แพลตฟอร์ม Android 16 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้มีผลกับแอปทั้งหมดเมื่อทำงานบน Android 16 ไม่ว่าจะมี targetSdkVersion หรือไม่ก็ตาม คุณควรทดสอบแอปแล้วแก้ไขแอปตามที่จำเป็นเพื่อรองรับการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ (หากมี)
โปรดตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่ส่งผลต่อแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 เท่านั้นด้วย
ฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งแก้ไขหรือขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพโควต้า JobScheduler
Starting in Android 16, we're adjusting regular and expedited job execution runtime quota based on the following factors:
- Which app standby bucket the application is in: in Android 16, active standby buckets will start being enforced by a generous runtime quota.
- If the job starts execution while the app is in a top state: in Android 16, Jobs started while the app is visible to the user and continues after the app becomes invisible, will adhere to the job runtime quota.
- If the job is executing while running a Foreground Service: in Android 16, jobs that are executing while concurrently with a foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota. If you're leveraging jobs for user initiated data transfer, consider using user initiated data transfer jobs instead.
This change impacts tasks scheduled using WorkManager, JobScheduler, and
DownloadManager. To debug why a job was stopped, we recommend logging why your
job was stopped by calling WorkInfo.getStopReason() (for
JobScheduler jobs, call JobParameters.getStopReason()).
For more information on battery-optimal best practices, refer to guidance on optimize battery use for task scheduling APIs.
We also recommend leveraging the new
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API introduced in
Android 16 to understand why a job has not executed.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable override of certain job quota optimizations as long as the app is running on an Android 16 device.
To disable enforcement of "top state will adhere to job runtime quota", run the
following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To disable enforcement of "jobs that are executing while concurrently with a
foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota", run the following
adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To test certain app standby bucket behavior, you can set the app standby bucket
of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
To understand the app standby bucket your app is in, you can get the app standby
bucket of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
เหตุผลที่หยุดงานว่างเปล่าที่หยุดทำงาน
An abandoned job occurs when the JobParameters object associated with the job
has been garbage collected, but JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) has not been called to signal job completion. This indicates that
the job may be running and being rescheduled without the app's awareness.
Apps that rely on JobScheduler, don't maintain a strong reference to the
JobParameters object, and timeout will now be granted the new job stop reason
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, instead of STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
If there are frequent occurrences of the new abandoned stop reason, the system will take mitigation steps to reduce job frequency.
Apps should use the new stop reason to detect and reduce abandoned jobs.
If you're using WorkManager, AsyncTask, or DownloadManager, you aren't impacted because these APIs manage the job lifecycle on your app's behalf.
เลิกใช้งาน JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground อย่างสมบูรณ์
วิธีการ JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) จะระบุความสำคัญของงานขณะที่แอปกำหนดเวลาอยู่เบื้องหน้าหรือเมื่อได้รับการยกเว้นจากข้อจำกัดของเบื้องหลังชั่วคราว
เราเลิกใช้งานเมธอดนี้ตั้งแต่ Android 12 (API ระดับ 31) ตั้งแต่ Android 16 เป็นต้นไป วิธีการนี้จะใช้งานไม่ได้อีกต่อไป และระบบจะไม่สนใจการเรียกใช้เมธอดนี้
การนําฟังก์ชันการทำงานนี้ออกจะมีผลกับJobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground() ด้วย ตั้งแต่ Android 16 เป็นต้นไป หากมีการเรียกใช้เมธอด เมธอดจะแสดงผลลัพธ์เป็น false
ขอบเขตลําดับความสําคัญของประกาศตามลําดับไม่ได้เป็นแบบทั่วโลกอีกต่อไป
Android apps are allowed to define priorities on broadcast receivers to control
the order in which the receivers receive and process the broadcast. For
manifest-declared receivers, apps can use the
android:priority attribute to define the priority and for
context-registered receivers, apps can use the
IntentFilter#setPriority() API to define the priority. When
a broadcast is sent, the system delivers it to receivers in order of their
priority, from highest to lowest.
In Android 16, broadcast delivery order using the android:priority attribute
or IntentFilter#setPriority() across different processes will not be
guaranteed. Broadcast priorities will only be respected within the same
application process rather than across all processes.
Also, broadcast priorities will be automatically confined to the range
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Only system components will be
allowed to set SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY as broadcast
priority.
Your app might be impacted if it does either of the following:
- Your application has declared multiple processes with the same broadcast intent, and has expectations around receiving those intents in a certain order based on the priority.
- Your application process interacts with other processes and has expectations around receiving a broadcast intent in a certain order.
If the processes need to coordinate with each other, they should communicate using other coordination channels.
การเปลี่ยนแปลงภายในของ ART
Android 16 includes the latest updates to the Android Runtime (ART) that improve the Android Runtime's (ART's) performance and provide support for additional Java features. Through Google Play System updates, these improvements are also available to over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher.
As these changes are released, libraries and app code that rely on internal structures of ART might not work correctly on devices running Android 16, along with earlier Android versions that update the ART module through Google Play system updates.
Relying on internal structures (such as non-SDK interfaces) can always lead to compatibility problems, but it's particularly important to avoid relying on code (or libraries containing code) that leverages internal ART structures, since ART changes aren't tied to the platform version the device is running on and they go out to over a billion devices through Google Play system updates.
All developers should check whether their app is impacted by testing their apps thoroughly on Android 16. In addition, check the known issues to see if your app depends on any libraries that we've identified that rely on internal ART structures. If you do have app code or library dependencies that are affected, seek public API alternatives whenever possible and request public APIs for new use cases by creating a feature request in our issue tracker.
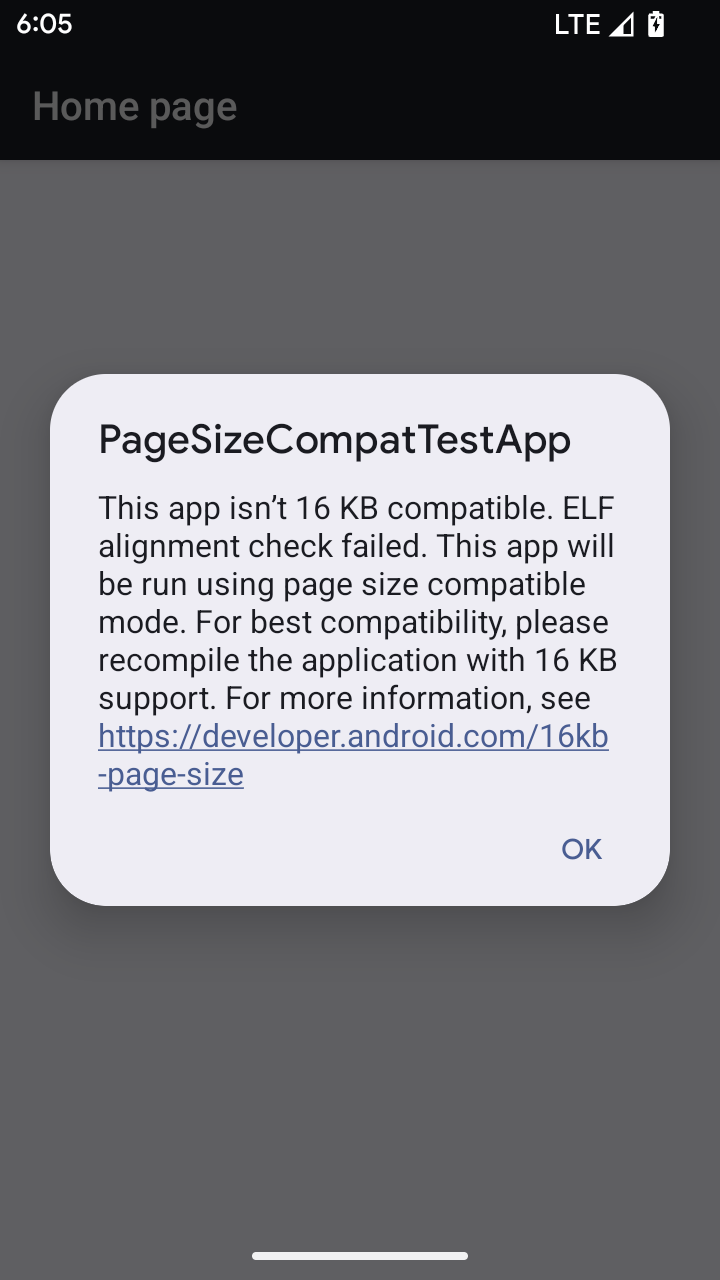
โหมดความเข้ากันได้กับขนาดหน้า 16 KB
Android 15 introduced support for 16 KB memory pages to optimize performance of the platform. Android 16 adds a compatibility mode, allowing some apps built for 4 KB memory pages to run on a device configured for 16 KB memory pages.
When your app is running on a device with Android 16 or higher, if Android
detects that your app has 4 KB aligned memory pages, it automatically uses
compatibility mode and display a notification dialog to the user. Setting the
android:pageSizeCompat property in the AndroidManifest.xml to enable the
backwards compatibility mode will prevent the display of the dialog when your
app launches. To use the android:pageSizeCompat property, compile your app
using the Android 16 SDK.
For best performance, reliability, and stability, your app should still be 16 KB aligned. Check out our recent blog post on updating your apps to support 16 KB memory pages for more details.
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งมีจุดประสงค์เพื่อมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่สม่ำเสมอและใช้งานง่ายยิ่งขึ้นแก่ผู้ใช้
การเลิกใช้งานการประกาศการช่วยเหลือพิเศษที่รบกวน
Android 16 เลิกใช้งานการประกาศการช่วยเหลือพิเศษ ซึ่งมีลักษณะการใช้งาน announceForAccessibility หรือการส่งเหตุการณ์การช่วยเหลือพิเศษ TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT การดำเนินการเหล่านี้อาจทำให้ผู้ใช้ TalkBack และโปรแกรมอ่านหน้าจอของ Android ได้รับประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ไม่สอดคล้องกัน และทางเลือกอื่นๆ จะตอบสนองความต้องการของผู้ใช้ได้หลากหลายมากขึ้นในเทคโนโลยีความช่วยเหลือพิเศษต่างๆ ของ Android
ตัวอย่างทางเลือกมีดังนี้
- สำหรับการเปลี่ยนแปลง UI ที่สำคัญ เช่น การเปลี่ยนแปลงหน้าต่าง ให้ใช้
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)และsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)ในโหมดเขียน ให้ใช้Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - หากต้องการแจ้งให้ผู้ใช้ทราบถึงการเปลี่ยนแปลง UI ที่สำคัญ ให้ใช้
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)ในโหมดเขียน ให้ใช้Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}คุณควรใช้ฟีเจอร์เหล่านี้อย่างจำกัดเนื่องจากอาจสร้างประกาศทุกครั้งที่มีการอัปเดตมุมมอง - หากต้องการแจ้งให้ผู้ใช้ทราบเกี่ยวกับข้อผิดพลาด ให้ส่ง
AccessibilityEventประเภทAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORและตั้งค่าAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)หรือใช้TextView#setError(CharSequence)
เอกสารอ้างอิงสําหรับ announceForAccessibility API ที่เลิกใช้งานแล้วมีรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับทางเลือกที่แนะนํา
การรองรับการไปยังส่วนต่างๆ แบบ 3 ปุ่ม
Android 16 brings predictive back support to the 3-button navigation for apps that have properly migrated to predictive back. Long-pressing the back button initiates a predictive back animation, giving you a preview of where the back swipe takes you.
This behavior applies across all areas of the system that support predictive back animations, including the system animations (back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity).
รูปแบบของอุปกรณ์
Android 16 (ระดับ API 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้สำหรับแอปเมื่อเจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนโปรเจ็กต์ไปยังจอแสดงผล
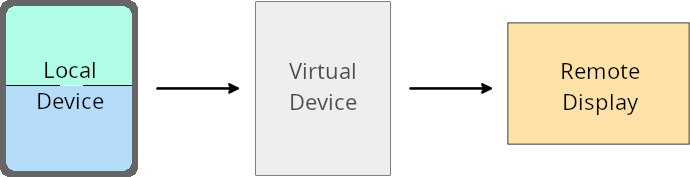
การลบล้างของเจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนจริง
A virtual device owner is a trusted or privileged app that creates and manages a virtual device. Virtual device owners run apps on a virtual device and then project the apps to the display of a remote device, such as a personal computer, virtual reality device, or car infotainment system. The virtual device owner is on a local device, such as a mobile phone.
Per-app overrides
On devices running Android 16 (API level 36), virtual device owners can override app settings on select virtual devices that the virtual device owners manage. For example, to improve app layout, a virtual device owner can ignore orientation, aspect ratio, and resizability restrictions when projecting apps onto an external display.
Common breaking changes
The Android 16 behavior might impact your app's UI on large screen form factors such as car displays or Chromebooks, especially layouts that were designed for small displays in portrait orientation. To learn how to make your app adaptive for all device form factors, see About adaptive layouts.
References
ความปลอดภัย
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งเสริมความปลอดภัยของระบบเพื่อช่วยปกป้องแอปและผู้ใช้จากแอปที่เป็นอันตราย
ปรับปรุงความปลอดภัยเพื่อป้องกันการโจมตีด้วยการเปลี่ยนเส้นทาง Intent
Android 16 มีการรักษาความปลอดภัยเริ่มต้นเพื่อป้องกันIntentการโจมตีด้วยการเปลี่ยนเส้นทางทั่วไป โดยมีการรองรับการทำงานร่วมกันขั้นต่ำและการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่นักพัฒนาแอปต้องทำ
เรากำลังเปิดตัวโซลูชันการปิดช่องโหว่เพื่อความปลอดภัยโดยค่าเริ่มต้นเพื่อIntent
ป้องกันการโจมตีด้วยการเปลี่ยนเส้นทาง ในกรณีส่วนใหญ่ แอปที่ใช้ Intent จะไม่พบปัญหาความเข้ากันได้ เนื่องจากเราได้รวบรวมเมตริกตลอดกระบวนการพัฒนาเพื่อตรวจสอบว่าแอปใดอาจพบปัญหา
การเปลี่ยนเส้นทาง Intent ใน Android เกิดขึ้นเมื่อผู้โจมตีควบคุมเนื้อหาของ Intent ที่ใช้เพื่อเปิดคอมโพเนนต์ใหม่ในบริบทของแอปที่มีช่องโหว่ได้บางส่วนหรือทั้งหมด ขณะที่แอปเหยื่อเปิด Intent ระดับย่อยที่ไม่น่าเชื่อถือในช่องเพิ่มเติมของ Intent ("ระดับบนสุด") ซึ่งอาจทําให้แอปของผู้โจมตีเปิดใช้งานคอมโพเนนต์ส่วนตัวในบริบทของแอปเหยื่อ ทริกเกอร์การดําเนินการที่มีสิทธิ์ หรือรับสิทธิ์เข้าถึง URI สําหรับข้อมูลที่ละเอียดอ่อน ซึ่งอาจทําให้เกิดการขโมยข้อมูลและการดำเนินการโค้ดตามอำเภอใจ
เลือกไม่ใช้การจัดการการเปลี่ยนเส้นทาง Intent
Android 16 เปิดตัว API ใหม่ที่ช่วยให้แอปเลือกไม่ใช้การป้องกันด้านความปลอดภัยเมื่อเปิดตัวได้ ซึ่งอาจจำเป็นในบางกรณีที่ลักษณะการทำงานด้านความปลอดภัยเริ่มต้นรบกวน Use Case ของแอปที่ถูกต้อง
สําหรับแอปพลิเคชันที่คอมไพล์กับ SDK ของ Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) ขึ้นไป
คุณสามารถใช้เมธอด removeLaunchSecurityProtection() กับออบเจ็กต์ Intent ได้โดยตรง
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
สําหรับแอปพลิเคชันที่คอมไพล์กับ Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) หรือต่ำกว่า
แม้ว่าเราจะไม่แนะนํา แต่คุณก็ใช้การสะท้อนเพื่อเข้าถึงเมธอด removeLaunchSecurityProtection() ได้
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
การเชื่อมต่อ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ในกองซ้อนบลูทูธเพื่อปรับปรุงการเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ต่อพ่วง
การจัดการการสูญเสียพันธบัตรที่ดีขึ้น
ตั้งแต่ Android 16 เป็นต้นไป สแต็กบลูทูธได้รับการอัปเดตเพื่อปรับปรุงความปลอดภัยและประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้เมื่อตรวจพบการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงระยะไกล ก่อนหน้านี้ ระบบจะนำการจับคู่ออกโดยอัตโนมัติและเริ่มกระบวนการจับคู่ใหม่ ซึ่งอาจนำไปสู่การจับคู่อีกครั้งโดยไม่ตั้งใจ เราพบว่ามีหลายครั้งที่แอปไม่ได้จัดการเหตุการณ์การสูญเสียพันธบัตรอย่างสม่ำเสมอ
Android 16 ได้ปรับปรุงการจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงกับระบบเพื่อรวมประสบการณ์การใช้งาน หากไม่สามารถตรวจสอบสิทธิ์อุปกรณ์บลูทูธที่จับคู่ไว้ก่อนหน้านี้เมื่อเชื่อมต่ออีกครั้ง ระบบจะยกเลิกการเชื่อมต่อ เก็บข้อมูลการจับคู่ในเครื่อง และแสดงกล่องโต้ตอบของระบบเพื่อแจ้งให้ผู้ใช้ทราบถึงการสูญเสียการจับคู่และนำผู้ใช้ไปยังการจับคู่อีกครั้ง

