Android 15 mang đến cho nhà phát triển các tính năng và API mới hữu ích. Các phần sau đây tóm tắt những tính năng này để giúp bạn làm quen với các API liên quan.
Để biết danh sách chi tiết về các API đã thêm, đã sửa đổi và đã xoá, hãy đọc báo cáo điểm khác biệt về API. Để biết thông tin chi tiết về các API được thêm, hãy truy cập tài liệu tham khảo về API cho Android. Đối với Android 15, hãy tìm các API được thêm vào API cấp 35. Để tìm hiểu những thay đổi của nền tảng có thể tác động đến ứng dụng của bạn, hãy nhớ tham khảo các thay đổi về hành vi của Android 15 đối với ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 15 và tất cả ứng dụng.
Camera và nội dung nghe nhìn
Android 15 có nhiều tính năng giúp cải thiện trải nghiệm về camera và nội dung nghe nhìn, đồng thời cung cấp cho bạn quyền truy cập vào các công cụ và phần cứng để hỗ trợ nhà sáng tạo hiện thực hoá ý tưởng của họ trên Android.
Để biết thêm thông tin về các tính năng mới nhất và giải pháp dành cho nhà phát triển về nội dung nghe nhìn và camera trên Android, hãy xem bài nói chuyện Xây dựng trải nghiệm nội dung nghe nhìn và camera hiện đại trên Android tại Google I/O.
Tăng cường ánh sáng yếu
Android 15 ra mắt tính năng Tăng cường ánh sáng yếu, một chế độ tự động phơi sáng có sẵn cho cả Camera 2 và tiện ích máy ảnh chế độ ban đêm. Tính năng Tăng cường ánh sáng yếu điều chỉnh độ phơi sáng của luồng Xem trước trong điều kiện ánh sáng yếu. Điều này khác với cách tiện ích máy ảnh chế độ ban đêm tạo ảnh tĩnh, vì chế độ ban đêm kết hợp một loạt ảnh để tạo một ảnh duy nhất, được nâng cao. Mặc dù chế độ ban đêm hoạt động rất tốt để tạo ảnh tĩnh, nhưng không thể tạo luồng khung hình liên tục, còn tính năng Tăng cường ánh sáng yếu thì có thể. Do đó, tính năng Cải tiến ánh sáng yếu sẽ hỗ trợ các tính năng của máy ảnh, chẳng hạn như:
- Cung cấp bản xem trước hình ảnh nâng cao để người dùng có thể căn chỉnh khung hình ảnh chụp trong điều kiện ánh sáng yếu tốt hơn
- Quét mã QR trong điều kiện ánh sáng yếu
Nếu bạn bật tính năng Tăng cường ánh sáng yếu, tính năng này sẽ tự động bật khi có mức độ ánh sáng yếu và tắt khi có nhiều ánh sáng hơn.
Các ứng dụng có thể ghi lại luồng Xem trước trong điều kiện ánh sáng yếu để lưu video được làm sáng.
Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem phần Tăng cường ánh sáng yếu.
Các chế độ điều khiển camera trong ứng dụng
Android 15 bổ sung một tiện ích để kiểm soát tốt hơn phần cứng máy ảnh và các thuật toán của phần cứng đó trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ:
- Tính năng Điều chỉnh cường độ đèn flash nâng cao cho phép kiểm soát chính xác cường độ đèn flash ở cả chế độ
SINGLEvàTORCHtrong khi chụp ảnh.
Kiểm soát khoảng không gian trống HDR
Android 15 chọn khoảng đầu vào HDR phù hợp với các tính năng cơ bản của thiết bị và độ sâu bit của bảng điều khiển. Đối với các trang có nhiều nội dung SDR, chẳng hạn như ứng dụng nhắn tin hiển thị một hình thu nhỏ HDR, hành vi này có thể ảnh hưởng bất lợi đến độ sáng được cảm nhận của nội dung SDR. Android 15 cho phép bạn kiểm soát khoảng đầu vào HDR bằng setDesiredHdrHeadroom để tạo ra sự cân bằng giữa nội dung SDR và HDR.
Kiểm soát độ lớn âm thanh

Android 15 hỗ trợ cho Tiêu chuẩn độ lớn CTA-2075 để trợ giúp bạn tránh sự không thống nhất về độ ồn của âm thanh và đảm bảo người dùng không phải liên tục điều chỉnh âm lượng khi chuyển đổi giữa các nội dung. Hệ thống tận dụng các đặc điểm đã biết của thiết bị đầu ra (tai nghe và loa) cùng với siêu dữ liệu về độ to trong nội dung âm thanh AAC để điều chỉnh độ to của âm thanh và mức độ nén phạm vi động một cách thông minh.
Để bật tính năng này, bạn cần đảm bảo siêu dữ liệu về độ to trong nội dung AAC và bật tính năng nền tảng trong ứng dụng. Để thực hiện việc này, bạn tạo bản sao của đối tượng LoudnessCodecController bằng cách gọi phương thức nhà máy create của đối tượng đó với mã phiên âm thanh từ AudioTrack được liên kết; thao tác này sẽ tự động bắt đầu áp dụng các bản cập nhật âm thanh. Bạn có thể truyền một OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener để sửa đổi hoặc lọc các thông số âm lượng trước khi áp dụng các thông số đó trên MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer cũng sẽ được cập nhật để sử dụng
Các API LoudnessCodecController để tích hợp liền mạch ứng dụng.
Thiết bị MIDI 2.0 ảo
Android 13 đã bổ sung tính năng hỗ trợ kết nối với thiết bị MIDI 2.0 bằng USB. Các thiết bị này giao tiếp bằng Gói MIDI phổ quát (UMP). Android 15 mở rộng tính năng hỗ trợ UMP cho các ứng dụng MIDI ảo, cho phép các ứng dụng sáng tác điều khiển các ứng dụng tổng hợp dưới dạng thiết bị MIDI 2.0 ảo giống như khi sử dụng thiết bị USB MIDI 2.0.
Giải mã phần mềm AV1 hiệu quả hơn

dav1d, bộ giải mã phần mềm AV1 phổ biến của VideoLAN, có sẵn cho các thiết bị Android không hỗ trợ giải mã AV1 trong phần cứng. dav1d có hiệu suất cao hơn gấp 3 lần so với bộ giải mã phần mềm AV1 cũ, cho phép phát AV1 ở độ phân giải cao cho nhiều người dùng hơn, bao gồm cả một số thiết bị cấp thấp và trung bình.
Ứng dụng của bạn cần chọn sử dụng dav1d bằng cách gọi theo tên "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". dav1d sẽ được đặt làm bộ giải mã phần mềm AV1 mặc định trong bản cập nhật tiếp theo. Tính năng hỗ trợ này được chuẩn hoá và điều chỉnh cho phiên bản cũ là các thiết bị Android 11 nhận được bản cập nhật hệ thống Google Play.
Năng suất và công cụ dành cho nhà phát triển
Mặc dù hầu hết công việc của chúng tôi nhằm cải thiện năng suất của bạn đều xoay quanh các công cụ như Android Studio, Jetpack Compose và các thư viện Android Jetpack, nhưng chúng tôi luôn tìm cách giúp bạn dễ dàng hiện thực hoá ý tưởng của mình hơn trên nền tảng này.
Nội dung cập nhật OpenJDK 17
Android 15 tiếp tục công cuộc làm mới các thư viện cốt lõi của Android để phù hợp với các tính năng trong bản phát hành LTS OpenJDK mới nhất.
Bao gồm các tính năng và điểm cải tiến chính sau đây:
- Cải thiện chất lượng cuộc sống xung quanh vùng đệm NIO
- Luồng
- Các phương thức
mathvàstrictmathbổ sung - Các bản cập nhật gói
utilbao gồmcollection,mapvàsettheo trình tự - Hỗ trợ
ByteBuffertrongDeflater - Các bản cập nhật bảo mật như
X500PrivateCredentialvà bản cập nhật khoá bảo mật
Các API này được cập nhật trên hơn một tỷ thiết bị chạy Android 12 (API cấp 31) trở lên thông qua bản cập nhật Hệ thống Google Play, nhờ đó, bạn có thể nhắm đến các tính năng lập trình mới nhất.
Cải thiện tệp PDF
Android 15 có các điểm cải tiến đáng kể đối với PdfRenderer
API. Ứng dụng có thể kết hợp các tính năng nâng cao như hiển thị các tệp được bảo vệ bằng mật khẩu, chú thích, chỉnh sửa biểu mẫu, tìm kiếm và lựa chọn bằng tính năng sao chép. PDF tuyến tính hóa
các tính năng tối ưu hoá được hỗ trợ để tăng tốc độ xem tệp PDF cục bộ và giảm mức sử dụng tài nguyên.
Thư viện PDF Jetpack sử dụng các API này để đơn giản hoá việc thêm các tính năng xem PDF vào ứng dụng.
PdfRenderer đã được chuyển sang một mô-đun có thể cập nhật bằng Google
Các bản cập nhật hệ thống của Google Play độc lập với bản phát hành nền tảng, đồng thời chúng tôi hỗ trợ
những thay đổi này trở lại Android 11 (API cấp 30) bằng cách tạo một phiên bản
phiên bản trước Android 15 của nền tảng API, được gọi là
PdfRendererPreV.
Tinh chỉnh tính năng tự động chuyển đổi ngôn ngữ
Android 14 đã thêm tính năng nhận dạng đa ngôn ngữ trên thiết bị trong âm thanh với tính năng tự động chuyển đổi giữa các ngôn ngữ, nhưng điều này có thể khiến các từ bị bỏ qua, đặc biệt là khi các ngôn ngữ chuyển đổi với thời gian tạm dừng ít hơn giữa hai cách phát âm. Android 15 bổ sung các chế độ điều khiển khác để giúp ứng dụng điều chỉnh việc chuyển đổi này cho phù hợp với trường hợp sử dụng của ứng dụng.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS giới hạn việc chuyển đổi tự động ở đầu phiên âm thanh, trong khi EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES sẽ vô hiệu hoá tính năng chuyển đổi ngôn ngữ sau một số lần chuyển đổi đã xác định. Các tuỳ chọn này đặc biệt hữu ích nếu bạn dự kiến sẽ có một ngôn ngữ duy nhất được nói trong phiên mà bạn muốn tự động phát hiện.
Cải thiện OpenType Variable Font API
Android 15 cải thiện khả năng hữu dụng của phông chữ biến đổi OpenType. Bạn có thể tạo
thực thể FontFamily từ phông chữ có thể thay đổi mà không chỉ định các trục trọng số
bằng API buildVariableFamily. Trình kết xuất văn bản ghi đè giá trị
trên trục wght để khớp với văn bản đang hiển thị.
Việc sử dụng API giúp đơn giản hoá đáng kể mã để tạo Typeface:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Trước đây, để tạo cùng một Typeface, bạn cần nhiều mã hơn:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Dưới đây là ví dụ về cách một Typeface được tạo bằng cả API cũ và mới
hiển thị:
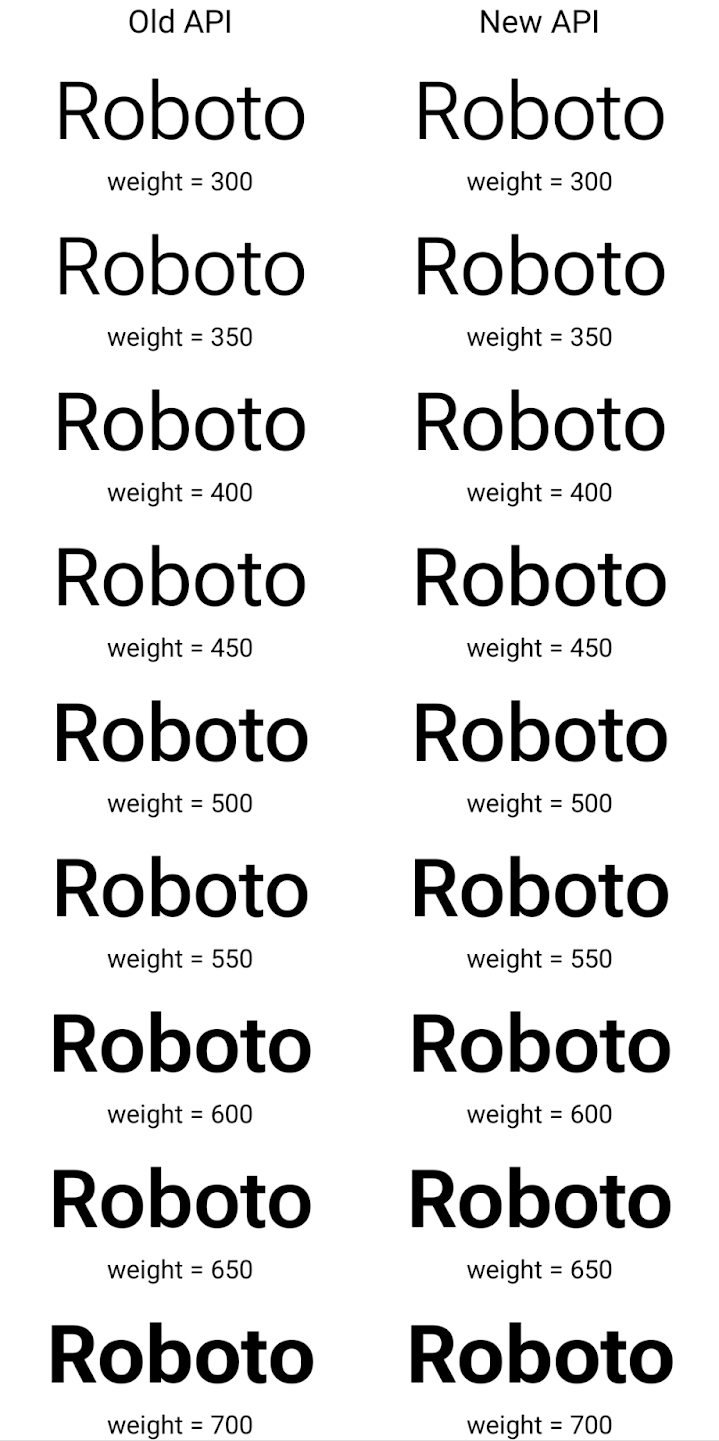
Trong ví dụ này, Typeface được tạo bằng API cũ không có khả năng tạo độ đậm phông chữ chính xác cho các thực thể Font 350, 450, 550 và 650, vì vậy, trình kết xuất sẽ quay lại độ đậm gần nhất. Vì vậy, trong trường hợp này, 300 được kết xuất thay vì 350, 400 được kết xuất thay vì 450, v.v. Ngược lại, Typeface được tạo bằng các API mới sẽ tự động tạo
thực thể Font cho một trọng số nhất định, do đó trọng số chính xác được hiển thị là 350,
450, 550 và 650.
Các chế độ kiểm soát chi tiết dấu ngắt dòng
Kể từ Android 15, TextView và trình ngắt dòng cơ bản có thể giữ nguyên phần văn bản nhất định trong cùng một dòng để cải thiện khả năng đọc. Bạn có thể tận dụng tính năng tuỳ chỉnh ngắt dòng này bằng cách sử dụng thẻ <nobreak> trong tài nguyên chuỗi hoặc createNoBreakSpan. Tương tự, bạn có thể giữ nguyên các từ không bị xuống dòng bằng cách sử dụng thẻ <nohyphen> hoặc createNoHyphenationSpan.
Ví dụ: tài nguyên chuỗi sau đây không có dấu ngắt dòng và hiển thị với văn bản "Pixel 8 Pro" bị ngắt ở vị trí không mong muốn:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
Ngược lại, tài nguyên chuỗi này bao gồm thẻ <nobreak>, thẻ này gói cụm từ "Pixel 8 Pro" và ngăn chặn dấu ngắt dòng:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
Sự khác biệt trong cách hiển thị các chuỗi này được thể hiện trong các hình ảnh sau:

<nobreak>.
<nobreak>.Lưu trữ ứng dụng
Android và Google Play đã công bố hỗ trợ tính năng lưu trữ ứng dụng vào năm ngoái, cho phép người dùng giải phóng dung lượng bằng cách xoá một phần các ứng dụng ít dùng trên thiết bị được phát hành bằng Android App Bundle trên Google Play. Android 15 hỗ trợ cấp hệ điều hành để lưu trữ và huỷ lưu trữ ứng dụng, giúp tất cả các cửa hàng ứng dụng dễ dàng triển khai tính năng này.
Các ứng dụng có quyền REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES có thể gọi
PackageInstaller requestArchive để yêu cầu lưu trữ một
đã cài đặt gói ứng dụng. Thao tác này sẽ xoá APK và mọi tệp đã lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm nhưng vẫn tồn tại
dữ liệu người dùng. Các ứng dụng đã lưu trữ được trả về dưới dạng ứng dụng có thể hiển thị thông qua các API LauncherApps; người dùng sẽ thấy một cách xử lý giao diện người dùng để làm nổi bật rằng các ứng dụng đó đã được lưu trữ. Nếu người dùng nhấn vào một ứng dụng đã lưu trữ, trình cài đặt chịu trách nhiệm sẽ nhận được yêu cầu huỷ lưu trữ ứng dụng đó và quá trình khôi phục có thể được theo dõi bằng thông báo truyền tin ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED.
Bật chế độ 16 KB trên thiết bị bằng cách sử dụng tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển
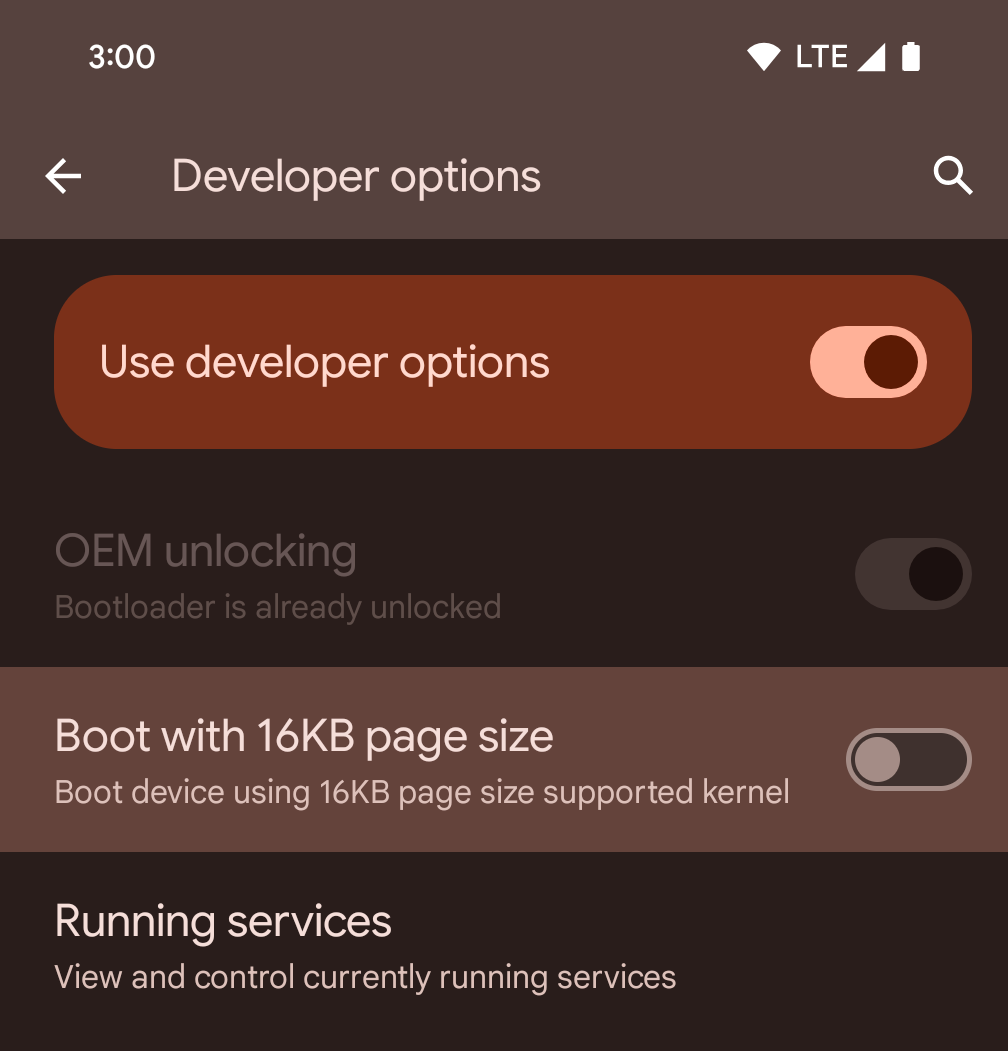
Bật/tắt lựa chọn cho nhà phát triển Khởi động với kích thước trang 16 KB để khởi động thiết bị ở chế độ 16 KB.
Trong các phiên bản QPR của Android 15, bạn có thể sử dụng tùy chọn cho nhà phát triển có trên một số thiết bị để khởi động thiết bị ở chế độ 16 KB và thực hiện kiểm thử trên thiết bị. Trước khi sử dụng tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển, hãy chuyển đến phần Cài đặt > Hệ thống > Bản cập nhật phần mềm rồi áp dụng mọi bản cập nhật hiện có.
Tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển này có trên các thiết bị sau:
Pixel 8 và 8 Pro (chạy Android 15 QPR1 trở lên)
Pixel 8a (chạy Android 15 QPR1 trở lên)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro và 9 Pro XL (chạy Android 15 QPR2 trở lên)
Pixel 9a (chạy Android 16 trở lên)
Đồ hoạ
Android 15 mang đến những điểm cải tiến mới nhất về đồ hoạ, bao gồm cả ANGLE và các điểm bổ sung cho hệ thống đồ hoạ Canvas.
Hiện đại hoá quyền truy cập vào GPU của Android

Phần cứng Android đã phát triển khá nhiều so với những ngày đầu khi hệ điều hành cốt lõi chạy trên một CPU và GPU được truy cập bằng các API dựa trên quy trình chức năng cố định. API đồ hoạ Vulkan® đã có trong NDK kể từ Android 7.0 (API cấp 24) với khả năng trừu tượng cấp thấp hơn phản ánh tốt hơn phần cứng GPU hiện đại, mở rộng tốt hơn để hỗ trợ nhiều nhân CPU và giảm hao tổn trình điều khiển CPU, nhờ đó cải thiện hiệu suất ứng dụng. Tất cả công cụ phát triển trò chơi hiện đại đều hỗ trợ Vulkan.
Vulkan là giao diện ưu tiên của Android cho GPU. Do đó, Android 15 bao gồm ANGLE dưới dạng một lớp không bắt buộc để chạy OpenGL® ES trên Vulkan. Việc chuyển sang ANGLE sẽ chuẩn hoá việc triển khai OpenGL của Android để cải thiện khả năng tương thích và trong một số trường hợp, cải thiện hiệu suất. Bạn có thể kiểm thử độ ổn định và hiệu suất của ứng dụng OpenGL ES bằng ANGLE bằng cách bật tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển trong phần Settings -> System -> Developer Options -> Experimental: Enable ANGLE (Cài đặt -> Hệ thống -> Tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển -> Thử nghiệm: Bật ANGLE) trên Android 15.
Lộ trình của Android ANGLE trên Vulkan
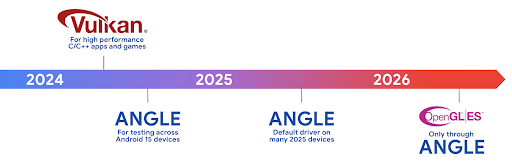
Để đơn giản hoá ngăn xếp GPU, trong tương lai, chúng tôi sẽ phân phối ANGLE làm trình điều khiển hệ thống GL trên nhiều thiết bị mới hơn, với kỳ vọng rằng OpenGL/ES sẽ chỉ có sẵn thông qua ANGLE. Tuy nhiên, chúng tôi dự định tiếp tục hỗ trợ OpenGL ES trên tất cả thiết bị.
Các bước nên làm tiếp theo
Sử dụng tuỳ chọn dành cho nhà phát triển để chọn trình điều khiển ANGLE cho OpenGL ES và kiểm thử ứng dụng. Đối với các dự án mới, bạn nên sử dụng Vulkan cho C/C++.
Những điểm cải tiến cho Canvas
Android 15 tiếp tục hiện đại hoá hệ thống đồ hoạ Canvas của Android bằng các tính năng bổ sung:
Matrix44cung cấp một ma trận 4x4 để biến đổi các toạ độ nên được sử dụng khi bạn muốn thao tác với canvas ở chế độ 3D.clipShadergiao nhau với đoạn cắt hiện tại bằng chương trình đổ bóng được chỉ định, trong khiclipOutShaderđặt đoạn cắt thành hiệu số của đoạn cắt hiện tại và chương trình đổ bóng, mỗi đoạn cắt coi chương trình đổ bóng là một mặt nạ alpha. Điều này hỗ trợ việc vẽ các hình dạng phức tạp một cách hiệu quả.
Hiệu suất và pin
Android tiếp tục tập trung vào việc giúp bạn cải thiện hiệu suất và chất lượng của ứng dụng. Android 15 giới thiệu các API giúp thực hiện các tác vụ trong ứng dụng của bạn hiệu quả hơn, tối ưu hoá hiệu suất ứng dụng và thu thập thông tin chi tiết về ứng dụng của bạn.
Để biết các phương pháp hay nhất giúp tiết kiệm pin, gỡ lỗi mức sử dụng mạng và điện năng, cũng như thông tin chi tiết về cách chúng tôi cải thiện hiệu suất sử dụng pin của hoạt động ở chế độ nền trong Android 15 và các phiên bản Android gần đây, hãy xem bài nói chuyện Cải thiện hiệu suất sử dụng pin của hoạt động ở chế độ nền trên Android trong Google I/O.
ApplicationStartInfo API
Trong các phiên bản Android trước, việc khởi động ứng dụng có phần bí ẩn. Khó xác định trong ứng dụng của bạn liệu ứng dụng đó có bắt đầu từ trạng thái nguội, ấm hay nóng hay không. Bạn cũng khó biết ứng dụng của mình đã mất bao lâu trong các giai đoạn khởi chạy: phân nhánh quy trình, gọi onCreate, vẽ khung đầu tiên, v.v. Khi lớp Application được tạo bản sao, bạn không có cách nào để biết liệu ứng dụng có bắt đầu từ một thông báo truyền tin, nhà cung cấp nội dung, công việc, bản sao lưu, khởi động hoàn tất, chuông báo hay Activity hay không.
API ApplicationStartInfo trên Android 15 cung cấp tất cả những tính năng này và nhiều tính năng khác. Bạn thậm chí có thể chọn thêm dấu thời gian của riêng mình vào quy trình để thu thập dữ liệu thời gian ở một nơi. Ngoài việc thu thập các chỉ số, bạn có thể sử dụng ApplicationStartInfo để giúp trực tiếp tối ưu hoá quá trình khởi động ứng dụng; ví dụ: bạn có thể loại bỏ việc tạo bản sao tốn kém của các thư viện liên quan đến giao diện người dùng trong lớp Application khi ứng dụng khởi động do một thông báo truyền tin.
Thông tin chi tiết về kích thước ứng dụng
Kể từ Android 8.0 (API cấp 26), Android đã đưa API StorageStats.getAppBytes vào để tóm tắt kích thước đã cài đặt của một ứng dụng dưới dạng một số byte duy nhất, là tổng kích thước APK, kích thước của các tệp được trích xuất từ APK và các tệp được tạo trên thiết bị, chẳng hạn như mã được biên dịch trước (AOT). Con số này không phản ánh rõ ràng cách ứng dụng của bạn đang sử dụng bộ nhớ.
Android 15 bổ sung API StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]), cho phép bạn nắm được thông tin chi tiết về cách ứng dụng sử dụng tất cả không gian đó, bao gồm cả các phần phân tách tệp APK, mã liên quan đến AOT và tăng tốc, siêu dữ liệu dex, thư viện và hồ sơ được hướng dẫn.
Lập hồ sơ do ứng dụng quản lý
Android 15 bao gồm lớp ProfilingManager, cho phép bạn thu thập thông tin phân tích tài nguyên từ trong ứng dụng, chẳng hạn như tệp báo lỗi, hồ sơ vùng nhớ khối xếp, lấy mẫu ngăn xếp, v.v. Mã này cung cấp lệnh gọi lại cho ứng dụng kèm theo thẻ đã cung cấp để xác định tệp đầu ra. Tệp này được phân phối đến thư mục tệp của ứng dụng. API này giới hạn tốc độ để giảm thiểu tác động đến hiệu suất.
Để đơn giản hoá việc tạo các yêu cầu phân tích tài nguyên trong ứng dụng, bạn nên sử dụng API AndroidX Profiling tương ứng, có trong Core 1.15.0-rc01 trở lên.
Cải thiện cơ sở dữ liệu SQLite
Android 15 giới thiệu các API SQLite hiển thị các tính năng nâng cao từ công cụ SQLite cơ bản nhắm đến các vấn đề hiệu suất cụ thể có thể xuất hiện trong ứng dụng. Các API này đi kèm với bản cập nhật SQLite cho phiên bản 3.44.3.
Nhà phát triển nên tham khảo các phương pháp hay nhất về hiệu suất SQLite để khai thác tối đa cơ sở dữ liệu SQLite, đặc biệt là khi làm việc với các cơ sở dữ liệu lớn hoặc khi chạy các truy vấn nhạy cảm với độ trễ.
- Giao dịch bị hoãn chỉ có thể đọc: khi thực hiện các giao dịch có
chỉ đọc (không bao gồm câu lệnh ghi), hãy sử dụng
beginTransactionReadOnly()vàbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)để phát hành giao dịchDEFERREDchỉ đọc. Các giao dịch như vậy có thể chạy đồng thời với nhau và nếu cơ sở dữ liệu ở chế độ WAL, chúng có thể chạy đồng thời với các giao dịchIMMEDIATEhoặcEXCLUSIVE. - Số lượng hàng và mã nhận dạng: Các API được thêm vào để truy xuất số lượng hàng đã thay đổi
hàng hoặc mã hàng được chèn gần đây nhất mà không tạo thêm truy vấn.
getLastChangedRowCount()trả về số lượng hàng được chèn, cập nhật hoặc xoá bởi câu lệnh SQL gần đây nhất trong giao dịch hiện tại, trong khigetTotalChangedRowCount()sẽ trả về số lượng trên kết nối hiện tại.getLastInsertRowId()trả vềrowidcủa hàng cuối cùng cần chèn vào kết nối hiện tại. - Câu lệnh thô: phát hành một câu lệnh SQlite thô, bỏ qua các trình bao bọc thuận tiện và mọi chi phí xử lý bổ sung mà chúng có thể phát sinh.
Bản cập nhật Khung hiệu suất động Android
Android 15 tiếp tục đầu tư vào Khung hiệu suất động Android (ADPF), một tập hợp API cho phép các trò chơi và ứng dụng cần nhiều hiệu suất tương tác trực tiếp hơn với hệ thống nguồn điện và nhiệt của thiết bị Android. Trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ, Android 15 bổ sung các tính năng của ADPF:
- Chế độ tiết kiệm điện năng cho các phiên gợi ý để cho biết rằng các luồng liên kết của chúng nên ưu tiên tiết kiệm điện năng hơn là hiệu suất, rất phù hợp với khối lượng công việc trong nền chạy trong thời gian dài.
- Bạn có thể báo cáo cả thời lượng công việc của GPU và CPU trong các phiên gợi ý, cho phép hệ thống điều chỉnh tần suất CPU và GPU cùng nhau để đáp ứng tốt nhất nhu cầu về khối lượng công việc.
- Ngưỡng khoảng nhiệt để diễn giải trạng thái điều tiết nhiệt có thể xảy ra dựa trên dự đoán khoảng nhiệt.
Để tìm hiểu thêm về cách sử dụng ADPF trong ứng dụng và trò chơi, hãy truy cập vào tài liệu.
Quyền riêng tư
Android 15 có nhiều tính năng giúp nhà phát triển ứng dụng bảo vệ quyền riêng tư của người dùng.
Phát hiện hoạt động ghi màn hình
Android 15 bổ sung tính năng hỗ trợ cho ứng dụng để phát hiện rằng ứng dụng đang được ghi lại. Lệnh gọi lại được gọi bất cứ khi nào ứng dụng chuyển đổi giữa trạng thái hiển thị hoặc không hiển thị trong bản ghi màn hình. Một ứng dụng được coi là hiển thị nếu các hoạt động thuộc quyền sở hữu của UID của quy trình đăng ký đang được ghi lại. Bằng cách này, nếu ứng dụng của bạn đang thực hiện một thao tác nhạy cảm, có thể thông báo cho người dùng rằng họ đang được ghi lại.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
Các chức năng mở rộng của IntentFilter
Android 15 tích hợp tính năng hỗ trợ độ phân giải Intent chính xác hơn thông qua UriRelativeFilterGroup. Tính năng này chứa một tập hợp các đối tượng UriRelativeFilter tạo thành một tập hợp các quy tắc so khớp Intent mà mỗi quy tắc phải được đáp ứng, bao gồm cả các tham số truy vấn URL, phân đoạn URL và các quy tắc chặn hoặc loại trừ.
Bạn có thể xác định các quy tắc này trong tệp XML AndroidManifest bằng thẻ <uri-relative-filter-group>. Thẻ này có thể bao gồm thẻ android:allow (không bắt buộc). Các thẻ này có thể chứa thẻ <data> sử dụng các thuộc tính thẻ dữ liệu hiện có cũng như thuộc tính android:query và android:fragment.
Sau đây là ví dụ về cú pháp AndroidManifest:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
Không gian riêng tư
Không gian riêng tư cho phép người dùng tạo một không gian riêng biệt trên thiết bị của họ, nơi họ có thể bảo vệ các ứng dụng nhạy cảm khỏi những ánh mắt tò mò, nhờ một lớp xác thực bổ sung. Không gian riêng tư sử dụng một hồ sơ người dùng riêng biệt. Người dùng có thể chọn sử dụng phương thức khoá thiết bị hoặc một phương thức khoá riêng biệt cho không gian riêng tư.
Các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư sẽ xuất hiện trong một vùng chứa riêng biệt trong trình chạy và bị ẩn khỏi chế độ xem gần đây, thông báo, phần cài đặt và các ứng dụng khác khi không gian riêng tư bị khoá. Nội dung do người dùng tạo và tải xuống (chẳng hạn như nội dung nghe nhìn hoặc tệp) và tài khoản được tách riêng giữa không gian riêng tư và không gian chính. Bạn có thể dùng trang chia sẻ nội dung của hệ thống và công cụ chọn ảnh để cấp cho ứng dụng quyền truy cập vào nội dung trên các không gian khi không gian riêng tư được mở khoá.
Người dùng không thể di chuyển các ứng dụng hiện có và dữ liệu của ứng dụng vào không gian riêng tư. Thay vào đó, người dùng chọn một tuỳ chọn cài đặt trong không gian riêng tư để cài đặt ứng dụng bằng bất kỳ cửa hàng ứng dụng nào họ muốn. Các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư được cài đặt dưới dạng bản sao riêng biệt với mọi ứng dụng trong không gian chính (bản sao mới của cùng một ứng dụng).
Khi người dùng khoá không gian riêng tư, hồ sơ sẽ bị dừng. Khi hồ sơ bị dừng, các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư sẽ không còn hoạt động và không thể thực hiện các hoạt động trên nền trước hoặc trong nền, bao gồm cả việc hiển thị thông báo.
Bạn nên kiểm thử ứng dụng của mình trong không gian riêng tư để đảm bảo ứng dụng hoạt động như mong đợi, đặc biệt là nếu ứng dụng của bạn thuộc một trong các danh mục sau:
- Các ứng dụng có logic cho hồ sơ công việc giả định rằng mọi bản sao đã cài đặt của ứng dụng không có trong hồ sơ chính đều nằm trong hồ sơ công việc.
- Ứng dụng y tế
- Ứng dụng trình chạy
- Ứng dụng trên cửa hàng ứng dụng
Truy vấn lựa chọn gần đây nhất của người dùng đối với quyền truy cập vào ảnh đã chọn
Giờ đây, các ứng dụng chỉ có thể làm nổi bật những ảnh và video được chọn gần đây nhất khi
quyền truy cập một phần vào quyền đối với nội dung nghe nhìn đã được cấp. Tính năng này có thể cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng cho những ứng dụng thường xuyên yêu cầu quyền truy cập vào ảnh và video. Để sử dụng tính năng này trong ứng dụng của bạn, hãy bật
Đối số QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY khi truy vấn MediaStore
đến ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Hộp cát về quyền riêng tư trên Android
Android 15 bao gồm các tiện ích Dịch vụ quảng cáo Android mới nhất, tích hợp phiên bản mới nhất của Hộp cát về quyền riêng tư trên Android. Việc bổ sung này là một phần trong nỗ lực phát triển các công nghệ giúp cải thiện quyền riêng tư của người dùng và mang lại trải nghiệm quảng cáo được cá nhân hoá hiệu quả cho các ứng dụng di động. Trang về hộp cát về quyền riêng tư của chúng tôi có thêm thông tin về các chương trình beta và bản dùng thử cho nhà phát triển của Hộp cát về quyền riêng tư trên Android để giúp bạn bắt đầu.
Health Connect
Android 15 tích hợp các tiện ích mới nhất Health Connect của Android, một ứng dụng bảo mật và tập trung để quản lý và chia sẻ dữ liệu sức khoẻ và thể chất do ứng dụng thu thập. Thông tin cập nhật này thêm tính năng hỗ trợ cho các loại dữ liệu khác về tính năng thể dục, dinh dưỡng, nhiệt độ trên da, kế hoạch tập luyện, v.v.
Tính năng theo dõi nhiệt độ trên da giúp người dùng lưu trữ và chia sẻ thông tin chính xác hơn dữ liệu về nhiệt độ từ thiết bị đeo hoặc thiết bị theo dõi khác.
Kế hoạch tập luyện là kế hoạch tập thể dục có cấu trúc để giúp người dùng đạt được mục tiêu về thể chất. Hỗ trợ kế hoạch tập luyện bao gồm nhiều mục tiêu về hiệu suất và hoàn thành:
- Mục tiêu hoàn thành liên quan đến lượng calo đã đốt cháy, quãng đường, thời lượng, số lần lặp lại và số bước.
- Mục tiêu về hiệu suất liên quan đến việc thực hiện nhiều lần nhất có thể (AMRAP), tốc độ, nhịp tim, công suất, tốc độ gắng sức được nhận thấy và tốc độ.
Tìm hiểu thêm về các bản cập nhật mới nhất cho Health Connect trong Android trong bài nói chuyện Tạo trải nghiệm thích ứng bằng Android Health tại Google I/O.
Chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng
Android 15 hỗ trợ tính năng chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng để người dùng có thể chỉ chia sẻ hoặc ghi lại một cửa sổ ứng dụng thay vì toàn bộ màn hình thiết bị. Tính năng này được bật lần đầu trong Android 14 QPR2, bao gồm các lệnh gọi lại MediaProjection cho phép ứng dụng của bạn tuỳ chỉnh trải nghiệm chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng. Xin lưu ý rằng đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 14 (API cấp 34) trở lên, bạn phải có sự đồng ý của người dùng đối với mỗi phiên chụp MediaProjection.
Trải nghiệm người dùng và giao diện người dùng hệ thống
Android 15 mang đến cho nhà phát triển ứng dụng và người dùng nhiều quyền kiểm soát và tính linh hoạt hơn khi định cấu hình thiết bị cho phù hợp với nhu cầu của họ.
Để tìm hiểu thêm về cách sử dụng những điểm cải tiến mới nhất trong Android 15 nhằm cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng của ứng dụng, hãy xem bài nói chuyện Cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng trong ứng dụng Android tại Google I/O.
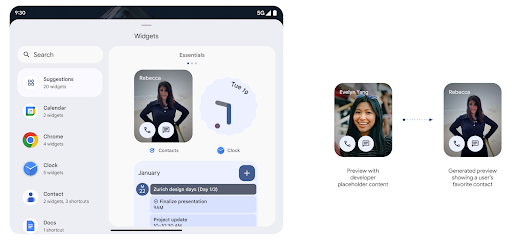
Xem trước tiện ích phong phú hơn bằng Generated Previews API
Trước Android 15, cách duy nhất để cung cấp bản xem trước bộ chọn tiện ích là chỉ định một hình ảnh hoặc tài nguyên bố cục tĩnh. Các bản xem trước này thường khác biệt đáng kể với giao diện của tiện ích thực tế khi được đặt trên màn hình chính. Ngoài ra, không thể tạo tài nguyên tĩnh bằng Jetpack Glance, vì vậy tính năng Glance nhà phát triển phải chụp ảnh màn hình tiện ích của họ hoặc tạo bố cục XML để có một bản xem trước tiện ích.
Android 15 bổ sung tính năng hỗ trợ cho bản xem trước đã tạo. Điều này có nghĩa là trình cung cấp tiện ích ứng dụng có thể tạo RemoteViews để dùng làm bản xem trước bộ chọn, thay vì tài nguyên tĩnh.
API Đẩy
Ứng dụng có thể cung cấp bản xem trước đã tạo thông qua API đẩy. Ứng dụng có thể cung cấp bản xem trước tại bất kỳ thời điểm nào trong vòng đời và không nhận được yêu cầu rõ ràng từ máy chủ lưu trữ để cung cấp bản xem trước. Bản xem trước được lưu trữ trong AppWidgetService và máy chủ lưu trữ có thể yêu cầu bản xem trước theo yêu cầu. Ví dụ sau đây tải tài nguyên bố cục tiện ích XML và đặt tài nguyên đó làm bản xem trước:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
Quy trình dự kiến là:
- Nhà cung cấp tiện ích sẽ gọi
setWidgetPreviewbất cứ lúc nào. Các bản xem trước được cung cấp sẽ được lưu trữ trongAppWidgetServicecùng với thông tin khác của nhà cung cấp. setWidgetPreviewthông báo cho máy chủ lưu trữ về bản xem trước đã cập nhật thông qua lệnh gọi lạiAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged. Để phản hồi, máy chủ của tiện ích sẽ tải lại tất cả thông tin của nhà cung cấp.- Khi hiển thị bản xem trước của tiện ích, máy chủ lưu trữ sẽ kiểm tra
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategoriesvà nếu được chọn có sẵn danh mục, hãy gọiAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewtới trả về bản xem trước đã lưu cho ứng dụng nhà cung cấp này.
Thời điểm gọi setWidgetPreview
Do không có lệnh gọi lại để cung cấp bản xem trước, ứng dụng có thể chọn gửi bản xem trước bất kỳ lúc nào khi chúng đang chạy. Tần suất cập nhật bản xem trước phụ thuộc vào trường hợp sử dụng tiện ích.
Danh sách sau đây mô tả hai danh mục chính của trường hợp sử dụng bản xem trước:
- Những nhà cung cấp cho thấy dữ liệu thực trong bản xem trước tiện ích, chẳng hạn như dữ liệu được cá nhân hoá hoặc thông tin gần đây. Các nhà cung cấp này có thể thiết lập bản xem trước sau khi người dùng đăng nhập hoặc đã định cấu hình ban đầu trong ứng dụng của họ. Sau đó, họ có thể thiết lập một tác vụ định kỳ để cập nhật bản xem trước theo tần suất mà họ chọn. Ví dụ về loại tiện ích này có thể là ảnh, lịch, thời tiết hoặc tin tức tiện ích.
- Các trình cung cấp hiển thị thông tin tĩnh trong bản xem trước hoặc tiện ích thao tác nhanh mà không hiển thị bất kỳ dữ liệu nào. Các nhà cung cấp này có thể đặt bản xem trước một lần, khi khởi chạy ứng dụng lần đầu tiên. Ví dụ về loại tiện ích này bao gồm trình đơn nhanh tiện ích hành động hoặc tiện ích lối tắt Chrome.
Một số nhà cung cấp có thể hiển thị bản xem trước tĩnh trên bộ chọn chế độ thiết bị trung tâm, nhưng thực tế thông tin trên bộ chọn màn hình chính. Các nhà cung cấp này phải tuân theo hướng dẫn cho cả hai trường hợp sử dụng này để đặt bản xem trước.
Hình trong hình
Android 15 giới thiệu các thay đổi trong tính năng Hình trong hình (PiP) để đảm bảo quá trình chuyển đổi diễn ra suôn sẻ hơn khi chuyển sang chế độ PiP. Điều này sẽ có lợi cho các ứng dụng có thành phần giao diện người dùng phủ lên trên giao diện người dùng chính và chuyển sang chế độ Hình trong hình.
Nhà phát triển dùng lệnh gọi lại onPictureInPictureModeChanged để xác định logic
bật/tắt chế độ hiển thị các phần tử ở lớp phủ trên giao diện người dùng. Lệnh gọi lại này là
được kích hoạt khi hoàn tất quá trình nhập hoặc thoát ảnh động PiP. Bắt đầu vào
Trên Android 15, lớp PictureInPictureUiState bao gồm một trạng thái khác.
Với trạng thái giao diện người dùng này, các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 15 (API cấp 35) sẽ tuân thủ
Lệnh gọi lại Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged đang được gọi bằng
isTransitioningToPip() ngay khi ảnh động trong Hình trong hình bắt đầu. Có
nhiều thành phần trên giao diện người dùng không liên quan đến ứng dụng khi ứng dụng ở chế độ PiP (Hình trong hình), đối với
thành phần hiển thị hoặc bố cục mẫu bao gồm thông tin như nội dung đề xuất,
video, mức phân loại và tiêu đề. Khi ứng dụng chuyển sang chế độ PiP, hãy sử dụng
Lệnh gọi lại onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged để ẩn các thành phần này trên giao diện người dùng. Khi ứng dụng chuyển sang chế độ toàn màn hình từ cửa sổ PiP, hãy sử dụng lệnh gọi lại onPictureInPictureModeChanged để ẩn các phần tử này, như minh hoạ trong các ví dụ sau:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
Nút bật/tắt chế độ hiển thị nhanh các thành phần không liên quan trên giao diện người dùng (đối với cửa sổ PiP) giúp đảm bảo ảnh động nhập PiP mượt mà và không nhấp nháy.
Cải thiện quy tắc Không làm phiền
AutomaticZenRule cho phép các ứng dụng tuỳ chỉnh các quy tắc Quản lý sự chú ý (Không làm phiền) và quyết định thời điểm kích hoạt hoặc huỷ kích hoạt các quy tắc đó. Android 15 cải thiện đáng kể các quy tắc này với mục tiêu cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng. Các điểm cải tiến sau đây:
- Thêm các loại vào
AutomaticZenRule, cho phép hệ thống áp dụng các loại đặc biệt xử lý tín dụng đối với một số quy tắc. - Thêm một biểu tượng vào
AutomaticZenRule, giúp cải thiện các chế độ có thể nhận ra. - Thêm một chuỗi
triggerDescriptionvàoAutomaticZenRuleđể mô tả các điều kiện mà quy tắc sẽ bắt đầu hoạt động cho người dùng. - Thêm
ZenDeviceEffectsvàoAutomaticZenRule, cho phép các quy tắc kích hoạt những tính năng như hiển thị thang màu xám, chế độ ban đêm hoặc giảm độ sáng hình nền.
Đặt VibrationEffect cho các kênh thông báo
Android 15 hỗ trợ chế độ rung mạnh cho các thông báo đến bằng cách
kênh của bạn bằng NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, vì vậy
người dùng có thể phân biệt giữa các loại thông báo khác nhau mà không cần
phải xem thiết bị của mình.
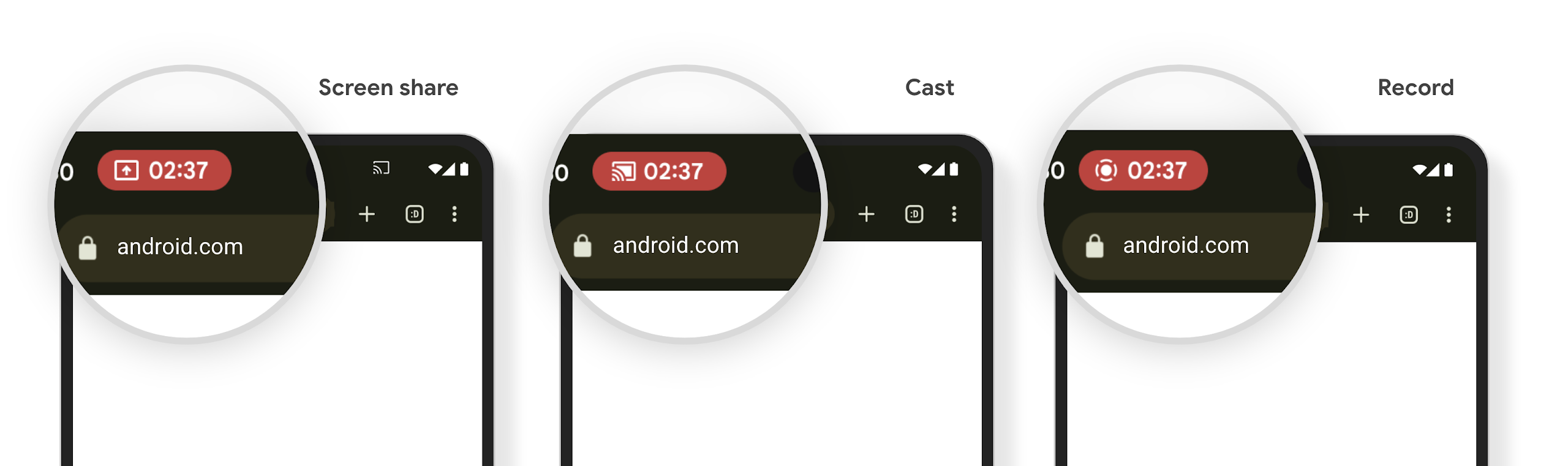
Khối nội dung trên thanh trạng thái của tính năng chiếu nội dung nghe nhìn và tính năng tự động dừng
Tính năng chiếu nội dung nghe nhìn có thể tiết lộ thông tin riêng tư của người dùng. Một khối thanh trạng thái mới, nổi bật giúp người dùng biết được mọi hoạt động chiếu màn hình đang diễn ra. Người dùng có thể nhấn vào khối này để dừng truyền, chia sẻ hoặc ghi màn hình. Ngoài ra, để mang lại trải nghiệm người dùng trực quan hơn, mọi hoạt động chiếu màn hình đang diễn ra hiện sẽ tự động dừng khi màn hình thiết bị bị khoá.
Màn hình lớn và kiểu dáng
Android 15 hỗ trợ các ứng dụng của bạn khai thác tối đa các kiểu dáng của Android, bao gồm cả màn hình lớn, thiết bị có thể lật và thiết bị có thể gập lại.
Cải thiện khả năng đa nhiệm trên màn hình lớn
Android 15 mang đến cho người dùng nhiều cách tốt hơn để làm nhiều việc cùng lúc trên các thiết bị có màn hình lớn. Để Ví dụ: người dùng có thể lưu các kiểu kết hợp ứng dụng mà họ yêu thích ở chế độ chia đôi màn hình để hãy truy cập và ghim thanh tác vụ trên màn hình để chuyển đổi nhanh giữa các ứng dụng. Điều này có nghĩa là việc đảm bảo ứng dụng của bạn có khả năng thích ứng là quan trọng hơn bao giờ hết.
Google I/O có các phiên về chủ đề Xây dựng Android thích ứng ứng dụng và Xây dựng giao diện người dùng bằng Material 3 thư viện thích ứng có thể hữu ích, và tài liệu của chúng tôi có nhiều tài liệu hơn để giúp bạn Thiết kế cho màn hình.
Hỗ trợ màn hình ngoài
Ứng dụng của bạn có thể khai báo một thuộc tính mà Android 15 sử dụng để cho phép Application hoặc Activity hiển thị trên màn hình nhỏ của các thiết bị có thể gập lại được hỗ trợ. Những màn hình này quá nhỏ để được coi là mục tiêu tương thích để chạy ứng dụng Android, nhưng ứng dụng của bạn có thể chọn hỗ trợ các màn hình này, giúp ứng dụng của bạn có mặt ở nhiều nơi hơn.
Khả năng kết nối
Android 15 cập nhật nền tảng để ứng dụng của bạn có thể sử dụng những tiến bộ mới nhất về công nghệ truyền thông và không dây.
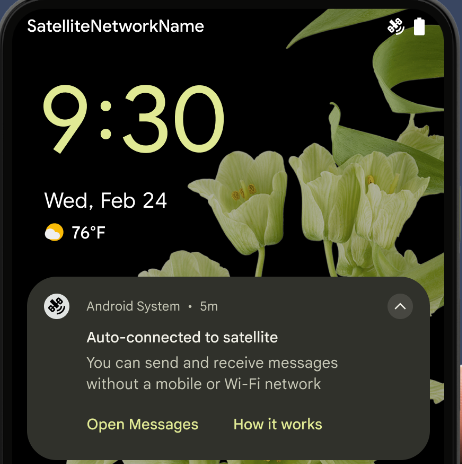
Hỗ trợ vệ tinh
Android 15 tiếp tục mở rộng khả năng hỗ trợ nền tảng cho khả năng kết nối vệ tinh và bao gồm một số thành phần trên giao diện người dùng để đảm bảo trải nghiệm người dùng nhất quán trên bối cảnh kết nối vệ tinh.
Các ứng dụng có thể dùng ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() để
phát hiện thời điểm thiết bị được kết nối với vệ tinh, giúp thiết bị nhận biết rõ hơn về
lý do tại sao dịch vụ mạng đầy đủ có thể không khả dụng. Ngoài ra, Android 15 còn hỗ trợ các ứng dụng SMS và MMS cũng như các ứng dụng RCS được tải sẵn để sử dụng kết nối vệ tinh nhằm gửi và nhận tin nhắn.
Trải nghiệm NFC mượt mà hơn
Android 15 đang nỗ lực để mang lại trải nghiệm thanh toán không tiếp xúc liền mạch và đáng tin cậy hơn, đồng thời tiếp tục hỗ trợ hệ sinh thái ứng dụng NFC mạnh mẽ của Android. Trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ, ứng dụng có thể yêu cầu NfcAdapter chuyển sang chế độ quan sát, trong đó thiết bị sẽ nghe nhưng không phản hồi với trình đọc NFC, gửi PollingFrame
đối tượng của dịch vụ NFC của ứng dụng để xử lý. Bạn có thể dùng đối tượng PollingFrame để xác thực trước khi giao tiếp lần đầu với đầu đọc NFC, cho phép giao dịch một lần nhấn trong nhiều trường hợp.
Ngoài ra, ứng dụng có thể đăng ký một bộ lọc trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ để có thể nhận thông báo về hoạt động của vòng lặp thăm dò ý kiến, cho phép hoạt động trơn tru với nhiều ứng dụng nhận biết NFC.
Vai trò trong Wallet
Android 15 ra mắt vai trò Wallet cho phép tích hợp chặt chẽ hơn với ứng dụng ví mà người dùng ưu tiên. Vai trò này thay thế chế độ cài đặt thanh toán không tiếp xúc mặc định bằng NFC. Người dùng có thể quản lý chủ sở hữu vai trò Wallet bằng cách chuyển đến phần Cài đặt > Ứng dụng > Ứng dụng mặc định.
Vai trò Wallet được dùng khi định tuyến các thao tác nhấn NFC cho AID được đăng ký trong danh mục thanh toán. Lượt nhấn luôn chuyển đến chủ sở hữu vai trò Wallet, trừ phi một ứng dụng khác đã đăng ký cho cùng một AID đang chạy ở nền trước.
Vai trò này cũng được dùng để xác định vị trí của ô Truy cập nhanh vào Wallet khi được kích hoạt. Khi vai trò được đặt thành "Không có", thẻ Quick Access (Quyền truy cập nhanh) sẽ không xuất hiện và các thao tác nhấn NFC thuộc danh mục thanh toán chỉ được phân phối đến ứng dụng trên nền trước.
Bảo mật
Android 15 giúp bạn tăng cường tính bảo mật cho ứng dụng, bảo vệ dữ liệu của ứng dụng và mang đến cho người dùng sự minh bạch cũng như quyền kiểm soát đối với dữ liệu của họ. Xem bài nói chuyện Bảo vệ tính bảo mật của người dùng trên Android tại Google I/O để biết thêm về những việc chúng tôi đang làm nhằm cải thiện các biện pháp bảo vệ người dùng và bảo vệ ứng dụng của bạn trước các mối đe doạ mới.
Tích hợp Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực với tính năng tự động điền
Kể từ Android 15, nhà phát triển có thể liên kết các thành phần hiển thị cụ thể như trường tên người dùng hoặc mật khẩu với các yêu cầu của Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực, giúp dễ dàng cung cấp trải nghiệm phù hợp cho người dùng trong quá trình đăng nhập. Khi người dùng tập trung vào một trong các chế độ xem này, một yêu cầu tương ứng sẽ được gửi đến Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực. Thông tin xác thực thu được được tổng hợp trên các trình cung cấp và hiển thị trong giao diện người dùng dự phòng tự động điền, chẳng hạn như đề xuất cùng dòng hoặc đề xuất thả xuống. Thư viện Jetpack androidx.credentials là điểm cuối ưu tiên mà nhà phát triển nên sử dụng và sẽ sớm ra mắt để nâng cao hơn nữa tính năng này trong Android 15 trở lên.
Tích hợp tính năng đăng ký và đăng nhập bằng một lần nhấn với lời nhắc sinh trắc học
Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực tích hợp lời nhắc sinh trắc học vào quy trình tạo thông tin xác thực và đăng nhập, giúp các nhà cung cấp không cần phải quản lý lời nhắc sinh trắc học. Do đó, trình cung cấp thông tin xác thực chỉ cần tập trung vào kết quả của quy trình tạo và nhận, được tăng cường bằng kết quả của quy trình sinh trắc học. Quy trình đơn giản này giúp tạo và truy xuất thông tin xác thực hiệu quả và đơn giản hơn.
Quản lý khoá để mã hoá hai đầu
Chúng tôi sẽ ra mắt E2eeContactKeysManager trong Android 15. API này hỗ trợ tính năng mã hoá hai đầu (E2EE) trong các ứng dụng Android của bạn bằng cách cung cấp API cấp hệ điều hành để lưu trữ khoá công khai mã hoá.
E2eeContactKeysManager được thiết kế để tích hợp với ứng dụng danh bạ của nền tảng nhằm cung cấp cho người dùng một cách tập trung để quản lý và xác minh khoá công khai của danh bạ.
Kiểm tra quyền đối với URI nội dung
Android 15 giới thiệu một bộ API thực hiện việc kiểm tra quyền trên URI nội dung:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: Thao tác này thực hiện một quy trình kiểm tra quyền đầy đủ đối với URI nội dung.- Thuộc tính tệp kê khai
ActivityrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: Thuộc tính này thực thi các quyền đã chỉ định trên URI nội dung được cung cấp khi khởi chạy hoạt động. - Lớp
ComponentCallercho phương thức gọiActivity: Lớp này đại diện cho ứng dụng đã khởi chạy hoạt động.
Hỗ trợ tiếp cận
Android 15 bổ sung các tính năng giúp cải thiện khả năng hỗ trợ tiếp cận cho người dùng.
Chữ nổi hiệu quả hơn
Trong Android 15, chúng tôi đã hỗ trợ TalkBack hỗ trợ màn hình chữ nổi đang sử dụng tiêu chuẩn HID qua cả USB và Bluetooth bảo mật.
Tiêu chuẩn này, giống như tiêu chuẩn mà chuột và bàn phím sử dụng, sẽ giúp Android hỗ trợ nhiều màn hình chữ nổi hơn theo thời gian.
Quốc tế hoá
Android 15 bổ sung các tính năng và chức năng bổ trợ cho trải nghiệm người dùng khi thiết bị được dùng bằng nhiều ngôn ngữ.
Phông chữ biến đổi CJK
Kể từ Android 15, tệp phông chữ cho các ngôn ngữ tiếng Trung, tiếng Nhật và tiếng Hàn (CJK), NotoSansCJK, hiện là một phông chữ biến. Phông chữ biến đổi mở ra nhiều khả năng cho kiểu chữ sáng tạo bằng các ngôn ngữ CJK. Nhà thiết kế có thể khám phá nhiều kiểu hơn và tạo bố cục bắt mắt mà trước đây khó hoặc không thể đạt được.

Căn chỉnh giữa các ký tự
Kể từ Android 15, bạn có thể căn chỉnh văn bản bằng cách sử dụng khoảng cách chữ cái bằng cách
đang sử dụng JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. Lý do giữa các từ cũ là
được ra mắt lần đầu trong Android 8.0 (API cấp 26) và liên ký tự
Dịch vụ này cung cấp các khả năng tương tự cho các ngôn ngữ sử dụng
ký tự khoảng trắng để phân đoạn, chẳng hạn như tiếng Trung, tiếng Nhật và các loại khác.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.Cấu hình ngắt dòng tự động
Android bắt đầu hỗ trợ ngắt dòng dựa trên cụm từ cho tiếng Nhật và tiếng Hàn bằng
Android 13 (API cấp 33). Tuy nhiên, mặc dù ngắt dòng dựa trên cụm từ sẽ cải thiện
mức độ dễ đọc của các dòng văn bản ngắn, nhưng chúng sẽ không phù hợp với các dòng văn bản dài.
Trên Android 15, ứng dụng chỉ có thể ngắt dòng dựa trên cụm từ cho các dòng ngắn
văn bản, sử dụng LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
. Lựa chọn này chọn kiểu từ phù hợp nhất cho văn bản.
Đối với các dòng văn bản ngắn, dấu ngắt dòng dựa trên cụm từ được sử dụng, hoạt động giống như LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, như minh hoạ trong hình sau:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
áp dụng ngắt dòng dựa trên cụm từ để cải thiện khả năng đọc văn bản.
Điều này giống như việc áp dụng LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.Đối với các dòng văn bản dài hơn, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO sử dụng ký tự no
kiểu chữ ngắt dòng, hoạt động giống như
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, như được hiển thị trong
hình ảnh sau đây:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
sẽ áp dụng kiểu chữ không ngắt dòng để cải thiện khả năng đọc văn bản.
Việc này cũng giống như áp dụng
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.Phông chữ Hentaigana tiếng Nhật bổ sung
Trong Android 15, một tệp phông chữ dành cho chữ Hiragana tiếng Nhật cũ (còn gọi là Hentaigana) được nhóm theo mặc định. Hình dạng độc đáo của các nhân vật trong Hentaigana có thể khiến nét đặc trưng riêng cho hình minh hoạ hoặc thiết kế, đồng thời vẫn giúp đảm bảo tính chính xác sự truyền tải và hiểu biết của các tài liệu cổ của Nhật Bản.

VideoLAN cone Bản quyền (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. Bất kỳ ai cũng có thể sử dụng hoặc sửa đổi biểu trưng này hoặc phiên bản sửa đổi để tham chiếu đến dự án VideoLAN hoặc bất kỳ sản phẩm nào do nhóm VideoLAN phát triển, nhưng điều này không có nghĩa là dự án này chứng thực.
Vulkan và biểu trưng Vulkan là các nhãn hiệu đã đăng ký của Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL là nhãn hiệu đã đăng ký và biểu trưng OpenGL ES là nhãn hiệu của Hewlett Packard Enterprise được sử dụng theo sự cho phép của Khronos.
