Before your app can communicate over Bluetooth or Bluetooth Low Energy,
you need to verify that Bluetooth is supported on the device, and if it is,
ensure that it is enabled. Note that this check is only necessary if the
android:required attribute in the <uses-feature.../> manifest file entry is
set to false.
If Bluetooth isn't supported, then you should gracefully disable any Bluetooth features. If Bluetooth is supported, but disabled, then you can request that the user enable Bluetooth without leaving your app.
The first step is adding the Bluetooth permissions to your manifest file in order to use the following APIs.
Once the permissions are in place, Bluetooth setup is accomplished in two steps
using the BluetoothAdapter:
Get the
BluetoothAdapter.The
BluetoothAdapteris required for any and all Bluetooth activity. TheBluetoothAdapterrepresents the device's own Bluetooth adapter (the Bluetooth radio). To get aBluetoothAdapter, you first need to have aContext. Use this context to obtain an instance of theBluetoothManagersystem service. CallingBluetoothManager#getAdapterwill give you aBluetoothAdapterobject. IfgetAdapter()returns null, then the device doesn't support Bluetooth.For example:
Kotlin
val bluetoothManager: BluetoothManager = getSystemService(BluetoothManager::class.java) val bluetoothAdapter: BluetoothAdapter? = bluetoothManager.getAdapter() if (bluetoothAdapter == null) { // Device doesn't support Bluetooth }
Java
BluetoothManager bluetoothManager = getSystemService(BluetoothManager.class); BluetoothAdapter bluetoothAdapter = bluetoothManager.getAdapter(); if (bluetoothAdapter == null) { // Device doesn't support Bluetooth }
Enable Bluetooth.
Next, you need to ensure that Bluetooth is enabled. Call
isEnabled()to check whether Bluetooth is currently enabled. If this method returns false, then Bluetooth is disabled. To request that Bluetooth be enabled, callstartActivityForResult(), passing in anACTION_REQUEST_ENABLEintent action. This call issues a request to enable Bluetooth through the system settings (without stopping your app).For example:
Kotlin
if (bluetoothAdapter?.isEnabled == false) { val enableBtIntent = Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE) startActivityForResult(enableBtIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT) }
Java
if (!bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) { Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE); startActivityForResult(enableBtIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT); }
A dialog appears requesting user permission to enable Bluetooth, as shown in figure 1. If the user grants permission, the system begins to enable Bluetooth, and focus returns to your app once the process completes (or fails).
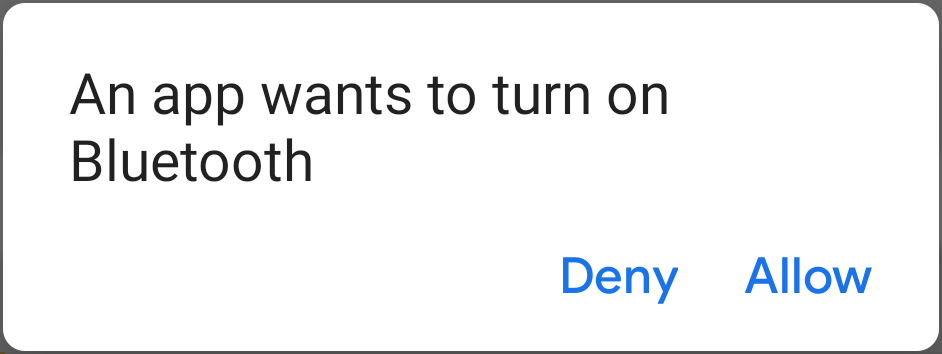
Figure 1. The enabling Bluetooth dialog.
The REQUEST_ENABLE_BT constant passed to
startActivityForResult()
is a locally-defined integer that must be greater than or equal to 0. The system
passes this constant back to you in your
onActivityResult()
implementation as the requestCode parameter.
If enabling Bluetooth succeeds, your activity receives the
RESULT_OK result code in the
onActivityResult() callback. If Bluetooth was not enabled due to an error (or
the user responded "Deny") then the result code is
RESULT_CANCELED.
Optionally, your app can also listen for the
ACTION_STATE_CHANGED
broadcast intent, which the system broadcasts whenever the Bluetooth state
changes. This broadcast contains the extra fields
EXTRA_STATE and
EXTRA_PREVIOUS_STATE,
containing the new and old Bluetooth states, respectively. Possible values for
these extra fields are
STATE_TURNING_ON,
STATE_ON,
STATE_TURNING_OFF,
and STATE_OFF.
Listening for this broadcast can be useful if your app needs to detect runtime
changes made to the Bluetooth state.
Once Bluetooth is enabled on the device, you can use both Bluetooth classic and Bluetooth Low Energy.
For Bluetooth classic, you can find Bluetooth devices and connect to Bluetooth devices.
For Bluetooth Low Energy, you can find BLE devices, connect to a GATT server, and transfer BLE data.
