This page lists the new features introduced in Android Studio preview releases. The preview builds provide early access to the latest features and improvements in Android Studio. You can download these preview versions. If you encounter any problems using a preview version of Android Studio, let us know. Your bug reports help to make Android Studio better.
Canary releases contain leading edge features under active development, and are lightly tested. While you can use Canary builds for development, be aware that features might be added or changed. Release Candidates (RC) are the next version of Android Studio, and are almost ready for stable release. The feature set for the next version has been stabilized. See Android Studio release names to understand Android Studio version naming.
For the latest news on Android Studio preview releases, including a list of notable fixes in each preview release, see the Release Updates in the Android Studio blog.
Current versions of Android Studio
The following table lists the current versions of Android Studio and their respective channels.
| Version | Channel |
|---|---|
| Android Studio Otter 3 Feature Drop | Stable |
| Android Gradle plugin 9.0 | Stable |
| Android Studio Panda 1 | RC |
| Android Studio Panda 2 | Canary |
Compatibility with Android Gradle plugin previews
Each preview version of Android Studio is published alongside a corresponding version of the Android Gradle plugin (AGP). Preview versions of Studio should work with any compatible stable version of AGP. However, if you're using a preview version of AGP, you must use the corresponding preview version of Studio (for example, Android Studio Chipmunk Canary 7 with AGP 7.2.0-alpha07). Attempts to use divergent versions (for example, Android Studio Chipmunk Beta 1 with AGP 7.2.0-alpha07) will cause a Sync failure, which results in a prompt to update to the corresponding version of AGP.
For a detailed log of Android Gradle plugin API deprecations and removals, see the Android Gradle plugin API updates.
Studio Labs
Studio Labs lets you try out the latest AI experimental features in a stable version of Android Studio, so you can more quickly integrate our AI assistance offerings in your development workflow. For more information, see Studio Labs.
The following are features currently available in Studio Labs.
| Feature | Description | Docs |
|---|---|---|
| Compose preview generation | Gemini can automatically generate Compose previews, including mock data for preview parameters, for a specific composable or all composables in a file. | Generate Compose previews |
| Transform UI | Use natural language to update your app UI directly from the Compose preview panel. | Transform UI |
| Journeys for Android Studio | Use natural language to describe steps and assertions for end-to-end tests. | Journeys for Android Studio |
Android Studio Panda 1
The following are new features in Android Studio Panda 1.
To see what's been fixed in this version of Android Studio, see the closed issues.
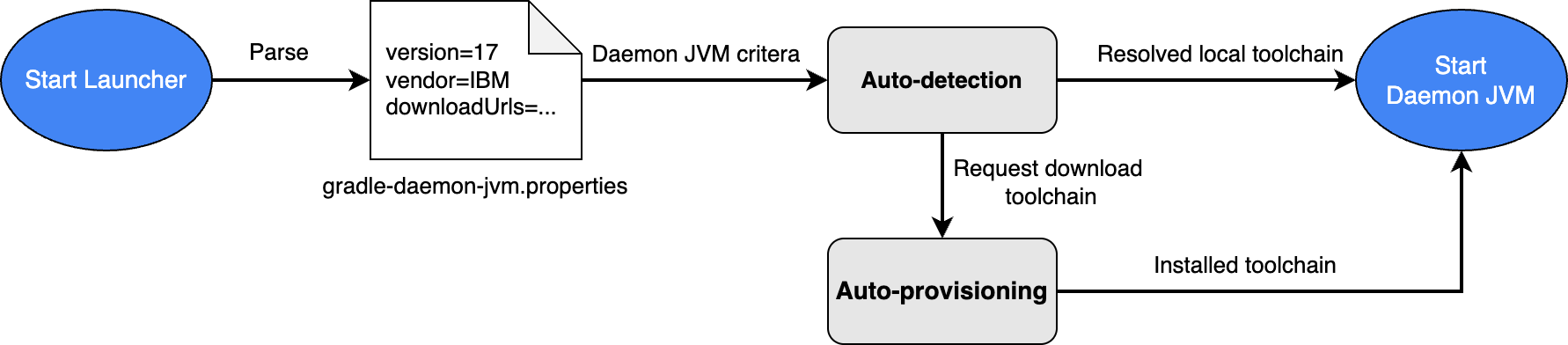
Simplified JDK management with Gradle Daemon JVM Criteria
To simplify JDK management for Gradle builds, Android Studio now uses Gradle Daemon JVM criteria by default for new projects. This feature lets Gradle to auto-detect compatible JDK for your project installed in your machine to execute Gradle builds or auto-provision the required JDK by downloading it if cannot be found locally. This feature was stabilized in Gradle 9.2.0.
This simplifies project setup and improves JDK management in several ways:
- Fewer setup errors: You no longer need to have a specific JDK installed to import and build a project, which reduces setup-related errors given invalid JDK selection.
- Consistent builds: JDK selection for Gradle builds is not only consistent across different machines but also between the IDE and command-line, which prevents spawning multiple Gradle Daemons that adversely affect performance.
For existing projects that use a compatible Gradle version, Android Studio shows a notification offering an option to automatically migrate your project's defined Gradle JDK configuration to Daemon JVM criteria, while maintaining the same specifications.
Android Studio Panda 2
The following are new features in Android Studio Panda 2.
To see what's been fixed in this version of Android Studio, see the closed issues.
Custom View Preview deprecation
We are deprecating the Custom View Preview feature in the coming releases.
As the Android ecosystem shifts toward Jetpack Compose, building custom UI components has become significantly more efficient and intuitive. Compose includes a powerful, built-in @Preview system that provides a superior workflow for developing custom UI elements compared to the legacy XML-based approach.
By deprecating the Custom View Preview, we are able to focus our resources on enhancing the preview experience within the Compose ecosystem while providing a leaner, more performant IDE.
Create a new project with AI
Use the power of generative AI to accelerate your Android development workflow. Starting with Android Studio Otter 1 Canary 5, the AI agent enables you go from idea to app prototype in minutes.
The agent is capable of generating a variety of multiscreen applications:
- Single-screen apps: Build basic apps with static UI layouts.
- Multipage apps: Create applications with basic navigation between screens.
- AI-enhanced apps: Integrate Gemini APIs to add generative AI features.
- Apps with public API integration: Build apps that display data from public APIs.
To use the project setup agent, do the following:
- Start Android Studio.
Select New Project on the Welcome to Android Studio screen (or File > New > New Project from within a project).
Start a new project. Select Create with AI.
Select a project template or create your app with Gemini. Type your prompt into the text entry field and click Next.
Dialog for setting up a new project. Name your app and click Finish to start the generation process.
Based on your prompt, Gemini in Android Studio generates a structured plan for your app. Once you approve the plan, the agent begins an autonomous generation loop to configure and build your app.
Update dependencies with the AI agent
Upgrading dependencies can be a complex and time-consuming task. Starting with Android Studio Otter 1 Canary 5, the AI agent automates and simplifies the dependency upgrade process, eliminating tedious work and improving project maintainability. With just a few clicks, you can seamlessly upgrade all your dependencies and get the benefits of the latest versions, so you can focus on building high-quality apps.
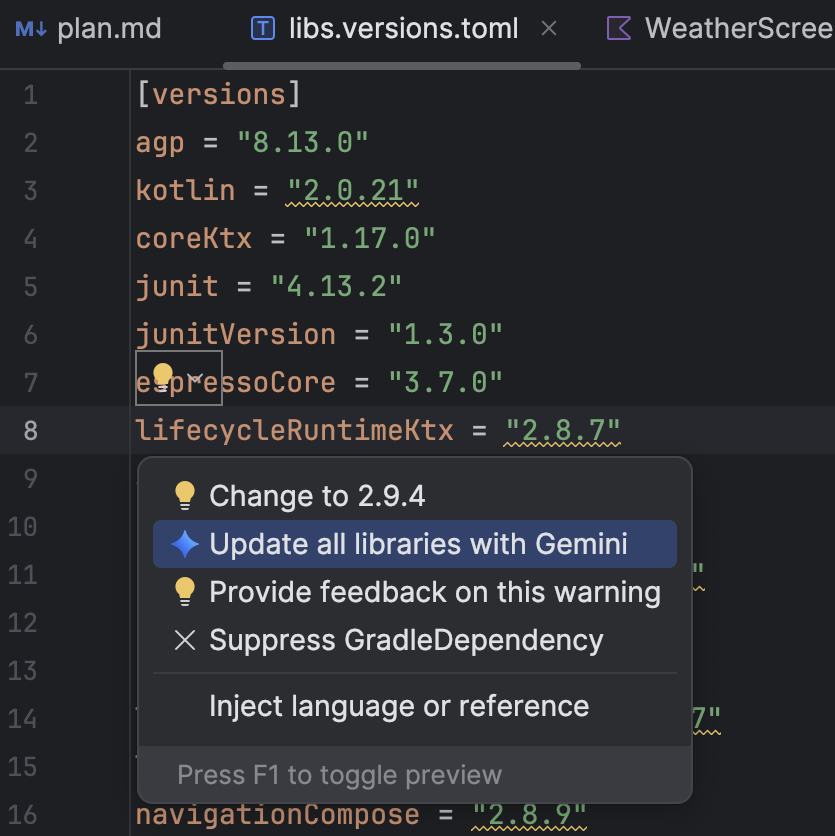
To update dependencies using the AI agent, do one of the following:
- Click Refactor (or right-click in the editor or project view) > Update dependencies.
In the
libs.versions.tomlfile, hover over a version that is underlined, click the Show Context Actions menu that appears, and then click Update all libraries with Gemini.
menu that appears, and then click Update all libraries with Gemini.
During the process, the agent provides a high-level overview of its upgrade plan so you can monitor progress step by step and review all changes before applying them. The agent iterates through the build process, resolving any build errors that arise from the upgrades. You can review, accept, or rollback changes or stop the agent at any point.
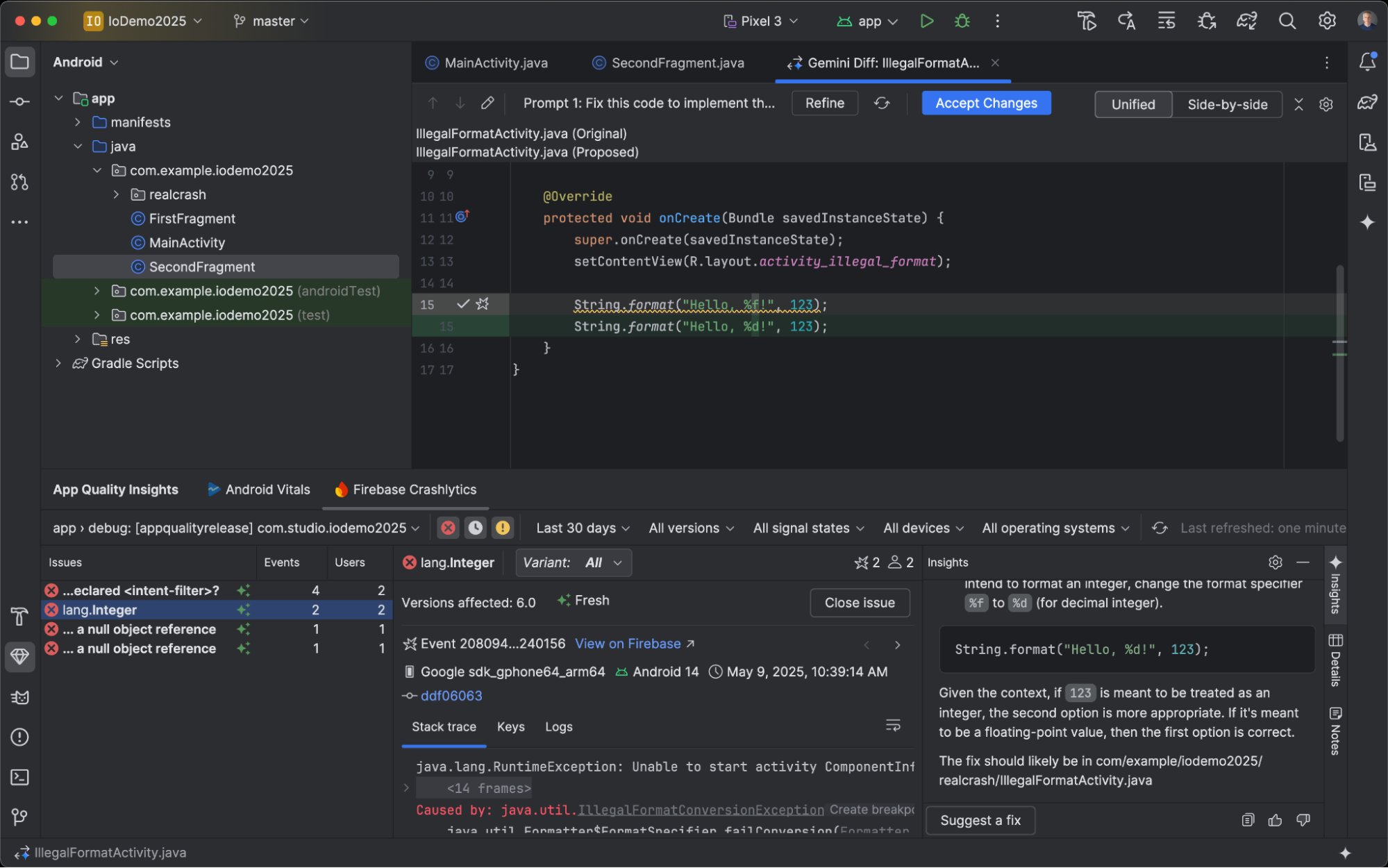
Suggested fixes for crashes
In Android Studio Meerkat Feature Drop, we launched Gemini insights for crashes reported in the App Quality Insights tool window. Now, Android Studio can use Gemini to analyze the crash data along with your source code to suggest potential fixes. After selecting a crash in the App Quality Insights tool window, navigate to the Insights tab and click Suggest a fix after Gemini generates an insight for the crash. Gemini then generates suggested code changes that you can review and accept in an editor diff tab.
Compose Preview Screenshot Testing tool
Use the Compose Preview Screenshot Testing tool to test your Compose UIs and prevent regressions. The new tool helps you generate HTML reports that let you visually detect any changes to your app's UI. Learn more at Compose Preview Screenshot Testing.
LeakCanary in Android Studio Profiler
Android Studio Panda includes a LeakCanary integration directly in the Android Studio Profiler as a dedicated task.
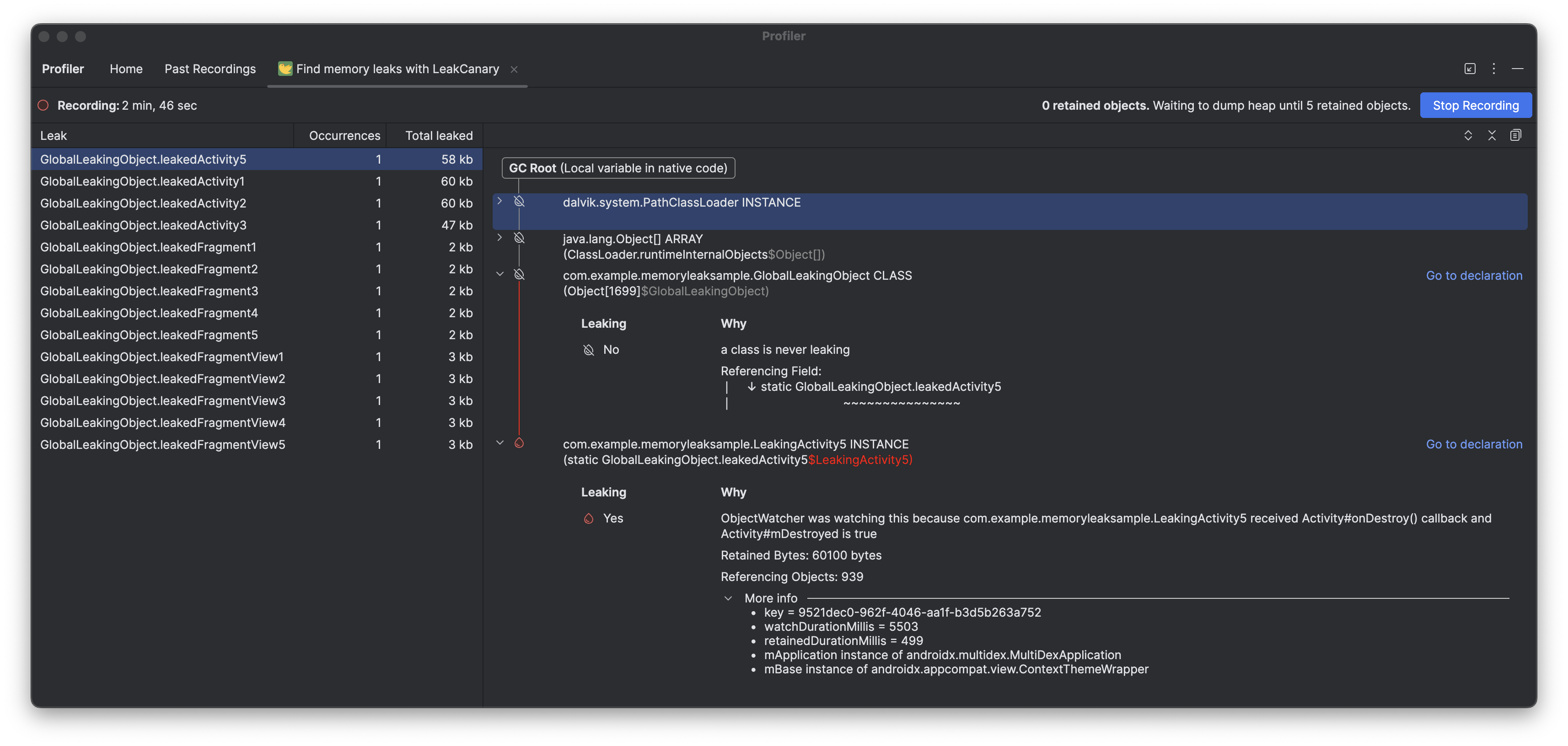
The LeakCanary profiler task in Android Studio actively moves the memory leak analysis from your device to your development machine, resulting in a significant performance boost during the leak analysis phase as compared to on-device leak analysis.
Additionally, the leak analysis is now contextualized within the IDE and fully integrated with your source code, providing features like Jump to Source and other helpful code connections that drastically reduce the friction and time required to investigate and fix memory leaks. You can also copy the entire leak analysis for further processing with Gemini. This can dramatically increase your productivity and improve your workflow during the development phase.
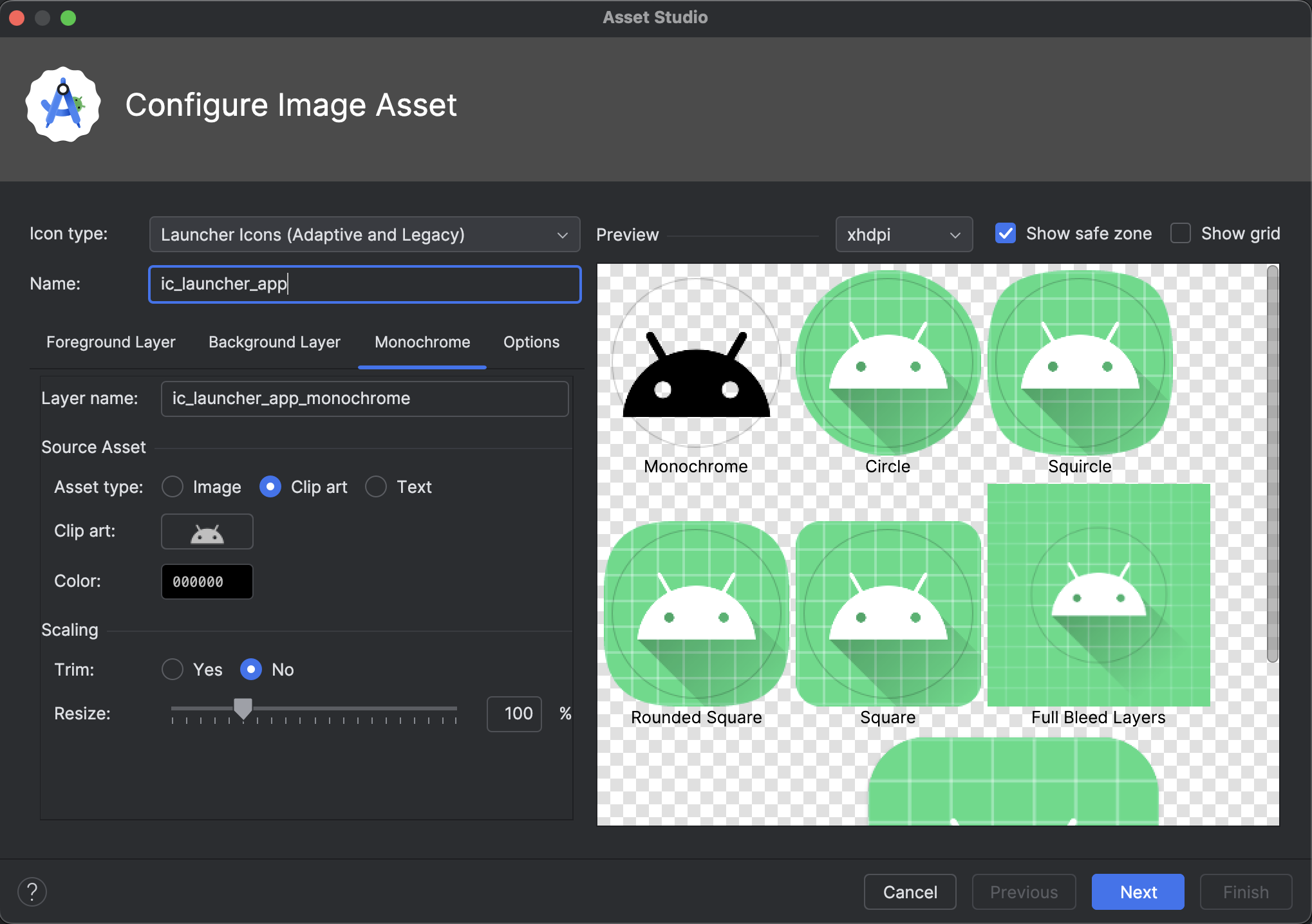
Monochrome icon support in Asset Studio
Android Studio Narwhal Feature Drop 2025.1.3 Canary 2 and later simplify the creation of themed app icons. With Android 13 (API level 33) and higher, users can opt for themed app icons, which adapt to the wallpaper and theme of the user's device.
To support this feature, Android Studio integrates a new monochrome icon option directly into the Image Asset Studio wizard. When you're creating an adaptive app icon, you now see a dedicated Monochrome tab in addition to the existing Foreground and Background tabs. You can either provide a separate monochrome app icon (see the design specs), or allow Android Studio to default to reusing the foreground layer of the adaptive icon for the monochrome layer.
You can access Image Asset Studio through the Resource Manager, or by right-clicking a project directory and navigating to New > Image Asset.
Select Launcher icons (Adaptive and Legacy) as the icon type to see the new Monochrome tab.
After importing the icons, you can preview your themed app icons.
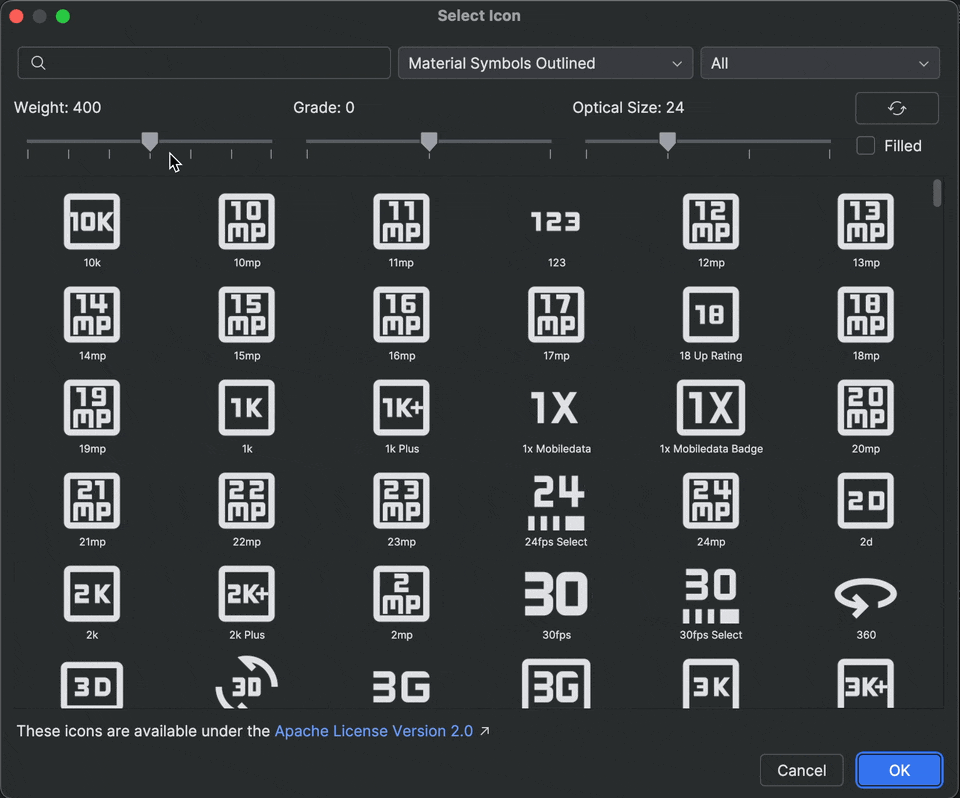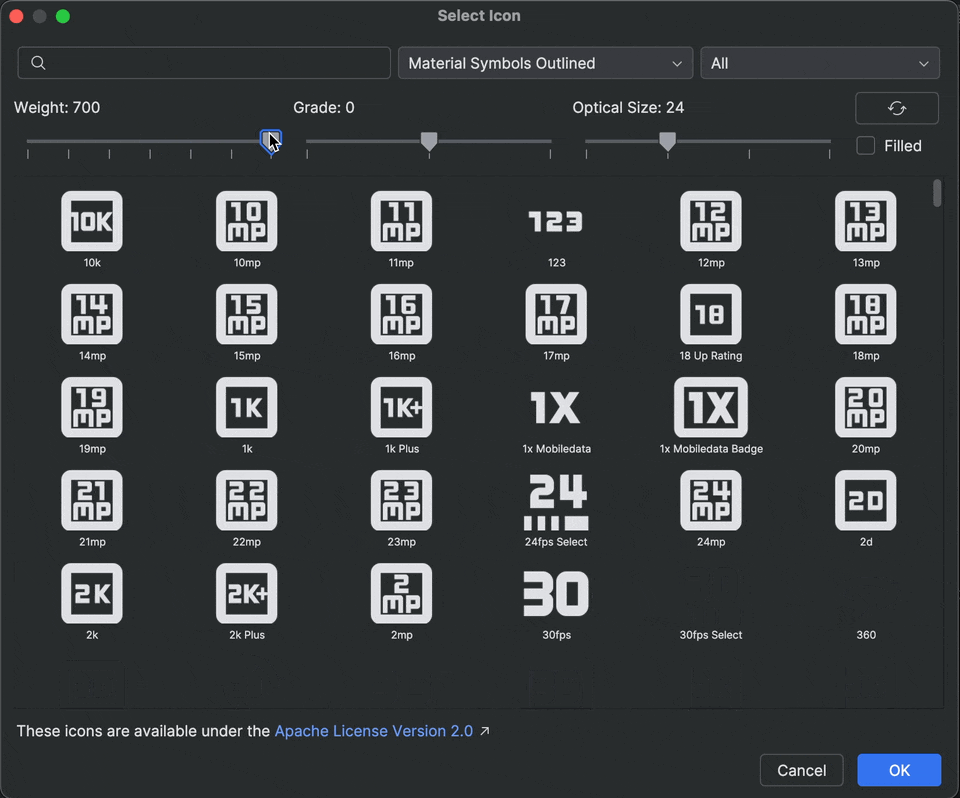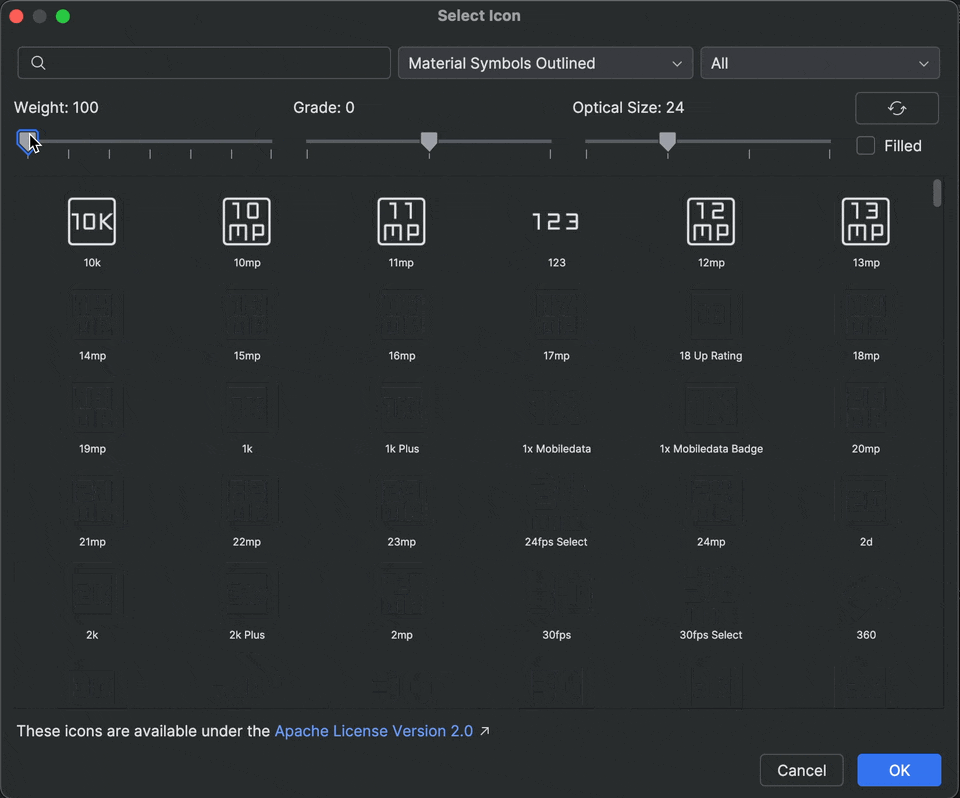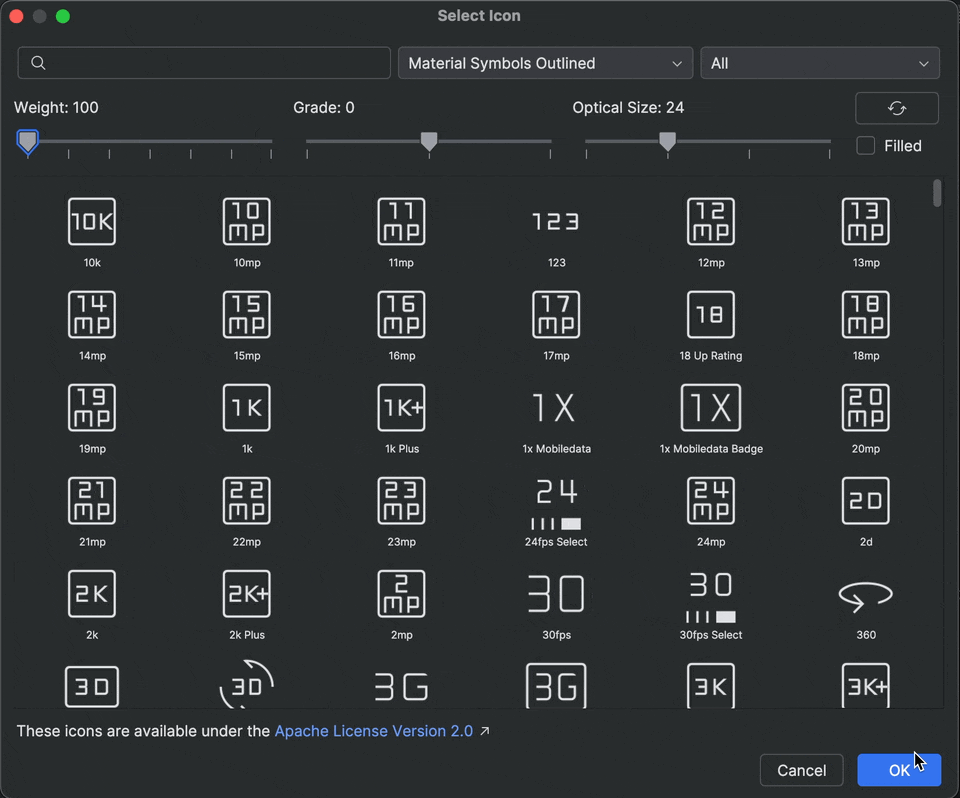
Material symbols support in Android Studio
Add and customize the latest Material symbols in your app with Android Studio Otter 2 Feature Drop. The Vector Asset Studio is now fully integrated with the Material symbols library from Google Fonts, giving you access to the complete catalog right inside the IDE.
You can now customize icon attributes like weight, grade, and optical size directly in the studio to perfectly match your design. Try it out in the latest canary build!
Layout Inspector 3D mode deprecation
In Android Studio Panda 2, we deprecated the 3D Mode feature in the Layout Inspector. While 3D Mode provided a way to visualize deep hierarchies, usage data indicates that the standard 2D view and Component Tree meet the vast majority of debugging needs. By removing this feature, we can direct our resources toward improving the overall support, performance, and stability of the Layout Inspector. You can continue to inspect view nesting and z-ordering using the Component Tree and the standard 2D layout view.
