مانند نسخههای قبلی، اندروید ۱۶ شامل تغییرات رفتاری است که ممکن است بر برنامه شما تأثیر بگذارد. تغییرات رفتاری زیر منحصراً برای برنامههایی اعمال میشود که اندروید ۱۶ یا بالاتر را هدف قرار میدهند. اگر برنامه شما اندروید ۱۶ یا بالاتر را هدف قرار میدهد، باید برنامه خود را برای پشتیبانی از این رفتارها، در صورت لزوم، اصلاح کنید.
حتماً فهرست تغییرات رفتاری که صرف نظر از targetSdkVersion برنامه شما، بر همه برنامههای در حال اجرا در اندروید ۱۶ تأثیر میگذارند را نیز بررسی کنید.
تجربه کاربری و رابط کاربری سیستم
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر است که برای ایجاد یک تجربه کاربری سازگارتر و شهودیتر در نظر گرفته شدهاند.
کنار رفتن گزینه انصراف از لبه تا لبه
Android 15 enforced edge-to-edge for apps targeting Android 15 (API
level 35), but your app could opt-out by setting
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement to true. For apps
targeting Android 16 (API level 36),
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement is deprecated and disabled, and your
app can't opt-out of going edge-to-edge.
- If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 15 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementcontinues to work. - If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 16 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementis disabled.
For testing in Android 16, ensure your app supports edge-to-edge and
remove any use of R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement so that your app
also supports edge-to-edge on an Android 15 device. To support edge-to-edge,
see the Compose and Views guidance.
مهاجرت یا انصراف برای بازگشت پیشبینیکننده الزامی است
برای برنامههایی که اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) یا بالاتر را هدف قرار میدهند و روی دستگاه اندروید ۱۶ یا بالاتر اجرا میشوند، انیمیشنهای سیستم بازگشت پیشبینیکننده (بازگشت به خانه، میانکاری و میانفعالیتی) به طور پیشفرض فعال هستند. علاوه بر این، onBackPressed فراخوانی نمیشود و KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK دیگر ارسال نمیشود.
اگر برنامه شما رویداد back را متوقف میکند و شما هنوز به حالت predictive back مهاجرت نکردهاید، برنامه خود را بهروزرسانی کنید تا از APIهای پشتیبانیشده برای ناوبری back استفاده کند ، یا با تنظیم ویژگی android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback به false در تگ <application> یا <activity> از فایل AndroidManifest.xml برنامه خود، موقتاً از این حالت خارج شوید.
APIهای فونت Elegant منسوخ و غیرفعال شدند
Apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) have the
elegantTextHeight
TextView attribute set to true by
default, replacing the compact font with one that is much more readable. You
could override this by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute to false.
Android 16 deprecates the
elegantTextHeight attribute,
and the attribute will be ignored once your app targets Android 16. The "UI
fonts" controlled by these APIs are being discontinued, so you should adapt any
layouts to ensure consistent and future proof text rendering in Arabic, Lao,
Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu or Thai.
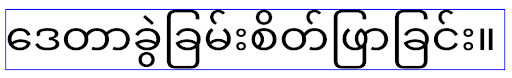
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
14 (API level 34) and lower, or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35)
that overrode the default by setting the elegantTextHeight
attribute to false.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
16 (API level 36), or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) that didn't
override the default by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute
to false.عملکرد اصلی
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر است که قابلیتهای اصلی مختلف سیستم اندروید را اصلاح یا گسترش میدهد.
بهینهسازی زمانبندی کار با نرخ ثابت
Prior to targeting Android 16, when scheduleAtFixedRate
missed a task execution due to being outside a valid
process lifecycle, all missed executions immediately
execute when the app returns to a valid lifecycle.
When targeting Android 16, at most one missed execution of
scheduleAtFixedRate is immediately executed when the app
returns to a valid lifecycle. This behavior change is expected to improve app
performance. Test this behavior in your app to check if your app is impacted.
You can also test by using the app compatibility framework
and enabling the STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat flag.
فاکتورهای شکل دستگاه
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر برای برنامهها هنگام نمایش در دستگاههای صفحه نمایش بزرگ است.
طرحبندیهای تطبیقی
With Android apps now running on a variety of devices (such as phones, tablets, foldables, desktops, cars, and TVs) and windowing modes on large screens (such as split screen and desktop windowing), developers should build Android apps that adapt to any screen and window size, regardless of device orientation. Paradigms like restricting orientation and resizability are too restrictive in today's multidevice world.
Ignore orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions no longer apply on displays with smallest width >= 600dp. Apps fill the entire display window, regardless of aspect ratio or a user's preferred orientation, and pillarboxing isn't used.
This change introduces a new standard platform behavior. Android is moving toward a model where apps are expected to adapt to various orientations, display sizes, and aspect ratios. Restrictions like fixed orientation or limited resizability hinder app adaptability. Make your app adaptive to deliver the best possible user experience.
You can also test this behavior by using the
app compatibility framework and enabling the
UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat flag.
Common breaking changes
Ignoring orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions might impact your app's UI on some devices, especially elements that were designed for small layouts locked in portrait orientation: for example, issues like stretched layouts and off-screen animations and components. Any assumptions about aspect ratio or orientation can cause visual issues with your app. Learn more about how to avoid them and improve your app's adaptive behaviour.
Allowing device rotation results in more activity re-creation, which can result in losing user state if not properly preserved. Learn how to correctly save UI state in Save UI states.
Implementation details
The following manifest attributes and runtime APIs are ignored across large screen devices in full-screen and multi-window modes:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
The following values for screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), and
getRequestedOrientation() are ignored:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Regarding display resizability, android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio, and android:maxAspectRatio have no effect.
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), app orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio constraints are ignored on large screens by default, but every app that isn't fully ready can temporarily override this behavior by opting out (which results in the previous behavior of being placed in compatibility mode).
Exceptions
The Android 16 orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions don't apply in the following situations:
- Games (based on the
android:appCategoryflag) - Users explicitly opting in to the app's default behavior in aspect ratio settings of the device
- Screens that are smaller than
sw600dp
Opt out temporarily
To opt out a specific activity, declare the
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY manifest property:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
If too many parts of your app aren't ready for Android 16, you can opt out completely by applying the same property at the application level:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
سلامت و تناسب اندام
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر در رابطه با دادههای سلامت و تناسب اندام است.
مجوزهای سلامت و تناسب اندام
برای برنامههایی که اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) یا بالاتر را هدف قرار میدهند، مجوزهای BODY_SENSORS از مجوزهای جزئیتری تحت android.permissions.health استفاده میکنند که Health Connect نیز از آن استفاده میکند. از اندروید ۱۶، هر API که قبلاً به BODY_SENSORS یا BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND نیاز داشت، به جای آن به مجوز android.permissions.health مربوطه نیاز دارد. این امر بر انواع داده، APIها و انواع سرویسهای پیشزمینه زیر تأثیر میگذارد:
-
HEART_RATE_BPMاز سرویسهای سلامت در Wear OS -
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEاز مدیریت حسگر اندروید -
heartRateAccuracyوheartRateBpmازProtoLayoutدر Wear OS -
FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHکه در آن به جایBODY_SENSORSمجوزandroid.permission.healthمربوطه مورد نیاز است.
اگر برنامه شما از این APIها استفاده میکند، باید مجوزهای جزئی مربوطه را درخواست کند:
- برای نظارت بر ضربان قلب، SpO2 یا دمای پوست در حین استفاده: مجوز جزئی را در
android.permissions.healthدرخواست کنید، مانندREAD_HEART_RATEبه جایBODY_SENSORS. - برای دسترسی به حسگرهای پسزمینه: به جای
BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUNDREAD_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDدرخواست کنید.
این مجوزها همان مجوزهایی هستند که دسترسی به خواندن دادهها از Health Connect ، پایگاه داده اندروید برای دادههای سلامت، تناسب اندام و تندرستی، را محدود میکنند.
اپلیکیشنهای موبایل
برنامههای موبایلی که به استفاده از READ_HEART_RATE و سایر مجوزهای جزئی مهاجرت میکنند، باید فعالیتی را نیز برای نمایش سیاست حفظ حریم خصوصی برنامه اعلام کنند . این همان الزام Health Connect است.
اتصال
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات زیر در پشته بلوتوث برای بهبود اتصال با دستگاههای جانبی است.
اهداف جدید برای مدیریت از دست دادن اوراق قرضه و تغییرات رمزگذاری
As part of the Improved bond loss handling, Android 16 also introduces 2 new intents to provide apps with greater awareness of bond loss and encryption changes.
Apps targeting Android 16 can now:
- Receive an
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent when remote bond loss is detected, allowing them to provide more informative user feedback and take appropriate actions. - Receive an
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent whenever encryption status of the link changes. This includes encryption status change, encryption algorithm change, and encryption key size change. Apps must consider the bond restored if the link is successfully encrypted upon receivingACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent later.
Adapting to varying OEM implementations
While Android 16 introduces these new intents, their implementation and broadcasting can vary across different device manufacturers (OEMs). To ensure your app provides a consistent and reliable experience across all devices, developers should design their bond loss handling to gracefully adapt to these potential variations.
We recommend the following app behaviors:
If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is broadcast:The ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less) link will be disconnected by the system, but the bond information for the device will be retained (as described here).
Your app should use this intent as the primary signal for bond loss detection and guiding the user to confirm the remote device is in range before initiating device forgetting or re-pairing.
If a device disconnects after
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGis received, your app should be cautious about reconnecting, as the device may no longer be bonded with the system.If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is NOT broadcast:The ACL link will remain connected, and the bond information for the device will be removed by the system, same to behavior in Android 15.
In this scenario, your app should continue its existing bond loss handling mechanisms as in previous Android releases, to detect and manage bond loss events.
روش جدید برای حذف اتصال بلوتوث
All apps targeting Android 16 are now able to unpair bluetooth devices using a
public API in CompanionDeviceManager. If a companion device is
being managed as a CDM association, then the app can trigger
bluetooth bond removal by using the new removeBond(int) API
on the associated device. The app can monitor the bond state changes by
listening to the bluetooth device broadcast event
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
امنیت
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات امنیتی زیر است.
قفل شدن نسخه MediaStore
For apps targeting Android 16 or higher, MediaStore#getVersion() will now
be unique to each app. This eliminates identifying properties from the version
string to prevent abuse and usage for fingerprinting techniques. Apps shouldn't
make any assumptions around the format of this version. Apps should already
handle version changes when using this API and in most cases shouldn't need to
change their current behavior, unless the developer has attempted to infer
additional information that is beyond the intended scope of this API.
مقاصد امنتر
The Safer Intents feature is a multi-phase security initiative designed to improve the security of Android's intent resolution mechanism. The goal is to protect apps from malicious actions by adding checks during intent processing and filtering intents that don't meet specific criteria.
In Android 15 the feature focused on the sending app, now with Android 16, shifts control to the receiving app, allowing developers to opt-in to strict intent resolution using their app manifest.
Two key changes are being implemented:
Explicit Intents Must Match the Target Component's Intent Filter: If an intent explicitly targets a component, it should match that component's intent filter.
Intents Without an Action Cannot Match any Intent Filter: Intents that don't have an action specified shouldn't be resolved to any intent filter.
These changes only apply when multiple apps are involved and don't affect intent handling within a single app.
Impact
The opt-in nature means that developers must explicitly enable it in their app manifest for it to take effect. As a result, the feature's impact will be limited to apps whose developers:
- Are aware of the Safer Intents feature and its benefits.
- Actively choose to incorporate stricter intent handling practices into their apps.
This opt-in approach minimizes the risk of breaking existing apps that may rely on the current less-secure intent resolution behavior.
While the initial impact in Android 16 may be limited, the Safer Intents initiative has a roadmap for broader impact in future Android releases. The plan is to eventually make strict intent resolution the default behavior.
The Safer Intents feature has the potential to significantly enhance the security of the Android ecosystem by making it more difficult for malicious apps to exploit vulnerabilities in the intent resolution mechanism.
However, the transition to opt-out and mandatory enforcement must be carefully managed to address potential compatibility issues with existing apps.
Implementation
Developers need to explicitly enable stricter intent matching using the
intentMatchingFlags attribute in their app manifest.
Here is an example where the feature is opt-in for the entire app,
but disabled/opt-out on a receiver:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
More on the supported flags:
| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Enforces stricter matching for incoming intents |
| none | Disables all special matching rules for incoming intents. When specifying multiple flags, conflicting values are resolved by giving precedence to the "none" flag |
| allowNullAction | Relaxes the matching rules to allow intents without an action to match. This flag to be used in conjunction with "enforceIntentFilter" to achieve a specific behavior |
Testing and Debugging
When the enforcement is active, apps should function correctly if the intent
caller has properly populated the intent.
However, blocked intents will trigger warning log messages like
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" and "Access blocked:"
with the tag "PackageManager."
This indicates a potential issue that could impact the app and requires
attention.
Logcat filter:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
فیلتر کردن فراخوانیهای سیستمی GPU
برای مقاومسازی سطح پردازنده گرافیکی Mali، IOCTLهای پردازنده گرافیکی Mali که منسوخ شدهاند یا صرفاً برای توسعه پردازنده گرافیکی در نظر گرفته شدهاند، در نسخههای تولیدی مسدود شدهاند. علاوه بر این، IOCTLهای مورد استفاده برای پروفایلسازی پردازنده گرافیکی به فرآیند پوسته یا برنامههای اشکالزداییشده محدود شدهاند. برای جزئیات بیشتر در مورد سیاست سطح پلتفرم، به بهروزرسانی SAC مراجعه کنید.
این تغییر در دستگاههای پیکسل که از پردازنده گرافیکی Mali (پیکسل ۶-۹) استفاده میکنند، رخ میدهد. آرم دستهبندی رسمی IOCTL های خود را در Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst از نسخه r54p2 خود ارائه کرده است. این لیست در نسخههای درایور آینده همچنان حفظ خواهد شد.
این تغییر بر APIهای گرافیکی پشتیبانیشده (از جمله Vulkan و OpenGL) تأثیری ندارد و انتظار نمیرود که توسعهدهندگان یا برنامههای موجود را نیز تحت تأثیر قرار دهد. ابزارهای پروفایلینگ GPU مانند Streamline Performance Analyzer و Android GPU Inspector تحت تأثیر قرار نخواهند گرفت.
آزمایش
اگر با خطای عدم پذیرش SELinux مشابه تصویر زیر مواجه شدید، احتمالاً برنامه شما تحت تأثیر این تغییر قرار گرفته است:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
اگر برنامه شما نیاز به استفاده از IOCTL های مسدود شده دارد، لطفاً یک اشکال (bug) ثبت کنید و آن را به android-partner-security@google.com ارجاع دهید.
سوالات متداول
آیا این تغییر سیاست برای همه تولیدکنندگان اصلی تجهیزات (OEM) اعمال میشود؟ این تغییر اختیاری خواهد بود، اما برای هر تولیدکننده اصلی تجهیزاتی که مایل به استفاده از این روش مقاومسازی باشند، در دسترس خواهد بود. دستورالعملهای اجرای این تغییر را میتوانید در مستندات پیادهسازی بیابید.
آیا برای پیادهسازی این تغییر، ایجاد تغییرات در کدبیس تولیدکننده اصلی (OEM) اجباری است یا اینکه بهطور پیشفرض با یک نسخه جدید AOSP همراه خواهد بود؟ تغییر در سطح پلتفرم بهطور پیشفرض با یک نسخه جدید AOSP همراه خواهد بود. فروشندگان میتوانند در صورت تمایل به اعمال این تغییر در کدبیس خود، آن را بپذیرند.
آیا SoCها مسئول بهروز نگه داشتن لیست IOCTL هستند؟ به عنوان مثال، اگر دستگاه من از پردازنده گرافیکی ARM Mali استفاده میکند، آیا باید برای هرگونه تغییر با ARM تماس بگیرم؟ SoCهای جداگانه باید لیستهای IOCTL خود را برای هر دستگاه پس از انتشار درایور بهروزرسانی کنند. به عنوان مثال، ARM لیست IOCTL منتشر شده خود را پس از بهروزرسانی درایور بهروزرسانی میکند. با این حال، OEMها باید مطمئن شوند که بهروزرسانیها را در SEPolicy خود لحاظ میکنند و در صورت نیاز، IOCTLهای سفارشی انتخاب شده را به لیستها اضافه میکنند.
آیا این تغییر به طور خودکار برای همه دستگاههای پیکسل موجود در بازار اعمال میشود یا برای اعمال این تغییر، اقدام کاربر لازم است؟ این تغییر برای همه دستگاههای پیکسل موجود در بازار که از پردازنده گرافیکی Mali استفاده میکنند (پیکسل ۶-۹) اعمال میشود. برای اعمال این تغییر نیازی به اقدام کاربر نیست.
آیا استفاده از این سیاست بر عملکرد درایور هسته تأثیر میگذارد؟ این سیاست با استفاده از GFXBench روی پردازنده گرافیکی Mali آزمایش شد و هیچ تغییر قابل اندازهگیری در عملکرد پردازنده گرافیکی مشاهده نشد.
آیا لازم است لیست IOCTL با نسخههای فعلی درایور فضای کاربری و هسته هماهنگ شود؟ بله، لیست IOCTLهای مجاز باید با IOCTLهای پشتیبانی شده توسط درایورهای فضای کاربری و هسته هماهنگ شوند. اگر IOCTLهای موجود در فضای کاربری یا درایور هسته بهروزرسانی شوند، لیست IOCTL در SEPolicy نیز باید بهروزرسانی شود تا با آنها مطابقت داشته باشد.
ARM، IOCTLها را به عنوان «محدود» / «ابزار دقیق» طبقهبندی کرده است، اما ما میخواهیم از برخی از آنها در موارد استفاده در تولید استفاده کنیم و/یا برخی دیگر را رد کنیم. تولیدکنندگان اصلی تجهیزات/SoCها مسئول تصمیمگیری در مورد نحوه طبقهبندی IOCTLهایی هستند که بر اساس پیکربندی کتابخانههای Mali فضای کاربری خود، استفاده میکنند. فهرست ARM میتواند برای تصمیمگیری در مورد این موارد استفاده شود، اما موارد استفاده هر تولیدکننده اصلی تجهیزات/SoC ممکن است متفاوت باشد.
حریم خصوصی
اندروید ۱۶ (سطح API ۳۶) شامل تغییرات حریم خصوصی زیر است.
مجوز شبکه محلی
دستگاههای موجود در شبکه محلی (LAN) میتوانند توسط هر برنامهای که مجوز INTERNET دارد، قابل دسترسی باشند. این امر اتصال برنامهها به دستگاههای محلی را آسان میکند، اما پیامدهایی برای حریم خصوصی مانند تشکیل اثر انگشت کاربر و تبدیل شدن به یک پروکسی برای موقعیت مکانی نیز دارد.
پروژه حفاظت از شبکههای محلی (Local Network Protections) با هدف محافظت از حریم خصوصی کاربر، دسترسی به شبکه محلی را با مجوز زمان اجرا (runtime permission) جدیدی مسدود میکند.
طرح انتشار
این تغییر به ترتیب بین دو نسخه، سهماهه دوم ۲۵ و سهماهه دوم ۲۶، اعمال خواهد شد. ضروری است که توسعهدهندگان این راهنما را برای سهماهه دوم ۲۵ دنبال کنند و بازخورد خود را به اشتراک بگذارند، زیرا این محافظتها در نسخه بعدی اندروید اعمال خواهند شد . علاوه بر این، آنها باید سناریوهایی را که به دسترسی ضمنی به شبکه محلی بستگی دارند، با استفاده از راهنمای زیر بهروزرسانی کنند و برای رد کاربر و لغو مجوز جدید آماده شوند.
تأثیر
در مرحله فعلی، LNP یک ویژگی اختیاری است، به این معنی که فقط برنامههایی که این ویژگی را انتخاب میکنند تحت تأثیر قرار میگیرند. هدف از مرحله اختیاری این است که توسعهدهندگان برنامه بفهمند کدام بخشهای برنامهشان به دسترسی ضمنی به شبکه محلی نیاز دارد تا بتوانند برای انتشار بعدی، از آنها محافظت کنند.
اگر برنامهها با استفاده از روشهای زیر به شبکه محلی کاربر دسترسی پیدا کنند، تحت تأثیر قرار خواهند گرفت:
- استفاده مستقیم یا کتابخانهای از سوکتهای خام روی آدرسهای شبکه محلی (مثلاً mDNS یا پروتکل کشف سرویس SSDP)
- استفاده از کلاسهای سطح چارچوب که به شبکه محلی دسترسی دارند (مثلاً NsdManager)
ترافیک ورودی و خروجی از یک آدرس شبکه محلی نیاز به مجوز دسترسی به شبکه محلی دارد. جدول زیر برخی از موارد رایج را فهرست میکند:
| عملیات شبکه سطح پایین برنامه | مجوز شبکه محلی مورد نیاز است |
|---|---|
| ایجاد یک اتصال TCP خروجی | بله |
| پذیرش اتصالات TCP ورودی | بله |
| ارسال UDP به صورت تک پخشی، چندپخشی، پخش همگانی | بله |
| دریافت یک UDP ورودی به صورت تک پخشی، چندپخشی، پخش همگانی | بله |
این محدودیتها در اعماق پشته شبکه پیادهسازی شدهاند و بنابراین بر همه APIهای شبکه اعمال میشوند. این شامل سوکتهای ایجاد شده با کد بومی یا مدیریتشده، کتابخانههای شبکه مانند Cronet و OkHttp و هر API پیادهسازی شده بر روی آنها میشود. تلاش برای حل مشکلات سرویسها در شبکه محلی (یعنی آنهایی که پسوند .local دارند) به مجوز شبکه محلی نیاز دارد.
استثنائات قوانین فوق:
- اگر سرور DNS یک دستگاه در یک شبکه محلی باشد، ترافیک ورودی یا خروجی از آن (در پورت ۵۳) نیازی به مجوز دسترسی به شبکه محلی ندارد.
- برنامههایی که از Output Switcher به عنوان انتخابگر درونبرنامهای خود استفاده میکنند، به مجوزهای شبکه محلی نیاز نخواهند داشت (راهنمایی بیشتر در سهماهه چهارم 2025 ارائه خواهد شد).
راهنمایی توسعهدهنده (انتخابی)
برای اعمال محدودیتهای شبکه محلی، موارد زیر را انجام دهید:
- دستگاه را به نسخهای با نسخه بتا ۳ از ۲۵Q2 یا بالاتر فلش کنید.
- برای تست، برنامه را نصب کنید.
تغییر وضعیت پرچم Appcompat در adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>دستگاه را ریبوت کنید
اکنون دسترسی برنامه شما به شبکه محلی محدود شده است و هرگونه تلاشی برای دسترسی به شبکه محلی منجر به خطاهای سوکت خواهد شد. اگر از APIهایی استفاده میکنید که عملیات شبکه محلی را خارج از فرآیند برنامه شما انجام میدهند (مثلاً: NsdManager)، در مرحله انتخاب، تحت تأثیر قرار نخواهند گرفت.
برای بازیابی دسترسی، باید به برنامه خود اجازه دسترسی به NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES را بدهید.
- مطمئن شوید که برنامه مجوز
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESرا در مانیفست خود اعلام کرده است. - به تنظیمات > برنامهها > [نام برنامه] > مجوزها > دستگاههای نزدیک > مجاز بروید.
اکنون دسترسی برنامه شما به شبکه محلی باید بازیابی شده باشد و تمام سناریوهای شما باید مانند قبل از فعال کردن برنامه، کار کنند.
زمانی که اجرای قانون حفاظت از شبکه محلی آغاز شود، در اینجا نحوه تأثیر آن بر ترافیک شبکه برنامه آمده است.
| اجازه | درخواست شبکه محلی خروجی | درخواست اینترنت خروجی/ورودی | درخواست شبکه محلی ورودی |
|---|---|---|---|
| اعطا شده | آثار | آثار | آثار |
| اعطا نشده | شکستها | آثار | شکستها |
برای غیرفعال کردن پرچم App-Compat از دستور زیر استفاده کنید.
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
خطاها
خطاهای ناشی از این محدودیتها، هر زمان که سوکت فراخوانی کننده، تابع send یا نوع دیگری از send را به یک آدرس شبکه محلی فراخوانی کند، به آن بازگردانده میشوند.
خطاهای مثال:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
تعریف شبکه محلی
منظور از شبکه محلی در این پروژه، شبکهای مبتنی بر IP است که از یک رابط شبکه با قابلیت پخش همگانی، مانند Wi-Fi یا Ethernet، استفاده میکند، اما اتصالات تلفن همراه (WWAN) یا VPN را شامل نمیشود.
موارد زیر به عنوان شبکههای محلی در نظر گرفته میشوند:
آیپیوی۴:
- ۱۶۹.۲۵۴.۰.۰/۱۶ // لینک محلی
- ۱۰۰.۶۴.۰.۰/۱۰ // سیجیانایتی
- ۱۰.۰.۰.۰/۸ // RFC۱۹۱۸
- ۱۷۲.۱۶.۰.۰/۱۲ // RFC۱۹۱۸
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
آیپیوی۶:
- لینک-محلی
- مسیرهای متصل مستقیم
- شبکههای خرد مانند Thread
- زیرشبکههای چندگانه (تاریخ انتشار نامشخص)
علاوه بر این، هر دو آدرس چندپخشی (224.0.0.0/4، ff00::/8) و آدرس پخش IPv4 (255.255.255.255) به عنوان آدرسهای شبکه محلی طبقهبندی میشوند.

