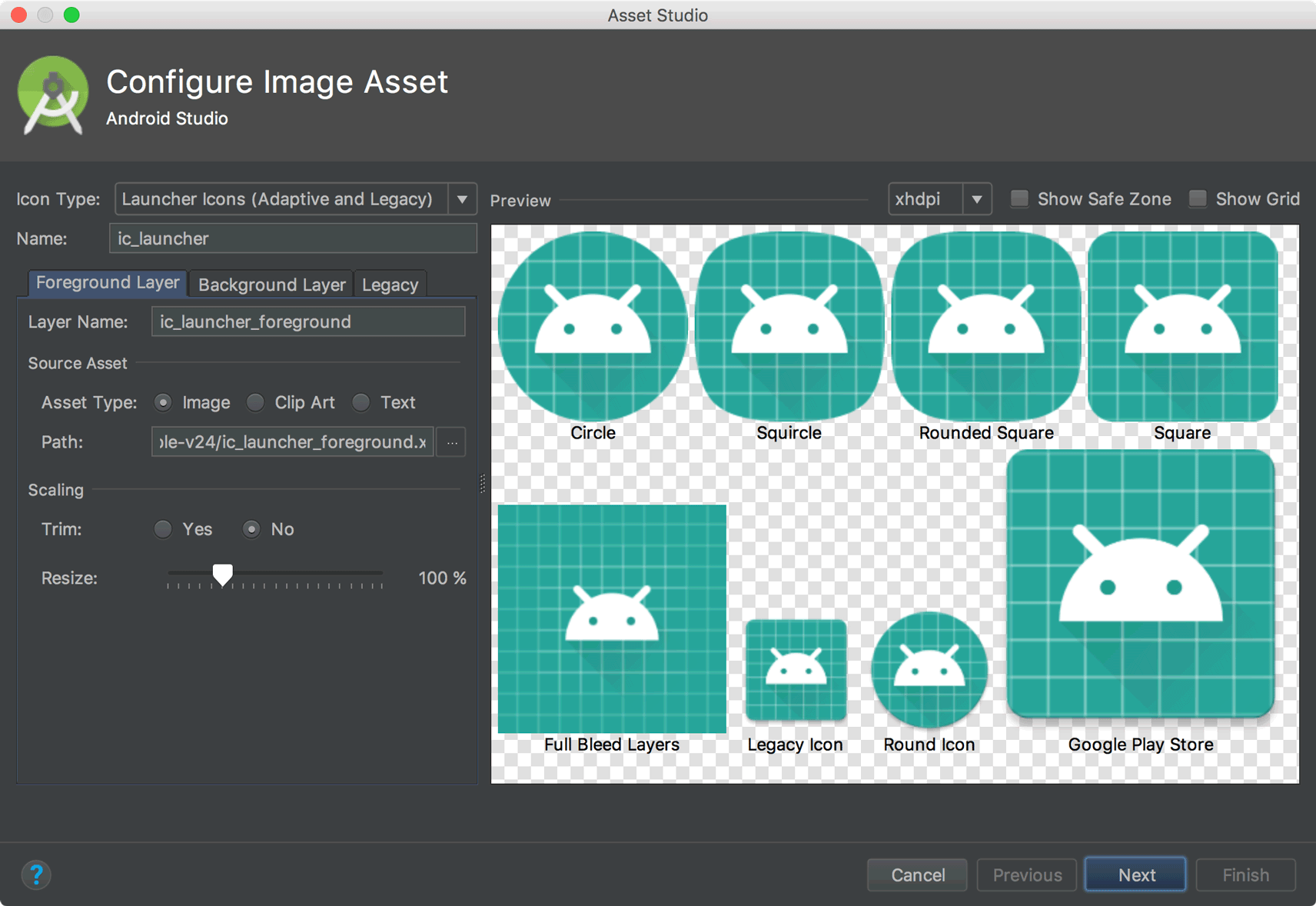
Support for font resources
To support the new font resources in Android 8.0, Android Studio includes a font resources selector to help bundle fonts into your app or configure your project to download the fonts on the device (when available). The layout editor can also preview the fonts in your layout.
To try downloadable fonts, ensure that your device or emulator is running Google Play Services v11.2.63 or higher. For more information, read about Downloadable Fonts.
Firebase App Indexing Assistant
The Firebase Assistant has been updated with a new tutorial to test App Indexing. To open the Assistant, select Tools > Firebase. Then select App Indexing > Test App Indexing.
The tutorial includes new buttons to test your public and personal content indexing:
- In step 2, click Preview search results to verify that your URLs are showing up in Google Search results.
- In step 3, click Check for errors to verify that the indexable objects in your app have been added to the personal content index.
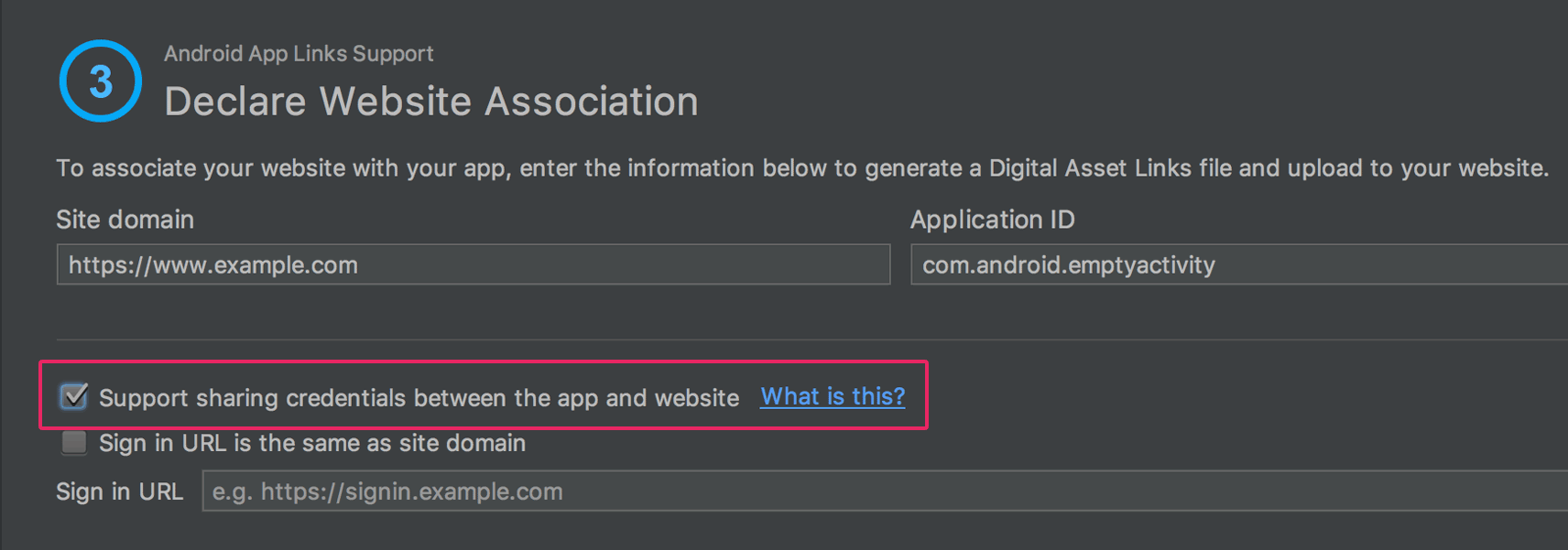
Android App Links Assistant
The App Links Assistant has been updated with the following new capabilities:
-
Add URL tests for each URL mapping to be sure your intent filters handle real-world URLs.
You can also define these URL tests by hand using the
<tools:validation>tag described below. -
Create a Digital Asset Links file with the appropriate object entry to support Google Smart Lock, and add the corresponding
asset_statements<meta-data>tag to your manifest file.
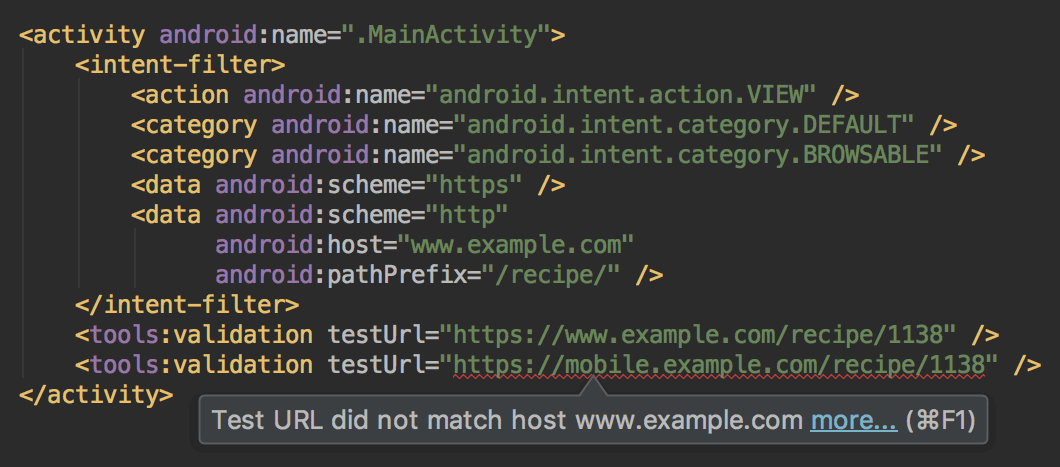
URL intent-filter validator
Android Studio now supports a special tag in the manifest file that allows you to test your intent filter URLs. These are the same tags that the App Links Assistant can create for you.
To declare a test URL
for an intent filter, add a <tools:validation> element alongside the
corresponding <intent-filter> element. For example:
<activity ...>
<intent-filter>
...
</intent-filter>
<tools:validation testUrl="https://www.example.com/recipe/1138" />
</activity>
Be sure to also include xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" in
the <manifest> tag.
If any one of the test URLs does not pass the intent filter definition, a lint error appears. Such an error still allows you to build debug variants, but it will break your release builds.
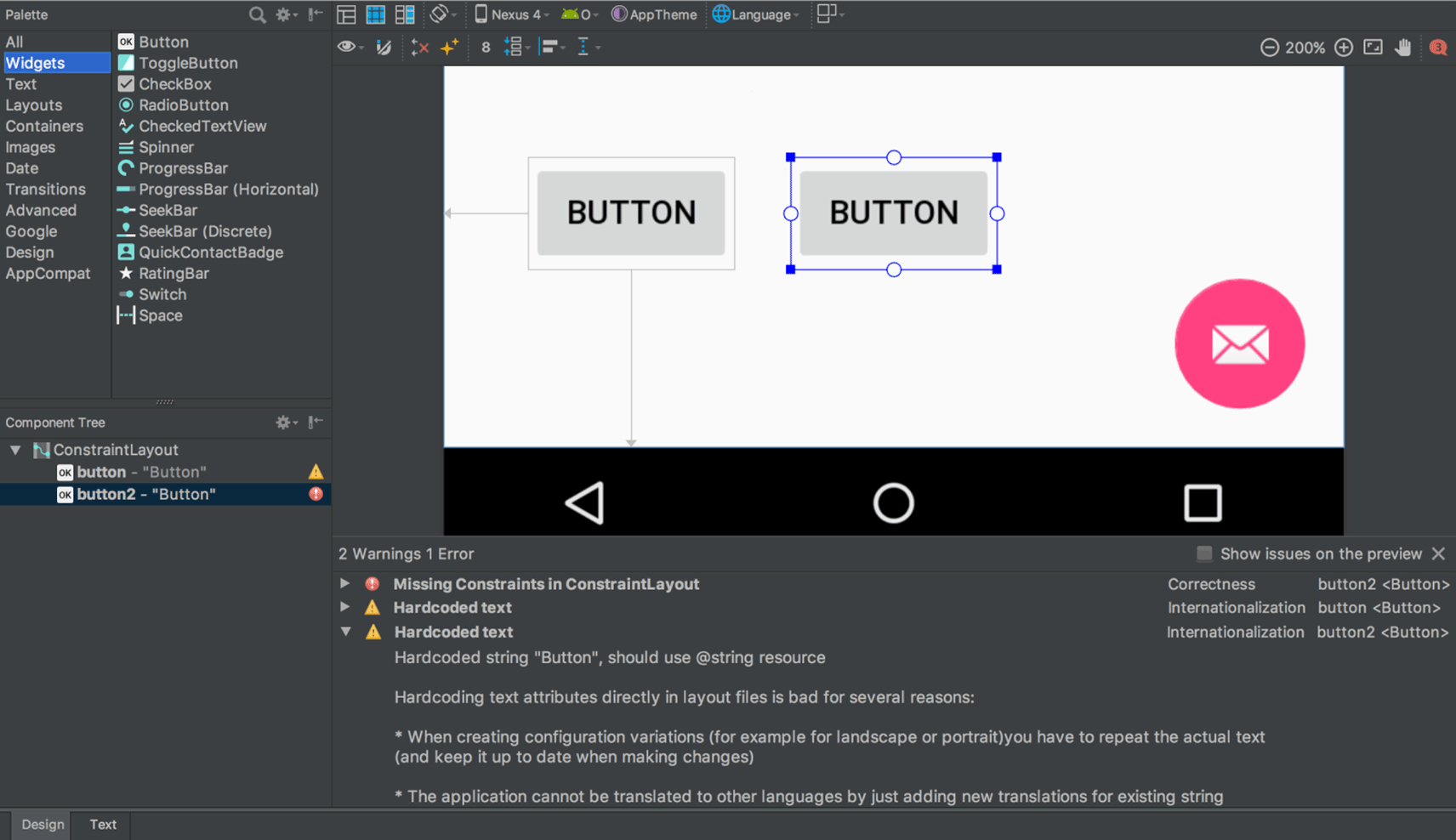
Layout Editor
The Layout Editor has been updated with a number of enhancements, including the following:
- New toolbar layout and icons.
- Updated layout in the component tree.
- Improved drag-and-drop view insertions.
- New error panel below the editor, showing all issues with suggestions to fix (if available).
- Various UI enhancements for building with
ConstraintLayout, including the following:- New support to create barriers.
- New support to create groups: In the toolbar, select Guidelines > Add Group (requires ConstraintLayout 1.1.0 beta 2 or higher)
- New UI to create chains: Select multiple views, and then right-click and select Chain.
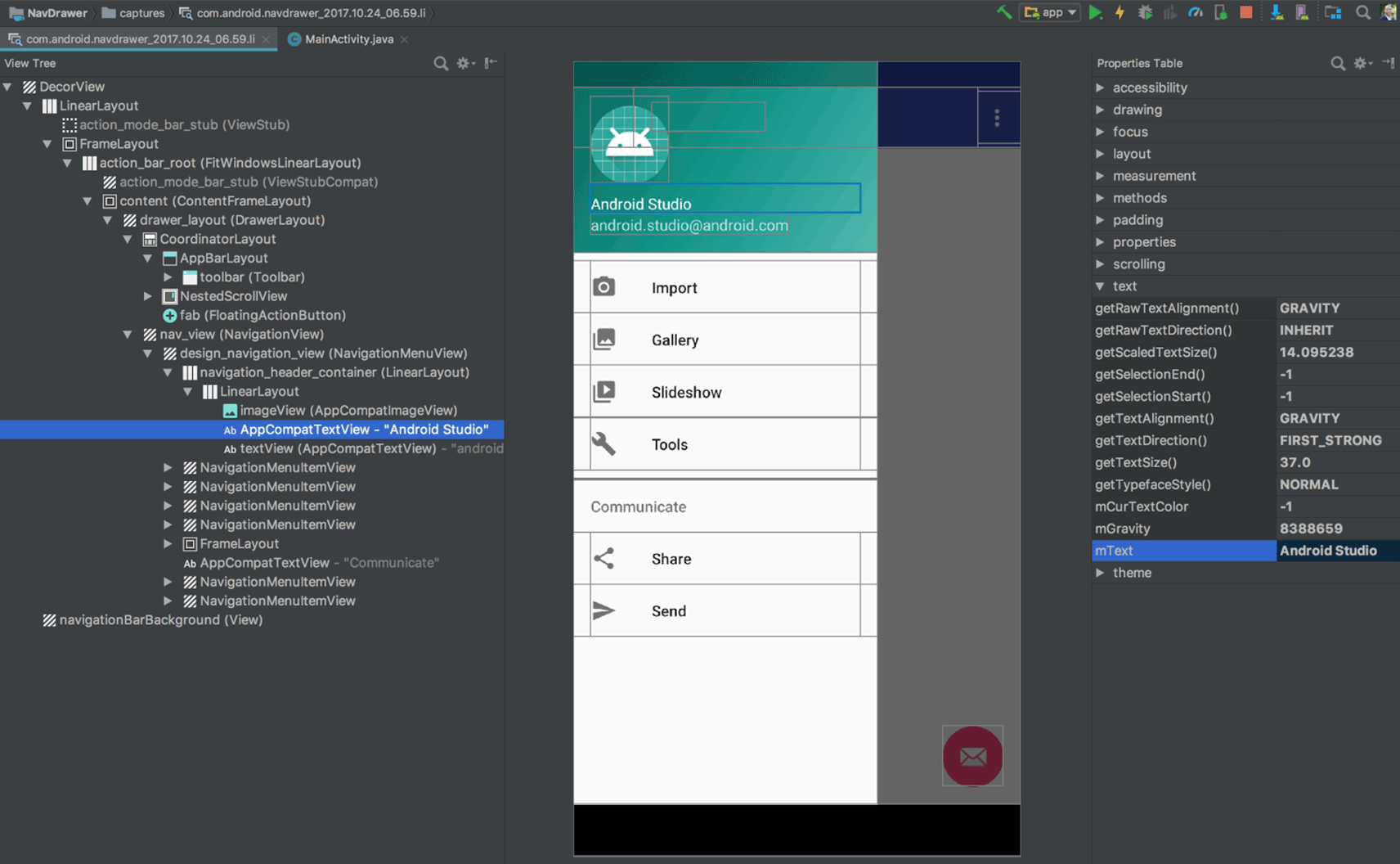
Layout Inspector
The Layout Inspector includes enhancements to make it easier to debug issues with your app layouts, including grouping properties into common categories and new search functionality in both the View Tree and the Properties panes.
APK Analyzer
You can now use the APK Analyzer from the command line with the
apkanalyzer tool.
The APK Analyzer has also been updated with the following improvements:
- For APKs built with ProGuard, you can load ProGuard mapping files that add
capabilities to the DEX viewer, including:
- Bolded nodes to indicate that the nodes should not be removed when shrinking code.
- A button to show nodes that were removed during the shrinking process.
- A button that restores the original names of nodes in the tree view that were obfuscated by ProGuard.
- The DEX Viewer now shows the estimated size impact of each package, class and method.
- New filtering options at the top to show and hide fields and methods.
- In the tree view, nodes that are references not defined in the DEX file appear in italics.
For more information, see Analyze Your Build with APK Analyzer.
Preview for D8 DEX compiler
Android Studio 3.0 includes an optional new DEX compiler called D8. It will eventually replace the DX compiler, but you can opt-in to use the new D8 compiler now.
DEX compilation directly impacts your app's build time, .dex file
size, and runtime performance. And when comparing the new D8 compiler with the
current DX compiler, D8 compiles faster and outputs smaller .dex files, while
having the same or better app runtime performance.
To try it, set the following in your project's gradle.properties file:
android.enableD8=true
For more information, see the blog post about the D8 compiler.
Google's Maven repository
Android Studio now uses Google’s Maven Repository by default instead of depending on the Android SDK Manager to get updates for Android Support Library, Google Play Services, Firebase, and other dependencies. This makes it easier to keep your libraries up to date, especially when using a continuous integration (CI) system.
All new projects now include the Google Maven repository by default. To update
your existing project, add google() in the repositories block of the
top-level build.gradle file:
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
}
}
Learn more about Google's Maven repository here.
Other changes
- Native debugging with Android Studio no longer supports 32-bit Windows. We've chosen to focus on other platforms because very few developers are using this platform. If you are using 32-bit Windows and you plan to debug native code, you should keep using Android Studio 2.3.
- Upgraded the base IDE to IntelliJ 2017.1.2, which adds a number of new features from 2016.3 and 2017.1, such as Java 8 language refactoring, parameter hints, semantic highlighting, draggable breakpoints, instant results in search, and much more.
- Added many new lint checks.
- Also see the latest Android Emulator updates.
