Platform Android 16 menyertakan perubahan perilaku yang mungkin memengaruhi aplikasi Anda.
Perubahan perilaku berikut ini berlaku untuk semua aplikasi saat dijalankan di Android 16,
terlepas dari targetSdkVersion. Sebaiknya uji aplikasi Anda, lalu modifikasi sesuai kebutuhan untuk mendukung perubahan ini, jika memungkinkan.
Selain itu, pastikan Anda meninjau daftar perubahan perilaku yang hanya memengaruhi aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16.
Fungsi inti
Android 16 (level API 36) mencakup perubahan berikut yang mengubah atau memperluas berbagai kemampuan inti sistem Android.
Pengoptimalan kuota JobScheduler
Mulai Android 16, kami menyesuaikan kuota runtime eksekusi tugas reguler dan dipercepat berdasarkan faktor-faktor berikut:
- Bucket siaga aplikasi tempat aplikasi berada: di Android 16, bucket siaga aktif akan mulai diterapkan dengan kuota runtime yang besar.
- Jika tugas mulai dieksekusi saat aplikasi berada dalam status teratas: di Android 16, Tugas yang dimulai saat aplikasi terlihat oleh pengguna dan berlanjut setelah aplikasi menjadi tidak terlihat, akan mematuhi kuota runtime tugas.
- Jika tugas sedang dieksekusi saat menjalankan Layanan Latar Depan: di Android 16, tugas yang dieksekusi secara bersamaan dengan layanan latar depan akan mematuhi kuota runtime tugas. Jika Anda memanfaatkan tugas untuk transfer data yang dimulai pengguna, sebaiknya gunakan tugas transfer data yang dimulai pengguna.
Perubahan ini memengaruhi tugas yang dijadwalkan menggunakan WorkManager, JobScheduler, dan
DownloadManager. Untuk men-debug alasan tugas dihentikan, sebaiknya catat alasan tugas Anda dihentikan dengan memanggil WorkInfo.getStopReason() (untuk tugas JobScheduler, panggil JobParameters.getStopReason()).
Untuk mengetahui informasi tentang pengaruh status aplikasi terhadap resource yang dapat digunakannya, lihat Batas resource pengelolaan daya. Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang praktik terbaik yang mengoptimalkan baterai, lihat panduan tentang mengoptimalkan penggunaan baterai untuk API penjadwalan tugas.
Sebaiknya manfaatkan juga API
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory baru yang diperkenalkan di
Android 16 untuk memahami alasan tugas belum dieksekusi.
Pengujian
Untuk menguji perilaku aplikasi, Anda dapat mengaktifkan penggantian pengoptimalan kuota tugas tertentu selama aplikasi berjalan di perangkat Android 16.
Untuk menonaktifkan penerapan "status teratas akan mematuhi kuota runtime tugas", jalankan perintah adb berikut:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Untuk menonaktifkan penerapan "tugas yang dieksekusi secara bersamaan dengan
layanan latar depan akan mematuhi kuota runtime tugas", jalankan perintah
adb berikut:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Untuk menguji perilaku bucket standby aplikasi tertentu, Anda dapat menyetel bucket standby aplikasi
menggunakan perintah adb berikut:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
Untuk memahami bucket standby aplikasi tempat aplikasi Anda berada, Anda bisa mendapatkan bucket standby aplikasi menggunakan perintah adb berikut:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Alasan penghentian tugas kosong yang ditinggalkan
Tugas yang ditinggalkan terjadi saat objek JobParameters yang terkait dengan tugas
telah dibersihkan sampah memorinya, tetapi JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) belum dipanggil untuk menandakan penyelesaian tugas. Hal ini menunjukkan bahwa
tugas mungkin sedang berjalan dan dijadwalkan ulang tanpa sepengetahuan aplikasi.
Aplikasi yang mengandalkan JobScheduler, tidak mempertahankan referensi yang kuat ke
objek JobParameters, dan waktu tunggu kini akan diberi alasan penghentian tugas baru
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, bukan STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
Jika alasan perhentian yang ditinggalkan baru sering terjadi, sistem akan mengambil langkah mitigasi untuk mengurangi frekuensi tugas.
Aplikasi harus menggunakan alasan penghentian baru untuk mendeteksi dan mengurangi tugas yang ditinggalkan.
Jika menggunakan WorkManager, AsyncTask, atau DownloadManager, Anda tidak akan terpengaruh karena API ini mengelola siklus proses tugas atas nama aplikasi Anda.
Menghentikan penggunaan JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground sepenuhnya
Metode JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean)
menunjukkan tingkat kepentingan tugas saat aplikasi penjadwalan berada di
latar depan atau saat dikecualikan sementara dari pembatasan latar belakang.
Metode ini tidak digunakan lagi sejak Android 12 (API level 31). Mulai Android 16, metode ini tidak lagi berfungsi secara efektif dan memanggil metode ini akan diabaikan.
Penghapusan fungsi ini juga berlaku untuk
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). Mulai Android
16, jika metode dipanggil, metode akan menampilkan false.
Cakupan prioritas siaran berurutan tidak lagi global
Aplikasi Android diizinkan untuk menentukan prioritas pada penerima siaran untuk mengontrol
urutan penerima menerima dan memproses siaran. Untuk
penerima yang dideklarasikan dalam manifes, aplikasi dapat menggunakan
atribut android:priority untuk menentukan prioritas dan untuk
penerima yang terdaftar dalam konteks, aplikasi dapat menggunakan
IntentFilter#setPriority() API untuk menentukan prioritas. Saat
siaran dikirim, sistem akan mengirimkannya ke penerima sesuai urutan
prioritasnya, dari yang tertinggi ke yang terendah.
Di Android 16, urutan pengiriman siaran menggunakan atribut android:priority
atau IntentFilter#setPriority() di berbagai proses tidak akan
dijamin. Prioritas siaran hanya akan dihormati dalam proses
aplikasi yang sama, bukan di semua proses.
Selain itu, prioritas siaran akan otomatis dibatasi pada rentang
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Hanya komponen sistem yang akan
diizinkan untuk menetapkan SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY sebagai
prioritas siaran.
Aplikasi Anda mungkin terpengaruh jika melakukan salah satu hal berikut:
- Aplikasi Anda telah mendeklarasikan beberapa proses dengan intent siaran yang sama, dan memiliki ekspektasi seputar penerimaan intent tersebut dalam urutan tertentu berdasarkan prioritas.
- Proses aplikasi Anda berinteraksi dengan proses lain dan memiliki ekspektasi tentang menerima intent siaran dalam urutan tertentu.
Jika proses perlu berkoordinasi satu sama lain, proses tersebut harus berkomunikasi menggunakan saluran koordinasi lain.
Perubahan internal ART
Android 16 menyertakan update terbaru ke Android Runtime (ART) yang meningkatkan performa Android Runtime (ART) dan memberikan dukungan untuk fitur Java tambahan. Melalui update Sistem Google Play, peningkatan ini juga tersedia untuk lebih dari satu miliar perangkat yang menjalankan Android 12 (API level 31) dan yang lebih tinggi.
Saat perubahan ini dirilis, library dan kode aplikasi yang mengandalkan struktur internal ART mungkin tidak berfungsi dengan benar di perangkat yang menjalankan Android 16, beserta versi Android sebelumnya yang mengupdate modul ART melalui update sistem Google Play.
Mengandalkan struktur internal (seperti antarmuka non-SDK) dapat selalu menyebabkan masalah kompatibilitas, tetapi sangat penting untuk menghindari mengandalkan kode (atau library yang berisi kode) yang memanfaatkan struktur ART internal, karena perubahan ART tidak terikat dengan versi platform yang dijalankan perangkat dan perubahan tersebut dikirim ke lebih dari satu miliar perangkat melalui update sistem Google Play.
Semua developer harus memeriksa apakah aplikasi mereka terpengaruh dengan menguji aplikasi secara menyeluruh di Android 16. Selain itu, periksa masalah umum untuk mengetahui apakah aplikasi Anda bergantung pada library yang telah kami identifikasi yang mengandalkan struktur ART internal. Jika Anda memiliki kode aplikasi atau dependensi library yang terpengaruh, cari alternatif API publik jika memungkinkan dan minta API publik untuk kasus penggunaan baru dengan membuat permintaan fitur di issue tracker kami.
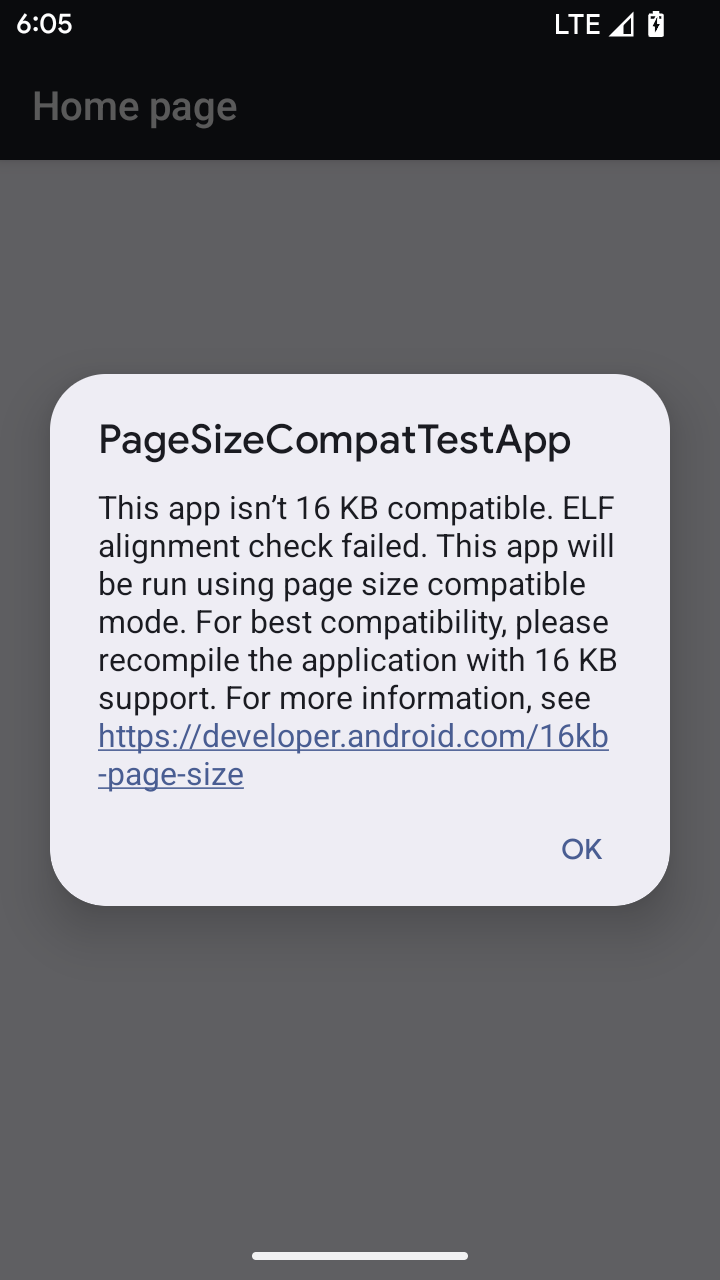
Mode kompatibilitas ukuran halaman 16 KB
Android 15 memperkenalkan dukungan untuk halaman memori 16 KB guna mengoptimalkan performa platform. Android 16 menambahkan mode kompatibilitas, yang memungkinkan beberapa aplikasi yang di-build untuk halaman memori 4 KB berjalan di perangkat yang dikonfigurasi untuk halaman memori 16 KB.
Saat aplikasi Anda berjalan di perangkat dengan Android 16 atau yang lebih tinggi, jika Android
mendeteksi bahwa aplikasi Anda memiliki halaman memori yang diselaraskan 4 KB, aplikasi akan otomatis menggunakan
mode kompatibilitas dan menampilkan dialog notifikasi kepada pengguna. Menetapkan
properti android:pageSizeCompat di AndroidManifest.xml untuk mengaktifkan
mode kompatibilitas mundur akan mencegah tampilan dialog saat
aplikasi diluncurkan. Untuk menggunakan properti android:pageSizeCompat, kompilasi aplikasi Anda
menggunakan Android 16 SDK.
Untuk performa, keandalan, dan stabilitas terbaik, aplikasi Anda harus tetap selaras dengan 16 KB. Lihat postingan blog terbaru kami tentang mengupdate aplikasi Anda untuk mendukung halaman memori 16 KB guna mengetahui detail selengkapnya.
Pengalaman pengguna dan UI sistem
Android 16 (level API 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut yang dimaksudkan untuk menciptakan pengalaman pengguna yang lebih konsisten dan intuitif.
Menghentikan penggunaan pengumuman aksesibilitas yang mengganggu
Android 16 tidak lagi menggunakan pengumuman aksesibilitas, yang ditandai dengan penggunaan
announceForAccessibility atau pengiriman
peristiwa aksesibilitas TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT. Hal ini dapat membuat
pengalaman pengguna yang tidak konsisten bagi pengguna TalkBack dan pembaca layar Android,
dan alternatifnya lebih baik memenuhi berbagai kebutuhan pengguna di berbagai
teknologi asistif Android.
Contoh alternatif:
- Untuk perubahan UI yang signifikan seperti perubahan jendela, gunakan
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)dansetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). Di Compose, gunakanModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - Untuk memberi tahu pengguna tentang perubahan pada UI penting, gunakan
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). Di Compose, gunakanModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. Fungsi ini sebaiknya digunakan seperlunya karena dapat menghasilkan pengumuman setiap kali Tampilan diperbarui. - Untuk memberi tahu pengguna tentang error, kirim
AccessibilityEventdari jenisAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORdan tetapkanAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence), atau gunakanTextView#setError(CharSequence).
Dokumentasi referensi untuk announceForAccessibility API
yang tidak digunakan lagi menyertakan detail selengkapnya tentang
alternatif yang disarankan.
Dukungan untuk navigasi 3 tombol
Android 16 menghadirkan dukungan kembali prediktif ke navigasi 3 tombol untuk aplikasi yang telah dimigrasikan dengan benar ke kembali prediktif. Menekan lama tombol kembali akan memulai animasi kembali prediktif, yang memberi Anda pratinjau tempat geser kembali akan membawa Anda.
Perilaku ini berlaku di semua area sistem yang mendukung animasi kembali prediktif, termasuk animasi sistem (kembali ke layar utama, lintas tugas, dan lintas aktivitas).
Ikon aplikasi bertema otomatis
Mulai dari Android 16 QPR 2, Android secara otomatis menerapkan tema ke ikon aplikasi untuk menciptakan pengalaman layar utama yang kohesif. Hal ini terjadi jika aplikasi tidak menyediakan ikon aplikasi bertemanya sendiri. Aplikasi dapat mengontrol desain ikon aplikasi bertema dengan menyertakan lapisan monokrom dalam ikon adaptif dan melihat pratinjau tampilan ikon aplikasi di Android Studio.
Faktor bentuk perangkat
Android 16 (level API 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut untuk aplikasi saat diproyeksikan ke layar oleh pemilik perangkat virtual.
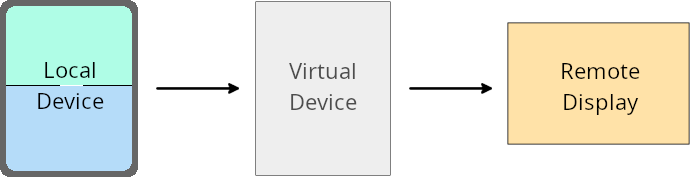
Penggantian pemilik perangkat virtual
Pemilik perangkat virtual adalah aplikasi tepercaya atau istimewa yang membuat dan mengelola perangkat virtual. Pemilik perangkat virtual menjalankan aplikasi di perangkat virtual, lalu memproyeksikan aplikasi ke layar perangkat jarak jauh, seperti komputer pribadi, perangkat virtual reality, atau sistem infotainment mobil. Pemilik perangkat virtual berada di perangkat lokal, seperti ponsel.
Penggantian per aplikasi
Di perangkat yang menjalankan Android 16 (level API 36), pemilik perangkat virtual dapat mengganti setelan aplikasi di perangkat virtual tertentu yang dikelola pemilik perangkat virtual. Misalnya, untuk meningkatkan tata letak aplikasi, pemilik perangkat virtual dapat mengabaikan batasan orientasi, rasio aspek, dan kemampuan pengubahan ukuran saat memproyeksikan aplikasi ke layar eksternal.
Perubahan umum yang dapat menyebabkan gangguan
Perilaku Android 16 dapat memengaruhi UI aplikasi Anda pada faktor bentuk layar besar seperti layar mobil atau Chromebook, terutama tata letak yang didesain untuk layar kecil dalam orientasi potret. Untuk mempelajari cara membuat aplikasi Anda adaptif untuk semua faktor bentuk perangkat, lihat Tentang tata letak adaptif.
Referensi
Keamanan
Android 16 (level API 36) menyertakan perubahan yang meningkatkan keamanan sistem untuk membantu melindungi aplikasi dan pengguna dari aplikasi berbahaya.
Peningkatan keamanan terhadap serangan pengalihan Intent
Android 16 memberikan keamanan default terhadap serangan pengalihan Intent umum, dengan kompatibilitas minimum dan perubahan developer yang diperlukan.
Kami memperkenalkan solusi penguatan keamanan secara default untuk Intenteksploitasi pengalihan. Pada umumnya, aplikasi yang menggunakan intent biasanya tidak akan mengalami masalah kompatibilitas; kami telah mengumpulkan metrik selama proses pengembangan untuk memantau aplikasi mana yang mungkin mengalami kerusakan.
Pengalihan intent di Android terjadi saat penyerang dapat mengontrol sebagian atau seluruh konten intent yang digunakan untuk meluncurkan komponen baru dalam konteks aplikasi yang rentan, sementara aplikasi korban meluncurkan intent sub-level yang tidak tepercaya di kolom tambahan Intent ("level teratas"). Hal ini dapat menyebabkan aplikasi penyerang meluncurkan komponen pribadi dalam konteks aplikasi korban, memicu tindakan istimewa, atau mendapatkan akses URI ke data sensitif, yang berpotensi menyebabkan pencurian data dan eksekusi kode arbitrer.
Memilih tidak ikut penanganan pengalihan Intent
Android 16 memperkenalkan API baru yang memungkinkan aplikasi memilih untuk tidak menggunakan perlindungan keamanan peluncuran. Hal ini mungkin diperlukan dalam kasus tertentu saat perilaku keamanan default mengganggu kasus penggunaan aplikasi yang sah.
Untuk aplikasi yang dikompilasi terhadap SDK Android 16 (level API 36) atau yang lebih tinggi
Anda dapat langsung menggunakan metode removeLaunchSecurityProtection() pada objek Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Untuk aplikasi yang dikompilasi terhadap Android 15 (level API 35) atau yang lebih rendah
Meskipun tidak direkomendasikan, Anda dapat menggunakan refleksi untuk mengakses metode
removeLaunchSecurityProtection().
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Aplikasi pendamping tidak lagi diberi tahu tentang waktu tunggu penemuan
Android 16 memperkenalkan perilaku baru selama
alur penyambungan perangkat pendamping untuk melindungi privasi
lokasi pengguna dari aplikasi berbahaya. Semua aplikasi pendamping yang berjalan di Android 16 tidak
lagi diberi tahu secara langsung tentang waktu tunggu penemuan yang habis menggunakan
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Sebagai gantinya, pengguna
akan diberi tahu tentang peristiwa waktu tunggu habis dengan dialog visual. Saat pengguna menutup
dialog, aplikasi akan diberi tahu tentang kegagalan pengaitan dengan
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
Durasi penelusuran juga telah diperpanjang dari 20 detik awal, dan penemuan perangkat dapat dihentikan oleh pengguna kapan saja selama penelusuran. Jika setidaknya satu perangkat ditemukan dalam 20 detik pertama sejak memulai penelusuran, CDM akan berhenti menelusuri perangkat tambahan.
Konektivitas
Android 16 (level API 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut dalam stack Bluetooth untuk meningkatkan konektivitas dengan perangkat periferal.
Peningkatan penanganan kehilangan ikatan
Mulai Android 16, stack Bluetooth telah diupdate untuk meningkatkan keamanan dan pengalaman pengguna saat kehilangan ikatan jarak jauh terdeteksi. Sebelumnya, sistem akan otomatis menghapus ikatan dan memulai proses penyambungan baru, yang dapat menyebabkan penyambungan ulang yang tidak disengaja. Kami telah melihat dalam banyak kasus aplikasi tidak menangani peristiwa kehilangan ikatan secara konsisten.
Untuk menyatukan pengalaman, Android 16 meningkatkan penanganan kehilangan ikatan ke sistem. Jika perangkat Bluetooth yang sebelumnya tersambung tidak dapat diautentikasi setelah terhubung kembali, sistem akan memutuskan hubungan link, mempertahankan informasi ikatan lokal, dan menampilkan dialog sistem yang memberi tahu pengguna tentang hilangnya ikatan dan mengarahkan mereka untuk menyambungkan kembali.

