Android 11 introduced new developer tools for testing and debugging your app against the behavior changes in newer versions of the Android platform. These tools are part of a compatibility framework that lets app developers turn breaking changes on and off individually using developer options or ADB. Use this flexibility as you prepare to target the latest stable API version and as you test your app with the preview release of the next Android version.
When you use the compatibility framework tools, the Android platform
automatically adapts its internal logic, so you don't need to change your
targetSDKVersion or recompile your app to perform basic testing. Because
changes are individually toggleable, you can isolate, test, and debug one
behavior change at a time or disable a single change that's causing issues if
you need to test something else first.
How to identify which changes are enabled
When a behavior change is enabled, it can affect how your app accesses the platform APIs that are affected by that change. You can check which behavior changes are enabled using the developer options, logcat, or ADB commands.
Identify enabled changes using developer options
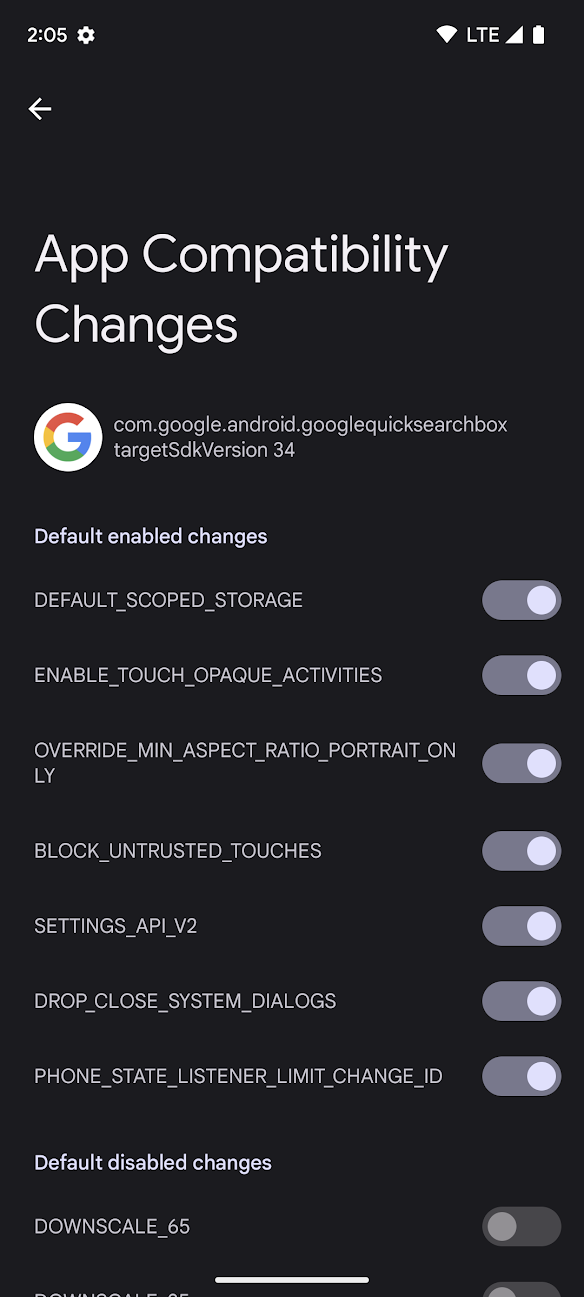
Figure 1. App Compatibility Changes screen in developer options.
You can see which changes are enabled and toggle those changes on or off in a device's developer options. To access these options, follow these steps:
- If developer options are not already enabled, enable them.
- Open your device's Settings app and navigate to System > Advanced > Developer options > App Compatibility Changes.
Select your app from the list.
Each behavior change usually belongs to one of the following two categories:
Changes that affect all apps that run on that version of Android, regardless of the app's
targetSdkVersion.These changes are enabled by default in the compatibility framework, and are listed in the UI in the Default Enabled Changes section.
Changes that only affect apps that are targeting certain Android versions. Because these changes only affect apps that target a specific version of Android, they are also referred to as changes that are gated by
targetSDKVersion.These changes are enabled by default in the compatibility framework if your app is targeting a higher version than the listed API version. For example, a behavior change that is gated by
targetSDKVersionin Android 13 (API level 33) would be listed in the UI a section titled Enabled for targetSdkVersion >=33. On some lower versions of Android, this section is titled "Enabled After SDK API_LEVEL" instead.
You'll also notice a section in figure 1 called Default Disabled Changes. Changes that fall into this section can serve a variety of purposes. Before enabling these changes, read the change description in the compatibility framework list for that Android version.
Identify enabled changes using logcat
For each behavior change, the first time during your app's process when your app calls the affected API, the system outputs a logcat message like this one:
D CompatibilityChangeReporter: Compat change id reported: 194833441; UID 10265; state: ENABLED
Each logcat message includes the following information:
- Change ID
- Indicates which change is affecting the app. This value maps to one of the
behavior changes that are listed on the App Compatibility Changes screen
(see figure 1). In this example,
194833441maps toNOTIFICATION_PERM_CHANGE_ID. - UID
- Indicates which app is affected by the change.
- State
Indicates whether the change is affecting the app.
The state can be one of these values:
State Meaning ENABLEDThe change is enabled and will affect the app's behavior if the app uses the APIs that were changed. DISABLEDThe change is disabled and won't affect the app.
Note: If this change is disabled because the app's
targetSDKVersionis below the required threshold, the change will be enabled by default when the app increases itstargetSDKVersionto target a higher version.LOGGEDThe change is being logged through the compatibility framework but can't be toggled on or off. Although this change can't be toggled, it might still affect your app's behavior. See the description of the change in the compatibility framework list for that Android version for more information. In many cases, these types of changes are experimental and can be ignored.
Identify enabled changes using ADB
Run the following ADB command to see the complete set of changes (both enabled and disabled) on the entire device:
adb shell dumpsys platform_compat
The output lists the following information for each change:
- Change ID
- A unique identifier for this behavior change. For example,
194833441. - Name
- The name of this behavior change. For example,
NOTIFICATION_PERM_CHANGE_ID. - targetSDKVersion criteria
Which
targetSDKVersionthe change is gated by (if any).For example, if this change is only enabled for apps targeting SDK version 33 or higher,
enableAfterTargetSdk=32is output. If the change is not gated bytargetSDKVersion,enableAfterTargetSdk=0is output.- Package overrides
The name of each package where the change's default state (either enabled or disabled) has been overridden.
For example, if this is a change that is enabled by default, your app's package name would be listed if you toggled the change off using either the developer options or ADB. In this case, the output would be:
packageOverrides={com.my.package=false}Changes that are gated by
targetSDKVersioncan be either enabled or disabled by default, so the list of packages can include instances of bothtrueorfalse, depending on each of those app'stargetSDKVersion. For example:packageOverrides={com.my.package=true, com.another.package=false}
Learn more about specific changes
The full list of behavior changes in the compatibility framework are included as part of the documentation for each Android version. See the following links for more information, depending on the version of Android you are testing your app for:
- Android 16 (API level 36)
- Android 15 (API level 35)
- Android 14 (API level 34)
- Android 13 (API level 33)
- Android 12 (API levels 31 and 32)
- Android 11 (API level 30)
When to toggle changes
The main purpose of the compatibility framework is to provide you with control and flexibility as you test your app with newer versions of Android. This section describes some strategies you can use to determine when to toggle changes on or off as you test and debug your app.
When to toggle changes off
Deciding when to toggle changes off usually depends on whether the change is
gated by targetSDKVersion or not.
- Changes enabled for all apps
Changes that affect all apps are enabled by default for a specific platform version, regardless of your app's
targetSDKVersion, so you can see if your app is affected by running your app on that platform version.For example, if you are preparing to target Android 16 (API level 36), you could begin by installing your app on a device running Android 16 and test your app using your typical testing workflows. If you app encounters issues, you could disable the change that is causing the issue so you could continue testing for other issues.
Because these changes can affect all apps regardless of
targetSDKVersion, you should usually test and update your app for these changes before changes that are gated bytargetSDKVersion. This helps ensure that your users won't have a degraded app experience when they update their device to a new platform version.You should also prioritize testing these changes because you can't toggle these changes off when using a public release build of Android. Ideally, you should perform testing on these changes for each version of Android while that version is in preview.
- Changes gated by
targetSDKVersion If your app is targeting a specific
targetSDKVersion, any changes that are gated by that version are enabled by default. So, as you switch your app'stargetSDKVersionto a new version, your app will start to be affected by many new changes at once.Because your app might be affected by more than one of these changes, you might need to toggle some of these changes off individually as you test and debug your app.
When to toggle changes on
Changes that are gated by a specific targetSDKVersion are disabled by default
whenever an app is targeting a lower SDK version than the gated version.
Typically, as you prepare to target a new targetSdkVersion, you'll have a list
of behavior changes that you'll need to test and debug your app for.
For example, you might be testing your app against a series of platform changes
in the next targetSdkVersion. Using developer options or ADB commands, you
could enable and test each gated change one by one, rather than changing your
app manifest and opting in to every change at once. This extra control can help
you test changes in isolation and avoid debugging and updating multiple parts of
your app at once.
After enabling a change, you can test and debug your app using your typical testing workflows. If you encounter issues, check your logs to help determine the cause of the problem. If it's not clear whether the problem is caused by a platform change that's enabled, try disabling that change and then retest that area of your app.
Toggle changes on or off
The compatibility framework lets you toggle each change on or off using the developer options or ADB commands. Because toggling changes on or off can cause your app to crash or disable important security changes, there are some restrictions on when you can toggle changes.
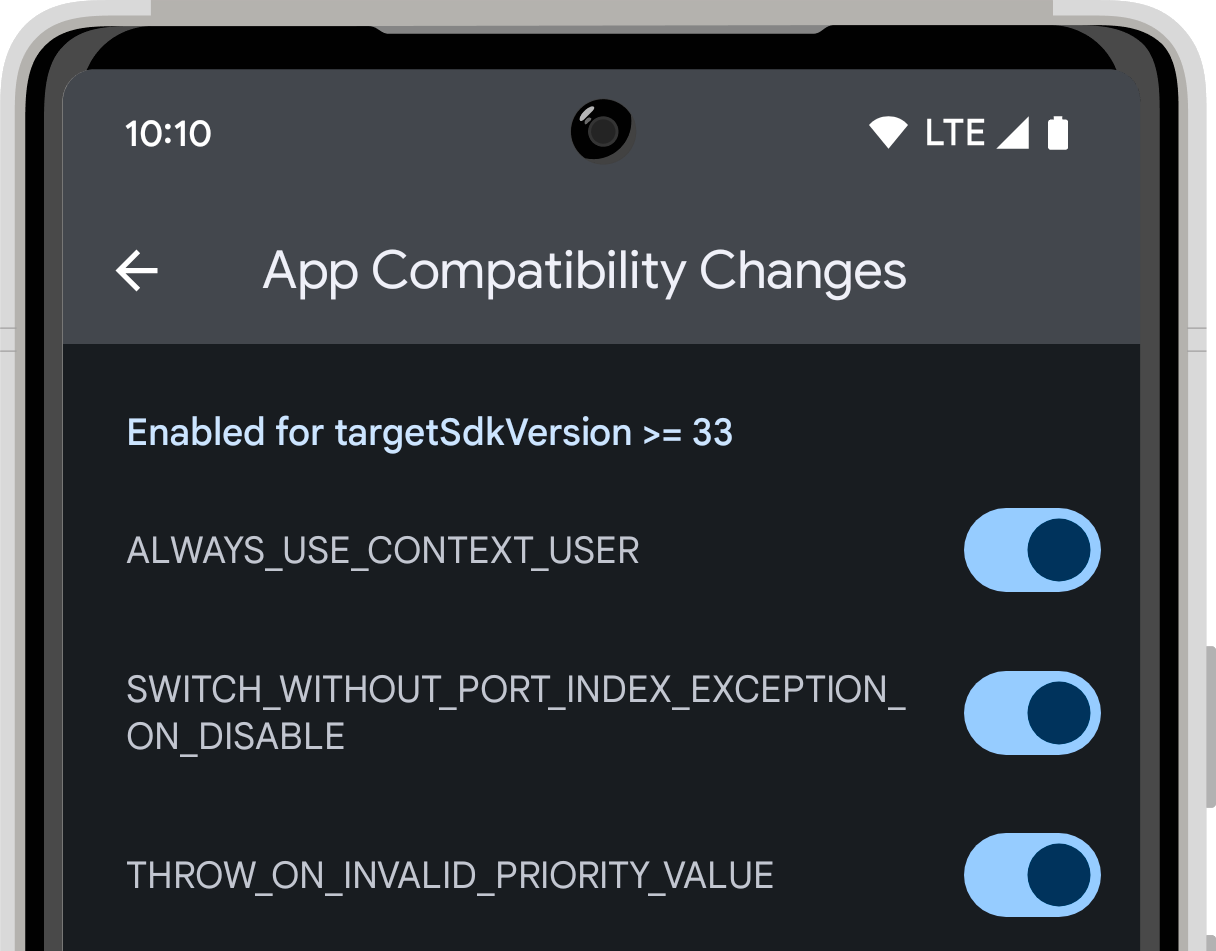
Toggle changes using the developer options
Use the developer options to toggle changes on or off. To find the developer options, follow these steps:
- If developer options are not already enabled, enable them.
- Open your device's Settings app and navigate to System > Advanced > Developer options > App Compatibility Changes.
- Select your app from the list.
From the list of changes, find the change that you want to toggle on or off and tap the switch.
Toggle changes using ADB
To toggle a change on or off using ADB, run one of the following commands:
adb shell am compat enable (CHANGE_ID|CHANGE_NAME) PACKAGE_NAMEadb shell am compat disable (CHANGE_ID|CHANGE_NAME) PACKAGE_NAME
Pass either the CHANGE_ID (for example, 194833441) or
the CHANGE_NAME (for example,
NOTIFICATION_PERM_CHANGE_ID) and your app's
PACKAGE_NAME.
You can also use the following command to reset a change back to its default state, removing any override that you've set using ADB or the developer options:
adb shell am compat reset (CHANGE_ID|CHANGE_NAME) PACKAGE_NAME
Restrictions on toggling changes
By default, each behavior change is either enabled or disabled. Changes that
affect all apps are enabled by default. Other changes are gated by a
targetSdkVersion. These changes are enabled by default when an app targets the
corresponding SDK version or higher and disabled by default when an app is
targeting an SDK version lower than the gated version. When you toggle a change
on or off, you override its default state.
To prevent the compatibility framework from being used maliciously, there are some restrictions on when you can toggle changes. Whether or not you can toggle a change depends on the type of change, whether your app is debuggable, and the type of build running on your device. The following table describes when you are allowed to toggle different types of changes:
| Build type | Non-debuggable app | Debuggable app | |
|---|---|---|---|
| All changes | Changes gated by targetSDKVersion | All other changes | |
| Developer Preview or Beta build | Can't toggle | Can toggle | Can toggle |
| Public user build | Can't toggle | Can toggle | Can't toggle |
