Android 16 introduce nuove fantastiche funzionalità e API per gli sviluppatori. Le sezioni seguenti riepilogano queste funzionalità per aiutarti a iniziare a utilizzare le API correlate.
Per un elenco dettagliato delle API nuove, modificate e rimosse, leggi il report diff API. Per informazioni dettagliate sulle nuove API, visita la documentazione di riferimento delle API Android. Le nuove API sono evidenziate per una maggiore visibilità.Devi anche esaminare le aree in cui le modifiche alla piattaforma potrebbero influire sulle tue app. Per maggiori informazioni, consulta le seguenti pagine:
- Modifiche al comportamento che interessano le app quando hanno come target Android 16
- Modifiche al comportamento che interessano tutte le app indipendentemente da
targetSdkVersion.
Funzionalità di base
Android include nuove API che espandono le funzionalità di base del sistema Android.
Due release dell'API Android nel 2025
- This preview is for the next major release of Android with a planned launch in Q2 of 2025. This release is similar to all of our API releases in the past, where we can have planned behavior changes that are often tied to a targetSdkVersion.
- We're planning the major release a quarter earlier (Q2 rather than Q3 in prior years) to better align with the schedule of device launches across our ecosystem, so more devices can get the major release of Android sooner. With the major release coming in Q2, you'll need to do your annual compatibility testing a few months earlier than in previous years to make sure your apps are ready.
- We plan to have another release in Q4 of 2025 which also will include new developer APIs. The Q2 major release will be the only release in 2025 to include planned behavior changes that could affect apps.
In addition to new developer APIs, the Q4 minor release will pick up feature updates, optimizations, and bug fixes; it will not include any app-impacting behavior changes.
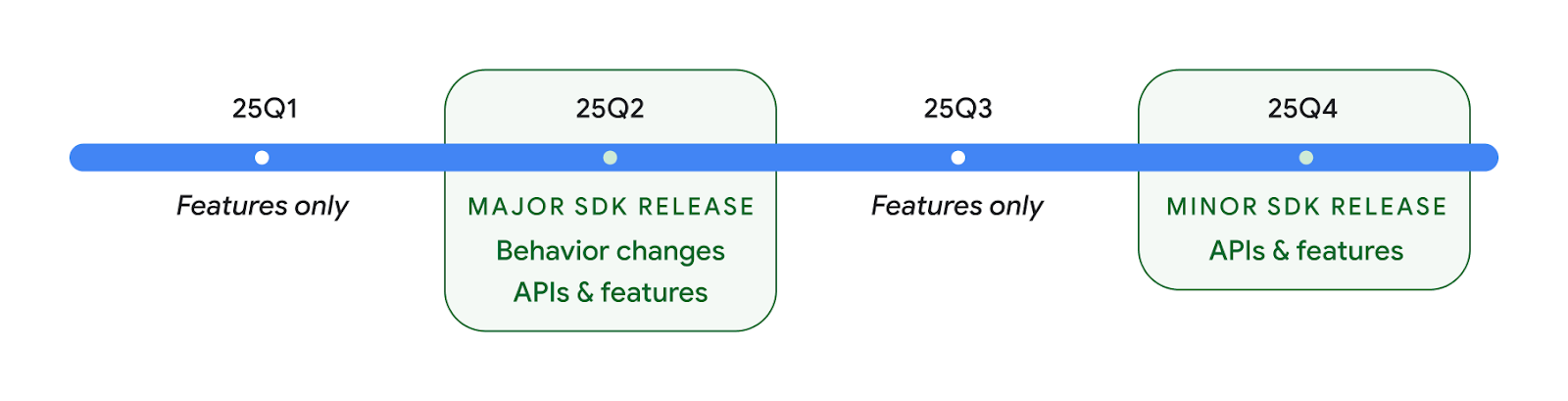
We'll continue to have quarterly Android releases. The Q1 and Q3 updates in-between the API releases will provide incremental updates to help ensure continuous quality. We're actively working with our device partners to bring the Q2 release to as many devices as possible.
Using new APIs with major and minor releases
Guarding a code block with a check for API level is done today using
the SDK_INT constant with
VERSION_CODES. This will continue
to be supported for major Android releases.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
The new SDK_INT_FULL
constant can be used for API checks against both major and minor versions with
the new VERSION_CODES_FULL
enumeration.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
You can also use the
Build.getMinorSdkVersion()
method to get just the minor SDK version.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
These APIs have not yet been finalized and are subject to change, so please send us feedback if you have any concerns.
Esperienza utente e UI di sistema
Android 16 offre a sviluppatori di app e utenti maggiore controllo e flessibilità per configurare il dispositivo in base alle proprie esigenze.
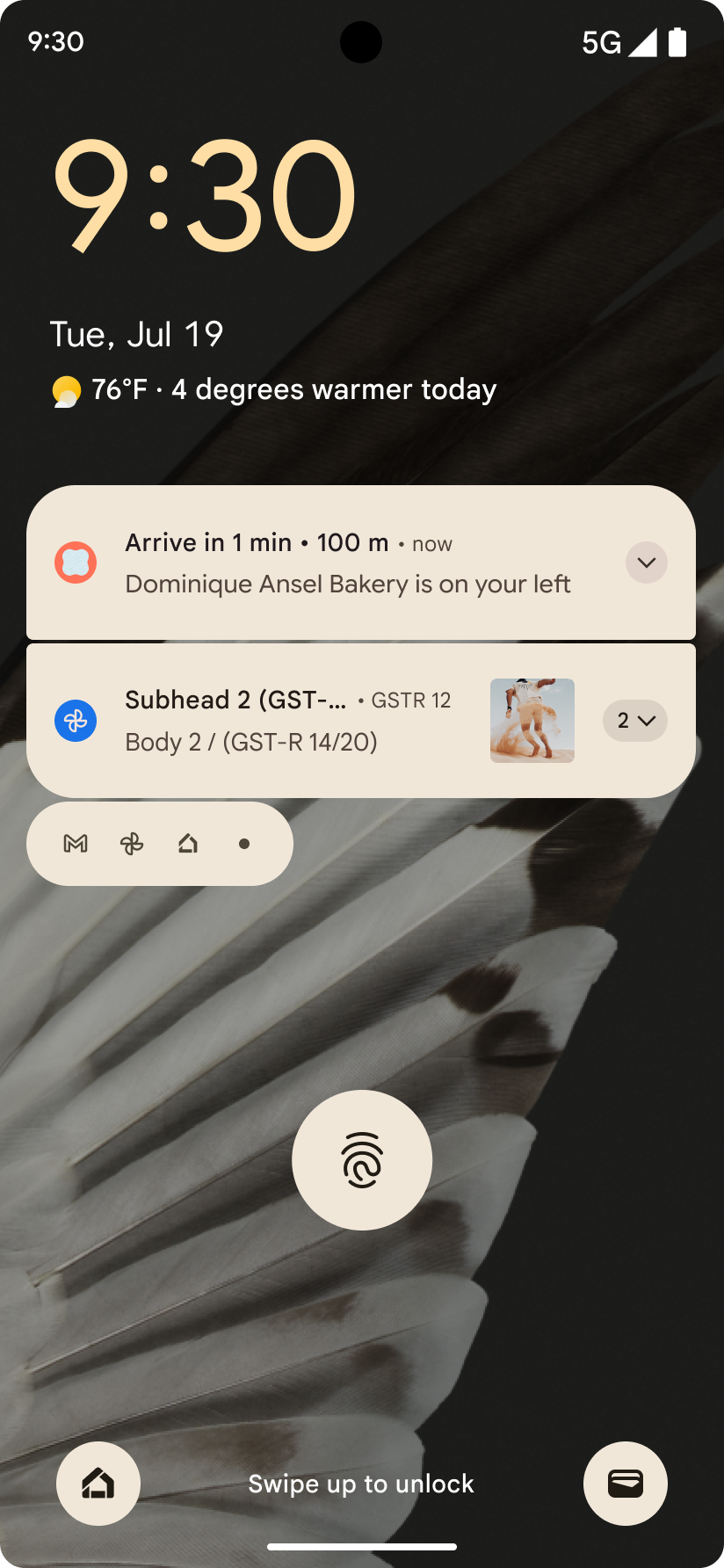
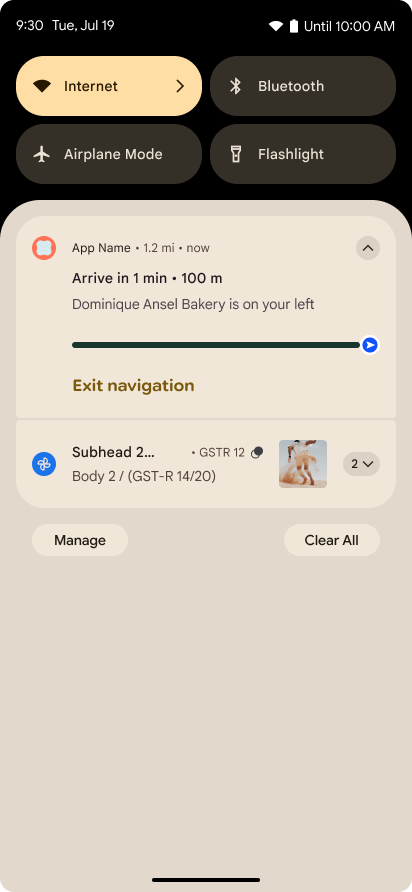
Notifiche incentrate sui progressi
Android 16 introduce notifiche incentrate sul progresso per aiutare gli utenti a monitorare senza problemi i percorsi end-to-end avviati dall'utente.
Notification.ProgressStyle è un nuovo stile di notifica che consente di creare notifiche incentrate sull'avanzamento. I casi d'uso principali includono condivisione di corse, consegna e navigazione. All'interno della classe Notification.ProgressStyle, puoi indicare gli stati e i traguardi di un percorso dell'utente utilizzando punti e segmenti.
To learn more, see the Progress-centric notifications documentation page.
Aggiornamenti di Indietro predittivo
Android 16 adds new APIs to help you enable predictive back system animations in
gesture navigation such as the back-to-home animation. Registering the
onBackInvokedCallback with the new
PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER allows your app to
receive the regular onBackInvoked call whenever the
system handles a back navigation without impacting the normal back navigation
flow.
Android 16 additionally adds the
finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() and
moveTaskToBackCallback. By registering these callbacks
with the OnBackInvokedDispatcher, the system can trigger
specific behaviors and play corresponding ahead-of-time animations when the back
gesture is invoked.
Feedback aptico più ricco
Android has exposed control over the haptic actuator ever since its inception.
Android 11 added support for more complex haptic effects that more advanced
actuators could support through
VibrationEffect.Compositions of device-defined semantic
primitives.
Android 16 adds haptic APIs that let apps define the amplitude and frequency curves of a haptic effect while abstracting away differences between device capabilities.
Produttività e strumenti per gli sviluppatori
La maggior parte del nostro lavoro per migliorare la tua produttività si concentra su strumenti come Android Studio, Jetpack Compose e le librerie Android Jetpack, ma cerchiamo sempre modi nella piattaforma per aiutarti a realizzare la tua visione.
Gestione dei contenuti per gli sfondi animati
In Android 16, il framework degli sfondi animati acquisirà una nuova API per i contenuti per rispondere alle sfide degli sfondi dinamici basati sugli utenti. Al momento, gli sfondi animati che incorporano contenuti forniti dagli utenti richiedono implementazioni complesse e specifiche per i servizi. Android 16 introduce
WallpaperDescription e
WallpaperInstance. WallpaperDescription consente di identificare istanze distinte di uno sfondo animato dello stesso servizio. Ad esempio, uno sfondo che ha istanze sia nella schermata Home sia nella schermata di blocco può avere contenuti unici in entrambe le posizioni. Il selettore di sfondi e
WallpaperManager utilizzano questi metadati per presentare meglio
gli sfondi agli utenti, semplificando la procedura per creare esperienze diverse e personalizzate con gli sfondi animati.
Prestazioni e batteria
Android 16 introduce API che aiutano a raccogliere informazioni sulle tue app.
Profilazione attivata dal sistema
ProfilingManager was
added in Android 15, giving apps the ability to
request profiling data collection using Perfetto on public devices in the field.
However, since this profiling must be started from the app, critical flows such
as startups or ANRs would be difficult or impossible for apps to capture.
To help with this, Android 16 introduces system-triggered profiling to
ProfilingManager. Apps can register interest in receiving traces for certain
triggers such as cold start reportFullyDrawn
or ANRs, and then the system starts and stops a trace on the app's behalf. After
the trace completes, the results are delivered to the app's data directory.
Avvia componente in ApplicationStartInfo
ApplicationStartInfo was added in Android
15, allowing an app to see reasons
for process start, start type, start times, throttling, and other useful
diagnostic data. Android 16 adds
getStartComponent()
to distinguish what component type triggered the start, which can be helpful for
optimizing the startup flow of your app.
Migliore introspezione dei job
The JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API returns a reason why a job
might be pending. However, a job might be pending for multiple reasons.
In Android 16, we are introducing a new API
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId), which returns multiple
reasons why a job is pending, due to both explicit constraints set by the
developer and implicit constraints set by the system.
We're also introducing
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId), which returns a list
of the most recent constraint changes.
We recommend using the API to help you debug why your jobs may not be executing, especially if you're seeing reduced success rates of certain tasks or have bugs around latency of certain job completion. For example, updating widgets in the background failed to occur or prefetch job failed to be called prior to app start.
This can also better help you understand if certain jobs are not completing due to system defined constraints versus explicitly set constraints.
Frequenza di aggiornamento adattiva
Adaptive refresh rate (ARR), introduced in Android 15, enables the display refresh rate on supported hardware to adapt to the content frame rate using discrete VSync steps. This reduces power consumption while eliminating the need for potentially jank-inducing mode-switching.
Android 16 introduces hasArrSupport() and
getSuggestedFrameRate(int) while restoring
getSupportedRefreshRates() to make it easier for your apps to take
advantage of ARR. RecyclerView
1.4 internally supports ARR when it is settling from a fling or
smooth scroll, and we're continuing our work to add ARR
support into more Jetpack libraries. This frame rate article covers
many of the APIs you can use to set the frame rate so that your app can directly
use ARR.
API Headroom in ADPF
The SystemHealthManager introduces the
getCpuHeadroom and
getGpuHeadroom APIs, designed to provide games and
resource-intensive apps with estimates of available CPU and GPU resources. These
methods offer a way for you to gauge how your app or game can best improve
system health, particularly when used in conjunction with other Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF) APIs that detect thermal
throttling.
By using CpuHeadroomParams and
GpuHeadroomParams on supported devices, you can
customize the time window used to compute the headroom and select between
average or minimum resource availability. This can help you reduce your CPU or
GPU resource usage accordingly, leading to better user experiences and improved
battery life.
Accessibilità
Android 16 aggiunge nuove API e funzionalità di accessibilità che possono aiutarti a rendere la tua app disponibile per tutti gli utenti.
API di accessibilità migliorate
Android 16 adds additional APIs to enhance UI semantics that help improve consistency for users that rely on accessibility services, such as TalkBack.
Outline text for maximum text contrast
Users with low vision often have reduced contrast sensitivity, making it challenging to distinguish objects from their backgrounds. To help these users, Android 16 introduces outline text, replacing high contrast text, which draws a larger contrasting area around text to greatly improve legibility.
Android 16 contains new AccessibilityManager APIs to let
your apps check or register a listener to
see if this mode is enabled. This is primarily for UI Toolkits like Compose to
offer a similar visual experience. If you maintain a UI Toolkit library or your
app performs custom text rendering that bypasses the
android.text.Layout class then you can use this to know
when outline text is enabled.
Duration added to TtsSpan
Android 16 extends TtsSpan with a TYPE_DURATION,
consisting of ARG_HOURS, ARG_MINUTES,
and ARG_SECONDS. This lets you directly annotate time
duration, ensuring accurate and consistent text-to-speech output with services
like TalkBack.
Support elements with multiple labels
Android currently allows UI elements to derive their accessibility label from
another, and now offers the ability for multiple labels to be associated, a
common scenario in web content. By introducing a list-based API within
AccessibilityNodeInfo, Android can directly support these
multi-label relationships. As part of this change, we've deprecated
AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy and
#getLabeledBy in favor of
#addLabeledBy, #removeLabeledBy, and
#getLabeledByList.
Improved support for expandable elements
Android 16 adds accessibility APIs that allow you to convey the expanded or
collapsed state of interactive elements, such as menus and expandable lists. By
setting the expanded state using setExpandedState and
dispatching TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents
with a CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED content change type,
you can ensure that screen readers like TalkBack announce
state changes, providing a more intuitive and inclusive user experience.
Indeterminate ProgressBars
Android 16 adds RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE, giving a way for
you to expose RangeInfo for both determinate and
indeterminate ProgressBar widgets, allowing services like
TalkBack to more consistently provide feedback for progress
indicators.
Tri-state CheckBox
The new AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked and setChecked(int)
methods in Android 16 now support a "partially checked" state in addition to
"checked" and "unchecked." This replaces the deprecated boolean
isChecked and setChecked(boolean).
Supplemental descriptions
When an accessibility service describes a ViewGroup, it
combines content labels from its child views. If you provide a
contentDescription for the ViewGroup, accessibility services assume you are
also overriding the description of non-focusable child views. This can be
problematic if you want to label things like a drop-down (for example, "Font
Family") while preserving the current selection for accessibility (for example,
"Roboto"). Android 16 adds setSupplementalDescription so
you can provide text that provides information about a ViewGroup without
overriding information from its children.
Required form fields
Android 16 adds setFieldRequired to
AccessibilityNodeInfo so apps can tell an accessibility
service that input to a form field is required. This is an important scenario
for users filling out many types of forms, even things as simple as a required
terms and conditions checkbox, helping users to consistently identify and
quickly navigate between required fields.
Smartphone come input del microfono per le chiamate vocali con apparecchi acustici LEA
Android 16 consente agli utenti di apparecchi acustici LE Audio di passare tra i microfoni integrati sugli apparecchi acustici e il microfono sullo smartphone per le chiamate vocali. Questa opzione può essere utile in ambienti rumorosi o in altre situazioni in cui i microfoni dell'apparecchio acustico potrebbero non funzionare bene.
Controlli del volume ambientale per apparecchi acustici LEA
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to adjust the volume of ambient sound that is picked up by the hearing aid's microphones. This can be helpful in situations where background noise is too loud or too quiet.
Fotocamera
Android 16 migliora il supporto per gli utenti di fotocamere professionali, consentendo l'esposizione automatica ibrida insieme a regolazioni precise di tinta e temperatura di colore. Un nuovo
indicatore della modalità notturna aiuta l'app a sapere quando passare a una sessione della fotocamera in modalità notturna e viceversa. Le nuove azioni Intent semplificano l'acquisizione di foto in movimento
e continuiamo a migliorare le immagini Ultra HDR con il supporto della codifica HEIC
e di nuovi parametri dello standard ISO 21496-1.
Esposizione automatica ibrida
Android 16 aggiunge nuove modalità di esposizione automatica ibrida a Camera2, consentendo di controllare manualmente aspetti specifici dell'esposizione lasciando che sia l'algoritmo di esposizione automatica (AE) a gestire il resto. Puoi controllare ISO + AE e tempo di esposizione + AE, offrendo una maggiore flessibilità rispetto all'approccio attuale in cui hai il controllo manuale completo o ti basi interamente sull'esposizione automatica.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
Regolazioni precise di tinta e temperatura di colore
Android 16 adds camera support for fine color temperature and tint adjustments
to better support professional video recording applications. In previous Android
versions, you could control white balance settings through
CONTROL_AWB_MODE, which contains options limited to a
preset list, such as Incandescent,
Cloudy, and Twilight. The
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT enables the use of
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE and
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT for precise adjustments of
white balance based on the correlated color temperature.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
The following examples show how a photo would look after applying different color temperature and tint adjustments:





Rilevamento della scena in modalità notturna della fotocamera
To help your app know when to switch to and from a night mode camera session,
Android 16 adds EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. If
supported, it's available in the CaptureResult within
Camera2.
This is the API we briefly mentioned as coming soon in the How Instagram enabled users to take stunning low light photos blog post. That post is a practical guide on how to implement night mode together with a case study that links higher-quality in-app night mode photos with an increase in the number of photos shared from the in-app camera.
Azioni intent di acquisizione di foto in movimento
Android 16 adds standard Intent actions —
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE, and
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE — which request that
the camera application capture a motion photo and return
it.
You must either pass an extra EXTRA_OUTPUT to control
where the image will be written, or a Uri through
Intent.setClipData(ClipData). If you don't set a
ClipData, it will be copied there for you when calling
Context.startActivity(Intent).
Miglioramenti delle immagini UltraHDR

Android 16 continues our work to deliver dazzling image quality with UltraHDR
images. It adds support for UltraHDR images in the HEIC file
format. These images will get ImageFormat type
HEIC_ULTRAHDR and will contain an embedded gainmap similar
to the existing UltraHDR JPEG format. We're working on AVIF support for UltraHDR
as well, so stay tuned.
In addition, Android 16 implements additional parameters in UltraHDR from the ISO 21496-1 draft standard, including the ability to get and set the colorspace that gainmap math should be applied in, as well as support for HDR encoded base images with SDR gainmaps.
Grafica
Android 16 include i più recenti miglioramenti grafici, come gli effetti grafici personalizzati con AGSL.
Effetti grafici personalizzati con AGSL
Android 16 aggiunge RuntimeColorFilter e
RuntimeXfermode, che ti consentono di creare effetti complessi come
Soglia, Seppia e Saturazione tonalità e applicarli alle chiamate di disegno. Da Android
13, puoi utilizzare AGSL per creare personalizzati
RuntimeShaders che estendono Shader. La nuova API riflette questo approccio, aggiungendo un RuntimeColorFilter basato su AGSL che estende ColorFilter e un effetto Xfermode che consente di implementare il compositing e l'unione personalizzati basati su AGSL tra i pixel di origine e di destinazione.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
Connettività
Android 16 aggiorna la piattaforma per consentire alla tua app di accedere agli ultimi progressi nelle tecnologie di comunicazione e wireless.
Rilevamento con sicurezza avanzata
Android 16 adds support for robust security features in Wi-Fi location on supported devices with Wi-Fi 6's 802.11az, allowing apps to combine the higher accuracy, greater scalability, and dynamic scheduling of the protocol with security enhancements including AES-256-based encryption and protection against MITM attacks. This allows it to be used more safely in proximity use cases, such as unlocking a laptop or a vehicle door. 802.11az is integrated with the Wi-Fi 6 standard, leveraging its infrastructure and capabilities for wider adoption and easier deployment.
API di misurazione generiche
Android 16 includes the new RangingManager, which provides
ways to determine the distance and angle on supported hardware between the local
device and a remote device. RangingManager supports the usage of a variety of
ranging technologies such as BLE channel sounding, BLE RSSI-based ranging, Ultra
Wideband, and Wi-Fi round trip time.
Presenza del dispositivo Gestione dispositivi companion
In Android 16, new APIs are being introduced for binding your companion app
service. Service will be bound when BLE is in range and Bluetooth is connected
and service will be unbound when BLE is out of range or Bluetooth is
disconnected. App will receives a new
'onDevicePresenceEvent()' callback based on various
of DevicePresenceEvent.
More details can be found in
'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'.
Media
Android 16 include una serie di funzionalità che migliorano l'esperienza multimediale.
Miglioramenti al selettore di foto
The photo picker provides a safe, built-in way for users to grant your app access to selected images and videos from both local and cloud storage, instead of their entire media library. Using a combination of Modular System Components through Google System Updates and Google Play services, it's supported back to Android 4.4 (API level 19). Integration requires just a few lines of code with the associated Android Jetpack library.
Android 16 includes the following improvements to the photo picker:
- Embedded photo picker: New APIs that enable apps to embed the photo picker into their view hierarchy. This allows it to feel like a more integrated part of the app while still leveraging the process isolation that allows users to select media without the app needing overly broad permissions. To maximize compatibility across platform versions and simplify your integration, you'll want to use the forthcoming Android Jetpack library if you want to integrate the embedded photo picker.
- Cloud search in photo picker: New APIs that enable searching from the cloud media provider for the Android photo picker. Search functionality in the photo picker is coming soon.
Video professionale avanzato
Android 16 introduces support for the Advanced Professional Video (APV) codec which is designed to be used for professional level high quality video recording and post production.
The APV codec standard has the following features:
- Perceptually lossless video quality (close to raw video quality)
- Low complexity and high throughput intra-frame-only coding (without pixel domain prediction) to better support editing workflows
- Support for high bit-rate range up to a few Gbps for 2K, 4K and 8K resolution content, enabled by a lightweight entropy coding scheme
- Frame tiling for immersive content and for enabling parallel encoding and decoding
- Support for various chroma sampling formats and bit-depths
- Support for multiple decoding and re-encoding without severe visual quality degradation
- Support multi-view video and auxiliary video like depth, alpha, and preview
- Support for HDR10/10+ and user-defined metadata
A reference implementation of APV is provided through the OpenAPV project. Android 16 will implement support for the APV 422-10 Profile that provides YUV 422 color sampling along with 10-bit encoding and for target bitrates of up to 2Gbps.
Privacy
Android 16 include una serie di funzionalità che aiutano gli sviluppatori di app a proteggere la privacy degli utenti.
Aggiornamenti di Connessione Salute
Health Connect adds ACTIVITY_INTENSITY, a data type defined according to World
Health Organization guidelines around moderate and vigorous activity. Each
record requires the start time, the end time, and whether the activity intensity
is moderate or vigorous.
Health Connect also contains updated APIs supporting medical records. This allows apps to read and write medical records in FHIR format with explicit user consent.
Privacy Sandbox su Android
Android 16 integra la versione più recente di Privacy Sandbox su Android, nell'ambito del nostro impegno continuo per sviluppare tecnologie in cui gli utenti sanno che la loro privacy è protetta. Sul nostro sito web puoi trovare ulteriori informazioni sul Programma beta per sviluppatori di Privacy Sandbox su Android per iniziare. Dai un'occhiata a SDK Runtime che consente agli SDK di essere eseguiti in un ambiente di runtime dedicato separato dall' app che stanno pubblicando, offrendo misure di salvaguardia più efficaci per la raccolta e la condivisione dei dati utente.
Sicurezza
Android 16 include funzionalità che ti aiutano a migliorare la sicurezza della tua app e a proteggere i dati dell'app.
API per la condivisione delle chiavi
Android 16 aggiunge API che supportano la condivisione dell'accesso alle chiavi del Keystore di Android con altre app. La nuova classe
KeyStoreManager supporta la concessione e la revoca dell'accesso alle chiavi
in base all'uid dell'app e include un'API per consentire alle app di accedere alle chiavi
condivise.
Fattori di forma dei dispositivi
Android 16 offre alle tue app il supporto per sfruttare al meglio i fattori di forma di Android.
Framework standardizzato per la qualità audio e video delle TV
Il nuovo MediaQuality
package in Android 16 espone
un insieme di API standardizzate per l'accesso ai profili audio e di immagini e alle
impostazioni relative all'hardware. In questo modo, le app di streaming possono eseguire query sui profili e applicarli ai contenuti multimediali in modo dinamico:
- I film masterizzati con una gamma dinamica più ampia richiedono una maggiore accuratezza del colore per vedere dettagli sottili nelle ombre e adattarsi alla luce ambientale, pertanto potrebbe essere appropriato un profilo che preferisca l'accuratezza del colore alla luminosità.
- Gli eventi sportivi dal vivo vengono spesso masterizzati con una gamma dinamica ristretta, ma spesso vengono guardati alla luce del giorno, quindi un profilo che preferisce la luminosità all'accuratezza del colore può dare risultati migliori.
- I contenuti completamente interattivi richiedono un'elaborazione minima per ridurre la latenza e una frequenza frame più elevata, motivo per cui molte TV sono dotate di un profilo di gioco.
L'API consente alle app di passare da un profilo all'altro e agli utenti di regolare le TV supportate in base ai loro contenuti.
Internazionalizzazione
Android 16 aggiunge funzionalità e capacità che completano l'esperienza utente quando un dispositivo viene utilizzato in lingue diverse.
Testo verticale
Android 16 adds low-level support for rendering and measuring text vertically to
provide foundational vertical writing support for library developers. This is
particularly useful for languages like Japanese that commonly use vertical
writing systems. A new flag,
VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG,
has been added to the Paint class. When
this flag is set using
Paint.setFlags, Paint's
text measurement APIs will report vertical advances instead of horizontal
advances, and Canvas will draw text
vertically.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
Personalizzazione del sistema di misurazione
Users can now customize their measurement system in regional preferences within
Settings. The user preference is included as part of the locale code, so you can
register a BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED to handle locale configuration changes when
regional preferences change.
Using formatters can help match the local experience. For example, "0.5 in" in English (United States), is "12,7 mm" for a user who has set their phone to English (Denmark) or who uses their phone in English (United States) with the metric system as the measurement system preference.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & region.
