Seperti rilis sebelumnya, Android 16 menyertakan perubahan perilaku yang mungkin memengaruhi aplikasi Anda. Perubahan perilaku berikut ini berlaku khusus bagi aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16 atau yang lebih tinggi. Jika aplikasi Anda menargetkan Android 16 atau yang lebih tinggi, Anda harus memodifikasi aplikasi untuk mendukung perilaku ini, jika berlaku.
Pastikan Anda juga meninjau daftar perubahan perilaku yang memengaruhi semua aplikasi yang berjalan di Android 16, terlepas dari targetSdkVersion aplikasi Anda.
Pengalaman pengguna dan UI sistem
Android 16 (level API 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut yang dimaksudkan untuk menciptakan pengalaman pengguna yang lebih konsisten dan intuitif.
Penghapusan opsi tidak menggunakan layar penuh
Android 15 menerapkan tampilan layar penuh untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 15 (level API 35), tetapi aplikasi Anda dapat memilih tidak menggunakan tampilan layar penuh dengan menyetel
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement ke true. Untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16 (level API 36),
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement tidak digunakan lagi dan dinonaktifkan, dan
aplikasi Anda tidak dapat memilih untuk tidak menggunakan tampilan layar penuh.
- Jika aplikasi Anda menargetkan Android 16 (level API 36) dan berjalan di perangkat Android 15,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementakan terus berfungsi. - Jika aplikasi Anda menargetkan Android 16 (level API 36) dan berjalan di
perangkat Android 16,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementdinonaktifkan.
Untuk pengujian di Android 16, pastikan aplikasi Anda mendukung layar penuh dan hapus penggunaan R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement agar aplikasi Anda juga mendukung layar penuh di perangkat Android 15. Untuk mendukung tampilan layar penuh, lihat panduan Compose dan View.
Migrasi atau penonaktifan diperlukan untuk kembali prediktif
Untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16 (level API 36) atau yang lebih tinggi dan berjalan di perangkat Android 16 atau yang lebih tinggi, animasi sistem kembali prediktif
(kembali ke layar utama, lintas tugas, dan lintas aktivitas) diaktifkan secara default.
Selain itu, onBackPressed tidak dipanggil dan
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK tidak dikirim lagi.
Jika aplikasi Anda mencegat peristiwa kembali dan Anda belum bermigrasi ke kembali
prediktif, update aplikasi Anda untuk menggunakan API navigasi kembali yang didukung, atau
nonaktifkan sementara dengan menetapkan atribut
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback ke false dalam tag
<application> atau <activity> pada file AndroidManifest.xml aplikasi Anda.
API font elegan tidak digunakan lagi dan dinonaktifkan
Aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 15 (level API 35) memiliki atribut
elegantTextHeight
TextView yang ditetapkan ke true secara
default, menggantikan font ringkas dengan font yang jauh lebih mudah dibaca. Anda dapat mengganti perilaku ini dengan menyetel atribut elegantTextHeight ke false.
Android 16 menghentikan penggunaan atribut
elegantTextHeight,
dan atribut akan diabaikan setelah aplikasi Anda menargetkan Android 16. "Font UI" yang dikontrol oleh API ini akan dihentikan, jadi Anda harus menyesuaikan tata letak apa pun untuk memastikan rendering teks yang konsisten dan siap untuk masa mendatang dalam bahasa Arab, Laos, Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu, atau Thai.
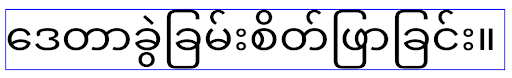 Perilaku
Perilaku elegantTextHeight untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android
14 (level API 34) dan yang lebih rendah, atau untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 15 (level API 35)
yang mengganti default dengan menyetel atribut elegantTextHeight
ke false. Perilaku
Perilaku elegantTextHeight untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android
16 (level API 36), atau untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 15 (level API 35) yang tidak
mengganti default dengan menyetel atribut elegantTextHeight
ke false.Fungsi inti
Android 16 (level API 36) mencakup perubahan berikut yang mengubah atau memperluas berbagai kemampuan inti sistem Android.
Pengoptimalan penjadwalan kerja tarif tetap
Sebelum menargetkan Android 16, saat scheduleAtFixedRate
melewatkan eksekusi tugas karena berada di luar
siklus proses yang valid, semua eksekusi yang terlewat akan segera
dijalankan saat aplikasi kembali ke siklus proses yang valid.
Saat menargetkan Android 16, maksimal satu eksekusi yang terlewat dari
scheduleAtFixedRate akan langsung dieksekusi saat aplikasi
kembali ke siklus proses yang valid. Perubahan perilaku ini diharapkan dapat meningkatkan performa
aplikasi. Uji perilaku ini di aplikasi Anda untuk memeriksa apakah aplikasi Anda terpengaruh.
Anda juga dapat menguji dengan menggunakan framework kompatibilitas aplikasi
dan mengaktifkan flag kompatibilitas STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS.
Faktor bentuk perangkat
Android 16 (level API 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut untuk aplikasi saat ditampilkan di perangkat layar besar.
Tata letak adaptif
Dengan aplikasi Android yang kini berjalan di berbagai perangkat (seperti ponsel, tablet, perangkat foldable, desktop, mobil, dan TV) dan mode tampilan jendela di layar besar (seperti tampilan layar terpisah dan tampilan jendela desktop), developer harus membuat aplikasi Android yang beradaptasi dengan ukuran layar dan jendela apa pun, terlepas dari orientasi perangkat. Paradigma seperti membatasi orientasi dan kemampuan mengubah ukuran terlalu membatasi di dunia multiperangkat saat ini.
Mengabaikan batasan orientasi, kemampuan mengubah ukuran, dan rasio aspek
Untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16 (level API 36), batasan orientasi, perubahan ukuran, dan rasio aspek tidak lagi berlaku pada layar dengan lebar terkecil >= 600 dp. Aplikasi mengisi seluruh jendela tampilan, terlepas dari rasio aspek atau orientasi pilihan pengguna, dan tidak menggunakan pillarboxing.
Perubahan ini memperkenalkan perilaku platform standar baru. Android beralih ke model yang mengharuskan aplikasi beradaptasi dengan berbagai orientasi, ukuran tampilan, dan rasio aspek. Batasan seperti orientasi tetap atau kemampuan mengubah ukuran yang terbatas menghambat kemampuan adaptasi aplikasi. Buat aplikasi Anda adaptif untuk memberikan pengalaman pengguna terbaik.
Anda juga dapat menguji perilaku ini menggunakan
framework kompatibilitas aplikasi dan mengaktifkan
flag kompatibilitas UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT.
Perubahan umum yang dapat menyebabkan gangguan
Mengabaikan batasan orientasi, kemampuan mengubah ukuran, dan rasio aspek dapat memengaruhi UI aplikasi Anda di beberapa perangkat, terutama elemen yang didesain untuk tata letak kecil yang terkunci dalam orientasi potret: misalnya, masalah seperti tata letak yang meregang dan animasi serta komponen di luar layar. Asumsi apa pun tentang rasio aspek atau orientasi dapat menyebabkan masalah visual pada aplikasi Anda. Pelajari lebih lanjut cara menghindarinya dan meningkatkan perilaku adaptif aplikasi Anda.
Mengizinkan rotasi perangkat akan menghasilkan pembuatan ulang aktivitas yang lebih banyak, yang dapat mengakibatkan hilangnya status pengguna jika tidak dipertahankan dengan benar. Pelajari cara menyimpan status UI dengan benar di Menyimpan status UI.
Detail implementasi
Atribut manifes dan API runtime berikut diabaikan di seluruh perangkat layar besar dalam mode layar penuh dan multi-aplikasi:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
Nilai berikut untuk screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), dan
getRequestedOrientation() diabaikan:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Terkait pengubahan ukuran tampilan, android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio, dan android:maxAspectRatio tidak berpengaruh.
Untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16 (level API 36), batasan orientasi, perubahan ukuran, dan rasio aspek aplikasi diabaikan di layar besar secara default, tetapi setiap aplikasi yang belum sepenuhnya siap dapat mengganti perilaku ini untuk sementara dengan memilih tidak ikut (yang menghasilkan perilaku sebelumnya, yaitu ditempatkan dalam mode kompatibilitas).
Pengecualian
Batasan orientasi, perubahan ukuran, dan rasio aspek Android 16 tidak berlaku dalam situasi berikut:
- Game (berdasarkan flag
android:appCategory) - Pengguna secara eksplisit memilih untuk menggunakan perilaku default aplikasi dalam setelan rasio aspek perangkat
- Layar yang lebih kecil dari
sw600dp
Nonaktifkan sementara
Untuk menonaktifkan aktivitas tertentu, deklarasikan properti manifes PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
Jika terlalu banyak bagian aplikasi Anda yang belum siap untuk Android 16, Anda dapat memilih untuk tidak ikut sepenuhnya dengan menerapkan properti yang sama di tingkat aplikasi:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Kesehatan dan kebugaran
Android 16 (level API 36) mencakup perubahan berikut terkait data kesehatan dan kebugaran.
Izin kesehatan dan kebugaran
Untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16 (level API 36) atau yang lebih tinggi, izin
BODY_SENSORS menggunakan izin yang lebih terperinci
di android.permissions.health, yang juga digunakan oleh Health Connect. Mulai Android 16, setiap API yang sebelumnya memerlukan BODY_SENSORS
atau BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND memerlukan izin android.permissions.health yang sesuai. Hal ini memengaruhi jenis data, API, dan jenis layanan latar depan berikut:
HEART_RATE_BPMdari Layanan Kesehatan di Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEdari Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracydanheartRateBpmdariProtoLayoutdi Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHjika izinandroid.permission.healthyang sesuai diperlukan sebagai penggantiBODY_SENSORS
Jika aplikasi Anda menggunakan API ini, aplikasi tersebut harus meminta izin terperinci yang sesuai:
- Untuk pemantauan Detak Jantung, SpO2, atau Suhu Kulit saat digunakan:
minta izin terperinci di
android.permissions.health, sepertiREAD_HEART_RATE, bukanBODY_SENSORS. - Untuk akses sensor latar belakang: minta
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND, bukanBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
Izin ini sama dengan izin yang melindungi akses untuk membaca data dari Health Connect, penyimpanan data Android untuk data kesehatan, kebugaran, dan kebugaran.
Aplikasi seluler
Aplikasi seluler yang bermigrasi untuk menggunakan READ_HEART_RATE dan izin
terperinci lainnya juga harus mendeklarasikan aktivitas untuk menampilkan
kebijakan privasi aplikasi. Persyaratan ini sama dengan Health Connect.
Konektivitas
Android 16 (level API 36) menyertakan perubahan berikut dalam stack Bluetooth untuk meningkatkan konektivitas dengan perangkat periferal.
Maksud baru untuk menangani perubahan enkripsi dan hilangnya koneksi
Sebagai bagian dari Peningkatan penanganan kehilangan ikatan, Android 16 juga memperkenalkan 2 intent baru untuk memberi aplikasi kesadaran yang lebih besar tentang kehilangan ikatan dan perubahan enkripsi.
Aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16 kini dapat:
- Menerima intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGsaat kehilangan ikatan jarak jauh terdeteksi, sehingga memungkinkannya memberikan masukan pengguna yang lebih informatif dan mengambil tindakan yang sesuai. - Menerima intent
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEsetiap kali status enkripsi link berubah. Hal ini mencakup perubahan status enkripsi, perubahan algoritma enkripsi, dan perubahan ukuran kunci enkripsi. Aplikasi harus mempertimbangkan pengikatan yang dipulihkan jika link berhasil dienkripsi setelah menerima intentACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEnanti.
Beradaptasi dengan berbagai implementasi OEM
Meskipun Android 16 memperkenalkan intent baru ini, penerapan dan siarannya dapat bervariasi di berbagai produsen perangkat (OEM). Untuk memastikan aplikasi Anda memberikan pengalaman yang konsisten dan andal di semua perangkat, developer harus mendesain penanganan kehilangan ikatan untuk beradaptasi dengan baik dengan potensi variasi ini.
Sebaiknya gunakan perilaku aplikasi berikut:
Jika intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGdisiarkan:Link ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less) akan terputus oleh sistem, tetapi informasi ikatan untuk perangkat akan dipertahankan (seperti yang dijelaskan di sini).
Aplikasi Anda harus menggunakan intent ini sebagai sinyal utama untuk deteksi hilangnya ikatan dan memandu pengguna untuk mengonfirmasi bahwa perangkat jarak jauh berada dalam jangkauan sebelum memulai penghapusan perangkat atau penyambungan ulang.
Jika perangkat terputus setelah
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGditerima, aplikasi Anda harus berhati-hati saat menghubungkan kembali, karena perangkat mungkin tidak lagi terikat dengan sistem.Jika intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGTIDAK disiarkan:Link ACL akan tetap terhubung, dan informasi ikatan untuk perangkat akan dihapus oleh sistem, sama dengan perilaku di Android 15.
Dalam skenario ini, aplikasi Anda harus melanjutkan mekanisme penanganan hilangnya obligasi yang ada seperti pada rilis Android sebelumnya, untuk mendeteksi dan mengelola peristiwa hilangnya obligasi.
Cara baru untuk menghapus koneksi bluetooth
Semua aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16 kini dapat membatalkan penyambungan perangkat Bluetooth menggunakan
API publik di CompanionDeviceManager. Jika perangkat pendamping
dikelola sebagai pengaitan CDM, aplikasi dapat memicu
penghapusan ikatan bluetooth menggunakan removeBond(int) API
baru di perangkat terkait. Aplikasi dapat memantau perubahan status ikatan dengan
memproses peristiwa siaran perangkat Bluetooth
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
Keamanan
Android 16 (level API 36) menghadirkan perubahan keamanan berikut.
Penguncian versi MediaStore
Untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 16 atau yang lebih tinggi, MediaStore#getVersion() kini
akan unik untuk setiap aplikasi. Hal ini menghilangkan properti identifikasi dari string
versi untuk mencegah penyalahgunaan dan penggunaan untuk teknik sidik jari. Aplikasi tidak boleh
membuat asumsi apa pun terkait format versi ini. Aplikasi seharusnya sudah
menangani perubahan versi saat menggunakan API ini dan dalam sebagian besar kasus tidak perlu
mengubah perilakunya saat ini, kecuali jika developer telah mencoba menyimpulkan
informasi tambahan yang berada di luar cakupan API ini yang dimaksudkan.
Intent yang Lebih Aman
Fitur Safer Intents adalah inisiatif keamanan multi-fase yang dirancang untuk meningkatkan keamanan mekanisme penyelesaian intent Android. Tujuannya adalah untuk melindungi aplikasi dari tindakan berbahaya dengan menambahkan pemeriksaan selama pemrosesan intent dan memfilter intent yang tidak memenuhi kriteria tertentu.
Di Android 15, fitur ini berfokus pada aplikasi pengirim, kini dengan Android 16, kontrol dialihkan ke aplikasi penerima, sehingga developer dapat memilih untuk menggunakan resolusi intent yang ketat menggunakan manifes aplikasi mereka.
Dua perubahan utama sedang diterapkan:
Intent Eksplisit Harus Cocok dengan Filter Intent Komponen Target: Jika intent secara eksplisit menargetkan komponen, intent tersebut harus cocok dengan filter intent komponen tersebut.
Intent Tanpa Tindakan Tidak Dapat Cocok dengan Filter Intent Apa Pun: Intent yang tidak memiliki tindakan yang ditentukan tidak boleh diselesaikan ke filter intent apa pun.
Perubahan ini hanya berlaku jika ada beberapa aplikasi yang terlibat dan tidak memengaruhi penanganan intent dalam satu aplikasi.
Dampak
Karena bersifat keikutsertaan, developer harus mengaktifkannya secara eksplisit di manifes aplikasi agar dapat diterapkan. Akibatnya, dampak fitur ini akan terbatas pada aplikasi yang developernya:
- Mengetahui fitur Maksud Lebih Aman dan manfaatnya.
- Secara aktif memilih untuk menerapkan praktik penanganan maksud yang lebih ketat ke dalam aplikasi mereka.
Pendekatan keikutsertaan ini meminimalkan risiko merusak aplikasi yang ada yang mungkin mengandalkan perilaku penyelesaian maksud yang kurang aman saat ini.
Meskipun dampak awal di Android 16 mungkin terbatas, inisiatif Safer Intents memiliki peta jalan untuk dampak yang lebih luas dalam rilis Android mendatang. Rencananya adalah menjadikan resolusi maksud yang ketat sebagai perilaku default.
Fitur Safer Intents berpotensi meningkatkan keamanan ekosistem Android secara signifikan dengan mempersulit aplikasi berbahaya mengeksploitasi kerentanan dalam mekanisme penyelesaian intent.
Namun, transisi ke penegakan wajib dan penegakan yang memungkinkan pengguna memilih untuk tidak ikut harus dikelola dengan cermat untuk mengatasi potensi masalah kompatibilitas dengan aplikasi yang ada.
Implementasi
Developer harus mengaktifkan pencocokan intent yang lebih ketat secara eksplisit menggunakan atribut
intentMatchingFlags dalam manifes aplikasi mereka.
Berikut adalah contoh saat fitur diaktifkan untuk seluruh aplikasi,
tetapi dinonaktifkan/tidak diaktifkan di penerima:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
Selengkapnya tentang tanda yang didukung:
| Nama Flag | Deskripsi |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Menerapkan pencocokan yang lebih ketat untuk intent yang masuk |
| none | Menonaktifkan semua aturan pencocokan khusus untuk maksud masuk. Saat menentukan beberapa tanda, nilai yang bertentangan akan diselesaikan dengan memberikan prioritas pada tanda "none" |
| allowNullAction | Melonggarkan aturan pencocokan untuk mengizinkan pencocokan maksud tanpa tindakan. Flag ini akan digunakan bersama dengan "enforceIntentFilter" untuk mencapai perilaku tertentu |
Pengujian dan Proses Debug
Saat penegakan aktif, aplikasi harus berfungsi dengan benar jika pemanggil intent telah mengisi intent dengan benar.
Namun, maksud yang diblokir akan memicu pesan log peringatan seperti
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" dan "Access blocked:"
dengan tag "PackageManager."
Hal ini menunjukkan potensi masalah yang dapat memengaruhi aplikasi dan memerlukan
perhatian.
Filter Logcat:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
Pemfilteran syscall GPU
Untuk memperkuat platform GPU Mali, IOCTL GPU Mali yang telah dihentikan atau ditujukan hanya untuk pengembangan GPU telah diblokir dalam build produksi. Selain itu, IOCTL yang digunakan untuk pembuatan profil GPU telah dibatasi untuk proses shell atau aplikasi yang dapat di-debug. Lihat pembaruan SAC untuk mengetahui detail selengkapnya tentang kebijakan tingkat platform.
Perubahan ini terjadi di perangkat Pixel yang menggunakan GPU Mali (Pixel 6-9). Arm
telah memberikan kategorisasi resmi IOCTL mereka di
Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst rilis r54p2. Daftar ini akan terus diperbarui dalam rilis driver mendatang.
Perubahan ini tidak memengaruhi API grafis yang didukung (termasuk Vulkan dan OpenGL), dan diperkirakan tidak akan memengaruhi developer atau aplikasi yang ada. Alat pembuatan profil GPU seperti Streamline Performance Analyzer dan Android GPU Inspector tidak akan terpengaruh.
Pengujian
Jika Anda melihat penolakan SELinux yang mirip dengan berikut ini, kemungkinan aplikasi Anda telah terpengaruh oleh perubahan ini:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
Jika aplikasi Anda perlu menggunakan IOCTL yang diblokir, laporkan bug dan tetapkan bug tersebut ke android-partner-security@google.com.
FAQ
Apakah perubahan kebijakan ini berlaku untuk semua OEM? Perubahan ini bersifat keikutsertaan, tetapi tersedia untuk OEM mana pun yang ingin menggunakan metode penguatan ini. Petunjuk untuk menerapkan perubahan dapat ditemukan dalam dokumentasi penerapan.
Apakah perubahan pada codebase OEM wajib dilakukan untuk menerapkan fitur ini, atau apakah fitur ini disertakan secara default dalam rilis AOSP baru? Perubahan tingkat platform akan hadir dengan rilis AOSP baru secara default. Vendor dapat memilih untuk menerapkan perubahan ini di codebase mereka jika ingin menerapkannya.
Apakah SoC bertanggung jawab untuk memperbarui daftar IOCTL? Misalnya, jika perangkat saya menggunakan GPU ARM Mali, apakah saya perlu menghubungi ARM untuk mengetahui perubahan apa pun? SoC individual harus memperbarui daftar IOCTL per perangkat saat rilis driver. Misalnya, ARM akan memperbarui daftar IOCTL yang dipublikasikan saat ada update driver. Namun, OEM harus memastikan bahwa mereka menyertakan pembaruan dalam SEPolicy mereka, dan menambahkan IOCTL kustom yang dipilih ke daftar sesuai kebutuhan.
Apakah perubahan ini diterapkan secara otomatis ke semua perangkat Pixel yang tersedia di pasar, atau apakah tindakan pengguna diperlukan untuk mengaktifkan sesuatu agar perubahan ini diterapkan? Perubahan ini berlaku untuk semua perangkat Pixel yang tersedia di pasar yang menggunakan GPU Mali (Pixel 6-9). Pengguna tidak perlu melakukan tindakan apa pun untuk menerapkan perubahan ini.
Apakah penggunaan kebijakan ini akan memengaruhi performa driver kernel? Kebijakan ini diuji di GPU Mali menggunakan GFXBench, dan tidak ada perubahan yang terukur pada performa GPU.
Apakah daftar IOCTL harus sesuai dengan versi driver kernel dan ruang pengguna saat ini? Ya, daftar IOCTL yang diizinkan harus disinkronkan dengan IOCTL yang didukung oleh driver ruang pengguna dan kernel. Jika IOCTL di ruang pengguna atau driver kernel diperbarui, daftar IOCTL SEPolicy harus diperbarui agar cocok.
ARM telah mengategorikan IOCTL sebagai 'dibatasi' / 'instrumentasi', tetapi kami ingin menggunakan beberapa di antaranya dalam kasus penggunaan produksi, dan/atau menolak yang lain. OEM/SoC masing-masing bertanggung jawab untuk memutuskan cara mengategorikan IOCTL yang mereka gunakan, berdasarkan konfigurasi library Mali ruang penggunanya. Daftar ARM dapat digunakan untuk membantu memutuskan hal ini, tetapi setiap kasus penggunaan OEM/SoC mungkin berbeda.
Privasi
Android 16 (level API 36) menyertakan perubahan privasi berikut.
Izin Jaringan Lokal
Perangkat di LAN dapat diakses oleh aplikasi apa pun yang memiliki izin INTERNET.
Hal ini memudahkan aplikasi terhubung ke perangkat lokal, tetapi juga memiliki implikasi privasi seperti membentuk sidik jari pengguna, dan menjadi proxy untuk lokasi.
Project Perlindungan Jaringan Lokal bertujuan untuk melindungi privasi pengguna dengan membatasi akses ke jaringan lokal menggunakan izin runtime baru.
Rencana rilis
Perubahan ini akan di-deploy antara dua rilis, 25Q2 dan 26Q2. Developer harus mengikuti panduan ini untuk 25Q2 dan memberikan masukan karena perlindungan ini akan diterapkan pada rilis Android mendatang. Selain itu, mereka harus memperbarui skenario yang bergantung pada akses jaringan lokal implisit dengan menggunakan panduan berikut dan bersiap menghadapi penolakan dan pencabutan izin baru oleh pengguna.
Dampak
Pada tahap saat ini, LNP adalah fitur keikutsertaan yang berarti hanya aplikasi yang memilih untuk menggunakan fitur ini yang akan terpengaruh. Tujuan fase keikutsertaan adalah agar developer aplikasi memahami bagian aplikasi mereka yang bergantung pada akses jaringan lokal implisit sehingga mereka dapat bersiap untuk mengamankan izinnya untuk rilis berikutnya.
Aplikasi akan terpengaruh jika mengakses jaringan lokal pengguna menggunakan:
- Penggunaan soket mentah secara langsung atau library pada alamat jaringan lokal (misalnya, protokol penemuan layanan mDNS atau SSDP)
- Penggunaan class tingkat framework yang mengakses jaringan lokal (misalnya, NsdManager)
Traffic ke dan dari alamat jaringan lokal memerlukan izin akses jaringan lokal. Tabel berikut mencantumkan beberapa kasus umum:
| Operasi Jaringan Tingkat Rendah Aplikasi | Izin Jaringan Lokal Diperlukan |
|---|---|
| Membuat koneksi TCP keluar | ya |
| Menerima koneksi TCP masuk | ya |
| Mengirim unicast, multicast, siaran UDP | ya |
| Menerima unicast, multicast, siaran UDP masuk | ya |
Pembatasan ini diterapkan jauh di dalam stack jaringan, sehingga berlaku untuk semua API jaringan. Hal ini mencakup soket yang dibuat dalam kode native atau terkelola, library jaringan seperti Cronet dan OkHttp, serta API apa pun yang diimplementasikan di atasnya. Mencoba menyelesaikan layanan di jaringan lokal (yaitu yang memiliki sufiks .local) akan memerlukan izin jaringan lokal.
Pengecualian untuk aturan di atas:
- Jika server DNS perangkat berada di jaringan lokal, traffic ke atau dari server tersebut (di port 53) tidak memerlukan izin akses jaringan lokal.
- Aplikasi yang menggunakan Pengalih Output sebagai pemilih dalam aplikasi tidak memerlukan izin jaringan lokal (panduan lebih lanjut akan tersedia pada Kuartal 4 2025).
Panduan Developer (Keikutsertaan)
Untuk mengaktifkan pembatasan jaringan lokal, lakukan langkah-langkah berikut:
- Lakukan flash perangkat ke build dengan 25Q2 Beta 3 atau yang lebih baru.
- Instal aplikasi yang akan diuji.
Mengaktifkan/menonaktifkan flag Appcompat di adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Mulai Ulang Perangkat
Sekarang akses aplikasi Anda ke jaringan lokal dibatasi dan setiap upaya untuk mengakses jaringan lokal akan menyebabkan error soket. Jika Anda menggunakan API yang melakukan operasi jaringan lokal di luar proses aplikasi Anda (misalnya: NsdManager), API tersebut tidak akan terpengaruh selama fase keikutsertaan.
Untuk memulihkan akses, Anda harus memberikan izin aplikasi Anda untuk NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Pastikan aplikasi mendeklarasikan izin
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESdalam manifesnya. - Buka Setelan > Aplikasi > [Nama Aplikasi] > Izin > Perangkat di sekitar > Izinkan.
Sekarang, akses aplikasi Anda ke jaringan lokal akan dipulihkan dan semua skenario Anda akan berfungsi seperti sebelum mengikutsertakan aplikasi.
Setelah penegakan perlindungan jaringan lokal dimulai, berikut dampak yang akan dialami traffic jaringan aplikasi.
| Izin | Permintaan LAN Keluar | Permintaan Internet Keluar/Masuk | Permintaan LAN Masuk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diberikan | Works | Works | Works |
| Tidak Diberikan | Gagal | Works | Gagal |
Gunakan perintah berikut untuk menonaktifkan flag App-Compat
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Error
Error yang timbul dari batasan ini akan dikembalikan ke soket panggilan setiap kali soket memanggil send atau varian send ke alamat jaringan lokal.
Contoh error:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Definisi Jaringan Lokal
Jaringan lokal dalam project ini mengacu pada jaringan IP yang menggunakan antarmuka jaringan yang mendukung siaran, seperti Wi-Fi atau Ethernet, tetapi tidak termasuk koneksi seluler (WWAN) atau VPN.
Berikut ini dianggap sebagai jaringan lokal:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Lokal
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- Rute yang terhubung langsung
- Jaringan stub seperti Thread
- Beberapa subnet (TBD)
Selain itu, alamat multicast (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) dan alamat siaran IPv4 (255.255.255.255) diklasifikasikan sebagai alamat jaringan lokal.
Foto milik aplikasi
Saat diminta untuk memberikan izin foto dan video oleh aplikasi yang menargetkan SDK 36 atau yang lebih tinggi di perangkat yang menjalankan Android 16 atau yang lebih tinggi, pengguna yang memilih untuk membatasi akses ke media yang dipilih akan melihat foto apa pun yang dimiliki oleh aplikasi yang telah dipilih sebelumnya di pemilih foto. Pengguna dapat membatalkan pilihan salah satu item yang telah dipilih sebelumnya, yang akan mencabut akses aplikasi ke foto dan video tersebut.
