Gemini Developer API cho phép bạn truy cập vào các mô hình Gemini của Google, nhờ đó bạn có thể tích hợp các tính năng AI tạo sinh tiên tiến vào ứng dụng Android của mình, bao gồm cả tính năng trò chuyện đàm thoại, tạo hình ảnh (bằng Nano Banana) và tạo văn bản dựa trên dữ liệu đầu vào là văn bản, hình ảnh, âm thanh và video.
Để truy cập vào các mô hình Gemini Pro và Flash, bạn có thể sử dụng Gemini Developer API với Firebase AI Logic. Bạn có thể bắt đầu mà không cần thẻ tín dụng và được hưởng một bậc miễn phí hào phóng. Sau khi xác thực việc tích hợp với một nhóm nhỏ người dùng, bạn có thể mở rộng quy mô bằng cách chuyển sang cấp trả phí.

Bắt đầu
Trước khi tương tác với Gemini API ngay từ ứng dụng của mình, trước tiên, bạn cần làm một số việc, bao gồm cả việc làm quen với tính năng tạo câu lệnh cũng như thiết lập Firebase và ứng dụng để sử dụng SDK.
Thử nghiệm với câu lệnh
Việc thử nghiệm với câu lệnh có thể giúp bạn tìm ra cách diễn đạt, nội dung và định dạng phù hợp nhất cho ứng dụng Android của mình. Google AI Studio là một Môi trường phát triển tích hợp (IDE) mà bạn có thể dùng để tạo nguyên mẫu và thiết kế câu lệnh cho các trường hợp sử dụng của ứng dụng.
Việc tạo ra các câu lệnh hiệu quả cho trường hợp sử dụng của bạn đòi hỏi phải thử nghiệm nhiều, đây là một phần quan trọng của quy trình. Bạn có thể tìm hiểu thêm về lời nhắc trong tài liệu về Firebase.
Sau khi hài lòng với câu lệnh, hãy nhấp vào nút <> để nhận các đoạn mã mà bạn có thể thêm vào mã của mình.
Thiết lập dự án Firebase và kết nối ứng dụng của bạn với Firebase
Khi bạn đã sẵn sàng gọi API từ ứng dụng của mình, hãy làm theo hướng dẫn trong "Bước 1" của hướng dẫn bắt đầu sử dụng Firebase AI Logic để thiết lập Firebase và SDK trong ứng dụng của bạn.
Thêm phần phụ thuộc vào Gradle
Thêm phần phụ thuộc Gradle sau đây vào mô-đun ứng dụng:
Kotlin
dependencies { // ... other androidx dependencies // Import the BoM for the Firebase platform implementation(platform("com.google.firebase:firebase-bom:34.7.0")) // Add the dependency for the Firebase AI Logic library When using the BoM, // you don't specify versions in Firebase library dependencies implementation("com.google.firebase:firebase-ai") }
Java
dependencies { // Import the BoM for the Firebase platform implementation(platform("com.google.firebase:34.7.0")) // Add the dependency for the Firebase AI Logic library When using the BoM, // you don't specify versions in Firebase library dependencies implementation("com.google.firebase:firebase-ai") // Required for one-shot operations (to use `ListenableFuture` from Guava // Android) implementation("com.google.guava:guava:31.0.1-android") // Required for streaming operations (to use `Publisher` from Reactive // Streams) implementation("org.reactivestreams:reactive-streams:1.0.4") }
Khởi chạy mô hình tạo sinh
Bắt đầu bằng cách tạo một thực thể GenerativeModel và chỉ định tên mô hình:
Kotlin
// Start by instantiating a GenerativeModel and specifying the model name: val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()) .generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash")
Java
GenerativeModel firebaseAI = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI()) .generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash"); GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(firebaseAI);
Tìm hiểu thêm về các mô hình hiện có để sử dụng với Gemini Developer API. Bạn cũng có thể tìm hiểu thêm về cách định cấu hình các tham số mô hình.
Tương tác với Gemini Developer API từ ứng dụng của bạn
Sau khi thiết lập Firebase và ứng dụng để sử dụng SDK, bạn đã sẵn sàng tương tác với Gemini Developer API từ ứng dụng của mình.
Tạo văn bản
Để tạo câu trả lời dạng văn bản, hãy gọi generateContent() bằng câu lệnh của bạn.
Kotlin
scope.launch { val response = model.generateContent("Write a story about a magic backpack.") }
Java
Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .addText("Write a story about a magic backpack.") .build(); ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String resultText = result.getText(); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
Tạo văn bản từ hình ảnh và nội dung nghe nhìn khác
Bạn cũng có thể tạo văn bản từ một câu lệnh có chứa văn bản cùng với hình ảnh hoặc nội dung nghe nhìn khác. Khi gọi generateContent(), bạn có thể truyền nội dung nghe nhìn dưới dạng dữ liệu nội tuyến.
Ví dụ: để sử dụng một bitmap, hãy dùng loại nội dung image:
Kotlin
scope.launch { val response = model.generateContent( content { image(bitmap) text("what is the object in the picture?") } ) }
Java
Content content = new Content.Builder() .addImage(bitmap) .addText("what is the object in the picture?") .build(); ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(content); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String resultText = result.getText(); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
Để truyền một tệp âm thanh, hãy sử dụng loại nội dung inlineData:
Kotlin
scope.launch { val contentResolver = applicationContext.contentResolver contentResolver.openInputStream(audioUri).use { stream -> stream?.let { val bytes = it.readBytes() val prompt = content { inlineData(bytes, "audio/mpeg") // Specify the appropriate audio MIME type text("Transcribe this audio recording.") } val response = model.generateContent(prompt) } } }
Java
ContentResolver resolver = applicationContext.getContentResolver(); try (InputStream stream = resolver.openInputStream(audioUri)) { File audioFile = new File(new URI(audioUri.toString())); int audioSize = (int) audioFile.length(); byte[] audioBytes = new byte[audioSize]; if (stream != null) { stream.read(audioBytes, 0, audioBytes.length); stream.close(); // Provide a prompt that includes audio specified earlier and text Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .addInlineData(audioBytes, "audio/mpeg") // Specify the appropriate audio MIME type .addText("Transcribe what's said in this audio recording.") .build(); // To generate text output, call `generateContent` with the prompt ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String text = result.getText(); Log.d(TAG, (text == null) ? "" : text); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to generate a response", t); } }, executor); } else { Log.e(TAG, "Error getting input stream for file."); // Handle the error appropriately } } catch (IOException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read the audio file", e); } catch (URISyntaxException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Invalid audio file", e); }
Để cung cấp tệp video, hãy tiếp tục sử dụng loại nội dung inlineData:
Kotlin
scope.launch { val contentResolver = applicationContext.contentResolver contentResolver.openInputStream(videoUri).use { stream -> stream?.let { val bytes = it.readBytes() val prompt = content { inlineData(bytes, "video/mp4") // Specify the appropriate video MIME type text("Describe the content of this video") } val response = model.generateContent(prompt) } } }
Java
ContentResolver resolver = applicationContext.getContentResolver(); try (InputStream stream = resolver.openInputStream(videoUri)) { File videoFile = new File(new URI(videoUri.toString())); int videoSize = (int) videoFile.length(); byte[] videoBytes = new byte[videoSize]; if (stream != null) { stream.read(videoBytes, 0, videoBytes.length); stream.close(); // Provide a prompt that includes video specified earlier and text Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .addInlineData(videoBytes, "video/mp4") .addText("Describe the content of this video") .build(); // To generate text output, call generateContent with the prompt ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String resultText = result.getText(); System.out.println(resultText); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (URISyntaxException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
Tương tự, bạn cũng có thể truyền tài liệu PDF (application/pdf) và văn bản thuần tuý (text/plain) bằng cách truyền Loại MIME tương ứng của chúng dưới dạng một tham số.
Cuộc trò chuyện nhiều lượt
Bạn cũng có thể hỗ trợ các cuộc trò chuyện nhiều lượt. Khởi tạo cuộc trò chuyện bằng hàm startChat(). Bạn có thể cung cấp cho mô hình một nhật ký tin nhắn (không bắt buộc). Sau đó, hãy gọi hàm sendMessage() để gửi tin nhắn trò chuyện.
Kotlin
val chat = model.startChat( history = listOf( content(role = "user") { text("Hello, I have 2 dogs in my house.") }, content(role = "model") { text("Great to meet you. What would you like to know?") } ) ) scope.launch { val response = chat.sendMessage("How many paws are in my house?") }
Java
Content.Builder userContentBuilder = new Content.Builder(); userContentBuilder.setRole("user"); userContentBuilder.addText("Hello, I have 2 dogs in my house."); Content userContent = userContentBuilder.build(); Content.Builder modelContentBuilder = new Content.Builder(); modelContentBuilder.setRole("model"); modelContentBuilder.addText("Great to meet you. What would you like to know?"); Content modelContent = modelContentBuilder.build(); List<Content> history = Arrays.asList(userContent, modelContent); // Initialize the chat ChatFutures chat = model.startChat(history); // Create a new user message Content.Builder messageBuilder = new Content.Builder(); messageBuilder.setRole("user"); messageBuilder.addText("How many paws are in my house?"); Content message = messageBuilder.build(); // Send the message ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = chat.sendMessage(message); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { String resultText = result.getText(); System.out.println(resultText); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
Tạo hình ảnh trên Android bằng Nano Banana
Mô hình hình ảnh Gemini 2.5 Flash (còn gọi là Nano Banana) có thể tạo và chỉnh sửa hình ảnh dựa trên kiến thức và khả năng suy luận về thế giới. Gemini tạo ra những hình ảnh phù hợp với ngữ cảnh, kết hợp hoặc xen kẽ văn bản và hình ảnh một cách liền mạch. Công cụ này cũng có thể tạo ra hình ảnh chính xác với các chuỗi văn bản dài và hỗ trợ chỉnh sửa hình ảnh theo cách đàm thoại trong khi vẫn duy trì bối cảnh.
Ngoài Gemini, bạn có thể sử dụng các mô hình Imagen, đặc biệt là để tạo hình ảnh chất lượng cao đòi hỏi tính chân thực như ảnh chụp, chi tiết nghệ thuật hoặc phong cách cụ thể. Tuy nhiên, đối với phần lớn các trường hợp sử dụng phía máy khách cho ứng dụng Android, Gemini sẽ đáp ứng được yêu cầu.
Hướng dẫn này mô tả cách sử dụng mô hình Gemini 2.5 Flash Image (Nano Banana) bằng SDK Firebase AI Logic cho Android. Để biết thêm thông tin về cách tạo hình ảnh bằng Gemini, hãy xem tài liệu Tạo hình ảnh bằng Gemini trên Firebase. Nếu bạn muốn sử dụng các mô hình Imagen, hãy xem tài liệu.
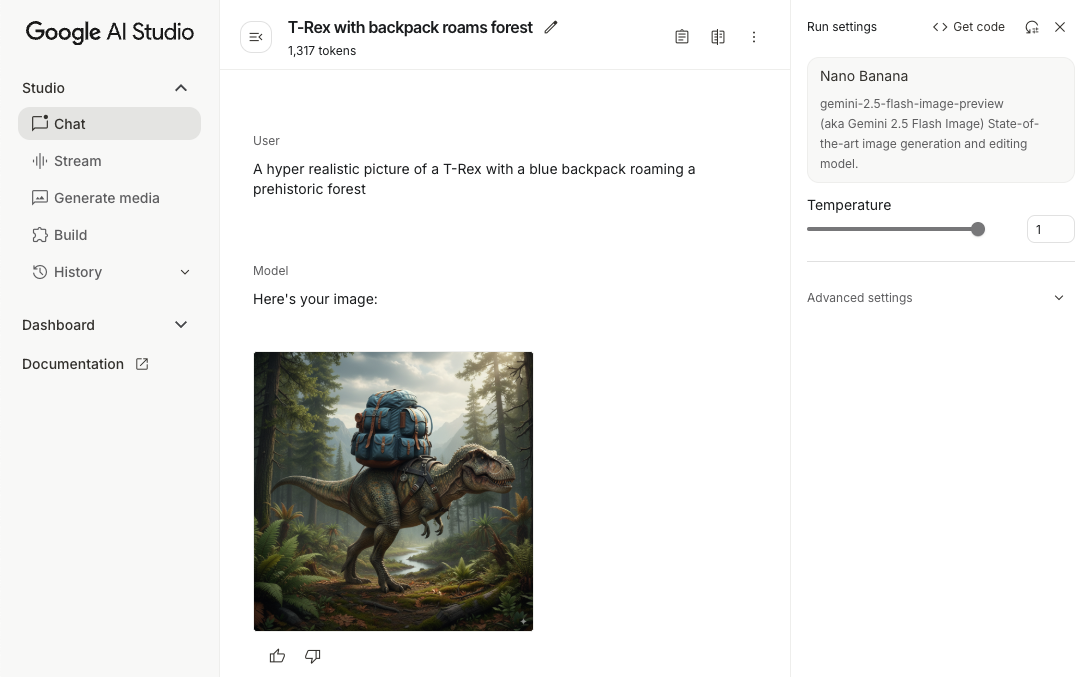
Khởi chạy mô hình tạo sinh
Tạo một GenerativeModel và chỉ định tên mô hình gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview. Xác minh rằng bạn định cấu hình responseModalities để bao gồm cả TEXT và IMAGE.
Kotlin
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel( modelName = "gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview", // Configure the model to respond with text and images (required) generationConfig = generationConfig { responseModalities = listOf( ResponseModality.TEXT, ResponseModality.IMAGE ) } )
Java
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel( "gemini-2.5-flash-image-preview", // Configure the model to respond with text and images (required) new GenerationConfig.Builder() .setResponseModalities(Arrays.asList(ResponseModality.TEXT, ResponseModality.IMAGE)) .build() ); GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
Tạo hình ảnh (chỉ nhập văn bản)
Bạn có thể hướng dẫn mô hình Gemini tạo hình ảnh bằng cách cung cấp câu lệnh chỉ chứa văn bản:
Kotlin
scope.launch { // Provide a text prompt instructing the model to generate an image val prompt = "A hyper realistic picture of a t-rex with a blue bag pack roaming a pre-historic forest." // To generate image output, call `generateContent` with the text input val generatedImageAsBitmap: Bitmap? = model.generateContent(prompt) .candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>() .firstOrNull()?.image }
Java
// Provide a text prompt instructing the model to generate an image Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .addText("Generate an image of the Eiffel Tower with fireworks in the background.") .build(); // To generate an image, call `generateContent` with the text input ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(prompt); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { // iterate over all the parts in the first candidate in the result object for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) { if (part instanceof ImagePart) { ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part; // The returned image as a bitmap Bitmap generatedImageAsBitmap = imagePart.getImage(); break; } } } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
Chỉnh sửa hình ảnh (nhập văn bản và hình ảnh)
Bạn có thể yêu cầu một mô hình Gemini chỉnh sửa hình ảnh hiện có bằng cách cung cấp cả văn bản và một hoặc nhiều hình ảnh trong câu lệnh:
Kotlin
scope.launch { // Provide a text prompt instructing the model to edit the image val prompt = content { image(bitmap) text("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon") } // To edit the image, call `generateContent` with the prompt (image and text input) val generatedImageAsBitmap: Bitmap? = model.generateContent(prompt) .candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>().firstOrNull()?.image // Handle the generated text and image }
Java
// Provide an image for the model to edit Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(resources, R.drawable.scones); // Provide a text prompt instructing the model to edit the image Content promptcontent = new Content.Builder() .addImage(bitmap) .addText("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon") .build(); // To edit the image, call `generateContent` with the prompt (image and text input) ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = model.generateContent(promptcontent); Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { // iterate over all the parts in the first candidate in the result object for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) { if (part instanceof ImagePart) { ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part; Bitmap generatedImageAsBitmap = imagePart.getImage(); break; } } } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
Lặp lại và chỉnh sửa hình ảnh thông qua cuộc trò chuyện nhiều lượt
Để chỉnh sửa hình ảnh theo cách trò chuyện, bạn có thể sử dụng tính năng trò chuyện nhiều lượt. Điều này cho phép các yêu cầu tiếp theo tinh chỉnh nội dung chỉnh sửa mà không cần gửi lại hình ảnh gốc.
Trước tiên, hãy khởi chạy một cuộc trò chuyện với startChat(), bạn có thể cung cấp nhật ký tin nhắn. Sau đó, hãy sử dụng sendMessage() cho các thông báo tiếp theo:
Kotlin
scope.launch { // Create the initial prompt instructing the model to edit the image val prompt = content { image(bitmap) text("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon") } // Initialize the chat val chat = model.startChat() // To generate an initial response, send a user message with the image and text prompt var response = chat.sendMessage(prompt) // Inspect the returned image var generatedImageAsBitmap: Bitmap? = response .candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>().firstOrNull()?.image // Follow up requests do not need to specify the image again response = chat.sendMessage("But make it old-school line drawing style") generatedImageAsBitmap = response .candidates.first().content.parts.filterIsInstance<ImagePart>().firstOrNull()?.image }
Java
// Provide an image for the model to edit Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(resources, R.drawable.scones); // Initialize the chat ChatFutures chat = model.startChat(); // Create the initial prompt instructing the model to edit the image Content prompt = new Content.Builder() .setRole("user") .addImage(bitmap) .addText("Edit this image to make it look like a cartoon") .build(); // To generate an initial response, send a user message with the image and text prompt ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response = chat.sendMessage(prompt); // Extract the image from the initial response ListenableFuture<Bitmap> initialRequest = Futures.transform(response, result -> { for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) { if (part instanceof ImagePart) { ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part; return imagePart.getImage(); } } return null; }, executor); // Follow up requests do not need to specify the image again ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> modelResponseFuture = Futures.transformAsync( initialRequest, generatedImage -> { Content followUpPrompt = new Content.Builder() .addText("But make it old-school line drawing style") .build(); return chat.sendMessage(followUpPrompt); }, executor); // Add a final callback to check the reworked image Futures.addCallback(modelResponseFuture, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() { @Override public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) { for (Part part : result.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts()) { if (part instanceof ImagePart) { ImagePart imagePart = (ImagePart) part; Bitmap generatedImageAsBitmap = imagePart.getImage(); break; } } } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { t.printStackTrace(); } }, executor);
Những điểm cần cân nhắc và giới hạn
Hãy lưu ý các điểm cần cân nhắc và giới hạn sau:
- Định dạng đầu ra: Hình ảnh được tạo dưới dạng tệp PNG với kích thước tối đa là 1024 px.
- Loại đầu vào: Mô hình này không hỗ trợ đầu vào âm thanh hoặc video để tạo hình ảnh.
- Ngôn ngữ được hỗ trợ: Để đạt hiệu suất tốt nhất, hãy sử dụng các ngôn ngữ sau: tiếng Anh (
en), tiếng Tây Ban Nha (Mexico) (es-mx), tiếng Nhật (ja-jp), tiếng Trung giản thể (zh-cn) và tiếng Hindi (hi-in). - Vấn đề về việc tạo:
- Tính năng tạo hình ảnh có thể không phải lúc nào cũng kích hoạt, đôi khi dẫn đến kết quả chỉ có văn bản. Hãy thử yêu cầu rõ ràng về kết quả là hình ảnh (ví dụ: "tạo một hình ảnh", "cung cấp hình ảnh trong quá trình trò chuyện", "cập nhật hình ảnh").
- Mô hình có thể ngừng tạo nội dung khi chưa hoàn tất. Thử lại hoặc thử một câu lệnh khác.
- Mô hình có thể tạo văn bản dưới dạng hình ảnh. Hãy thử yêu cầu rõ ràng về đầu ra là văn bản (ví dụ: "tạo văn bản tường thuật cùng với hình minh hoạ").
Hãy xem tài liệu về Firebase để biết thêm thông tin chi tiết.
Các bước tiếp theo
Sau khi thiết lập ứng dụng, hãy cân nhắc các bước tiếp theo sau đây:
- Xem ứng dụng mẫu Bắt đầu nhanh với Firebase cho Android và Danh mục mẫu AI cho Android trên GitHub.
- Chuẩn bị ứng dụng của bạn cho quá trình phát hành công khai, bao gồm cả việc thiết lập tính năng Kiểm tra ứng dụng Firebase để bảo vệ Gemini API khỏi hành vi sai trái của các ứng dụng trái phép.
- Tìm hiểu thêm về Firebase AI Logic trong tài liệu của Firebase.

