Android 15에는 개발자를 위한 훌륭한 기능과 API가 도입되었습니다. 다음 섹션에서는 관련 API를 시작하는 데 도움이 되도록 이러한 기능을 요약합니다.
추가된 API, 수정된 API, 삭제된 API에 관한 자세한 목록은 API 차이점 보고서를 참고하세요. 추가된 API에 관한 자세한 내용은 Android API 참조를 참고하세요. Android 15의 경우 API 수준 35에 추가된 API를 찾아보세요. 플랫폼 변경이 앱에 영향을 줄 수 있는 분야에 관해 알아보려면 Android 15를 타겟팅하는 앱 및 모든 앱의 Android 15 동작 변경사항을 확인해야 합니다.
카메라 및 미디어
Android 15에는 카메라 및 미디어 환경을 개선하고 크리에이터가 Android에서 자신의 비전을 실현할 수 있도록 지원하는 도구와 하드웨어에 액세스할 수 있는 다양한 기능이 포함되어 있습니다.
Android 미디어 및 카메라의 최신 기능과 개발자 솔루션에 관한 자세한 내용은 Google I/O의 최신 Android 미디어 및 카메라 환경 빌드 강연을 참고하세요.
어두운 조명 모드
Android 15에서는 Camera 2와 야간 모드 카메라 확장 프로그램에서 모두 사용할 수 있는 자동 노출 모드인 어두운 조명 모드를 도입합니다. 어두운 조명 모드는 저조도 환경에서 미리보기 스트림의 노출을 조정합니다. 야간 모드는 연속 촬영한 사진을 결합하여 하나의 향상된 이미지를 만들기 때문에 야간 모드 카메라 확장 프로그램이 정지 이미지를 만드는 방식과는 다릅니다. 야간 모드는 정지 이미지를 만드는 데 매우 효과적이지만 연속 프레임 스트림을 만들 수는 없습니다. 하지만 저조도 부스트는 가능합니다. 따라서 저조도 부스트를 사용하면 다음과 같은 카메라 기능을 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 사용자가 저조도 사진을 더 잘 찍을 수 있도록 향상된 이미지 미리보기를 제공합니다.
- 저조도에서 QR 코드 스캔
어두운 조명 모드를 사용 설정하면 조명이 어두울 때 자동으로 켜지고 밝을 때는 꺼집니다.
앱은 저조도 환경에서 미리보기 스트림을 녹화하여 밝기가 향상된 동영상을 저장할 수 있습니다.
자세한 내용은 저조도 부스트를 참고하세요.
인앱 카메라 컨트롤
Android 15 adds an extension for more control over the camera hardware and its algorithms on supported devices:
- Advanced flash strength adjustments enabling precise control of flash
intensity in both
SINGLEandTORCHmodes while capturing images.
HDR 헤드룸 제어
Android 15는 기본 기기 기능과 패널의 비트 심도에 적합한 HDR 헤드룸을 선택합니다. 단일 HDR 썸네일을 표시하는 메시지 앱과 같이 SDR 콘텐츠가 많은 페이지의 경우 이 동작으로 인해 SDR 콘텐츠의 인식된 밝기에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. Android 15에서는 setDesiredHdrHeadroom를 사용하여 HDR 헤드룸을 제어하여 SDR 콘텐츠와 HDR 콘텐츠 간의 균형을 맞출 수 있습니다.
라우드니스 제어

Android 15에서는 CTA-2075 음량 표준을 오디오 음량 불일치를 피하고 사용자가 콘텐츠 전환 시 볼륨 조정 이 시스템은 AAC 오디오 콘텐츠에서 사용할 수 있는 소리 크기 메타데이터와 함께 출력 장치(헤드폰 및 스피커)의 알려진 특성을 활용하여 오디오 소리 크기와 다이내믹 레인지 압축 수준을 지능적으로 조정합니다.
이 기능을 사용 설정하려면 AAC 콘텐츠에서 음량 메타데이터를 사용할 수 있는지 확인하고 앱에서 플랫폼 기능을 사용 설정해야 합니다. 이렇게 하려면 연결된 AudioTrack의 오디오 세션 ID를 사용하여 create 팩토리 메서드를 호출하여 LoudnessCodecController 객체를 인스턴스화합니다. 그러면 오디오 업데이트가 자동으로 적용됩니다. OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener를 전달하여 볼륨 매개변수가 MediaCodec에 적용되기 전에 수정하거나 필터링할 수 있습니다.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer도
원활한 앱 통합을 위한 LoudnessCodecController API
가상 MIDI 2.0 기기
Android 13 added support for connecting to MIDI 2.0 devices using USB, which communicate using Universal MIDI Packets (UMP). Android 15 extends UMP support to virtual MIDI apps, enabling composition apps to control synthesizer apps as a virtual MIDI 2.0 device just like they would with an USB MIDI 2.0 device.
더 효율적인 AV1 소프트웨어 디코딩

dav1d, the popular AV1 software decoder from VideoLAN is available for Android devices that don't support AV1 decode in hardware. dav1d is up to 3x more performant than the legacy AV1 software decoder, enabling HD AV1 playback for more users, including some low and mid tier devices.
Your app needs to opt-in to using dav1d by invoking it by name
"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". dav1d will be made the default AV1 software
decoder in a subsequent update. This support is standardized and backported to
Android 11 devices that receive Google Play system updates.
개발자 생산성 및 도구
생산성 향상을 위한 대부분의 작업은 Android 스튜디오, Jetpack Compose, Android Jetpack 라이브러리와 같은 도구를 중심으로 이루어지지만, Google에서는 플랫폼에서 비전을 더 쉽게 실현할 수 있는 방법을 항상 모색하고 있습니다.
OpenJDK 17 업데이트
Android 15에서는 최신 OpenJDK LTS 출시의 기능과 일치하도록 Android의 핵심 라이브러리를 새로고침하는 작업을 계속하고 있습니다.
다음과 같은 주요 기능과 개선사항이 포함됩니다.
- NIO 버퍼 관련 편의성 개선
- 스트림
- 추가
math및strictmath메서드 - 순서가 지정된
collection,map,set를 포함한util패키지 업데이트 Deflater의ByteBuffer지원X500PrivateCredential및 보안 키 업데이트와 같은 보안 업데이트
이러한 API는 Google Play 시스템 업데이트를 통해 Android 12 (API 수준 31) 및 이후 버전을 실행하는 10억 대 이상의 기기에서 업데이트되므로 최신 프로그래밍 기능을 타겟팅할 수 있습니다.
PDF 개선사항
Android 15에서는 PdfRenderer API가 크게 개선되었습니다. 앱에는 렌더링과 같은 고급 기능을
비밀번호로 보호된 파일, 주석, 양식 수정,
검색, 선택(사본 포함) 선형화된 PDF
로컬 PDF 보기의 속도를 높이고 리소스 사용을 줄이기 위해 최적화가 지원됩니다.
Jetpack PDF 라이브러리는 이러한 API를 사용하여 PDF 추가를 간소화합니다.
앱에 추가할 수 있습니다.
PdfRenderer를 Google을 사용하여 업데이트할 수 있는 모듈로 이동했습니다.
플랫폼 출시와는 별개인 Play 시스템 업데이트(Google에서는
Android 11 (API 수준 30)으로 다시 돌아가
API 노출 영역 Android 15 이전 버전
PdfRendererPreV
자동 언어 전환 개선사항
Android 14에서는 언어 간에 자동으로 전환되는 오디오의 기기 내 다중 언어 인식을 추가했지만, 이로 인해 단어가 누락될 수 있습니다. 특히 두 발화 간에 언어가 전환되는 시점에 휴식 시간이 거의 없을 때 그렇습니다. Android 15에서는 앱이 이 전환을 사용 사례에 맞게 조정하는 데 도움이 되는 추가 제어 기능을 제공합니다.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS는 자동 전환을 오디오 세션 시작으로 제한하고 EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES는 지정된 전환 횟수 후에 언어 전환을 비활성화합니다. 이러한 옵션은 세션 중에 자동 감지되어야 하는 단일 언어가 사용될 것으로 예상되는 경우에 특히 유용합니다.
개선된 OpenType 가변 글꼴 API
Android 15 improves the usability of the OpenType variable font. You can create
a FontFamily instance from a variable font without specifying weight axes
with the buildVariableFamily API. The text renderer overrides the value
of wght axis to match the displaying text.
Using the API simplifies the code for creating a Typeface considerably:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Previously, to create the same Typeface, you would need much more code:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Here's an example of how a Typeface created with both the old and new APIs
renders:
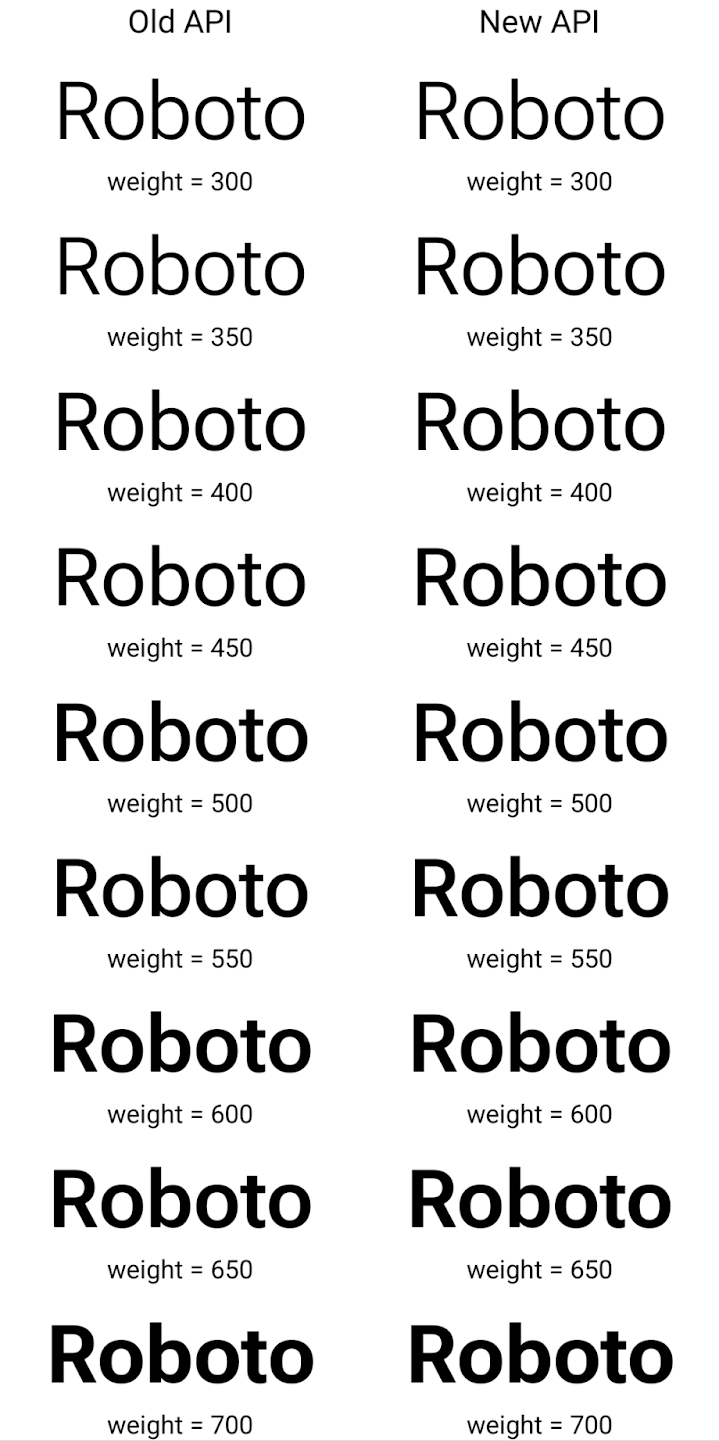
In this example, the Typeface created with the old API doesn't have the
capability to create accurate font weights for the 350, 450, 550 and 650
Font instances, so the renderer falls back to the closest weight. So in
this case, 300 is rendered instead of 350, 400 is rendered instead of 450, and
so on. By contrast, the Typeface created with the new APIs dynamically creates
a Font instance for a given weight, so accurate weights are rendered for 350,
450, 550, and 650 as well.
세부적인 줄바꿈 제어
Starting in Android 15, a TextView and the underlying
line breaker can preserve the given portion of text in the same line to improve
readability. You can take advantage of this line break customization by using
the <nobreak> tag in string resources or
createNoBreakSpan. Similarly, you can preserve words from
hyphenation by using the <nohyphen> tag or
createNoHyphenationSpan.
For example, the following string resource doesn't include a line break, and renders with the text "Pixel 8 Pro." breaking in an undesirable place:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
In contrast, this string resource includes the <nobreak> tag, which wraps the
phrase "Pixel 8 Pro." and prevents line breaks:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
The difference in how these strings are rendered is shown in the following images:

<nobreak> tag.
<nobreak> tag.앱 보관처리
Android and Google Play announced support for app archiving last year, allowing users to free up space by partially removing infrequently used apps from the device that were published using Android App Bundle on Google Play. Android 15 includes OS level support for app archiving and unarchiving, making it easier for all app stores to implement it.
Apps with the REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES permission can call the
PackageInstaller requestArchive method to request archiving an
installed app package, which removes the APK and any cached files, but persists
user data. Archived apps are returned as displayable apps through the
LauncherApps APIs; users will see a UI treatment to highlight that those
apps are archived. If a user taps on an archived app, the responsible installer
will get a request to unarchive it, and the restoration process can be
monitored by the ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED broadcast.
개발자 옵션을 사용하여 기기에서 16KB 모드 사용 설정
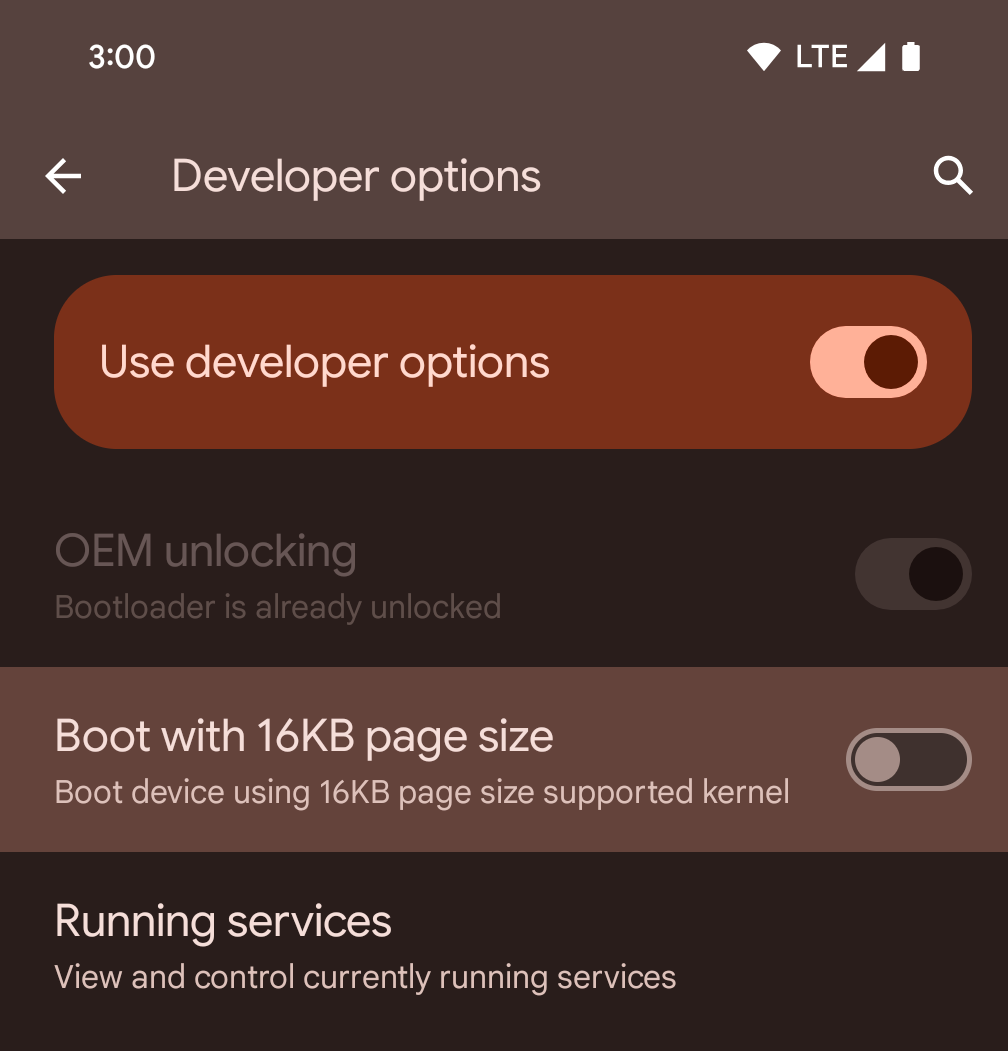
16KB 페이지 크기로 부팅 개발자 옵션을 전환하여 16KB 모드로 기기를 부팅합니다.
Android 15의 QPR 버전에서는 특정 기기에서 사용할 수 있는 개발자 옵션을 사용하여 기기를 16KB 모드로 부팅하고 온디바이스 테스트를 실행할 수 있습니다. 개발자 옵션을 사용하기 전에 설정 > 시스템 > 소프트웨어 업데이트로 이동하여 사용 가능한 업데이트를 적용합니다.
이 개발자 옵션은 다음 기기에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
Pixel 8 및 8 Pro (Android 15 QPR1 이상)
Pixel 8a (Android 15 QPR1 이상)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro, 9 Pro XL (Android 15 QPR2 베타 2 이상)
그래픽
Android 15에는 ANGLE 및 Canvas 그래픽 시스템 추가 등 최신 그래픽 개선사항이 적용되었습니다.
Android의 GPU 액세스 현대화

Android 하드웨어는 핵심 OS가 단일 CPU에서 실행되고 GPU에 고정 기능 파이프라인을 기반으로 하는 API를 사용하여 액세스하던 초기부터 상당히 발전했습니다. Vulkan® 그래픽 API는 Android 7.0 (API 수준 24)부터 NDK에서 최신 GPU 하드웨어를 더 잘 반영하고, 여러 CPU 코어를 지원하도록 더 효과적으로 확장하며, CPU 드라이버 오버헤드를 줄여 앱 성능을 개선하는 하위 수준 추상화를 통해 사용할 수 있습니다. Vulkan은 모든 최신 게임 엔진에서 지원됩니다.
Vulkan은 Android에서 GPU에 사용하는 기본 인터페이스입니다. 따라서 Android 15에는 Vulkan 위에 OpenGL® ES를 실행하기 위한 선택적 레이어로 ANGLE가 포함되어 있습니다. ANGLE로 전환하면 Android OpenGL 구현이 표준화되어 호환성이 개선되고 경우에 따라 성능이 개선됩니다. Android 15에서 설정 -> 시스템 -> 개발자 옵션 -> 실험용: ANGLE 사용 설정에서 개발자 옵션을 사용 설정하여 ANGLE로 OpenGL ES 앱 안정성과 성능을 테스트할 수 있습니다.
Vulkan 기반 Android ANGLE 로드맵
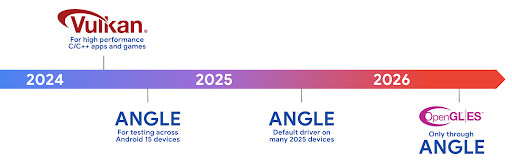
GPU 스택을 간소화하기 위한 일환으로 앞으로 더 많은 새 기기에서 ANGLE을 GL 시스템 드라이버로 제공할 예정이며, 향후 OpenGL/ES는 ANGLE을 통해서만 제공될 것으로 예상됩니다. 하지만 모든 기기에서 OpenGL ES를 계속 지원할 계획입니다.
권장되는 다음 단계
개발자 옵션을 사용하여 OpenGL ES용 ANGLE 드라이버를 선택하고 앱을 테스트합니다. 새 프로젝트의 경우 C/C++에 Vulkan을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
Canvas 개선사항
Android 15 continues our modernization of Android's Canvas graphics system with additional capabilities:
Matrix44provides a 4x4 matrix for transforming coordinates that should be used when you want to manipulate the canvas in 3D.clipShaderintersects the current clip with the specified shader, whileclipOutShadersets the clip to the difference of the current clip and the shader, each treating the shader as an alpha mask. This supports the drawing of complex shapes efficiently.
성능 및 배터리
Android는 앱의 성능과 품질을 개선하는 데 계속해서 집중하고 있습니다. Android 15에서는 앱에서 작업을 더 효율적으로 실행하고, 앱 성능을 최적화하고, 앱에 관한 유용한 정보를 수집하는 데 도움이 되는 API를 도입합니다.
배터리 효율적인 권장사항, 네트워크 및 전력 사용량 디버깅, Android 15 및 최신 버전의 Android에서 백그라운드 작업의 배터리 효율성을 개선하는 방법에 관한 자세한 내용은 Google I/O의 Android에서 백그라운드 작업의 배터리 효율성 개선 강연을 참고하세요.
ApplicationStartInfo API
In previous versions of Android, app startup has been a bit of a mystery. It was
challenging to determine within your app whether it started from a cold, warm,
or hot state. It was also difficult to know how long your app spent during the
various launch phases: forking the process, calling onCreate, drawing the
first frame, and more. When your Application class was instantiated, you had no
way of knowing whether the app started from a broadcast, a content provider, a
job, a backup, boot complete, an alarm, or an Activity.
The ApplicationStartInfo API on Android 15 provides
all of this and more. You can even choose to add your own timestamps into the
flow to help collect timing data in one place. In addition to collecting
metrics, you can use ApplicationStartInfo to help directly optimize app
startup; for example, you can eliminate the costly instantiation of UI-related
libraries within your Application class when your app is starting up due to a
broadcast.
자세한 앱 크기 정보
Since Android 8.0 (API level 26), Android has included the
StorageStats.getAppBytes API that summarizes the installed
size of an app as a single number of bytes, which is a sum of the APK size, the
size of files extracted from the APK, and files that were generated on the
device such as ahead-of-time (AOT) compiled code. This number is not very
insightful in terms of how your app is using storage.
Android 15 adds the
StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API, which lets
you get insight into how your app is using up all that space, including APK file
splits, AOT and speedup related code, dex metadata, libraries, and guided
profiles.
앱 관리 프로파일링
Android 15에는 힙 덤프, 힙 프로필, 스택 샘플링과 같은 프로파일링 정보를 앱 내에서 수집할 수 있는 ProfilingManager 클래스가 포함되어 있습니다. 앱의 파일 디렉터리에 전송되는 출력 파일을 식별하는 제공된 태그와 함께 앱에 콜백을 제공합니다. API는 성능 영향을 최소화하기 위해 비율 제한을 사용합니다.
앱에서 프로파일링 요청 구성을 간소화하려면 Core 1.15.0-rc01 이상에서 사용할 수 있는 상응하는 Profiling AndroidX API를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
SQLite 데이터베이스 개선사항
Android 15에서는 특정 성능 문제를 대상으로 하는 기본 SQLite 엔진의 매니페스트 파일에 있습니다 이러한 API는 SQLite를 버전으로 업데이트하면서 3.44.3.
특히 대규모 데이터베이스를 사용하거나 지연 시간에 민감한 쿼리를 실행할 때는 SQLite 성능 권장사항을 참고하여 SQLite 데이터베이스를 최대한 활용해야 합니다.
- 읽기 전용 지연된 트랜잭션:
읽기 전용 (쓰기 문은 포함하지 않음), 사용
beginTransactionReadOnly()및beginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)읽기 전용DEFERRED거래를 발행할 수 있습니다. 이러한 트랜잭션은 서로 동시에 실행될 수 있으며, 데이터베이스가 WAL 모드인 경우IMMEDIATE또는EXCLUSIVE트랜잭션과 동시에 실행될 수 있습니다. - 행 수 및 ID: 변경된 행 수를 검색하기 위해 API가 추가되었습니다.
행 또는 마지막으로 삽입된 행 ID를 반환할 수 있습니다.
getLastChangedRowCount()는 현재 트랜잭션 내에서 가장 최근 SQL 문에 의해 삽입, 업데이트 또는 삭제된 행 수를 반환하고getTotalChangedRowCount()는 현재 연결의 개수를 반환합니다.getLastInsertRowId()는 마지막 행의rowid를 반환합니다. 현재 연결에 삽입됩니다. - 원시 문: 편의를 우회하여 원시 SQlite 문을 실행합니다. 발생할 수 있는 추가 처리 오버헤드에 대해 걱정할 필요가 없습니다.
Android 동적 성능 프레임워크 업데이트
Android 15 continues our investment in the Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF), a set of APIs that allow games and performance intensive apps to interact more directly with power and thermal systems of Android devices. On supported devices, Android 15 adds ADPF capabilities:
- A power-efficiency mode for hint sessions to indicate that their associated threads should prefer power saving over performance, great for long-running background workloads.
- GPU and CPU work durations can both be reported in hint sessions, allowing the system to adjust CPU and GPU frequencies together to best meet workload demands.
- Thermal headroom thresholds to interpret possible thermal throttling status based on headroom prediction.
To learn more about how to use ADPF in your apps and games, head over to the documentation.
개인 정보 보호
Android 15에는 앱 개발자가 사용자 개인 정보를 보호하는 데 도움이 되는 다양한 기능이 포함되어 있습니다.
화면 녹화 감지
Android 15 adds support for apps to detect that they are being recorded. A callback is invoked whenever the app transitions between being visible or invisible within a screen recording. An app is considered visible if activities owned by the registering process's UID are being recorded. This way, if your app is performing a sensitive operation, you can inform the user that they're being recorded.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
확장된 IntentFilter 기능
Android 15는 UriRelativeFilterGroup를 통해 더 정확한 Intent 해상도를 지원합니다. 여기에는 URL 쿼리 매개변수, URL 프래그먼트, 차단 또는 제외 규칙 등 각각 충족해야 하는 Intent 매칭 규칙 집합을 형성하는 UriRelativeFilter 객체의 집합이 포함됩니다.
이러한 규칙은 android:allow 태그를 선택적으로 포함할 수 있는 <uri-relative-filter-group> 태그를 사용하여 AndroidManifest XML 파일에서 정의할 수 있습니다. 이러한 태그에는 기존 데이터 태그 속성과 android:query 및 android:fragment 속성을 사용하는 <data> 태그가 포함될 수 있습니다.
다음은 AndroidManifest 문법의 예입니다.
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
비공개 스페이스
Private space lets users create a separate space on their device where they can keep sensitive apps away from prying eyes, under an additional layer of authentication. The private space uses a separate user profile. The user can choose to use the device lock or a separate lock factor for the private space.
Apps in the private space show up in a separate container in the launcher, and are hidden from the recents view, notifications, settings, and from other apps when the private space is locked. User-generated and downloaded content (such as media or files) and accounts are separated between the private space and the main space. The system sharesheet and the photo picker can be used to give apps access to content across spaces when the private space is unlocked.
Users can't move existing apps and their data into the private space. Instead, users select an install option in the private space to install an app using whichever app store they prefer. Apps in the private space are installed as separate copies from any apps in the main space (new copies of the same app).
When a user locks the private space, the profile is stopped. While the profile is stopped, apps in the private space are no longer active and can't perform foreground or background activities, including showing notifications.
We recommend that you test your app with private space to make sure your app works as expected, especially if your app falls into one of the following categories:
- Apps with logic for work profiles that assumes that any installed copies of their app that aren't in the main profile are in the work profile.
- Medical apps
- Launcher apps
- App store apps
선택한 사진 액세스에 대한 가장 최근 사용자 선택 쿼리
Apps can now highlight only the most-recently-selected photos and videos when
partial access to media permissions is granted. This feature can improve
the user experience for apps that frequently request access to photos and
videos. To use this feature in your app, enable the
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY argument when querying MediaStore
through ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Android의 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스
Android 15에는 최신 버전의 Android의 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스를 통합한 최신 Android 광고 서비스 확장 프로그램이 포함되어 있습니다. 이번 추가는 사용자 개인 정보 보호를 개선하고 모바일 앱에 효과적인 개인 맞춤 광고 경험을 제공하는 기술을 개발하기 위한 Google의 노력의 일환입니다. 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스 페이지에서 Android의 개인 정보 보호 샌드박스 개발자 프리뷰 및 베타 프로그램에 관한 자세한 내용을 확인하고 시작해 보세요.
헬스 커넥트
Android 15 integrates the latest extensions around Health Connect by Android, a secure and centralized platform to manage and share app-collected health and fitness data. This update adds support for additional data types across fitness, nutrition, skin temperature, training plans, and more.
Skin temperature tracking allows users to store and share more accurate temperature data from a wearable or other tracking device.
Training plans are structured workout plans to help a user achieve their fitness goals. Training plans support includes a variety of completion and performance goals:
- Completion goals around calories burned, distance, duration, repetition, and steps.
- Performance goals around as many repetitions as possible (AMRAP), cadence, heart rate, power, perceived rate of exertion, and speed.
Learn more about the latest updates to Health Connect in Android in the Building adaptable experiences with Android Health talk from Google I/O.
앱 화면 공유
Android 15 supports app screen sharing so users can share or record just an
app window rather than the entire device screen. This feature, first enabled in
Android 14 QPR2, includes
MediaProjection callbacks that allow your app
to customize the app screen sharing experience. Note that for apps targeting
Android 14 (API level 34) or higher,
user consent is required for each
MediaProjection capture session.
사용자 경험 및 시스템 UI
Android 15에서는 앱 개발자와 사용자가 필요에 맞게 기기를 구성할 수 있는 더 많은 제어 기능과 유연성을 제공합니다.
Android 15의 최신 개선사항을 사용하여 앱의 사용자 환경을 개선하는 방법을 자세히 알아보려면 Google I/O의 Android 앱의 사용자 환경 개선 강연을 참고하세요.
생성된 미리보기 API를 사용한 풍부한 위젯 미리보기
Before Android 15, the only way to provide widget picker previews was to specify a static image or layout resource. These previews often differ significantly from the look of the actual widget when it is placed on the home screen. Also, static resources can't be created with Jetpack Glance, so a Glance developer had to screenshot their widget or create an XML layout to have a widget preview.
Android 15 adds support for generated previews. This means that app widget
providers can generate RemoteViews to use as the picker preview, instead
of a static resource.
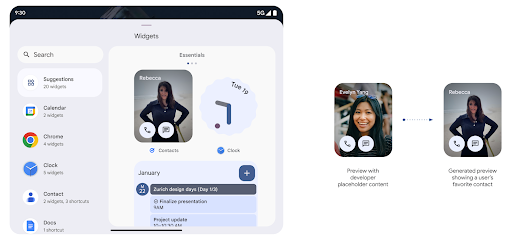
Push API
Apps can provide generated previews through a push API. Apps can provide
previews at any point in their lifecycle, and don't receive an explicit request
from the host to provide previews. Previews are persisted in AppWidgetService,
and hosts can request them on-demand. The following example loads an XML widget
layout resource and sets it as the preview:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
The expected flow is:
- At any time, the widget provider calls
setWidgetPreview. The provided previews are persisted inAppWidgetServicewith other provider info. setWidgetPreviewnotifies hosts of an updated preview through theAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChangedcallback. In response, the widget host reloads all of its provider information.- When displaying a widget preview, the host checks
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories, and if the chosen category is available, callsAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewto return the saved preview for this provider.
When to call setWidgetPreview
Because there is no callback to provide previews, apps can choose to send previews at any point when they are running. How often to update the preview depends on the widget's use case.
The following list describes the two main categories of preview use cases:
- Providers that show real data in their widget previews, such as personalized or recent information. These providers can set the preview once the user has signed in or has done initial configuration in their app. After this, they can set up a periodic task to update the previews at their chosen cadence. Examples of this type of widget could be a photo, calendar, weather or news widget.
- Providers that show static information in previews or quick-action widgets that don't display any data. These providers can set previews once, when the app first launches. Examples of this type of widget include a drive quick actions widget or chrome shortcuts widget.
Some providers might show static previews on the hub mode picker, but real information on the homescreen picker. These providers should follow the guidance for both of these use cases to set previews.
PIP 모드
Android 15 introduces changes in Picture-in-Picture (PiP) ensuring an even smoother transition when entering into PiP mode. This will be beneficial for apps having UI elements overlaid on top of their main UI, which goes into PiP.
Developers use the onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to define logic
that toggles the visibility of the overlaid UI elements. This callback is
triggered when the PiP enter or exit animation is completed. Beginning in
Android 15, the PictureInPictureUiState class includes another state.
With this UI state, apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) will observe the
Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback being invoked with
isTransitioningToPip() as soon as the PiP animation starts. There are
many UI elements that are not relevant for the app when it is in PiP mode, for
example views or layout that include information such as suggestions, upcoming
video, ratings, and titles. When the app goes to PiP mode, use the
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback to hide these UI elements. When the
app goes to full screen mode from the PiP window, use
onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to unhide these elements, as shown in
the following examples:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
This quick visibility toggle of irrelevant UI elements (for a PiP window) helps ensure a smoother and flicker-free PiP enter animation.
향상된 방해 금지 모드 규칙
AutomaticZenRule lets apps customize Attention
Management (Do Not Disturb) rules and decide when to activate or deactivate
them. Android 15 greatly enhances these rules with the goal of improving the
user experience. The following enhancements are included:
- Adding types to
AutomaticZenRule, allowing the system to apply special treatment to some rules. - Adding an icon to
AutomaticZenRule, helping to make the modes be more recognizable. - Adding a
triggerDescriptionstring toAutomaticZenRulethat describes the conditions on which the rule should become active for the user. - Added
ZenDeviceEffectstoAutomaticZenRule, allowing rules to trigger things like grayscale display, night mode, or dimming the wallpaper.
알림 채널의 VibrationEffect 설정
Android 15 supports setting rich vibrations for incoming notifications by
channel using NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, so
your users can distinguish between different types of notifications without
having to look at their device.
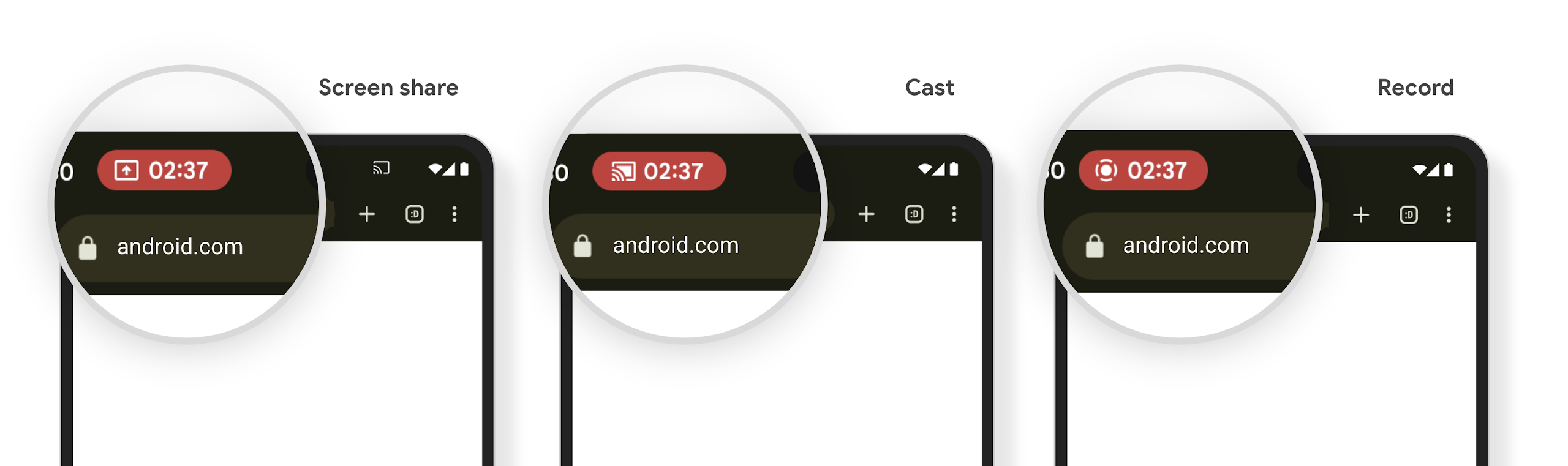
미디어 프로젝션 상태 표시줄 칩 및 자동 중지
Media projection can expose private user information. A new, prominent status bar chip makes users aware of any ongoing screen projection. Users can tap the chip to stop screen casting, sharing, or recording. Also, for a more intuitive user experience, any in‑progress screen projection now automatically stops when the device screen is locked.
대형 화면 및 폼 팩터
Android 15는 앱이 대형 화면, 플립형, 폴더블을 비롯한 Android의 폼 팩터를 최대한 활용할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
향상된 대형 화면 멀티태스킹
Android 15는 사용자가 대형 화면 기기에서 멀티태스킹하는 더 나은 방법을 제공합니다. 대상 예를 들어 사용자는 자주 사용하는 화면 분할 앱 조합을 저장하여 빠르게 화면의 태스크 바에 액세스하고 고정하여 앱 간에 빠르게 전환할 수 있습니다. 다시 말해 하는 것이 그 어느 때보다 중요하다고 생각합니다.
Google I/O의 적응형 Android 빌드 빌드 앱 및 Material 3으로 UI 빌드 적응형 라이브러리 이 문서에는 대규모 캠페인을 위한 디자인 화면을 선택합니다.
커버 화면 지원
Your app can declare a property that Android 15 uses to
allow your Application or Activity to be presented on the small cover
screens of supported flippable devices. These screens are too small to be
considered as compatible targets for Android apps to run on, but your app can
opt in to supporting them, making your app available in more places.
연결
Android 15는 앱이 최신 통신 및 무선 기술을 이용할 수 있도록 플랫폼을 업데이트합니다.
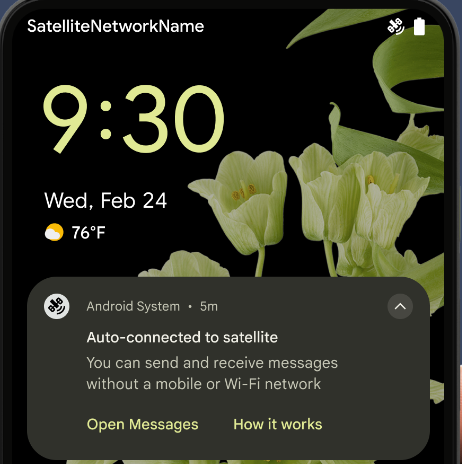
위성 지원
Android 15 continues to extend platform support for satellite connectivity and includes some UI elements to ensure a consistent user experience across the satellite connectivity landscape.
Apps can use ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() to
detect when a device is connected to a satellite, giving them more awareness of
why full network services might be unavailable. Additionally, Android 15
provides support for SMS and MMS apps as well as preloaded RCS apps to use
satellite connectivity for sending and receiving messages.
더 원활한 NFC 환경
Android 15 is working to make the tap to pay experience more seamless and
reliable while continuing to support Android's robust NFC app ecosystem. On
supported devices, apps can request the NfcAdapter to enter
observe mode, where the device listens but doesn't respond to NFC
readers, sending the app's NFC service PollingFrame
objects to process. The PollingFrame objects can be used to auth
ahead of the first communication to the NFC reader, allowing for a one tap
transaction in many cases.
In addition, apps can register a filter on supported devices so they can be notified of polling loop activity, which allows for smooth operation with multiple NFC-aware applications.
월렛 역할
Android 15 introduces a Wallet role that allows tighter integration with the user's preferred wallet app. This role replaces the NFC default contactless payment setting. Users can manage the Wallet role holder by navigating to Settings > Apps > Default Apps.
The Wallet role is used when routing NFC taps for AIDs registered in the payment category. Taps always go to the Wallet role holder unless another app that is registered for the same AID is running in the foreground.
This role is also used to determine where the Wallet Quick Access tile should go when activated. When the role is set to "None", the Quick Access tile isn't available and payment category NFC taps are only delivered to the foreground app.
보안
Android 15를 사용하면 앱의 보안을 강화하고 앱의 데이터를 보호할 수 있으며 사용자에게 데이터에 대한 투명성과 제어 기능을 더 많이 제공할 수 있습니다. Google I/O의 Android에서 사용자 보안 보호 강연에서 사용자 보호 조치를 개선하고 새로운 위협으로부터 앱을 보호하기 위해 Google이 어떤 노력을 기울이고 있는지 자세히 알아보세요.
자동 완성과 인증 관리자 통합
Starting with Android 15, developers can link specific views like username or password fields with Credential Manager requests, making it easier to provide a tailored user experience during the sign-in process. When the user focuses on one of these views, a corresponding request is sent to Credential Manager. The resulting credentials are aggregated across providers and displayed in autofill fallback UIs, such as inline suggestions or drop-down suggestions. The Jetpack androidx.credentials library is the preferred endpoint for developers to use and will soon be available to further enhance this feature in Android 15 and higher.
원탭 가입 및 로그인을 생체 인식 메시지와 통합
Credential Manager integrates biometric prompts into the credential creation and sign-in processes, eliminating the need for providers to manage biometric prompts. As a result, credential providers only need to focus on the results of the create and get flows, augmented with the biometric flow result. This simplified process creates a more efficient and streamlined credential creation and retrieval process.
엔드 투 엔드 암호화 키 관리
We are introducing the E2eeContactKeysManager in Android 15, which
facilitates end-to-end encryption (E2EE) in your Android apps by providing an
OS-level API for the storage of cryptographic public keys.
The E2eeContactKeysManager is designed to integrate with the platform
contacts app to give users a centralized way to manage and verify their
contacts' public keys.
콘텐츠 URI에 대한 권한 확인
Android 15에서는 콘텐츠 URI에 대한 권한 확인을 실행하는 API 세트를 도입합니다.
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: 콘텐츠 URI에 대한 전체 권한 검사를 실행합니다.Activity매니페스트 속성requireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: 활동 시작 시 제공된 콘텐츠 URI에 지정된 권한을 적용합니다.Activity호출자를 위한ComponentCaller클래스: 활동을 실행한 앱을 나타냅니다.
접근성
Android 15에는 사용자의 접근성을 개선하는 기능이 추가되었습니다.
점자 개선
In Android 15, we've made it possible for TalkBack to support Braille displays that are using the HID standard over both USB and secure Bluetooth.
This standard, much like the one used by mice and keyboards, will help Android support a wider range of Braille displays over time.
다국어 지원
Android 15에서는 기기가 여러 언어로 사용될 때 사용자 환경을 보완하는 기능이 추가되었습니다.
CJK 가변 글꼴
Starting with Android 15, the font file for Chinese, Japanese, and Korean (CJK) languages, NotoSansCJK, is now a variable font. Variable fonts open up possibilities for creative typography in CJK languages. Designers can explore a broader range of styles and create visually striking layouts that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve.

문자 간 정렬
Starting with Android 15, text can be justified utilizing letter spacing by
using JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. Inter-word justification was
first introduced in Android 8.0 (API level 26), and inter-character
justification provides similar capabilities for languages that use the
whitespace character for segmentation, such as Chinese, Japanese, and others.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.자동 줄바꿈 구성
Android는 일본어와 한국어의 구문 기반 줄바꿈을
Android 13 (API 수준 33) 그러나 구문 기반 줄바꿈은 짧은 텍스트 줄의 가독성을 개선하지만 긴 텍스트 줄에는 적합하지 않습니다.
Android 15에서는 앱이 짧은 줄에만 구문 기반 줄바꿈을 적용할 수 있습니다.
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO를 사용하여 텍스트 생성
옵션을 선택합니다. 이 옵션을 선택하면 텍스트에 가장 적합한 단어 스타일 옵션이 선택됩니다.
짧은 텍스트 줄의 경우 동일하게 작동하는 구문 기반 줄바꿈이 사용됨
다음과 같이 LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE로 설정합니다.
다음 이미지:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO은 짧은 텍스트 줄의 경우 구문 기반 줄바꿈을 적용하여 텍스트의 가독성을 개선합니다.
이 방법은
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE텍스트가 더 긴 경우 LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO는 no를 사용합니다.
줄바꿈 단어 스타일로,
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE
다음 이미지:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
줄바꿈 단어 스타일을 적용하지 않으므로 텍스트의 가독성이 향상됩니다.
이 방법은
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE추가 일본어 변체 가나 글꼴
In Android 15, a font file for old Japanese Hiragana (known as Hentaigana) is bundled by default. The unique shapes of Hentaigana characters can add a distinctive flair to artwork or design while also helping to preserve accurate transmission and understanding of ancient Japanese documents.

VideoLAN 원뿔 저작권 (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. 이 로고 또는 수정된 버전은 누구나 VideoLAN 프로젝트 또는 VideoLAN팀에서 개발한 제품을 언급하기 위해 사용하거나 수정할 수 있지만, 프로젝트의 추천을 나타내지는 않습니다.
Vulkan 및 Vulkan 로고는 Khronos Group Inc.의 등록 상표입니다.
OpenGL은 등록된 상표이며 OpenGL ES 로고는 Khronos의 허가를 받아 Hewlett Packard Enterprise의 상표입니다.

