كما هو الحال في الإصدارات السابقة، يتضمّن Android 16 تغييرات في السلوك قد تؤثّر في تطبيقك. تنطبق تغييرات السلوك التالية حصريًا على التطبيقات التي تستهدف Android 16 أو الإصدارات الأحدث. إذا كان تطبيقك يستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android أو الإصدارات الأحدث، عليك تعديل تطبيقك ليتوافق مع هذه السلوكيات، حيثما ينطبق ذلك.
احرص أيضًا على مراجعة قائمة التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثر في جميع التطبيقات
التي تعمل على Android 16 بغض النظر عن targetSdkVersion لتطبيقك.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية التي تهدف إلى توفير تجربة مستخدم أكثر اتساقًا وسهولة.
إيقاف العرض من الحافة إلى الحافة نهائيًا
Android 15 enforced edge-to-edge for apps targeting Android 15 (API
level 35), but your app could opt-out by setting
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement to true. For apps
targeting Android 16 (API level 36),
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement is deprecated and disabled, and your
app can't opt-out of going edge-to-edge.
- If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 15 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementcontinues to work. - If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 16 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementis disabled.
For testing in Android 16, ensure your app supports edge-to-edge and
remove any use of R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement so that your app
also supports edge-to-edge on an Android 15 device. To support edge-to-edge,
see the Compose and Views guidance.
يجب نقل البيانات أو إيقاف ميزة "الرجوع التنبؤي"
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher and running on an
Android 16 or higher device, the predictive back system animations
(back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity) are enabled by default.
Additionally, onBackPressed is not called and
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK is not dispatched anymore.
If your app intercepts the back event and you haven't migrated to predictive
back yet, update your app to use supported back navigation APIs, or
temporarily opt out by setting the
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback attribute to false in the
<application> or <activity> tag of your app's AndroidManifest.xml file.
إيقاف واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الخاصة بالخطوط الأنيقة نهائيًا
Apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) have the
elegantTextHeight
TextView attribute set to true by
default, replacing the compact font with one that is much more readable. You
could override this by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute to false.
Android 16 deprecates the
elegantTextHeight attribute,
and the attribute will be ignored once your app targets Android 16. The "UI
fonts" controlled by these APIs are being discontinued, so you should adapt any
layouts to ensure consistent and future proof text rendering in Arabic, Lao,
Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu or Thai.
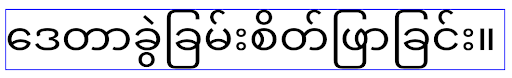
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
14 (API level 34) and lower, or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35)
that overrode the default by setting the elegantTextHeight
attribute to false.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
16 (API level 36), or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) that didn't
override the default by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute
to false.الوظيفة الأساسية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية التي تعدّل أو توسّع العديد من الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام Android.
تحسين جدولة العمل بمعدّل ثابت
Prior to targeting Android 16, when scheduleAtFixedRate
missed a task execution due to being outside a valid
process lifecycle, all missed executions immediately
execute when the app returns to a valid lifecycle.
When targeting Android 16, at most one missed execution of
scheduleAtFixedRate is immediately executed when the app
returns to a valid lifecycle. This behavior change is expected to improve app
performance. Test this behavior in your app to check if your app is impacted.
You can also test by using the app compatibility framework
and enabling the STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat flag.
أشكال الأجهزة
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية للتطبيقات عند عرضها على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة.
التنسيقات التكيّفية
With Android apps now running on a variety of devices (such as phones, tablets, foldables, desktops, cars, and TVs) and windowing modes on large screens (such as split screen and desktop windowing), developers should build Android apps that adapt to any screen and window size, regardless of device orientation. Paradigms like restricting orientation and resizability are too restrictive in today's multidevice world.
Ignore orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions no longer apply on displays with smallest width >= 600dp. Apps fill the entire display window, regardless of aspect ratio or a user's preferred orientation, and pillarboxing isn't used.
This change introduces a new standard platform behavior. Android is moving toward a model where apps are expected to adapt to various orientations, display sizes, and aspect ratios. Restrictions like fixed orientation or limited resizability hinder app adaptability. Make your app adaptive to deliver the best possible user experience.
You can also test this behavior by using the
app compatibility framework and enabling the
UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat flag.
Common breaking changes
Ignoring orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions might impact your app's UI on some devices, especially elements that were designed for small layouts locked in portrait orientation: for example, issues like stretched layouts and off-screen animations and components. Any assumptions about aspect ratio or orientation can cause visual issues with your app. Learn more about how to avoid them and improve your app's adaptive behaviour.
Allowing device rotation results in more activity re-creation, which can result in losing user state if not properly preserved. Learn how to correctly save UI state in Save UI states.
Implementation details
The following manifest attributes and runtime APIs are ignored across large screen devices in full-screen and multi-window modes:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
The following values for screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), and
getRequestedOrientation() are ignored:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Regarding display resizability, android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio, and android:maxAspectRatio have no effect.
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), app orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio constraints are ignored on large screens by default, but every app that isn't fully ready can temporarily override this behavior by opting out (which results in the previous behavior of being placed in compatibility mode).
Exceptions
The Android 16 orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions don't apply in the following situations:
- Games (based on the
android:appCategoryflag) - Users explicitly opting in to the app's default behavior in aspect ratio settings of the device
- Screens that are smaller than
sw600dp
Opt out temporarily
To opt out a specific activity, declare the
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY manifest property:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
If too many parts of your app aren't ready for Android 16, you can opt out completely by applying the same property at the application level:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
الصحة واللياقة البدنية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية المتعلّقة ببيانات الصحة واللياقة البدنية.
أذونات الصحة واللياقة البدنية
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher,
BODY_SENSORS permissions use more granular permissions
under android.permissions.health, which Health Connect
also uses. As of Android 16, any API previously requiring BODY_SENSORS
or BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND requires the corresponding
android.permissions.health permission instead. This affects the following data
types, APIs, and foreground service types:
HEART_RATE_BPMfrom Health Services on Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEfrom Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyandheartRateBpmfromProtoLayouton Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHwhere the respectiveandroid.permission.healthpermission is needed in place ofBODY_SENSORS
If your app uses these APIs, it should request the respective granular permissions:
- For while-in-use monitoring of Heart Rate, SpO2, or Skin Temperature:
request the granular permission under
android.permissions.health, such asREAD_HEART_RATEinstead ofBODY_SENSORS. - For background sensor access: request
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDinstead ofBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
These permissions are the same as those that guard access to reading data from Health Connect, the Android datastore for health, fitness, and wellness data.
Mobile apps
Mobile apps migrating to use the READ_HEART_RATE and other granular
permissions must also declare an activity to display
the app's privacy policy. This is the same requirement as Health Connect.
إمكانية الاتصال
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية في حزمة بروتوكول البلوتوث لتحسين إمكانية الاتصال بالأجهزة الطرفية.
أهداف جديدة للتعامل مع فقدان الربط والتغييرات في التشفير
As part of the Improved bond loss handling, Android 16 also introduces 2 new intents to provide apps with greater awareness of bond loss and encryption changes.
Apps targeting Android 16 can now:
- Receive an
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent when remote bond loss is detected, allowing them to provide more informative user feedback and take appropriate actions. - Receive an
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent whenever encryption status of the link changes. This includes encryption status change, encryption algorithm change, and encryption key size change. Apps must consider the bond restored if the link is successfully encrypted upon receivingACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent later.
Adapting to varying OEM implementations
While Android 16 introduces these new intents, their implementation and broadcasting can vary across different device manufacturers (OEMs). To ensure your app provides a consistent and reliable experience across all devices, developers should design their bond loss handling to gracefully adapt to these potential variations.
We recommend the following app behaviors:
If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is broadcast:The ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less) link will be disconnected by the system, but the bond information for the device will be retained (as described here).
Your app should use this intent as the primary signal for bond loss detection and guiding the user to confirm the remote device is in range before initiating device forgetting or re-pairing.
If a device disconnects after
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGis received, your app should be cautious about reconnecting, as the device may no longer be bonded with the system.If the
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent is NOT broadcast:The ACL link will remain connected, and the bond information for the device will be removed by the system, same to behavior in Android 15.
In this scenario, your app should continue its existing bond loss handling mechanisms as in previous Android releases, to detect and manage bond loss events.
طريقة جديدة لإزالة ربط البلوتوث
All apps targeting Android 16 are now able to unpair bluetooth devices using a
public API in CompanionDeviceManager. If a companion device is
being managed as a CDM association, then the app can trigger
bluetooth bond removal by using the new removeBond(int) API
on the associated device. The app can monitor the bond state changes by
listening to the bluetooth device broadcast event
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
الأمان
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) تغييرات الأمان التالية.
قفل إصدار MediaStore
For apps targeting Android 16 or higher, MediaStore#getVersion() will now
be unique to each app. This eliminates identifying properties from the version
string to prevent abuse and usage for fingerprinting techniques. Apps shouldn't
make any assumptions around the format of this version. Apps should already
handle version changes when using this API and in most cases shouldn't need to
change their current behavior, unless the developer has attempted to infer
additional information that is beyond the intended scope of this API.
Safer Intents
ميزة "نقل نوايا أكثر أمانًا" هي مبادرة أمان متعدّدة المراحل مصمَّمة لتحسين أمان آلية تحديد الغرض في Android. والهدف من ذلك هو حماية التطبيقات من الإجراءات الضارة من خلال إضافة عمليات تحقّق أثناء معالجة الأهداف وتصفية الأهداف التي لا تستوفي معايير محدّدة.
في Android 15، ركّزت الميزة على تطبيق المرسِل، ولكن مع Android 16، أصبح تطبيق المتلقي هو الذي يتحكّم في العملية، ما يتيح للمطوّرين تفعيل ميزة تحليل الأهداف بدقة باستخدام بيان التطبيق.
سيتم تنفيذ تغييران رئيسيان:
يجب أن تتطابق الأهداف الصريحة (Explicit Intents) مع فلتر Intent الخاص بالمكوِّن المستهدف: إذا كانت الأهداف الصريحة تستهدف مكوِّنًا بشكل صريح، يجب أن تتطابق مع فلتر Intent الخاص بهذا المكوِّن.
لا يمكن أن تتطابق الأهداف التي لا تتضمّن إجراءً مع أي فلتر Intent: يجب ألا يتم تحليل الأهداف التي لا تتضمّن إجراءً محدّدًا إلى أي فلتر Intent.
لا تنطبق هذه التغييرات إلا عند استخدام تطبيقات متعددة، ولا تؤثّر في معالجة الأهداف داخل تطبيق واحد.
التأثير
ويعني ذلك أنّ على المطوّرين تفعيلها بشكل صريح في بيان التطبيق لكي تصبح سارية. نتيجةً لذلك، سيقتصر تأثير الميزة على التطبيقات التي يستوفي مطوّروها الشروط التالية:
- أن تكون على دراية بميزة "نوايا أكثر أمانًا" وفوائدها
- اختيار دمج ممارسات أكثر صرامة للتعامل مع الأهداف في تطبيقاتهم
يقلّل نهج الموافقة هذا من خطر تعطيل التطبيقات الحالية التي قد تعتمد على السلوك الحالي الأقل أمانًا في حلّ الأهداف.
على الرغم من أنّ التأثير الأوّلي لمبادرة "نوايا أكثر أمانًا" في Android 16 قد يكون محدودًا، إلا أنّ هناك خارطة طريق لتحقيق تأثير أوسع في إصدارات Android المستقبلية. ونخطّط في النهاية لجعل حلّ النية الصارمة هو السلوك التلقائي.
يمكن أن تؤدي ميزة "نقل نوايا أكثر أمانًا" إلى تحسين أمان منظومة Android المتكاملة بشكل كبير من خلال الحد من قدرة التطبيقات الضارة على استغلال الثغرات الأمنية في آلية تحديد الغرض.
ومع ذلك، يجب إدارة عملية الانتقال إلى خيار إيقاف الميزة وفرضها بشكل إلزامي بعناية لمعالجة المشاكل المحتملة المتعلّقة بالتوافق مع التطبيقات الحالية.
التنفيذ
على المطوّرين تفعيل ميزة مطابقة الأهداف الأكثر صرامة بشكلٍ صريح باستخدام السمة intentMatchingFlags في بيان التطبيق.
في ما يلي مثال على حالة تكون فيها الميزة متاحة في التطبيق بأكمله، ولكنها غير مفعّلة أو تم إيقافها في جهاز استقبال:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
مزيد من المعلومات عن العلامات المتوافقة:
| اسم العلامة | الوصف |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | فرض مطابقة أكثر صرامة لرسائل Intent الواردة |
| لا شيء | يؤدي ذلك إلى إيقاف جميع قواعد المطابقة الخاصة للطلبات الواردة. عند تحديد علامات متعدّدة، يتم حل القيم المتعارضة من خلال منح الأولوية للعلامة "none". |
| allowNullAction | يخفّف من قواعد المطابقة للسماح بمطابقة الأهداف بدون إجراء. يجب استخدام هذا الخيار مع الخيار "enforceIntentFilter" لتحقيق سلوك معيّن. |
الاختبار وتصحيح الأخطاء
عندما يكون التنفيذ نشطًا، من المفترض أن تعمل التطبيقات بشكل صحيح إذا كان برنامج استدعاء الغرض قد ملأ الغرض بشكل صحيح.
ومع ذلك، ستؤدي النوايا المحظورة إلى ظهور رسائل تحذيرية في سجلّ الأخطاء، مثل
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" و"Access blocked:"
مع العلامة "PackageManager."
يشير ذلك إلى مشكلة محتملة قد تؤثر في التطبيق وتتطلّب
الانتباه.
فلتر Logcat:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
فلترة طلبات النظام لوحدة معالجة الرسومات
To harden the Mali GPU surface, Mali GPU IOCTLs that have been deprecated or are intended solely for GPU development have been blocked in production builds. Additionally, IOCTLs used for GPU profiling have been restricted to the shell process or debuggable applications. Refer to the SAC update for more details on the platform-level policy.
This change takes place on Pixel devices using the Mali GPU (Pixel 6-9). Arm
has provided official categorization of their IOCTLs in
Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst of their r54p2 release. This
list will continue to be maintained in future driver releases.
This change does not impact supported graphics APIs (including Vulkan and OpenGL), and is not expected to impact developers or existing applications. GPU profiling tools such as the Streamline Performance Analyzer and the Android GPU Inspector won't be affected.
Testing
If you see a SELinux denial similar to the following, it is likely your application has been impacted by this change:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
If your application needs to use blocked IOCTLs, please file a bug and assign it to android-partner-security@google.com.
FAQ
Does this policy change apply to all OEMs? This change will be opt-in, but available to any OEMs who would like to use this hardening method. Instructions for implementing the change can be found in the implementation documentation.
Is it mandatory to make changes in the OEM codebase to implement this, or does it come with a new AOSP release by default? The platform-level change will come with a new AOSP release by default. Vendors may opt-in to this change in their codebase if they would like to apply it.
Are SoCs responsible for keeping the IOCTL list up to date? For example, if my device uses an ARM Mali GPU, would I need to reach out to ARM for any of the changes? Individual SoCs must update their IOCTL lists per device upon driver release. For example, ARM will update their published IOCTL list upon driver updates. However, OEMs should make sure that they incorporate the updates in their SEPolicy, and add any selected custom IOCTLs to the lists as needed.
Does this change apply to all Pixel in-market devices automatically, or is a user action required to toggle something to apply this change? This change applies to all Pixel in-market devices using the Mali GPU (Pixel 6-9). No user action is required to apply this change.
Will use of this policy impact the performance of the kernel driver? This policy was tested on the Mali GPU using GFXBench, and no measurable change to GPU performance was observed.
Is it necessary for the IOCTL list to align with the current userspace and kernel driver versions? Yes, the list of allowed IOCTLs must be synchronized with the IOCTLs supported by both the userspace and kernel drivers. If the IOCTLs in the user space or kernel driver are updated, the SEPolicy IOCTL list must be updated to match.
ARM has categorized IOCTLs as 'restricted' / 'instrumentation', but we want to use some of them in production use-cases, and/or deny others. Individual OEMs/SoCs are responsible for deciding on how to categorize the IOCTLs they use, based on the configuration of their userspace Mali libraries. ARM's list can be used to help decide on these, but each OEM/SoC's use-case may be different.
الخصوصية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) تغييرات الخصوصية التالية.
إذن الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية
يمكن لأي تطبيق لديه إذن INTERNET الوصول إلى الأجهزة على الشبكة المحلية.
يسهّل ذلك على التطبيقات الاتصال بالأجهزة المحلية، ولكن له أيضًا آثار على الخصوصية، مثل إنشاء بصمة رقمية للمستخدم، والعمل كخادم وكيل للموقع الجغرافي.
يهدف مشروع "حماية الشبكة المحلية" إلى حماية خصوصية المستخدم من خلال حصر الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية بإذن جديد أثناء التشغيل.
خطة الإصدار
سيتم طرح هذا التغيير بين إصدارَين، 25Q2 و26Q2 على التوالي. من الضروري أن يلتزم المطوّرون بهذه الإرشادات في الربع الثاني من عام 2025 وأن يشاركوا ملاحظاتهم، لأنّ هذه الحمايات سيتم فرضها في إصدار Android لاحق. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، عليهم تعديل السيناريوهات التي تعتمد على الوصول الضمني إلى الشبكة المحلية باتّباع الإرشادات التالية والاستعداد لرفض المستخدمين وإلغاء الإذن الجديد.
التأثير
في المرحلة الحالية، ميزة "الشبكة المحلية فقط" هي ميزة اختيارية، ما يعني أنّ التطبيقات التي تفعّلها فقط ستتأثر بها. والهدف من مرحلة الموافقة هو أن يفهم مطوّرو التطبيقات الأجزاء التي تعتمد على الوصول الضمني إلى الشبكة المحلية، حتى يتمكّنوا من إعدادها لتكون محمية بإذن في الإصدار التالي.
ستتأثر التطبيقات إذا كانت تصل إلى الشبكة المحلية للمستخدم باستخدام:
- الاستخدام المباشر أو استخدام المكتبة للمقابس الأولية على عناوين الشبكة المحلية (مثل بروتوكول mDNS أو SSDP لاكتشاف الخدمات)
- استخدام فئات على مستوى إطار العمل يمكنها الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية (مثل NsdManager)
تتطلّب حركة البيانات من عنوان شبكة محلية وإليه إذنًا بالوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية. يسرد الجدول التالي بعض الحالات الشائعة:
| عمليات الشبكة المنخفضة المستوى في التطبيق | يجب منح إذن الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية |
|---|---|
| إجراء اتصال TCP صادر | نعم |
| قبول اتصالات TCP الواردة | نعم |
| إرسال بث أحادي أو بث متعدّد أو بث عادي عبر UDP | نعم |
| تلقّي بث أحادي أو متعدد أو عادي وارد عبر UDP | نعم |
يتم تنفيذ هذه القيود في أعماق حزمة الشبكات، وبالتالي تنطبق على جميع واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المتعلقة بالشبكات. ويشمل ذلك المقابس التي تم إنشاؤها في الرموز البرمجية الأصلية أو المُدارة، ومكتبات الشبكات مثل Cronet وOkHttp، وأي واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تم تنفيذها فوق هذه المكتبات. ستتطلّب محاولة حلّ الخدمات على الشبكة المحلية (أي تلك التي تتضمّن اللاحقة .local) إذنًا بالوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية.
استثناءات للقواعد أعلاه:
- إذا كان خادم DNS الخاص بجهاز معيّن متصلاً بشبكة محلية، لن يتطلّب نقل البيانات من الجهاز أو إليه (على المنفذ 53) إذنًا بالوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية.
- لن تحتاج التطبيقات التي تستخدم أداة Output Switcher كأداة اختيار داخل التطبيق إلى أذونات الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية (ستتوفّر المزيد من الإرشادات في الربع الرابع من عام 2025).
إرشادات للمطوّرين (تفعيل)
لإيقاف القيود على الشبكة المحلية، اتّبِع الخطوات التالية:
- تثبيت إصدار يتضمّن الإصدار التجريبي 3 من 25Q2 أو إصدار أحدث على الجهاز
- ثبِّت التطبيق الذي تريد اختباره.
بدِّل علامة Appcompat في adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>إعادة تشغيل الجهاز
سيتم الآن تقييد وصول تطبيقك إلى الشبكة المحلية، وسيؤدي أي محاولة للوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية إلى حدوث أخطاء في المقبس. إذا كنت تستخدم واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تنفّذ عمليات على الشبكة المحلية خارج عملية تطبيقك (مثل NsdManager)، لن تتأثّر هذه العمليات خلال مرحلة الموافقة.
لاستعادة إمكانية الوصول، يجب منح تطبيقك الإذن بالوصول إلى NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- تأكَّد من أنّ التطبيق يعلن عن إذن
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESفي بيان التطبيق. - انتقِل إلى الإعدادات > التطبيقات > [اسم التطبيق] > الأذونات > الأجهزة القريبة > السماح.
من المفترض الآن أن يكون قد تم استعادة إذن وصول تطبيقك إلى الشبكة المحلية، وأن تعمل جميع السيناريوهات كما كانت قبل منح التطبيق الإذن.
بعد بدء فرض حماية الشبكة المحلية، إليك تأثير ذلك في عدد الزيارات الواردة إلى شبكة التطبيق.
| الإذن | Outbound LAN Request | طلب الإنترنت الصادر/الوارد | طلب شبكة LAN وارد |
|---|---|---|---|
| تم منح الأذونات | Works | Works | Works |
| لم يتم المنح | الإخفاقات | Works | الإخفاقات |
استخدِم الأمر التالي لإيقاف علامة App-Compat
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
الأخطاء
سيتم عرض الأخطاء الناتجة عن هذه القيود في مقبس الاتصال الذي تم استدعاؤه عندما يستدعي الأمر send أو أحد متغيراته إلى عنوان شبكة محلية.
أمثلة على الأخطاء:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
تعريف الشبكة المحلية
تشير الشبكة المحلية في هذا المشروع إلى شبكة IP تستخدم واجهة شبكة متوافقة مع البث، مثل Wi-Fi أو إيثرنت، ولكنها تستبعد الاتصالات عبر شبكة الجوّال (WWAN) أو شبكة VPN.
تُعدّ الشبكات التالية شبكات محلية:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- المسارات المرتبطة مباشرةً
- شبكات الأجهزة الوهمية، مثل Thread
- الشبكات الفرعية المتعددة (يُحدَّد لاحقًا)
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يتم تصنيف كل من عناوين البث المتعدد (224.0.0.0/4 وff00::/8) وعنوان البث IPv4 (255.255.255.255) كعناوين شبكة محلية.
الصور التي يملكها التطبيق
When prompted for photo and video permissions by an app targeting SDK 36 or higher on devices running Android 16 or higher, users who choose to limit access to selected media will see any photos owned by the app pre-selected in the photo picker. Users can deselect any of these pre-selected items, which will revoke the app's access to those photos and videos.

