After you've added a 3D model to your app, you can enhance the visual experience by defining custom material properties and applying textures to the object. Jetpack XR's material system is based on the glTF™ 2.0 specification, and 3D models are rendered using physically-based rendering (PBR). These are open standards maintained by the Khronos Group.
Material attributes can be adjusted during runtime to change an object's appearance dynamically based on user input or the current state of the app.
For details about each supported property and the customizable parameters in Android XR, see our reference documentation. To better understand these properties, see the Khronos glossary.
Customize the material properties of your 3D model
A Material defines a set of visual properties for an object's surface and
determines how that surface interacts with light in the scene.
In Jetpack XR, the KhronosPbrMaterial and KhronosUnlitMaterial
classes are used to create and manipulate these materials. As the name implies,
KhronosUnlitMaterials are unlit and not impacted by scene
lighting. KhronosPbrMaterial lets you customize a wider range of
properties, such as sheen color, how metallic or rough an object is, and whether
it emits light.
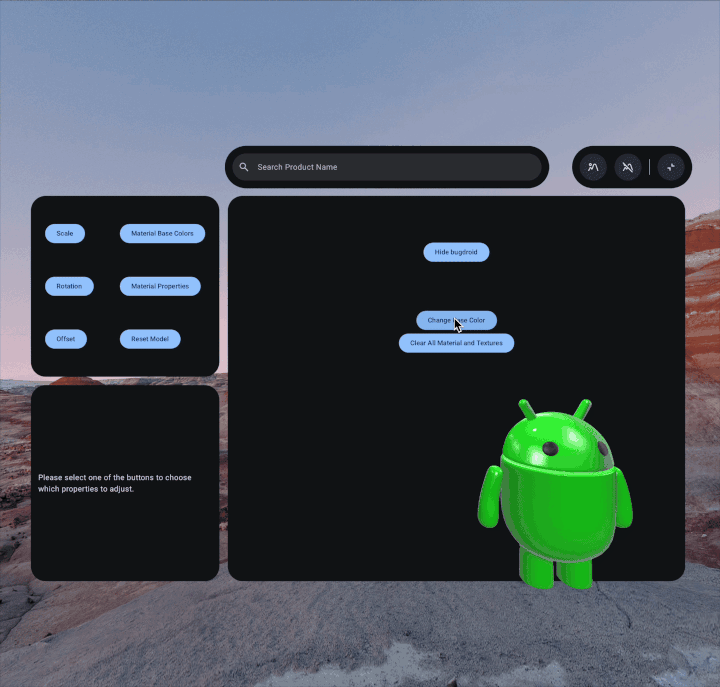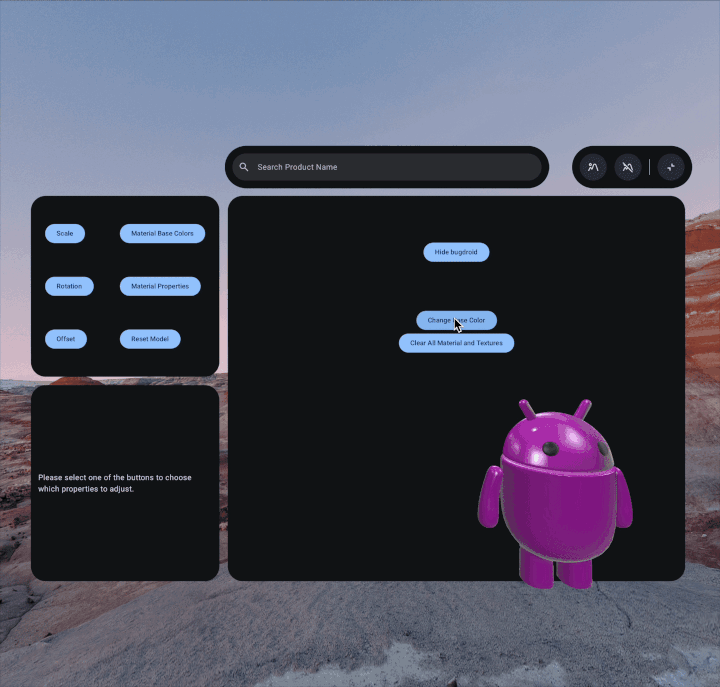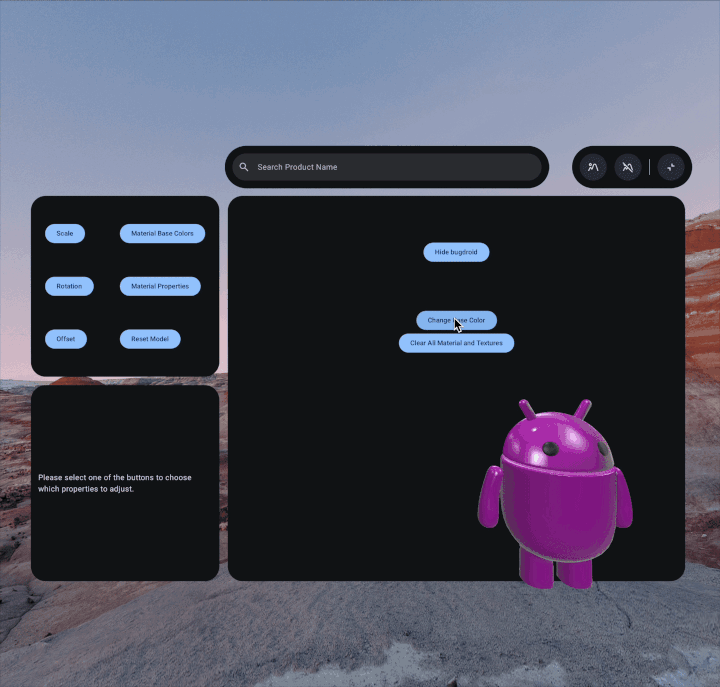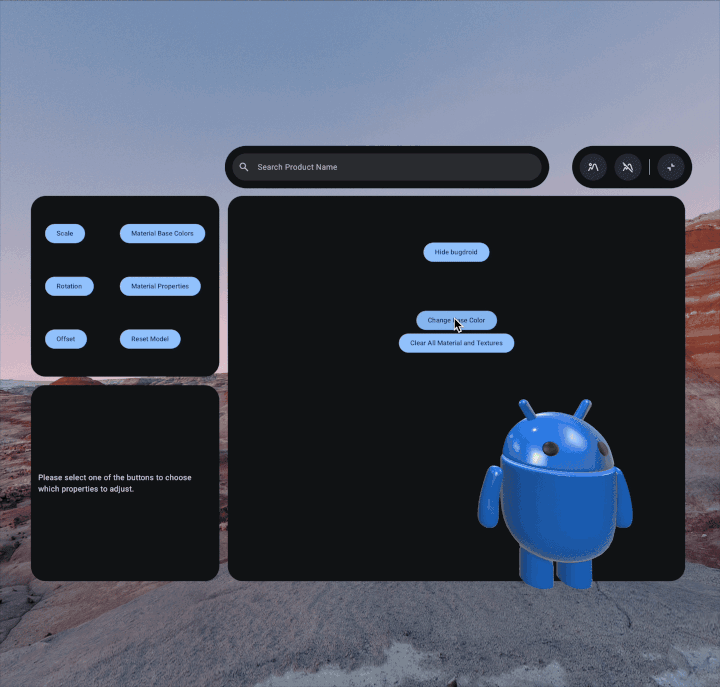
To customize the material properties of your 3D model, first you'll create the
new material using KhronosPbrMaterial. You'll need to set the appropriate
AlphaMode for the visual appearance you are trying to achieve:
val pbrMaterial = KhronosPbrMaterial.create( session = xrSession, alphaMode = AlphaMode.OPAQUE )
Next, define the properties you want to modify. In this example, we use
setBaseColorFactor to change the base color. This method requires a
Vector4, where the x, y, z, and w components correspond to the RGBA
(Red, Green, Blue, and Alpha) values respectively:
pbrMaterial.setBaseColorFactor( Vector4( x = 0.5f, y = 0.0f, z = 0.5f, w = 0.0f ) )
Create custom textures for your 3D model
A Texture is an image asset that you can apply to the surface of a 3D
model to provide color, detail, or other surface information. The Jetpack XR
Texture API lets you load image data, such as PNG files, from your app's
/assets/ folder asynchronously.
When loading a texture, you can specify a TextureSampler, which controls
how the texture is rendered. The sampler defines filtering properties (for when
the texture appears smaller or larger than its original size) and wrapping modes
(for handling coordinates outside the standard [0, 1] range).
A Texture object by itself is just data; it must be assigned to a Material
to have a visual effect on a 3D model.
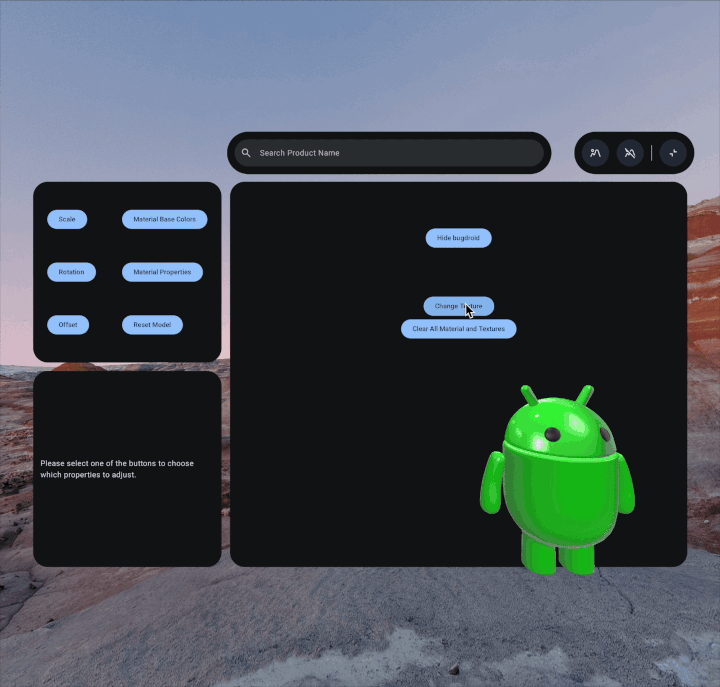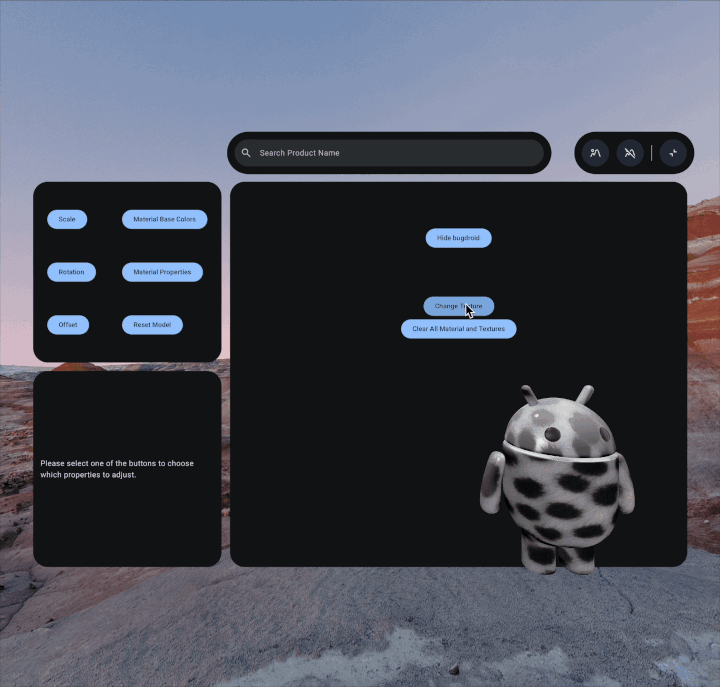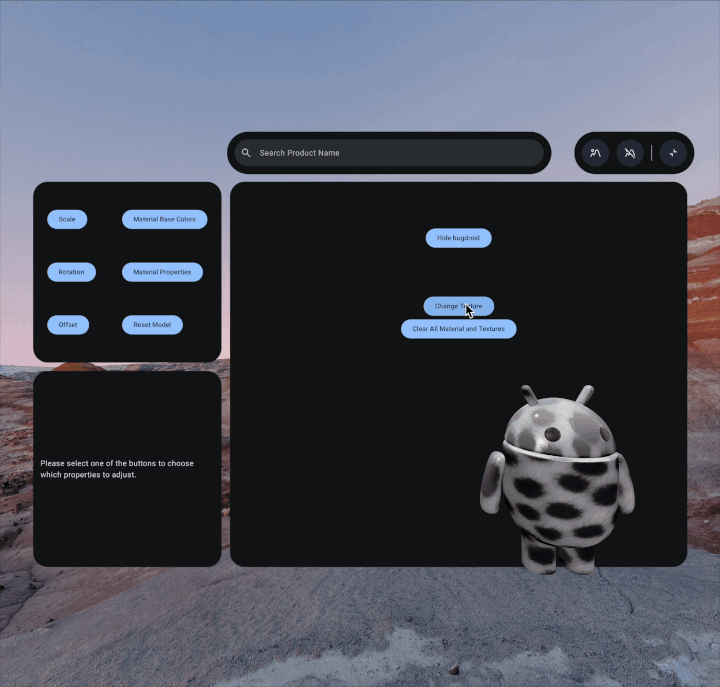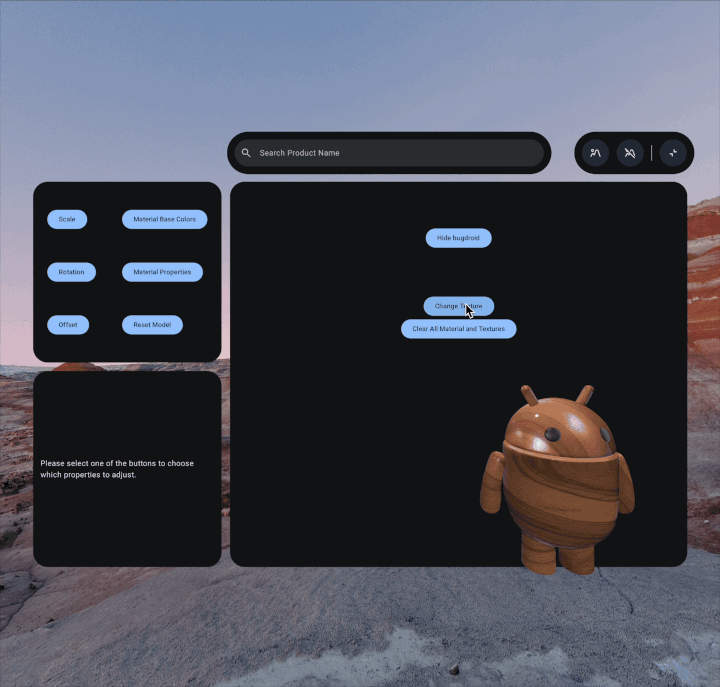
To create a custom texture, first you'll need to save the image file to your
/assets/ folder. As a best practice, you may want to create a textures
subdirectory in that folder as well.
After you've saved the file in the appropriate directory, create the texture
with the Texture API. This is also where you would apply an optional
TextureSampler if needed:
val texture = Texture.create( session = xrSession, path = Path("textures/texture_file.png") )
Next, define the type of texture and set its corresponding parameters. In this example, we apply an occlusion texture and set the strength:
pbrMaterial.setOcclusionTexture( texture = texture, strength = 1.0f )
Apply materials and textures to your 3D objects
To apply the new material or texture, override the existing material for a
specific node on your glTF entity. Do this by calling
setMaterialOverride on the GltfModelEntity:
gltfModelEntity.setMaterialOverride( material = pbrMaterial, nodeName = "Node Name" )
To remove the newly-created materials, call clearMaterialOverride on
the previously overridden node on your GltfModelEntity. This returns
your 3D Model to its default state:
gltfModelEntity.clearMaterialOverride( nodeName = "Node Name" )
glTF and the glTF logo are trademarks of the Khronos Group Inc.


