Android 16 प्लैटफ़ॉर्म में, ऐसे बदलाव शामिल हैं जिनका असर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन पर पड़ सकता है.
Android 16 पर चलने वाले सभी ऐप्लिकेशन पर, यहां दिए गए बदलाव लागू होते हैं. भले ही, targetSdkVersion कुछ भी हो. आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की जांच करनी चाहिए. इसके बाद, जहां ज़रूरी हो वहां इन बदलावों को लागू करने के लिए, उसमें बदलाव करना चाहिए.
Android 16 को टारगेट करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन पर असर डालने वाले बदलावों की सूची भी ज़रूर देखें.
मुख्य फ़ंक्शन
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में ये बदलाव शामिल हैं. इनसे Android सिस्टम की कई मुख्य क्षमताओं में बदलाव होता है या उन्हें बढ़ाया जाता है.
JobScheduler के कोटे को ऑप्टिमाइज़ करना
Android 16 से, हम सामान्य और तेज़ी से टास्क पूरा करने के लिए, रनटाइम कोटे में बदलाव कर रहे हैं. यह बदलाव इन बातों के आधार पर किया जा रहा है:
- ऐप्लिकेशन, ऐप्लिकेशन स्टैंडबाय बकेट की किस कैटगरी में है: Android 16 में, ऐक्टिव स्टैंडबाय बकेट के लिए रनटाइम कोटा लागू किया जाएगा.
- अगर ऐप्लिकेशन के टॉप स्टेट में होने के दौरान जॉब शुरू होती है: Android 16 में, अगर ऐप्लिकेशन के दिखने के दौरान जॉब शुरू होती है और ऐप्लिकेशन के न दिखने के बाद भी जारी रहती है, तो जॉब रनटाइम कोटे का पालन किया जाएगा.
- अगर फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा चालू होने के दौरान जॉब को एक्ज़ीक्यूट किया जा रहा है: Android 16 में, फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा के साथ-साथ एक्ज़ीक्यूट की जा रही जॉब, जॉब के रनटाइम कोटे का पालन करेंगी. अगर आपको उपयोगकर्ता की ओर से शुरू किए गए डेटा ट्रांसफ़र के लिए टास्क का इस्तेमाल करना है, तो उपयोगकर्ता की ओर से शुरू किए गए डेटा ट्रांसफ़र के टास्क का इस्तेमाल करें.
इस बदलाव का असर, WorkManager, JobScheduler, और DownloadManager का इस्तेमाल करके शेड्यूल किए गए टास्क पर पड़ता है. किसी जॉब को क्यों रोका गया, यह डीबग करने के लिए हमारा सुझाव है कि आप यह लॉग करें कि आपकी जॉब को WorkInfo.getStopReason() को कॉल करके क्यों रोका गया (JobScheduler जॉब के लिए, JobParameters.getStopReason() को कॉल करें).
आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की स्थिति से, इस्तेमाल किए जा सकने वाले संसाधनों पर क्या असर पड़ता है, इस बारे में जानने के लिए पावर मैनेजमेंट के संसाधनों की सीमाएं देखें. बैटरी के इस्तेमाल को ऑप्टिमाइज़ करने के सबसे सही तरीकों के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, टास्क शेड्यूल करने वाले एपीआई के लिए बैटरी के इस्तेमाल को ऑप्टिमाइज़ करने से जुड़े दिशा-निर्देश देखें.
हमारा यह भी सुझाव है कि Android 16 में लॉन्च किए गए नए JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करें. इससे आपको यह समझने में मदद मिलेगी कि कोई जॉब क्यों नहीं हुई.
टेस्ट करना
अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के व्यवहार की जांच करने के लिए, कुछ जॉब कोटा ऑप्टिमाइज़ेशन को तब तक के लिए बंद किया जा सकता है, जब तक ऐप्लिकेशन Android 16 डिवाइस पर चल रहा हो.
"सबसे ऊपर मौजूद स्थिति, नौकरी के रनटाइम कोटे का पालन करेगी" को लागू करने की सुविधा बंद करने के लिए, यह adb कमांड चलाएं:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
"फ़ोरग्राउंड सेवा के साथ-साथ चल रही जॉब, जॉब के रनटाइम कोटा का पालन करेंगी" को लागू करने की सुविधा बंद करने के लिए, यह adb कमांड चलाएं:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
ऐप्लिकेशन स्टैंडबाय बकेट के कुछ व्यवहारों की जांच करने के लिए, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए ऐप्लिकेशन स्टैंडबाय बकेट सेट की जा सकती है. इसके लिए, यहां दिया गया adb कमांड इस्तेमाल करें:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, ऐप्लिकेशन स्टैंडबाय बकेट में किस लेवल पर है, यह जानने के लिए, यहां दिए गए adb कमांड का इस्तेमाल करके, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन का ऐप्लिकेशन स्टैंडबाय बकेट पता लगाया जा सकता है:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
खाली नौकरियों के विज्ञापन बंद करने की वजह
जब जॉब से जुड़े JobParameters ऑब्जेक्ट को गै़रबैज इकट्ठा करने की प्रोसेस के तहत हटा दिया जाता है, लेकिन जॉब पूरा होने का सिग्नल देने के लिए JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) को कॉल नहीं किया जाता है, तो जॉब को छोड़ दिया जाता है. इससे पता चलता है कि ऐप्लिकेशन के बिना, शायद जॉब चल रहा हो और उसे फिर से शेड्यूल किया जा रहा हो.
JobScheduler पर निर्भर ऐप्लिकेशन, JobParameters ऑब्जेक्ट का सटीक रेफ़रंस नहीं रखते. साथ ही, टाइम आउट होने पर अब STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT के बजाय, STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED को नौकरी के रुकने की नई वजह के तौर पर इस्तेमाल किया जाएगा.
अगर 'नया काम बंद होने की वजह' बार-बार दिखती है, तो सिस्टम, जॉब की फ़्रीक्वेंसी कम करने के लिए कदम उठाएगा.
ऐप्लिकेशन को, 'कार्रवाई रोकने की नई वजह' का इस्तेमाल करके, अधूरे रह गए टास्क का पता लगाना चाहिए और उनकी संख्या कम करनी चाहिए.
अगर आपने WorkManager, AsyncTask या DownloadManager का इस्तेमाल किया है, तो आप पर इसका कोई असर नहीं पड़ेगा. ऐसा इसलिए, क्योंकि ये एपीआई आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की ओर से जॉब लाइफ़साइकल को मैनेज करते हैं.
JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground को पूरी तरह से बंद किया जा रहा है
JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) तरीका, शेड्यूलिंग ऐप्लिकेशन के फ़ोरग्राउंड में होने या बैकग्राउंड में काम करने से जुड़ी पाबंदियों से कुछ समय के लिए छूट मिलने पर, किसी टास्क की अहमियत दिखाता है.
Android 12 (एपीआई लेवल 31) के बाद, यह तरीका काम नहीं करता. Android 16 से, यह तरीका ठीक से काम नहीं करता. साथ ही, इस तरीके को कॉल करने पर, उसे अनदेखा कर दिया जाएगा.
यह सुविधा हटाने का फ़ैसला, JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground() पर भी लागू होता है. Android
16 में, अगर इस तरीके को कॉल किया जाता है, तो यह false दिखाता है.
ब्रॉडकास्ट की प्राथमिकता के क्रम का दायरा अब ग्लोबल नहीं है
Android ऐप्लिकेशन, ब्रॉडकास्ट रिसीवर पर प्राथमिकताएं तय कर सकते हैं. इससे, यह कंट्रोल किया जा सकता है कि रिसीवर, ब्रॉडकास्ट को किस क्रम में पाएं और प्रोसेस करें. मेनिफ़ेस्ट में बताए गए रिसीवर के लिए, ऐप्लिकेशन प्राथमिकता तय करने के लिए android:priority एट्रिब्यूट का इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं. वहीं, कॉन्टेक्स्ट के हिसाब से रजिस्टर किए गए रिसीवर के लिए, ऐप्लिकेशन प्राथमिकता तय करने के लिए IntentFilter#setPriority() एपीआई का इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं. जब कोई ब्रॉडकास्ट भेजा जाता है, तो सिस्टम उसे पाने वालों को उनकी प्राथमिकता के हिसाब से डिलीवर करता है. इसमें, सबसे ज़्यादा प्राथमिकता वाले व्यक्ति से लेकर सबसे कम प्राथमिकता वाले व्यक्ति तक का क्रम होता है.
Android 16 में, अलग-अलग प्रोसेस में android:priority एट्रिब्यूट या IntentFilter#setPriority() का इस्तेमाल करके, ब्रॉडकास्ट डिलीवरी के क्रम की गारंटी नहीं दी जाएगी. ब्रॉडकास्ट की प्राथमिकताएं, सभी प्रोसेस के बजाय सिर्फ़ एक ही आवेदन की प्रोसेस में लागू होंगी.
साथ ही, ब्रॉडकास्ट की प्राथमिकताएं अपने-आप इस सीमा में सीमित हो जाएंगी (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). सिर्फ़ सिस्टम कॉम्पोनेंट को SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY को ब्रॉडकास्ट प्राथमिकता के तौर पर सेट करने की अनुमति होगी.
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन इनमें से कोई एक काम करता है, तो उस पर असर पड़ सकता है:
- आपके ऐप्लिकेशन ने एक ही ब्रॉडकास्ट इंटेंट के साथ कई प्रोसेस का एलान किया है. साथ ही, प्राथमिकता के आधार पर उन इंटेंट को किसी खास क्रम में पाने की उम्मीद की है.
- आपके ऐप्लिकेशन की प्रोसेस, अन्य प्रोसेस के साथ इंटरैक्ट करती है. साथ ही, यह किसी खास क्रम में ब्रॉडकास्ट इंटेंट पाने की उम्मीद करती है.
अगर प्रोसेस को एक-दूसरे के साथ काम करना है, तो उन्हें अन्य चैनलों का इस्तेमाल करके कम्यूनिकेट करना चाहिए.
एआरटी में हुए आंतरिक बदलाव
Android 16 में, Android Runtime (ART) के नए अपडेट शामिल हैं. इनसे Android Runtime (ART) की परफ़ॉर्मेंस बेहतर होती है और Java की अन्य सुविधाओं के साथ काम करने में मदद मिलती है. Google Play के सिस्टम अपडेट की मदद से, ये सुधार Android 12 (एपीआई लेवल 31) और उसके बाद के वर्शन वाले एक अरब से ज़्यादा डिवाइसों के लिए भी उपलब्ध हैं.
ये बदलाव रिलीज़ होने के बाद, हो सकता है कि ART के इंटरनल स्ट्रक्चर पर निर्भर रहने वाली लाइब्रेरी और ऐप्लिकेशन कोड, Android 16 वाले डिवाइसों पर सही से काम न करें. साथ ही, ऐसा उन Android वर्शन पर भी हो सकता है जो Google Play के सिस्टम अपडेट के ज़रिए ART मॉड्यूल को अपडेट करते हैं.
डिवाइस के अंदर मौजूद स्ट्रक्चर (जैसे, नॉन-SDK इंटरफ़ेस) पर भरोसा करने से, काम करने से जुड़ी समस्याएं हमेशा हो सकती हैं. हालांकि, यह ज़रूरी है कि आप ऐसे कोड (या कोड वाली लाइब्रेरी) पर भरोसा न करें जो डिवाइस के अंदर मौजूद ART स्ट्रक्चर का इस्तेमाल करता हो. ऐसा इसलिए, क्योंकि ART में होने वाले बदलाव, डिवाइस पर चल रहे प्लैटफ़ॉर्म के वर्शन से जुड़े नहीं होते. साथ ही, ये बदलाव Google Play के सिस्टम अपडेट के ज़रिए एक अरब से ज़्यादा डिवाइसों पर लागू होते हैं.
सभी डेवलपर को यह देखना चाहिए कि Android 16 पर अपने ऐप्लिकेशन की पूरी तरह से जांच करने पर, उन पर असर पड़ा है या नहीं. इसके अलावा, जानी-पहचानी समस्याओं की सूची देखें. इससे आपको पता चलेगा कि आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, उन लाइब्रेरी पर निर्भर है या नहीं जिनकी पहचान हमने की है और जो इंटरनल ART स्ट्रक्चर पर निर्भर हैं. अगर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन कोड या लाइब्रेरी डिपेंडेंसी पर असर पड़ा है, तो जब भी हो सके सार्वजनिक एपीआई के विकल्प खोजें. साथ ही, नए इस्तेमाल के उदाहरणों के लिए सार्वजनिक एपीआई का अनुरोध करें. इसके लिए, हमारे समस्या ट्रैकर में सुविधा का अनुरोध करें.
16 केबी वाले पेज साइज़ के साथ काम करने वाला मोड
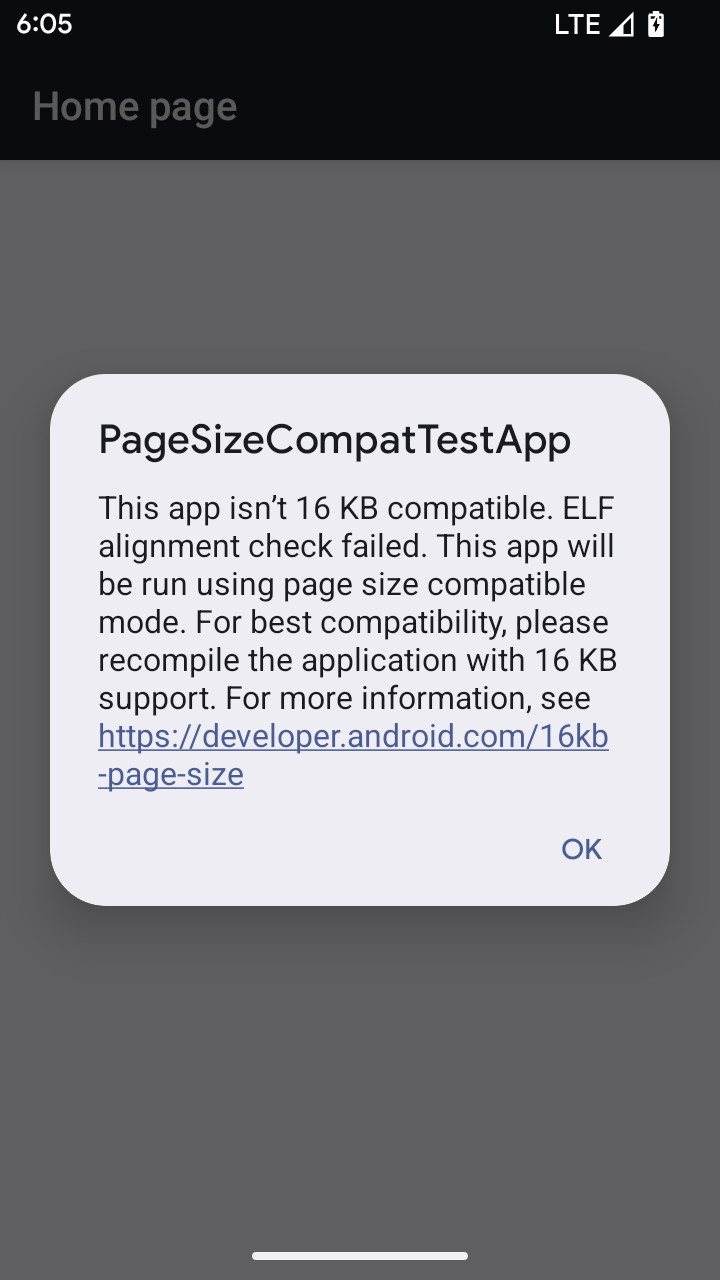
Android 15 में 16 केबी मेमोरी वाले पेजों के लिए सहायता जोड़ी गई है, ताकि प्लैटफ़ॉर्म की परफ़ॉर्मेंस को ऑप्टिमाइज़ किया जा सके. Android 16 में कंपैटबिलिटी मोड जोड़ा गया है. इसकी मदद से, 4 केबी मेमोरी वाले पेजों के लिए बनाए गए कुछ ऐप्लिकेशन, 16 केबी मेमोरी वाले पेजों के लिए कॉन्फ़िगर किए गए डिवाइस पर चल सकते हैं.
अगर आपका ऐप्लिकेशन Android 16 या उसके बाद के वर्शन वाले डिवाइस पर चल रहा है और Android को पता चलता है कि आपके ऐप्लिकेशन में 4 केबी के अलाइन किए गए मेमोरी पेज हैं, तो यह अपने-आप कंपैटबिलिटी मोड का इस्तेमाल करता है और उपयोगकर्ता को सूचना वाला डायलॉग बॉक्स दिखाता है. बैकवर्ड कम्पैटिबिलिटी मोड को चालू करने के लिए, AndroidManifest.xml में android:pageSizeCompat प्रॉपर्टी को सेट करने पर, ऐप्लिकेशन लॉन्च होने पर डायलॉग नहीं दिखेगा. android:pageSizeCompat प्रॉपर्टी का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, Android 16 SDK का इस्तेमाल करके अपना ऐप्लिकेशन कंपाइल करें.
बेहतर परफ़ॉर्मेंस, भरोसेमंदता, और स्थिरता के लिए, आपके ऐप्लिकेशन का साइज़ अब भी 16 केबी होना चाहिए. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, 16 केबी मेमोरी वाले पेजों के साथ काम करने के लिए, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन अपडेट करने के बारे में हमारी हाल ही की ब्लॉग पोस्ट देखें.
उपयोगकर्ता अनुभव और सिस्टम यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई)
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में ये बदलाव शामिल हैं. इनका मकसद, उपयोगकर्ताओं को बेहतर अनुभव देना है.
परेशान करने वाली सुलभता से जुड़ी सूचनाएँ पढ़कर सुनाने की सुविधा बंद की जा रही है
Android 16 में, सुलभता से जुड़ी सूचनाओं का इस्तेमाल नहीं किया जा सकता. इन सूचनाओं के लिए, announceForAccessibility का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है या TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT सुलभता इवेंट भेजे जाते हैं. इनकी वजह से, TalkBack और Android के स्क्रीन रीडर का इस्तेमाल करने वाले लोगों को अलग-अलग अनुभव मिल सकते हैं. साथ ही, Android की सहायक तकनीकों की मदद से, लोगों की ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा ज़रूरतों को पूरा करने के लिए, इन विकल्पों का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है.
विकल्पों के उदाहरण:
- विंडो में बदलाव जैसे यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) में होने वाले अहम बदलावों के लिए,
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)औरsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)का इस्तेमाल करें. लिखने के लिए इस्तेमाल होने वाले टूल में,Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" }का इस्तेमाल करें - ज़रूरी यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) में हुए बदलावों के बारे में उपयोगकर्ता को बताने के लिए,
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)का इस्तेमाल करें. लिखें में,Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}का इस्तेमाल करें . इनका इस्तेमाल कम से कम करना चाहिए, क्योंकि हर बार व्यू अपडेट होने पर ये सूचनाएं जनरेट कर सकते हैं. - उपयोगकर्ताओं को गड़बड़ियों के बारे में सूचना देने के लिए, टाइप के
AccessibilityEventको भेजेंAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORऔरAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)सेट करें याTextView#setError(CharSequence)का इस्तेमाल करें.
बंद किए गए announceForAccessibility एपीआई के रेफ़रंस दस्तावेज़ में, सुझाए गए विकल्पों के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी शामिल है.
तीन बटन वाले नेविगेशन की सुविधा
Android 16 में, तीन बटन वाले नेविगेशन के लिए, ऐप्लिकेशन के पिछले पेज पर जाने की सुविधा जोड़ी गई है. हालांकि, यह सुविधा सिर्फ़ उन ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए उपलब्ध है जिन्हें पिछले पेज पर जाने की सुविधा के लिए सही तरीके से माइग्रेट किया गया हो. 'वापस जाएं' बटन को दबाकर रखने पर, प्रिडिक्टिव बैक ऐनिमेशन शुरू होता है. इससे आपको यह झलक मिलती है कि 'वापस जाएं' स्वाइप करने पर, आपको कहां ले जाया जाएगा.
यह सुविधा, सिस्टम के उन सभी हिस्सों पर लागू होती है जिनमें प्रिडिक्टिव बैक ऐनिमेशन काम करते हैं. इनमें सिस्टम ऐनिमेशन (होम स्क्रीन पर वापस जाने, एक टास्क से दूसरे टास्क पर जाने, और एक गतिविधि से दूसरी गतिविधि पर जाने) भी शामिल हैं.
थीम वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के आइकॉन अपने-आप जनरेट होने की सुविधा
Android 16 QPR 2 से, Android अपने-आप ऐप्लिकेशन के आइकॉन को थीम के हिसाब से बदल देगा, ताकि होम स्क्रीन पर एक जैसा अनुभव मिले. ऐसा तब होता है, जब कोई ऐप्लिकेशन थीम वाला आइकॉन नहीं देता. ऐप्लिकेशन, थीम वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के आइकॉन के डिज़ाइन को कंट्रोल कर सकते हैं. इसके लिए, वे अडैप्टिव आइकॉन में मोनोक्रोम लेयर शामिल करते हैं. साथ ही, Android Studio में झलक देख सकते हैं कि उनका ऐप्लिकेशन आइकॉन कैसा दिखेगा.
डिवाइस के नाप या आकार
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में, वर्चुअल डिवाइस के मालिकों के डिसप्ले पर प्रोजेक्ट किए जाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए ये बदलाव किए गए हैं.
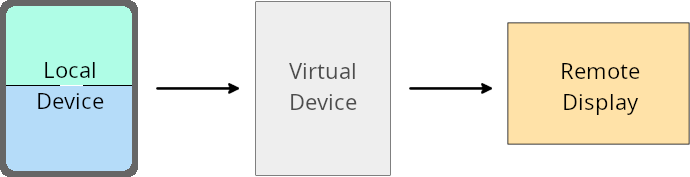
वर्चुअल डिवाइस के मालिक के लिए उपलब्ध सुविधाएं
वर्चुअल डिवाइस का मालिक, भरोसेमंद या खास अधिकार वाला ऐप्लिकेशन होता है. यह वर्चुअल डिवाइस बनाता है और उसे मैनेज करता है. वर्चुअल डिवाइस के मालिक, वर्चुअल डिवाइस पर ऐप्लिकेशन चलाते हैं. इसके बाद, वे ऐप्लिकेशन को किसी रिमोट डिवाइस के डिसप्ले पर प्रोजेक्ट करते हैं. जैसे, निजी कंप्यूटर, वर्चुअल रियलिटी डिवाइस या कार का इंफ़ोटेनमेंट सिस्टम. वर्चुअल डिवाइस का मालिक, किसी लोकल डिवाइस पर हो, जैसे कि मोबाइल फ़ोन.
हर ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए ओवरराइड
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) पर काम करने वाले डिवाइसों पर, वर्चुअल डिवाइस के मालिक, वर्चुअल डिवाइसों पर ऐप्लिकेशन की सेटिंग बदल सकते हैं. ये वर्चुअल डिवाइस, वर्चुअल डिवाइस के मालिक मैनेज करते हैं. उदाहरण के लिए, ऐप्लिकेशन के लेआउट को बेहतर बनाने के लिए, वर्चुअल डिवाइस का मालिक किसी बाहरी डिसप्ले पर ऐप्लिकेशन प्रोजेक्ट करते समय, ओरिएंटेशन, आसपेक्ट रेशियो, और साइज़ बदलने से जुड़ी पाबंदियों को अनदेखा कर सकता है.
नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले सामान्य बदलाव
Android 16 के व्यवहार की वजह से, बड़ी स्क्रीन वाले डिवाइसों (जैसे, कार के डिसप्ले या Chromebook) पर आपके ऐप्लिकेशन के यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस (यूआई) पर असर पड़ सकता है. खास तौर पर, पोर्ट्रेट मोड में छोटी स्क्रीन के लिए डिज़ाइन किए गए लेआउट पर. अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को सभी डिवाइसों के फ़ॉर्म फ़ैक्टर के हिसाब से अडैप्टिव बनाने का तरीका जानने के लिए, अडैप्टिव लेआउट के बारे में जानकारी लेख पढ़ें.
रेफ़रंस
कंपैनियन ऐप्लिकेशन की स्ट्रीमिंग
सुरक्षा
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में ऐसे बदलाव किए गए हैं जिनसे सिस्टम की सुरक्षा को बढ़ावा मिलता है. इससे ऐप्लिकेशन और उपयोगकर्ताओं को नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन से बचाने में मदद मिलती है.
इन्टेंट रीडायरेक्शन के हमलों से बचने के लिए बेहतर सुरक्षा
Android 16 में, सामान्य Intent रीडायरेक्शन हमलों से डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से सुरक्षा मिलती है. इसके लिए, डेवलपर को कम से कम बदलाव करने पड़ते हैं और यह कम से कम ज़रूरी शर्तों को पूरा करता है.
हम Intent
रीडायरेक्ट करने से जुड़े जोखिमों से बचने के लिए, डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से सुरक्षा को बेहतर बनाने वाले समाधान पेश कर रहे हैं. ज़्यादातर मामलों में, इंटेंट का इस्तेमाल करने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन में आम तौर पर, काम न करने से जुड़ी कोई समस्या नहीं आती. हमने डेवलपमेंट प्रोसेस के दौरान मेट्रिक इकट्ठा की हैं, ताकि यह मॉनिटर किया जा सके कि किन ऐप्लिकेशन में समस्याएं आ सकती हैं.
Android में इंटेंट रीडायरेक्शन तब होता है, जब हमलावर किसी कमज़ोर ऐप्लिकेशन के कॉन्टेक्स्ट में, नए कॉम्पोनेंट को लॉन्च करने के लिए इस्तेमाल किए गए इंटेंट के कॉन्टेंट को कुछ हद तक या पूरी तरह से कंट्रोल कर सकता है. वहीं, पीड़ित ऐप्लिकेशन ("टॉप-लेवल") इंटेंट के एक्स्ट्रा फ़ील्ड में, गैर-भरोसेमंद सब-लेवल इंटेंट लॉन्च करता है. इससे, हमलावर ऐप्लिकेशन, पीड़ित ऐप्लिकेशन के कॉन्टेक्स्ट में निजी कॉम्पोनेंट लॉन्च कर सकता है, खास अधिकारों वाली कार्रवाइयां ट्रिगर कर सकता है या संवेदनशील डेटा के यूआरआई का ऐक्सेस पा सकता है. इससे डेटा चोरी हो सकता है और मनमाने कोड को एक्ज़ीक्यूट किया जा सकता है.
इंटेंट रीडायरेक्शन हैंडलिंग से ऑप्ट आउट करना
Android 16 में एक नया एपीआई पेश किया गया है. इससे ऐप्लिकेशन, लॉन्च के दौरान सुरक्षा से जुड़ी सुविधाओं से ऑप्ट आउट कर सकते हैं. ऐसा कुछ मामलों में ज़रूरी हो सकता है, जब सुरक्षा से जुड़ी डिफ़ॉल्ट सेटिंग, ऐप्लिकेशन के सही इस्तेमाल में रुकावट डालती है.
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) या इसके बाद के वर्शन वाले एसडीके के साथ कंपाइल किए गए ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए
Intent ऑब्जेक्ट पर, removeLaunchSecurityProtection() तरीके का सीधे तौर पर इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Android 15 (एपीआई लेवल 35) या इससे पहले के वर्शन के लिए कंपाइल किए गए ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए
हमारा सुझाव है कि आप रिफ़्लेक्शन का इस्तेमाल न करें. हालांकि, removeLaunchSecurityProtection() तरीके को ऐक्सेस करने के लिए, रिफ़्लेक्शन का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
साथी ऐप्लिकेशन को अब डिवाइस खोजने के लिए तय समयसीमा खत्म होने की सूचना नहीं दी जाएगी
Android 16 में, साथ काम करने वाले डिवाइस को जोड़ने की प्रोसेस के दौरान, उपयोगकर्ता की जगह की जानकारी की निजता को नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले ऐप्लिकेशन से सुरक्षित रखने के लिए, एक नई सुविधा जोड़ी गई है. Android 16 पर चलने वाले सभी कंपैनियन ऐप्लिकेशन को, RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT का इस्तेमाल करके, डिस्कवरी टाइम आउट की सूचना अब सीधे तौर पर नहीं दी जाती. इसके बजाय, उपयोगकर्ता को विज़ुअल डायलॉग के ज़रिए टाइम आउट इवेंट की सूचना दी जाती है. जब उपयोगकर्ता डायलॉग को खारिज करता है, तो ऐप्लिकेशन को RESULT_USER_REJECTED से असोसिएशन न हो पाने की चेतावनी मिलती है.
डिवाइस खोजने की अवधि को भी 20 सेकंड से बढ़ाकर 30 सेकंड कर दिया गया है. साथ ही, उपयोगकर्ता डिवाइस खोजने की प्रोसेस को किसी भी समय रोक सकता है. अगर खोज शुरू करने के पहले 20 सेकंड में कम से कम एक डिवाइस मिल जाता है, तो सीडीएम अन्य डिवाइसों को खोजना बंद कर देता है.
कनेक्टिविटी
Android 16 (एपीआई लेवल 36) में, ब्लूटूथ स्टैक में ये बदलाव किए गए हैं, ताकि सहायक डिवाइसों से कनेक्टिविटी को बेहतर बनाया जा सके.
बॉन्ड के नुकसान को बेहतर तरीके से मैनेज करने की सुविधा
Android 16 से, ब्लूटूथ स्टैक को अपडेट किया गया है. इससे, रिमोट बॉन्ड के हटने का पता चलने पर, सुरक्षा और उपयोगकर्ता अनुभव को बेहतर बनाया जा सकेगा. पहले, सिस्टम अपने-आप बॉन्ड हटा देता था और फिर से जोड़ने की नई प्रोसेस शुरू कर देता था. इस वजह से, अनजाने में डिवाइस फिर से कनेक्ट हो सकता था. हमने कई मामलों में देखा है कि ऐप्लिकेशन, बॉन्ड के खत्म होने के इवेंट को लगातार ट्रैक नहीं करते.
एक जैसा अनुभव देने के लिए, Android 16 में सिस्टम के लिए, बॉन्ड के खो जाने की समस्या को मैनेज करने की सुविधा को बेहतर बनाया गया है. अगर पहले से कनेक्ट किए गए किसी ब्लूटूथ डिवाइस को फिर से कनेक्ट करने पर उसकी पुष्टि नहीं की जा सकी, तो सिस्टम उस लिंक को डिसकनेक्ट कर देगा. हालांकि, वह स्थानीय तौर पर कनेक्ट किए गए डिवाइस की जानकारी को सेव रखेगा. साथ ही, सिस्टम एक डायलॉग बॉक्स दिखाएगा, जिसमें उपयोगकर्ताओं को कनेक्टिविटी के बंद होने की जानकारी दी जाएगी. साथ ही, उन्हें फिर से जोड़ने का निर्देश दिया जाएगा.
