Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณเช่นเดียวกับรุ่นก่อนหน้า การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้จะมีผลกับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไปเท่านั้น หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไป คุณควรแก้ไขแอปให้รองรับลักษณะการทำงานเหล่านี้อย่างเหมาะสมในกรณีที่ เกี่ยวข้อง
นอกจากนี้ โปรดตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่ส่งผลต่อแอปทั้งหมด
ที่ทำงานบน Android 15 ไม่ว่า targetSdkVersion ของแอปจะเป็นอย่างไร
ฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 15 จะแก้ไขหรือขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเปลี่ยนแปลงบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
We are making the following changes to foreground services with Android 15.
- Data sync foreground service timeout behavior
- New media processing foreground service type
- Restrictions on
BOOT_COMPLETEDbroadcast receivers launching foreground services - Restrictions on starting foreground services while an app holds the
SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOWpermission
Data sync foreground service timeout behavior
Android 15 เปิดตัวลักษณะการหมดเวลาใหม่สำหรับ dataSync ในแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ขึ้นไป ลักษณะการทำงานนี้มีผลกับmediaProcessingบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าประเภทใหม่ด้วย
ระบบอนุญาตให้บริการ dataSync ของแอปทำงานได้นาน 6 ชั่วโมงโดยรวมในระยะเวลา 24 ชั่วโมง หลังจากนั้นระบบจะเรียกใช้เมธอด Service.onTimeout(int, int) ของบริการที่ทำงานอยู่ (เปิดตัวใน Android 15) ในขณะนี้บริการมีเวลา 2-3 วินาทีในการเรียกใช้ Service.stopSelf() เมื่อมีการเรียกใช้ Service.onTimeout() บริการดังกล่าวจะไม่ถือว่าเป็นบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าอีกต่อไป หากบริการไม่ได้เรียกใช้ Service.stopSelf() ระบบจะแสดงข้อผิดพลาดภายใน ระบบจะบันทึกข้อยกเว้นใน Logcat โดยมีข้อความต่อไปนี้
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
หากต้องการหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานนี้ คุณสามารถทำอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่งต่อไปนี้
- ขอให้บริการของคุณใช้วิธีการ
Service.onTimeout(int, int)ใหม่ เมื่อแอปได้รับการติดต่อกลับ ให้โทรหาstopSelf()ภายใน 2-3 วินาที (หากคุณไม่หยุดแอปทันที ระบบจะสร้างสถานะ "ไม่สำเร็จ") - ตรวจสอบว่าบริการ
dataSyncของแอปไม่ทำงานเป็นเวลารวม 6 ชั่วโมงในช่วง 24 ชั่วโมงใดก็ได้ (เว้นแต่ผู้ใช้โต้ตอบกับแอป จะเป็นการรีเซ็ตตัวจับเวลา) - เริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
dataSyncเฉพาะในกรณีที่มีการโต้ตอบโดยตรงจากผู้ใช้ เนื่องจากแอปของคุณอยู่เบื้องหน้าเมื่อบริการเริ่มทำงาน บริการของคุณจึงมีเวลา 6 ชั่วโมงเต็มหลังจากที่แอปเปลี่ยนไปทำงานในเบื้องหลัง - ใช้API อื่นแทน
dataSyncบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
หากบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า dataSync ของแอปทำงานเป็นเวลา 6 ชั่วโมงในช่วง 24 ชั่วโมงที่ผ่านมา คุณจะไม่สามารถเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า dataSync อื่นได้เว้นแต่ผู้ใช้จะนำแอปของคุณไปไว้ที่เบื้องหน้า (ซึ่งจะรีเซ็ตตัวจับเวลา) หากคุณพยายามเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า dataSync อื่น ระบบจะแสดง ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException พร้อมข้อความแสดงข้อผิดพลาด เช่น "หมดเวลาสำหรับบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าประเภท dataSync แล้ว"
การทดสอบ
หากต้องการทดสอบลักษณะการทํางานของแอป คุณสามารถเปิดใช้การหมดเวลาการซิงค์ข้อมูลได้แม้ว่าแอปจะไม่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ก็ตาม (ตราบใดที่แอปทํางานบนอุปกรณ์ Android 15) หากต้องการเปิดใช้การหมดเวลา ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังปรับระยะเวลาหมดเวลาเพื่อให้ทดสอบลักษณะการทํางานของแอปเมื่อถึงขีดจํากัดได้ง่ายขึ้นได้ด้วย หากต้องการตั้งค่าระยะเวลาหมดเวลาใหม่ ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
New media processing foreground service type
Android 15 ขอแนะนำบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าประเภทใหม่ ได้แก่ mediaProcessing บริการประเภทนี้เหมาะสำหรับการดำเนินการต่างๆ เช่น การแปลงไฟล์สื่อ เช่น แอปสื่ออาจดาวน์โหลดไฟล์เสียงและต้องแปลงไฟล์เป็นรูปแบบอื่นก่อนเล่น คุณสามารถใช้mediaProcessingบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าเพื่อให้ Conversion ดำเนินต่อไปได้แม้ว่าแอปจะทำงานอยู่เบื้องหลัง
ระบบอนุญาตให้บริการ mediaProcessing ของแอปทำงานได้นาน 6 ชั่วโมงโดยรวมในระยะเวลา 24 ชั่วโมง หลังจากนั้นระบบจะเรียกใช้เมธอด Service.onTimeout(int, int) ของบริการที่ทำงานอยู่ (เปิดตัวใน Android 15) ขณะนี้บริการมีเวลา 2-3 วินาทีในการโทรไปที่ Service.stopSelf() หากบริการไม่ได้เรียกใช้ Service.stopSelf() ระบบจะแสดงข้อยกเว้นภายใน ระบบจะบันทึกข้อยกเว้นใน Logcat พร้อมข้อความต่อไปนี้
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
หากต้องการหลีกเลี่ยงการมีข้อยกเว้น ให้ทําอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่งต่อไปนี้
- ให้บริการของคุณใช้วิธีการ
Service.onTimeout(int, int)ใหม่ เมื่อแอปได้รับการติดต่อกลับ โปรดโทรหาstopSelf()ภายในไม่กี่วินาที (หากคุณไม่หยุดแอปในทันที ระบบจะล้มเหลว) - ตรวจสอบว่าบริการ
mediaProcessingของแอปไม่ทำงานเป็นเวลานานกว่า 6 ชั่วโมงในทุกๆ 24 ชั่วโมง (เว้นแต่ผู้ใช้โต้ตอบกับแอป จะเป็นการรีเซ็ตตัวจับเวลา) - เริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
mediaProcessingเฉพาะในกรณีที่มีการโต้ตอบโดยตรงจากผู้ใช้ เนื่องจากแอปของคุณอยู่เบื้องหน้าเมื่อบริการเริ่มทำงาน บริการของคุณจึงมีเวลา 6 ชั่วโมงเต็มหลังจากที่แอปเปลี่ยนไปทำงานในเบื้องหลัง - ใช้ API อื่น เช่น WorkManager แทนบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าของ
mediaProcessing
หากบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า mediaProcessing ของแอปทำงานเป็นเวลา 6 ชั่วโมงในช่วง 24 ชั่วโมงที่ผ่านมา คุณจะไม่สามารถเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า mediaProcessing อื่นได้เว้นแต่ผู้ใช้จะนำแอปของคุณไปไว้ที่เบื้องหน้า (ซึ่งจะรีเซ็ตตัวจับเวลา) หากคุณพยายามเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า mediaProcessing รายการอื่น ระบบจะแสดงForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedExceptionพร้อมข้อความแสดงข้อผิดพลาด เช่น "บริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าประเภท mediaProcessing หมดเวลาแล้ว"
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับประเภทบริการ mediaProcessing ได้ที่การเปลี่ยนแปลงประเภทบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าสำหรับ Android 15: การประมวลผลสื่อ
การทดสอบ
หากต้องการทดสอบลักษณะการทำงานของแอป ให้เปิดใช้ระยะหมดเวลาการประมวลผลสื่อ แม้ว่าแอปจะไม่ได้กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ก็ตาม (ตราบใดที่แอปทำงานอยู่ในอุปกรณ์ Android 15) หากต้องการเปิดใช้การหมดเวลา ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังปรับระยะเวลาหมดเวลาเพื่อให้ทดสอบลักษณะการทํางานของแอปเมื่อถึงขีดจํากัดได้ง่ายขึ้นได้ด้วย หากต้องการตั้งค่าระยะเวลาหมดเวลาใหม่ ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
Restrictions on BOOT_COMPLETED broadcast receivers launching foreground services
There are new restrictions on BOOT_COMPLETED broadcast receivers launching
foreground services. BOOT_COMPLETED receivers are not allowed to launch the
following types of foreground services:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(this restriction has been in place formicrophonesince Android 14)
If a BOOT_COMPLETED receiver tries to launch any of those types of foreground
services, the system throws ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable these new restrictions even if your
app is not targeting Android 15 (as long as the app is running on an Android 15
device). Run the following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
To send a BOOT_COMPLETED broadcast without restarting the device,
run the following adb command:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
Restrictions on starting foreground services while an app holds the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permission
ก่อนหน้านี้ หากแอปมีสิทธิ์ SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW แอปจะเปิดบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าได้แม้ว่าในขณะนั้นแอปจะทำงานอยู่เบื้องหลังก็ตาม (ตามที่ได้อธิบายไว้ในการยกเว้นจากการจำกัดการเริ่มทำงานในเบื้องหลัง)
หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 การยกเว้นนี้จะแคบลงแล้ว ตอนนี้แอปต้องมีสิทธิ์ SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW และต้องมีหน้าต่างวางซ้อนที่มองเห็นได้ กล่าวคือ แอปต้องเปิดหน้าต่าง TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY ก่อน และหน้าต่างต้องปรากฏขึ้นก่อนที่คุณจะเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
หากแอปพยายามเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจากเบื้องหลังโดยไม่เป็นไปตามข้อกำหนดใหม่เหล่านี้ (และไม่มีข้อยกเว้นอื่นๆ) ระบบจะแสดงข้อผิดพลาด ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException
หากแอปประกาศสิทธิ์ SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW และเปิดบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจากเบื้องหลัง แอปอาจได้รับผลกระทบจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ หากแอปได้รับ ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException ให้ตรวจสอบลําดับการทํางานของแอปและตรวจสอบว่าแอปมีหน้าต่างวางซ้อนที่ใช้งานอยู่ก่อนที่จะพยายามเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจากเบื้องหลัง คุณสามารถตรวจสอบว่าขณะนี้หน้าต่างวางซ้อนแสดงอยู่หรือไม่โดยเรียกใช้ View.getWindowVisibility() หรือจะลบล้าง View.onWindowVisibilityChanged() เพื่อรับการแจ้งเตือนทุกครั้งที่ระดับการแชร์มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงก็ได้
การทดสอบ
หากต้องการทดสอบลักษณะการทํางานของแอป คุณสามารถเปิดใช้ข้อจํากัดใหม่เหล่านี้ได้แม้ว่าแอปของคุณจะไม่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ก็ตาม (ตราบใดที่แอปทํางานบนอุปกรณ์ Android 15) หากต้องการเปิดใช้ข้อจำกัดใหม่เหล่านี้เกี่ยวกับการเริ่มบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจากเบื้องหลัง ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
การเปลี่ยนแปลงเวลาที่แอปจะแก้ไขสถานะส่วนกลางของโหมดห้ามรบกวนได้
แอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ขึ้นไปจะไม่สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะหรือนโยบายแบบรวมของโหมดห้ามรบกวน (DND) ในอุปกรณ์ได้อีกต่อไป (ไม่ว่าจะแก้ไขการตั้งค่าของผู้ใช้หรือปิดโหมด DND) แต่แอปต้องส่งAutomaticZenRule ซึ่งระบบจะรวมเข้ากับนโยบายส่วนกลางโดยใช้รูปแบบ "นโยบายที่เข้มงวดที่สุดจะชนะ" ที่มีอยู่ การเรียก API ที่มีอยู่ซึ่งก่อนหน้านี้ส่งผลต่อสถานะส่วนกลาง (setInterruptionFilter,
setNotificationPolicy) จะส่งผลให้มีการสร้างหรืออัปเดต AutomaticZenRule ที่ไม่ชัดแจ้ง ซึ่งจะเปิดและปิดอยู่โดยขึ้นอยู่กับรอบการเรียกของ API เหล่านั้น
โปรดทราบว่าการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้มีผลต่อลักษณะการทำงานที่สังเกตได้เฉพาะในกรณีที่แอปเรียกใช้ setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) และคาดว่าการเรียกใช้ดังกล่าวจะปิดใช้งาน AutomaticZenRule ที่เจ้าของเปิดใช้งานไว้ก่อนหน้านี้
การเปลี่ยนแปลง API ของ OpenJDK
Android 15 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases.
Some of these changes can affect app compatibility for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35):
Changes to string formatting APIs: Validation of argument index, flags, width, and precision are now more strict when using the following
String.format()andFormatter.format()APIs:String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
For example, the following exception is thrown when an argument index of 0 is used (
%0in the format string):IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0In this case, the issue can be fixed by using an argument index of 1 (
%1in the format string).Changes to component type of
Arrays.asList(...).toArray(): When usingArrays.asList(...).toArray(), the component type of the resulting array is now anObject—not the type of the underlying array's elements. So the following code throws aClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();For this case, to preserve
Stringas the component type in the resulting array, you could useCollection.toArray(Object[])instead:String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);Changes to language code handling: When using the
LocaleAPI, language codes for Hebrew, Yiddish, and Indonesian are no longer converted to their obsolete forms (Hebrew:iw, Yiddish:ji, and Indonesian:in). When specifying the language code for one of these locales, use the codes from ISO 639-1 instead (Hebrew:he, Yiddish:yi, and Indonesian:id).Changes to random int sequences: Following the changes made in https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574, the following
Random.ints()methods now return a different sequence of numbers than theRandom.nextInt()methods do:Generally, this change shouldn't result in app-breaking behavior, but your code shouldn't expect the sequence generated from
Random.ints()methods to matchRandom.nextInt().
The new SequencedCollection API can affect your app's compatibility
after you update compileSdk in your app's build configuration to use
Android 15 (API level 35):
Collision with
MutableList.removeFirst()andMutableList.removeLast()extension functions inkotlin-stdlibThe
Listtype in Java is mapped to theMutableListtype in Kotlin. Because theList.removeFirst()andList.removeLast()APIs have been introduced in Android 15 (API level 35), the Kotlin compiler resolves function calls, for examplelist.removeFirst(), statically to the newListAPIs instead of to the extension functions inkotlin-stdlib.If an app is re-compiled with
compileSdkset to35andminSdkset to34or lower, and then the app is run on Android 14 and lower, a runtime error is thrown:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;The existing
NewApilint option in Android Gradle Plugin can catch these new API usages../gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()To fix the runtime exception and lint errors, the
removeFirst()andremoveLast()function calls can be replaced withremoveAt(0)andremoveAt(list.lastIndex)respectively in Kotlin. If you're using Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 or higher, it also provides a quick fix option for these errors.Consider removing
@SuppressLint("NewApi")andlintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }if the lint option has been disabled.Collision with other methods in Java
New methods have been added into the existing types, for example,
ListandDeque. These new methods might not be compatible with the methods with the same name and argument types in other interfaces and classes. In the case of a method signature collision with incompatibility, thejavaccompiler outputs a build-time error. For example:Example error 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface ListExample error 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 errorExample error 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 errorTo fix these build errors, the class implementing these interfaces should override the method with a compatible return type. For example:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
ความปลอดภัย
Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งเสริมความปลอดภัยของระบบเพื่อช่วยปกป้องแอป และผู้ใช้จากแอปที่เป็นอันตราย
เวอร์ชัน TLS ที่ถูกจำกัด
Android 15 จำกัดการใช้ TLS เวอร์ชัน 1.0 และ 1.1 ก่อนหน้านี้ Android ได้เลิกใช้งานเวอร์ชันเหล่านี้แล้ว แต่ตอนนี้ไม่อนุญาตให้แอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ใช้เวอร์ชันดังกล่าว
เปิดใช้กิจกรรมในเบื้องหลังที่ปลอดภัย
Android 15 ปกป้องผู้ใช้จากแอปที่เป็นอันตรายและให้ผู้ใช้ควบคุมอุปกรณ์ได้มากขึ้น โดยการเพิ่มการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ป้องกันไม่ให้แอปที่เป็นอันตรายซึ่งทำงานในเบื้องหลัง นำแอปอื่นๆ มาไว้ที่เบื้องหน้า ยกระดับสิทธิ์ และละเมิด การโต้ตอบของผู้ใช้ การเปิดใช้กิจกรรมในเบื้องหลังถูกจำกัดตั้งแต่ Android 10 (API ระดับ 29)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงอื่นๆ
- เปลี่ยนให้ครีเอเตอร์
PendingIntentบล็อกการเปิดใช้กิจกรรมในเบื้องหลังโดย ค่าเริ่มต้น ซึ่งจะช่วยป้องกันไม่ให้แอปสร้างPendingIntentโดยไม่ได้ตั้งใจ ซึ่งผู้ไม่ประสงค์ดีอาจนำไปใช้ในทางที่ผิดได้ - อย่านำแอปมาไว้เบื้องหน้า เว้นแต่
PendingIntentผู้ส่ง จะอนุญาต การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้มีจุดมุ่งหมายเพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้แอปที่เป็นอันตรายใช้ความสามารถในการเริ่มกิจกรรมในเบื้องหลังในทางที่ผิด โดยค่าเริ่มต้น แอปจะไม่ได้รับอนุญาตให้นำสแต็กงานมาไว้ที่เบื้องหน้า เว้นแต่ผู้สร้างจะอนุญาตสิทธิ์ในการเปิดกิจกรรมในเบื้องหลัง หรือผู้ส่งมีสิทธิ์ในการเปิดกิจกรรมในเบื้องหลัง - ควบคุมวิธีที่กิจกรรมบนสุดของสแต็กงานจะทำงานให้เสร็จ หากกิจกรรมที่อยู่ด้านบนสุดทำงานเสร็จแล้ว Android จะกลับไปที่งานที่ใช้งานล่าสุด นอกจากนี้ หากกิจกรรมที่ไม่ใช่กิจกรรมที่อยู่ด้านบนสุดทำงานเสร็จ Android จะ กลับไปที่หน้าจอหลัก และจะไม่บล็อกการสิ้นสุดของกิจกรรมที่ไม่ใช่กิจกรรมที่อยู่ด้านบนสุดนี้
- ป้องกันไม่ให้แอปอื่นๆ เปิดกิจกรรมที่กำหนดเองในงานของคุณ การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะป้องกันไม่ให้แอปที่เป็นอันตรายฟิชชิงผู้ใช้โดยการสร้าง กิจกรรมที่ดูเหมือนมาจากแอปอื่นๆ
- บล็อกไม่ให้ระบบพิจารณาหน้าต่างที่มองไม่เห็นสำหรับการเปิดใช้กิจกรรมในเบื้องหลัง ซึ่งจะช่วยป้องกันไม่ให้แอปที่เป็นอันตรายใช้การเปิดใช้งานในเบื้องหลังในทางที่ผิดเพื่อแสดงเนื้อหาที่ไม่พึงประสงค์หรือเนื้อหาที่เป็นอันตรายต่อผู้ใช้
Intent ที่ปลอดภัยกว่า
Android 15 introduces StrictMode for
intents.
In order to see detailed logs about Intent usage violations, use following
method:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 15 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างที่มีจุดประสงค์เพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกันมากขึ้น และใช้งานง่าย
การเปลี่ยนแปลงส่วนที่เว้นไว้ในหน้าต่าง
There are two changes related to window insets in Android 15: edge-to-edge is enforced by default, and there are also configuration changes, such as the default configuration of system bars.
การบังคับใช้แบบไร้ขอบ
Apps are edge-to-edge by default on devices running Android 15 if the app is targeting Android 15 (API level 35).
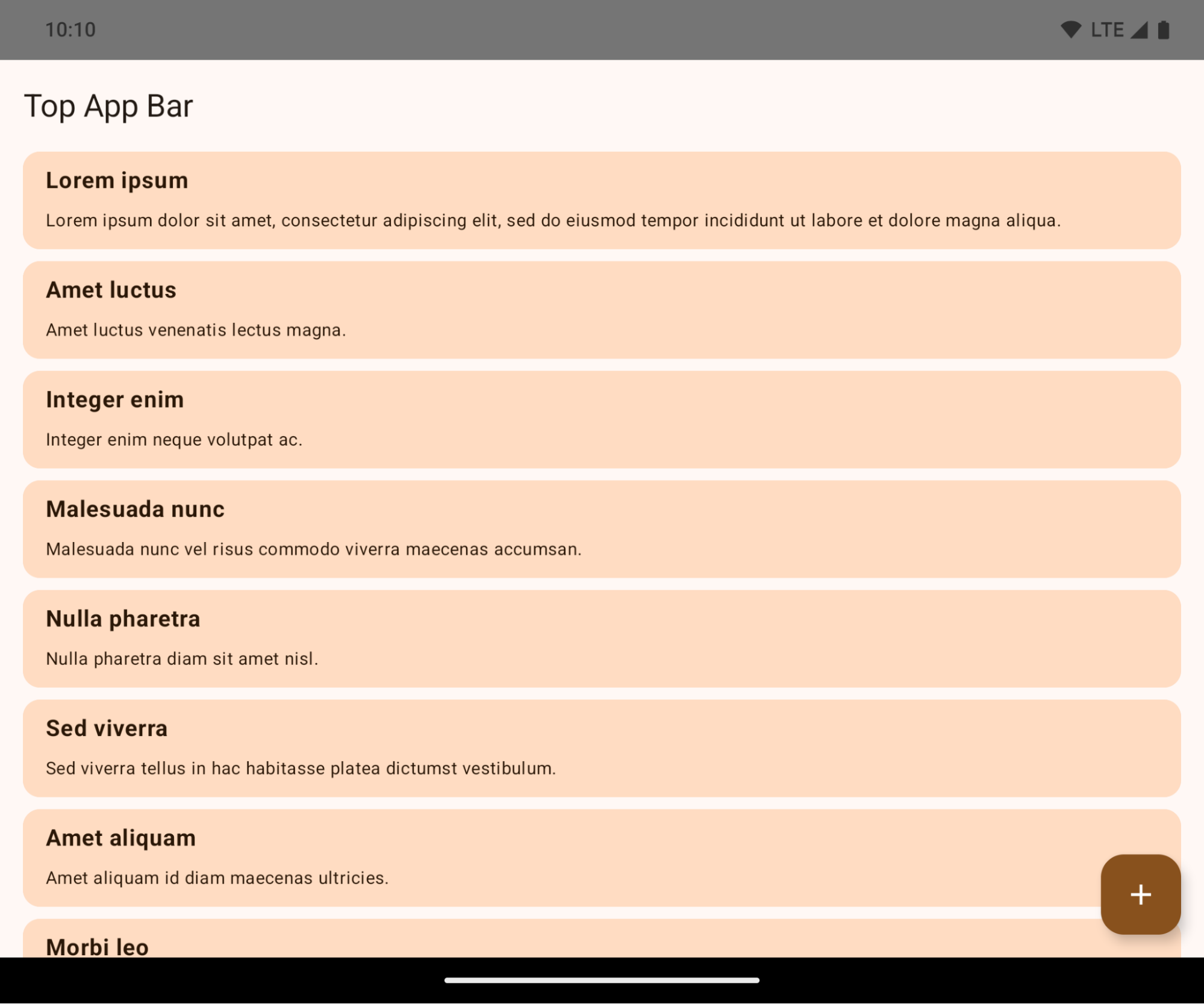
This is a breaking change that might negatively impact your app's UI. The changes affect the following UI areas:
- Gesture handle navigation bar
- Transparent by default.
- Bottom offset is disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare deprecated and don't affect gesture navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedcontinue to have no effect on gesture navigation.
- 3-button navigation
- Opacity set to 80% by default, with color possibly matching the window background.
- Bottom offset disabled so content draws behind the system navigation bar unless insets are applied.
setNavigationBarColorandR.attr#navigationBarColorare set to match the window background by default. The window background must be a color drawable for this default to apply. This API is deprecated but continues to affect 3-button navigation.setNavigationBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforcedis true by default, which adds an 80% opaque background across 3-button navigation.
- Status bar
- Transparent by default.
- The top offset is disabled so content draws behind the status bar unless insets are applied.
setStatusBarColorandR.attr#statusBarColorare deprecated and have no effect on Android 15.setStatusBarContrastEnforcedandR.attr#statusBarContrastEnforcedare deprecated but still have an effect on Android 15.
- Display cutout
layoutInDisplayCutoutModeof non-floating windows must beLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS.SHORT_EDGES,NEVER, andDEFAULTare interpreted asALWAYSso that users don't see a black bar caused by the display cutout and appear edge-to-edge.
The following example shows an app before and after targeting Android 15 (API level 35), and before and after applying insets. This example is not comprehensive, this might appear differently on Android Auto.
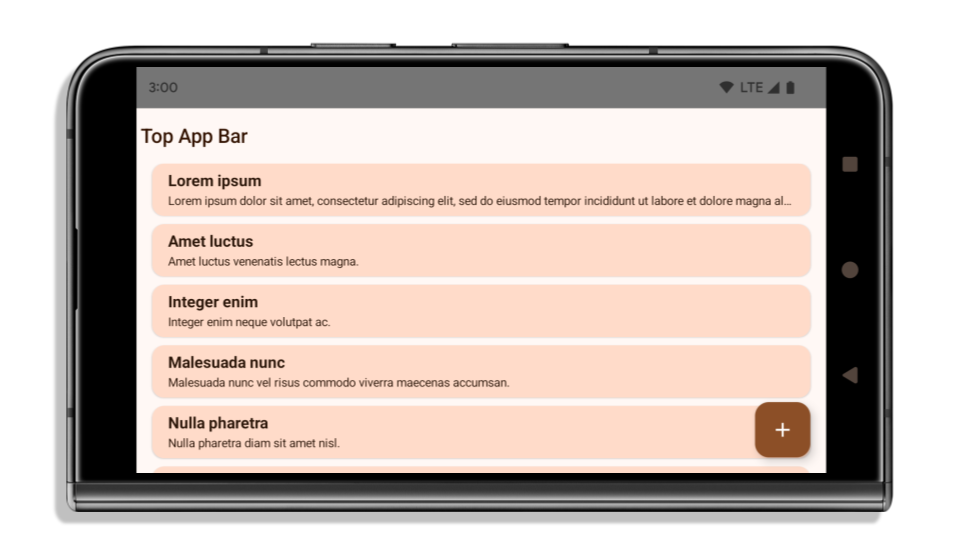

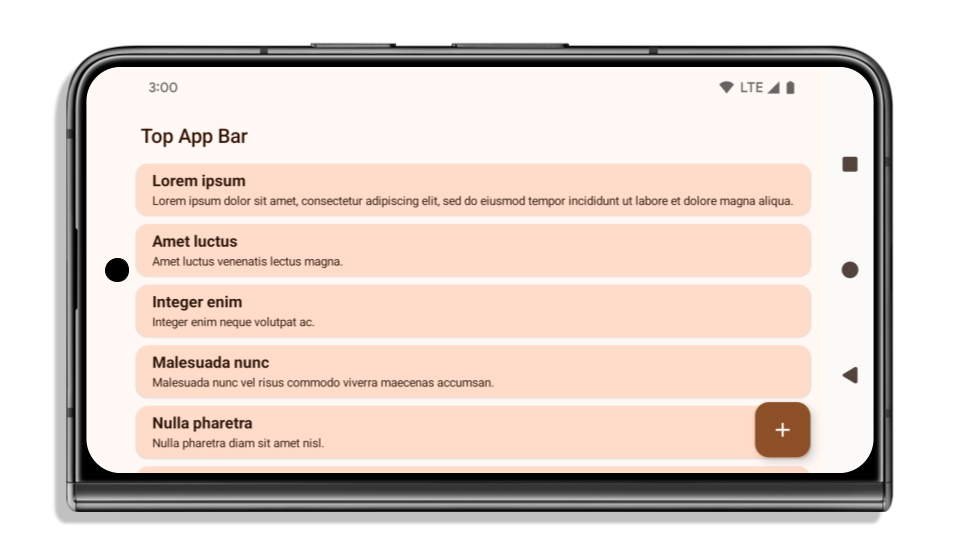
What to check if your app is already edge-to-edge
If your app is already edge-to-edge and applies insets, you are mostly unimpacted, except in the following scenarios. However, even if you think you aren't impacted, we recommend you test your app.
- You have a non-floating window, such as an
Activitythat usesSHORT_EDGES,NEVERorDEFAULTinstead ofLAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS. If your app crashes on launch, this might be due to your splashscreen. You can either upgrade the core splashscreen dependency to 1.2.0-alpha01 or later or setwindow.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always. - There might be lower-traffic screens with occluded UI. Verify these
less-visited screens don't have occluded UI. Lower-traffic screens include:
- Onboarding or sign-in screens
- Settings pages
What to check if your app is not already edge-to-edge
If your app is not already edge-to-edge, you are most likely impacted. In addition to the scenarios for apps that are already edge-to-edge, you should consider the following:
- If your app uses Material 3 Components (
androidx.compose.material3) in compose, such asTopAppBar,BottomAppBar, andNavigationBar, these components are likely not impacted because they automatically handle insets. - If your app is using Material 2 Components (
androidx.compose.material) in Compose, these components don't automatically handle insets. However, you can get access to the insets and apply them manually. In androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 and later, use thewindowInsetsparameter to apply the insets manually forBottomAppBar,TopAppBar,BottomNavigation, andNavigationRail. Likewise, use thecontentWindowInsetsparameter forScaffold. - If your app uses views and Material Components
(
com.google.android.material), most views-based Material Components such asBottomNavigationView,BottomAppBar,NavigationRailView, orNavigationView, handle insets and require no additional work. However, you need to addandroid:fitsSystemWindows="true"if usingAppBarLayout. - For custom composables, apply the insets manually as padding. If your
content is within a
Scaffold, you can consume insets using theScaffoldpadding values. Otherwise, apply padding using one of theWindowInsets. - If your app is using views and
BottomSheet,SideSheetor custom containers, apply padding usingViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener. ForRecyclerView, apply padding using this listener and also addclipToPadding="false".
What to check if your app must offer custom background protection
If your app must offer custom background protection to 3-button navigation or
the status bar, your app should place a composable or view behind the system bar
using WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() to get the 3-button
navigation bar height or WindowInsets.Type#statusBars.
Additional edge-to-edge resources
See the Edge to Edge Views and Edge to Edge Compose guides for additional considerations on applying insets.
Deprecated APIs
The following APIs are deprecated but not disabled:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for 3 button navigation, with 80% alpha)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
The following APIs are deprecated and disabled:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(for gesture navigation)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
การกำหนดค่าที่เสถียร
หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ขึ้นไป Configuration จะไม่
รวมแถบระบบอีกต่อไป หากใช้ขนาดหน้าจอในคลาส Configuration เพื่อคำนวณเลย์เอาต์ คุณควรแทนที่ด้วยตัวเลือกอื่นที่ดีกว่า เช่น ViewGroup, WindowInsets หรือ WindowMetricsCalculator ที่เหมาะสม ทั้งนี้ขึ้นอยู่กับความต้องการของคุณ
Configuration พร้อมใช้งานตั้งแต่ API 1 โดยปกติแล้วจะได้รับจาก
Activity.onConfigurationChanged โดยจะให้ข้อมูล เช่น ความหนาแน่นของหน้าต่าง
การวางแนว และขนาด ลักษณะสำคัญอย่างหนึ่งเกี่ยวกับขนาดหน้าต่างที่ส่งคืนจาก Configuration คือก่อนหน้านี้จะไม่รวมแถบระบบ
โดยปกติแล้ว ขนาดการกำหนดค่าจะใช้สำหรับการเลือกทรัพยากร เช่น
/res/layout-h500dp และนี่ก็ยังคงเป็น Use Case ที่ถูกต้อง อย่างไรก็ตาม เราไม่แนะนำให้ใช้สำหรับ
การคำนวณเลย์เอาต์มาโดยตลอด หากคุณกำลังทำเช่นนั้น คุณควรเลิกทำ
ตั้งแต่ตอนนี้ คุณควรแทนที่การใช้ Configuration ด้วยสิ่งอื่นที่เหมาะสมกว่าตามกรณีการใช้งาน
หากใช้เพื่อคำนวณเลย์เอาต์ ให้ใช้ ViewGroup ที่เหมาะสม เช่น
CoordinatorLayout หรือ ConstraintLayout หากคุณใช้เพื่อกำหนดความสูง
ของแถบนำทางของระบบ ให้ใช้ WindowInsets หากต้องการทราบขนาดปัจจุบัน
ของหน้าต่างแอป ให้ใช้ computeCurrentWindowMetrics
รายการต่อไปนี้อธิบายฟิลด์ที่ได้รับผลกระทบจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้
- ขนาด
Configuration.screenWidthDpและscreenHeightDpจะไม่ ยกเว้นแถบระบบอีกต่อไป Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDpได้รับผลกระทบทางอ้อมจากการเปลี่ยนแปลง ในscreenWidthDpและscreenHeightDpConfiguration.orientationได้รับผลกระทบโดยอ้อมจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงในscreenWidthDpและscreenHeightDpในอุปกรณ์ที่มีสัดส่วนใกล้เคียงกับสี่เหลี่ยมจัตุรัสDisplay.getSize(Point)ได้รับผลกระทบโดยอ้อมจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงในConfigurationซึ่งเลิกใช้งานตั้งแต่ API ระดับ 30 เป็นต้นไปDisplay.getMetrics()ทำงานในลักษณะนี้มาตั้งแต่ API ระดับ 33 แล้ว
แอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight จะมีค่าเริ่มต้นเป็น true
For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), the
elegantTextHeight TextView attribute
becomes true by default, replacing the compact font used by default with some
scripts that have large vertical metrics with one that is much more readable.
The compact font was introduced to prevent breaking layouts; Android 13 (API
level 33) prevents many of these breakages by allowing the text layout to
stretch the vertical height utilizing the fallbackLineSpacing
attribute.
In Android 15, the compact font still remains in the system, so your app can set
elegantTextHeight to false to get the same behavior as before, but it is
unlikely to be supported in upcoming releases. So, if your app supports the
following scripts: Arabic, Lao, Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam,
Odia, Telugu or Thai, test your app by setting elegantTextHeight to true.
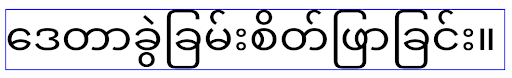
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 14 (API level 34) and lower.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android 15.การเปลี่ยนแปลงความกว้างของ TextView สำหรับรูปร่างตัวอักษรที่ซับซ้อน
ใน Android เวอร์ชันเก่า แบบอักษรตัวเขียนบางแบบหรือภาษาที่มีรูปร่างซับซ้อนอาจวาดตัวอักษรในพื้นที่ของตัวอักษรก่อนหน้าหรือถัดไปตามลำดับ
ในบางกรณี ตัวอักษรเหล่านั้นอาจถูกตัดออกตั้งแต่จุดเริ่มต้นหรือจุดสิ้นสุด
ตั้งแต่ Android 15 เป็นต้นไป TextView จะจัดสรรความกว้างสำหรับการวาดตัวอักษรดังกล่าวให้มีพื้นที่เพียงพอ และอนุญาตให้แอปขอการถ่วงข้อความเพิ่มเติมทางด้านซ้ายเพื่อป้องกันการตัดข้อความ
เนื่องจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ส่งผลต่อวิธีที่ TextView กำหนดความกว้าง TextView จะจัดสรรความกว้างเพิ่มเติมโดยค่าเริ่มต้นหากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ขึ้นไป คุณเปิดหรือปิดใช้ลักษณะการทำงานนี้ได้โดยเรียกใช้ setUseBoundsForWidth API ใน TextView
เนื่องจากการเพิ่มระยะห่างจากขอบด้านซ้ายอาจทําให้เลย์เอาต์ที่มีอยู่ไม่สอดคล้องกัน ระบบจึงไม่เพิ่มระยะห่างจากขอบโดยค่าเริ่มต้น แม้แต่สําหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไป
อย่างไรก็ตาม คุณสามารถเพิ่มการเว้นวรรคเพิ่มเติมเพื่อป้องกันการตัดได้โดยเรียกใช้
setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงให้เห็นว่าการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ช่วยปรับปรุงเลย์เอาต์ข้อความสำหรับแบบอักษรและภาษาบางแบบได้อย่างไร

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
ความสูงของบรรทัดเริ่มต้นที่รับรู้ภาษาสำหรับ EditText
In previous versions of Android, the text layout stretched the height of the
text to meet the line height of the font that matched the current locale. For
example, if the content was in Japanese, because the line height of the Japanese
font is slightly larger than the one of a Latin font, the height of the text
became slightly larger. However, despite these differences in line heights, the
EditText element was sized uniformly, regardless
of the locale being used, as illustrated in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText is the same, even though these languages
have different line heights from each other.For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), a minimum line height is now
reserved for EditText to match the reference font for the specified Locale, as
shown in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText now includes space to accommodate the
default line height for these languages' fonts.If needed, your app can restore the previous behavior by specifying the
useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum attribute
to false, and your app can set custom minimum vertical metrics using the
setMinimumFontMetrics API in Kotlin and Java.
กล้องและสื่อ
Android 15 จะทำการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานของกล้องและสื่อสำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 ขึ้นไปดังนี้
ข้อจำกัดในการขอโฟกัสเสียง
Apps that target Android 15 (API level 35) must be the top app or running a
foreground service in order to request audio focus. If an app
attempts to request focus when it does not meet one of these requirements, the
call returns AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED.
You can learn more about audio focus at Manage audio focus.
ข้อจำกัดที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ที่อัปเดตแล้ว
Android 15 มีรายการอัปเดตของอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ซึ่งถูกจำกัด โดยการทำงานร่วมกับนักพัฒนาแอป Android และการทดสอบภายในล่าสุด เราจะตรวจสอบว่ามีทางเลือกอื่นที่เผยแพร่ต่อสาธารณะพร้อมใช้งานก่อนที่จะจำกัดอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ทุกครั้งที่ทำได้
หากแอปไม่ได้กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 การเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่างเหล่านี้ อาจไม่มีผลกับคุณในทันที อย่างไรก็ตาม แม้ว่าแอปของคุณจะ เข้าถึงอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK บางรายการได้ ขึ้นอยู่กับระดับ API เป้าหมายของแอป แต่การใช้เมธอดหรือฟิลด์ที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ใดๆ ก็มีความเสี่ยงสูงที่จะทำให้แอปขัดข้องเสมอ
หากไม่แน่ใจว่าแอปใช้อินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK หรือไม่ คุณสามารถทดสอบแอปเพื่อดูได้ หากแอปของคุณใช้อินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK คุณควรเริ่มวางแผนย้ายไปใช้ทางเลือกอื่นที่เป็น SDK อย่างไรก็ตาม เราเข้าใจว่าแอปบางแอปมี Use Case ที่ถูกต้องสำหรับการใช้ อินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK หากไม่พบวิธีอื่นแทนการใช้อินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK สำหรับฟีเจอร์ในแอป คุณควรขอ API สาธารณะใหม่
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการเปลี่ยนแปลงใน Android เวอร์ชันนี้ได้ที่การอัปเดตข้อจำกัดของอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK ใน Android 15 ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK โดยทั่วไปได้ที่ข้อจำกัดเกี่ยวกับอินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK
