Android 14에는 개발자를 위한 훌륭한 기능과 API가 도입되었습니다. 다음을 통해 앱의 기능을 알아보고 관련 API를 시작할 수 있습니다.
추가, 수정, 삭제된 API에 대한 자세한 목록은 API 차이점 보고서를 참조하세요. 추가된 API에 관한 자세한 내용은 Android API 참조를 참고하세요. Android 14의 경우 API 수준 34에 추가된 API를 찾아보세요. 지역에 대해 알아보기 위해 플랫폼 변경사항이 앱에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 경우 Android 14 Android 14를 타겟팅하는 앱 및 모든 앱의 동작 변경사항
다국어 지원
앱별 언어 설정
Android 14에서는 Android 13(API 수준 33)에서 도입된 앱별 언어 기능을 다음과 같은 추가 기능으로 확장합니다.
앱의
localeConfig자동으로 생성: Android 스튜디오 Giraffe Canary 7 및 AGP 8.1.0-alpha07부터 앱이 앱별 언어 설정을 자동으로 지원하도록 구성할 수 있습니다. Android Gradle 플러그인은 프로젝트 리소스를 기반으로LocaleConfig파일을 생성하고 최종 매니페스트 파일에 이에 대한 참조를 추가하므로 더 이상 수동으로 파일을 만들거나 업데이트할 필요가 없습니다. AGP는 앱 모듈의res폴더에 있는 리소스 및 모든 라이브러리 모듈 종속 항목을 사용하여LocaleConfig파일에 포함할 언어를 결정합니다.앱의
localeConfig동적 업데이트:LocaleManager에서setOverrideLocaleConfig()및getOverrideLocaleConfig()메서드를 사용하여 기기의 시스템 설정에서 앱의 지원되는 언어 목록을 동적으로 업데이트합니다. 앱에서 현지화에 서버 측 푸시를 활용하는 경우 이러한 유연성을 사용하여 지역별 지원되는 언어 목록을 맞춤설정하거나 A/B 실험을 실행하거나 업데이트된 언어 목록을 제공합니다.입력 방식 편집기(IME)의 앱 언어 공개 상태: IME는
getApplicationLocales()메서드를 활용하여 현재 앱의 언어를 확인하고 IME 언어를 해당 언어와 일치시킬 수 있습니다.
Grammatical Inflection API
30억 명의 사용자가 성별이 지정된 언어를 사용합니다. 이 언어는 이야기하는 사람과 사물의 성별에 따라 문법적 카테고리(예: 명사, 동사, 형용사, 전치사)가 영향을 받는 언어입니다. 일반적으로 성별이 지정된 많은 언어에서 남성형 문법적 성별을 기본 성별이나 일반 성별로 사용합니다.
여성을 남성형 문법적 성별로 언급하는 등 잘못된 문법적 성별로 사용자를 언급하면 사용자의 실적과 태도에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 반면 사용자의 문법적 성별을 올바르게 반영하는 언어로 된 UI는 사용자 참여를 개선하고 보다 맞춤설정되고 자연스러운 사용자 환경을 제공할 수 있습니다.
To help you build a user-centric UI for gendered languages, Android 14 introduces the Grammatical Inflection API, which lets you add support for grammatical gender without refactoring your app.
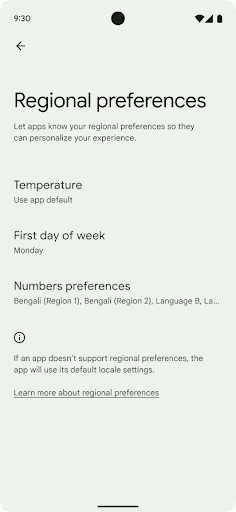
지역 설정
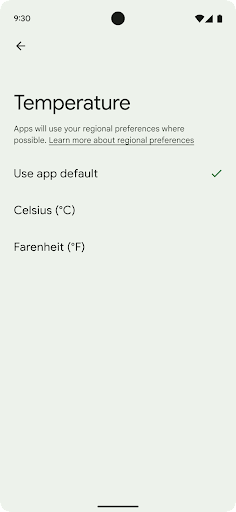
Regional preferences enable users to personalize temperature units, the first day of the week, and numbering systems. A European living in the United States might prefer temperature units to be in Celsius rather than Fahrenheit and for apps to treat Monday as the beginning of the week instead of the US default of Sunday.
New Android Settings menus for these preferences provide users with a
discoverable and centralized location to change app preferences. These
preferences also persist through backup and restore. Several APIs and
intents—such as
getTemperatureUnit
and
getFirstDayOfWeek—
grant your app read access to user preferences, so your app can adjust how it
displays information. You can also register a
BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
to handle locale configuration changes when regional preferences change.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & input > Regional preferences.
접근성
비선형 글꼴 크기 200%로 조정
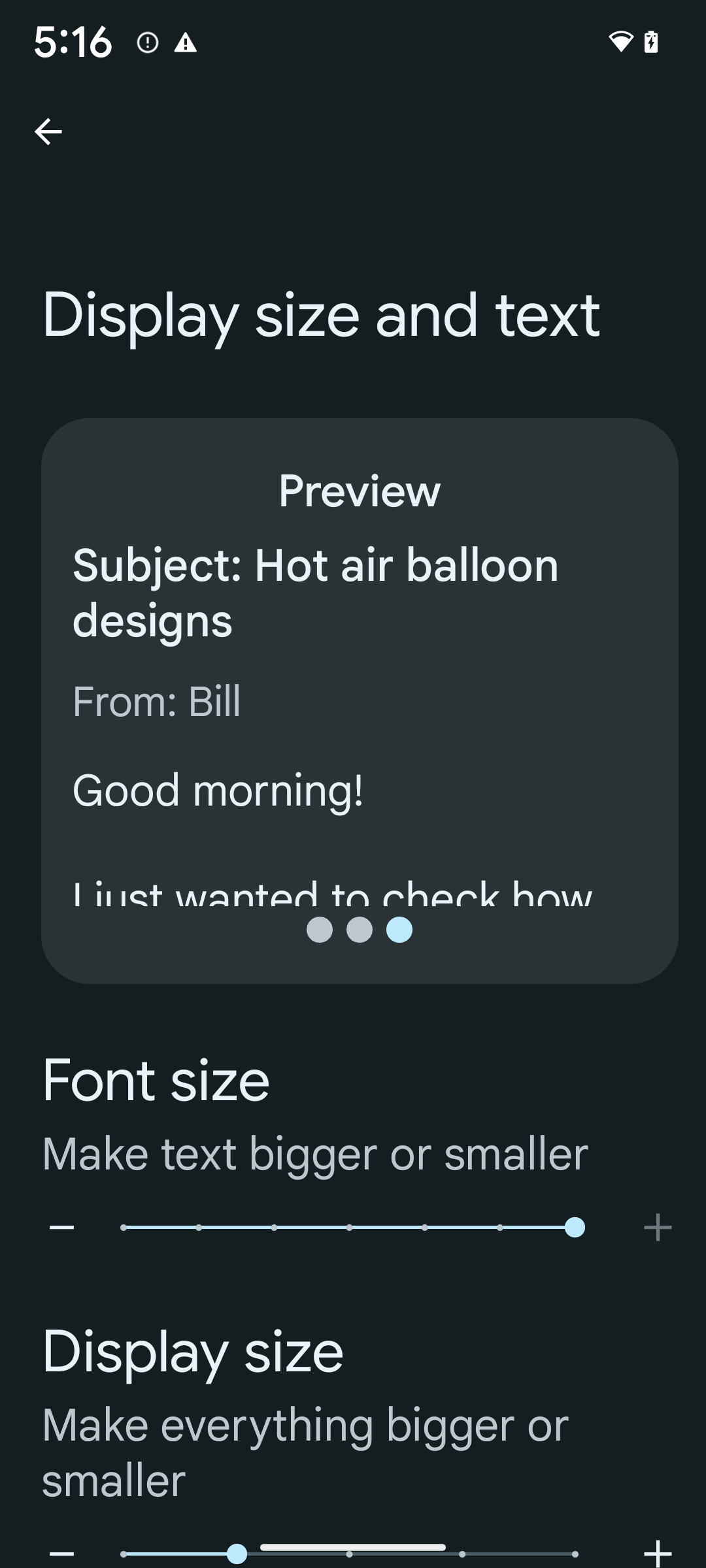
Starting in Android 14, the system supports font scaling up to 200%, providing low-vision users with additional accessibility options that align with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
To prevent large text elements on screen from scaling too large, the system applies a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling strategy means that large text doesn't scale at the same rate as smaller text. Nonlinear font scaling helps preserve the proportional hierarchy between elements of different sizes while mitigating issues with linear text scaling at high degrees (such as text being cut off or text that becomes harder to read due to an extremely large display sizes).
Test your app with nonlinear font scaling
If you already use scaled pixels (sp) units to define text sizing, then these additional options and scaling improvements are applied automatically to the text in your app. However, you should still perform UI testing with the maximum font size enabled (200%) to ensure that your app applies the font sizes correctly and can accommodate larger font sizes without impacting usability.
To enable 200% font size, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Accessibility > Display size and text.
- For the Font size option, tap the plus (+) icon until the maximum font size setting is enabled, as shown in the image that accompanies this section.
Use scaled pixel (sp) units for text-sizes
Remember to always specify text sizes in sp units. When your app uses sp units, Android can apply the user's preferred text size and scale it appropriately.
Don't use sp units for padding or define view heights assuming implicit padding: with nonlinear font scaling sp dimensions might not be proportional, so 4sp + 20sp might not equal 24sp.
Convert scaled pixel (sp) units
Use TypedValue.applyDimension() to convert from sp units
to pixels, and use TypedValue.deriveDimension() to
convert pixels to sp. These methods apply the appropriate nonlinear scaling
curve automatically.
Avoid hardcoding equations using
Configuration.fontScale or
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Because font scaling is
nonlinear, the scaledDensity field is no longer accurate. The fontScale
field should be used for informational purposes only because fonts are no longer
scaled with a single scalar value.
Use sp units for lineHeight
Always define android:lineHeight using sp units instead
of dp, so the line height scales along with your text. Otherwise, if your text
is sp but your lineHeight is in dp or px, it doesn't scale and looks cramped.
TextView automatically corrects the lineHeight so that your intended
proportions are preserved, but only if both textSize and lineHeight are
defined in sp units.
카메라 및 미디어
이미지용 울트라 HDR

Android 14 adds support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) images that retain more of the information from the sensor when taking a photo, which enables vibrant colors and greater contrast. Android uses the Ultra HDR format, which is fully backward compatible with JPEG images, allowing apps to seamlessly interoperate with HDR images, displaying them in Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) as needed.
Rendering these images in the UI in HDR is done automatically by the framework
when your app opts in to using HDR UI for its Activity Window, either through a
manifest entry or at runtime by calling
Window.setColorMode(). You can also capture compressed Ultra
HDR still images on supported devices. With more colors recovered
from the sensor, editing in post can be more flexible. The
Gainmap associated with Ultra HDR images can be used to render
them using OpenGL or Vulkan.
카메라 확장 프로그램의 확대/축소, 초점, Postview 등
Android 14 upgrades and improves camera extensions, allowing apps to handle longer processing times, which enables improved images using compute-intensive algorithms like low-light photography on supported devices. These features give users an even more robust experience when using camera extension capabilities. Examples of these improvements include:
- Dynamic still capture processing latency estimation provides much more
accurate still capture latency estimates based on the current scene and
environment conditions. Call
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()to get aStillCaptureLatencyobject that has two latency estimation methods. ThegetCaptureLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureStartedandonCaptureProcessStarted(), and thegetProcessingLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureProcessStarted()and the final processed frame being available. - Support for capture progress callbacks so that apps can display the current
progress of long-running, still-capture processing operations. You can check
if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable, and if it is, you implement theonCaptureProcessProgressed()callback, which has the progress (from 0 to 100) passed in as a parameter. Extension specific metadata, such as
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHfor dialing in the amount of an extension effect, such as the amount of background blur withEXTENSION_BOKEH.Postview Feature for Still Capture in camera extensions, which provides a less-processed image more quickly than the final image. If an extension has increased processing latency, a postview image could be provided as a placeholder to improve UX and switched out later for the final image. You can check if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Then you can pass anOutputConfigurationtoExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Support for
SurfaceViewallowing for a more optimized and power-efficient preview render path.Support for tap to focus and zoom during extension usage.
센서 내 확대/축소
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
무손실 USB 오디오
Android 14에서는 USB 유선 헤드셋을 통한 오디오필 수준의 환경을 위한 무손실 오디오 형식을 지원합니다. USB 기기에서 기본 믹서 속성을 쿼리하고, 기본 믹서 속성 변경에 관한 리스너를 등록하고, AudioMixerAttributes 클래스를 사용하여 믹서 속성을 구성할 수 있습니다. 이 클래스는 채널 마스크, 샘플링 레이트, 오디오 믹서의 동작과 같은 형식을 나타냅니다. 이 클래스를 사용하면 믹싱, 볼륨 조정 또는 효과 처리 없이 오디오를 직접 전송할 수 있습니다.
개발자 생산성 및 도구
인증 관리자
Android 14 adds Credential Manager as a platform API, with additional support back to Android 4.4 (API level 19) devices through a Jetpack Library using Google Play services. Credential Manager aims to make sign-in easier for users with APIs that retrieve and store credentials with user-configured credential providers. Credential Manager supports multiple sign-in methods, including username and password, passkeys, and federated sign-in solutions (such as Sign-in with Google) in a single API.
Passkeys provide many advantages. For example, passkeys are built on industry standards, can work across different operating systems and browser ecosystems, and can be used with both websites and apps.
For more information, see the Credential Manager and passkeys documentation and the blogpost about Credential Manager and passkeys.
헬스 커넥트
헬스 커넥트는 사용자 건강/피트니스 데이터를 위한 기기 내 저장소입니다. 이를 통해 사용자는 자주 사용하는 앱 간에 데이터를 공유할 수 있으며, 한곳에서 이러한 앱과 공유할 데이터를 제어할 수 있습니다.
Android 14 이전 버전의 Android를 실행하는 기기에서는 Google Play 스토어에서 헬스 커넥트를 앱으로 다운로드할 수 있습니다. Android 14부터 헬스 커넥트는 플랫폼의 일부가 되며 별도의 다운로드 없이 Google Play 시스템 업데이트를 통해 업데이트를 수신합니다. 이를 통해 헬스 커넥트를 자주 업데이트할 수 있으며 앱은 Android 14 이상을 실행하는 기기에서 헬스 커넥트를 사용할 수 있다는 점을 활용할 수 있습니다. 사용자는 시스템 설정에 통합된 개인 정보 보호 설정을 통해 기기의 설정에서 헬스 커넥트에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
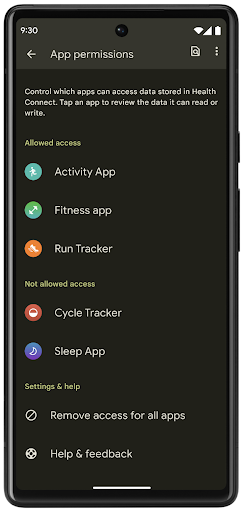
헬스 커넥트에는 운동 경로와 같은 Android 14의 몇 가지 새로운 기능이 포함되어 있어 사용자가 지도에 시각화할 수 있는 운동 경로를 공유할 수 있습니다. 경로는 일정 기간 내에 저장된 위치 목록으로 정의되며 앱은 운동 세션에 경로를 삽입하여 서로 연결할 수 있습니다. 사용자가 이 민감한 정보를 완전히 제어할 수 있도록 하려면 사용자가 개별 경로를 다른 앱과 공유하도록 허용해야 합니다.
자세한 내용은 헬스 커넥트 문서 및 Android 헬스의 새로운 기능 블로그 게시물을 참고하세요.
OpenJDK 17 업데이트
Android 14 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases, including both library updates and Java 17 language support for app and platform developers.
The following features and improvements are included:
- Updated approximately 300
java.baseclasses to Java 17 support. - Text Blocks, which introduce multi-line string literals to the Java programming language.
- Pattern Matching for instanceof, which allows an object to
be treated as having a specific type in an
instanceofwithout any additional variables. - Sealed classes, which allow you restrict which classes and interfaces can extend or implement them.
Thanks to Google Play system updates (Project Mainline), over 600 million devices are enabled to receive the latest Android Runtime (ART) updates that include these changes. This is part of our commitment to give apps a more consistent, secure environment across devices, and to deliver new features and capabilities to users independent of platform releases.
Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
앱 스토어 개선사항
Android 14 introduces several PackageInstaller APIs that
allow app stores to improve their user experience.
Request install approval before downloading
Installing or updating an app might require user approval.
For example, when an installer making use of the
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES permission attempts to install a
new app. In prior Android versions, app stores can only request user approval
after APKs are written to the install session and the
session is committed.
Starting with Android 14, the requestUserPreapproval()
method lets installers request user approval before committing the install
session. This improvement lets an app store defer downloading any APKs until
after the installation has been approved by the user. Furthermore, once a user
has approved installation, the app store can download and install the app in the
background without interrupting the user.
Claim responsibility for future updates
The setRequestUpdateOwnership() method allows an installer
to indicate to the system that it intends to be responsible for future updates
to an app it is installing. This capability enables update ownership
enforcement, meaning that only the update owner is permitted
to install automatic updates to the app. Update ownership enforcement helps to
ensure that users receive updates only from the expected app store.
Any other installer, including those making use of the
INSTALL_PACKAGES permission, must receive explicit user
approval in order to install an update. If a user decides to proceed with an
update from another source, update ownership is lost.
Update apps at less-disruptive times
App stores typically want to avoid updating an app that is actively in use because this leads to the app's running processes being killed, which potentially interrupts what the user was doing.
Starting with Android 14, the InstallConstraints API
gives installers a way to ensure that their app updates happen at an opportune
moment. For example, an app store can call the
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() method to
make sure that an update is only committed when the user is no longer
interacting with the app in question.
Seamlessly install optional splits
With split APKs, features of an app can be delivered in separate APK files,
rather than as a monolithic APK. Split APKs allow app stores to optimize the
delivery of different app components. For example, app stores might optimize
based on the properties of the target device. The
PackageInstaller API has supported splits since its
introduction in API level 22.
In Android 14, the setDontKillApp() method allows an
installer to indicate that the app's running processes shouldn't be killed when
new splits are installed. App stores can use this feature to seamlessly install
new features of an app while the user is using the app.
앱 메타데이터 번들
Starting in Android 14, the Android package installer lets you specify app metadata, such as data safety practices, to include on app store pages such as Google Play.
사용자가 기기 스크린샷을 찍을 때 감지
To create a more standardized experience for detecting screenshots, Android 14 introduces a privacy-preserving screenshot detection API. This API lets apps register callbacks on a per-activity basis. These callbacks are invoked, and the user is notified, when the user takes a screenshot while that activity is visible.
사용자 환경
Sharesheet 맞춤 작업 및 개선된 순위 지정
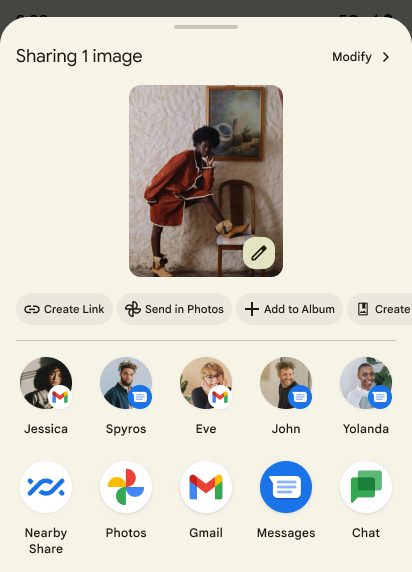
Android 14 updates the system sharesheet to support custom app actions and more informative preview results for users.
Add custom actions
With Android 14, your app can add custom actions to the system sharesheet it invokes.
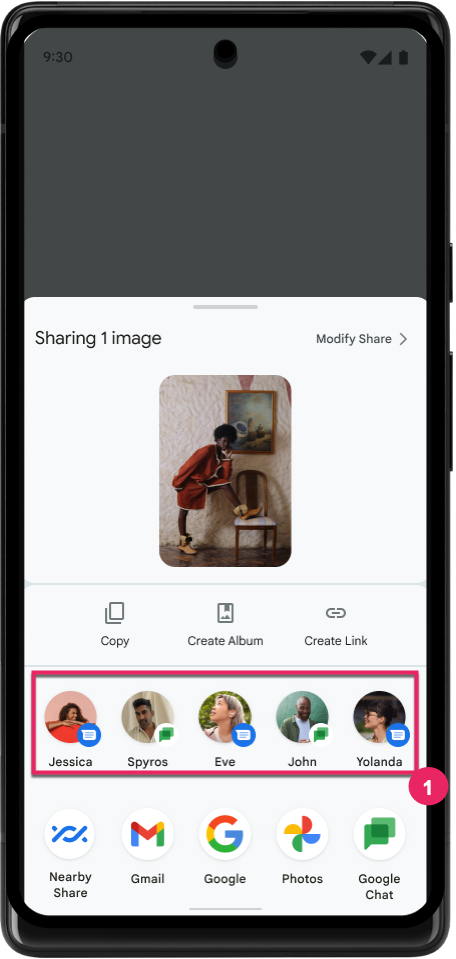
Improve ranking of Direct Share targets
Android 14 uses more signals from apps to determine the ranking of the direct share targets to provide more helpful results for the user. To provide the most useful signal for ranking, follow the guidance for improving rankings of your Direct Share targets. Communication apps can also report shortcut usage for outgoing and incoming messages.
뒤로 탐색 예측을 위한 내장 및 맞춤 애니메이션 지원
Android 13 introduced the predictive back-to-home animation behind a developer option. When used in a supported app with the developer option enabled, swiping back shows an animation indicating that the back gesture exits the app back to the home screen.
Android 14 includes multiple improvements and new guidance for Predictive Back:
- You can set
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueto opt in to predictive back system animations per-Activity instead of for the entire app. - We've added new system animations to accompany the back-to-home animation from Android 13. The new system animations are cross-activity and cross-task, which you get automatically after migrating to Predictive Back.
- We've added new Material Component animations for Bottom sheets, Side sheets, and Search.
- We've created design guidance for creating custom in-app animations and transitions.
- We've added new APIs to support custom in-app transition animations:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Use
overrideActivityTransitioninstead ofoverridePendingTransitionfor transitions that respond as the user swipes back.
With this Android 14 preview release, all features of Predictive Back remain behind a developer option. See the developer guide to migrate your app to predictive back, as well as the developer guide to creating custom in-app transitions.
대형 화면 기기 제조업체의 앱별 재정의
앱별 재정의를 사용하면 기기 제조업체가 대형 화면 기기에서 앱의 동작을 변경할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 FORCE_RESIZE_APP 재정의는 앱 매니페스트에 resizeableActivity="false"가 설정되어 있더라도 디스플레이 크기에 맞게 앱의 크기를 조절하도록 시스템에 지시합니다 (크기 호환성 모드 피하기).
재정의는 대형 화면에서 사용자 환경을 개선하기 위한 것입니다.
새 매니페스트 속성을 사용하면 앱에 대한 일부 기기 제조업체 재정의를 사용 중지할 수 있습니다.
대형 화면 사용자 앱별 재정의
Per-app overrides change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE device manufacturer override sets the app aspect ratio to 16:9 regardless of the app's configuration.
Android 14 QPR1 enables users to apply per‑app overrides by means of a new settings menu on large screen devices.
앱 화면 공유
App screen sharing enables users to share an app window instead of the entire device screen during screen content recording.
With app screen sharing, the status bar, navigation bar, notifications, and other system UI elements are excluded from the shared display. Only the content of the selected app is shared.
App screen sharing improves productivity and privacy by enabling users to run multiple apps but limit content sharing to a single app.
Pixel 8 Pro Gboard의 LLM 기반 스마트 답장
On Pixel 8 Pro devices with the December Feature Drop, developers can try out higher-quality smart replies in Gboard powered by on-device Large Language Models (LLMs) running on Google Tensor.
This feature is available as a limited preview for US English in WhatsApp, Line, and KakaoTalk. It requires using a Pixel 8 Pro device with Gboard as your keyboard.
To try it out, first enable the feature in Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent.
Next, open a conversation in a supported app to see LLM-powered Smart Reply in Gboard's suggestion strip in response to incoming messages.
그래픽
경로를 쿼리하고 보간할 수 있음
Android's Path API is a powerful and flexible mechanism for
creating and rendering vector graphics, with the ability to stroke or fill a
path, construct a path from line segments or quadratic or cubic curves, perform
boolean operations to get even more complex shapes, or all of these
simultaneously. One limitation is the ability to find out what is actually in a
Path object; the internals of the object are opaque to callers after creation.
To create a Path, you call methods such as
moveTo(), lineTo(), and
cubicTo() to add path segments. But there has been no way to
ask that path what the segments are, so you must retain that information at
creation time.
Starting in Android 14, you can query paths to find out what's inside of them.
First, you need to get a PathIterator object using the
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Next, you can call PathIterator to iterate through the segments
one by one, retrieving all of the necessary data for each segment. This example
uses PathIterator.Segment objects, which packages up the data
for you:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator also has a non-allocating version of next() where you can pass
in a buffer to hold the point data.
One of the important use cases of querying Path data is interpolation. For
example, you might want to animate (or morph) between two different paths. To
further simplify that use case, Android 14 also includes the
interpolate() method on Path. Assuming the two paths have
the same internal structure, the interpolate() method creates a new Path
with that interpolated result. This example returns a path whose shape is
halfway (a linear interpolation of .5) between path and otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
The Jetpack graphics-path library enables similar APIs for earlier versions of Android as well.
꼭짓점 및 프래그먼트 셰이더가 있는 맞춤 메시
Android has long supported drawing triangle meshes with custom shading, but the input mesh format has been limited to a few predefined attribute combinations. Android 14 adds support for custom meshes, which can be defined as triangles or triangle strips, and can, optionally, be indexed. These meshes are specified with custom attributes, vertex strides, varying, and vertex and fragment shaders written in AGSL.
The vertex shader defines the varyings, such as position and color, while the
fragment shader can optionally define the color for the pixel, typically by
using the varyings created by the vertex shader. If color is provided by the
fragment shader, it is then blended with the current Paint
color using the blend mode selected when
drawing the mesh. Uniforms can be passed
into the fragment and vertex shaders for additional flexibility.
캔버스용 하드웨어 버퍼 렌더기
Android의 Canvas API를 사용하여 하드웨어 가속으로 HardwareBuffer에 그리는 것을 지원하기 위해 Android 14에서는 HardwareBufferRenderer를 도입합니다. 이 API는
시스템과의 통신이 포함된 사용 사례에 특히 유용합니다
짧은 지연 시간을 위해 SurfaceControl를 통한 컴포지터
있습니다.

