Android-powered devices with SIM cards and eSIMs use the following IDs in the telephony
APIs, including
TelephonyManager and
SubscriptionManager:
- Subscription ID: unique ID for a mobile subscription.
- Logical slot index or ID: unique index referring to a logical SIM slot. Logical slot IDs start at 0 and go up depending on the number of supported active slots on a device. For example, a dual-SIM device typically has slot 0 and slot 1. If a device has multiple physical slots but only supports one active slot, it will have only the logical slot ID 0.
- Physical slot index or ID: unique index referring to a physical SIM slot. Physical slot IDs start at 0 and go up depending on the number of physical slots on the device. This differs from the number of logical slots a device has, which corresponds to the number of active slots a device is capable of using. For example, a device which switches between dual-SIM and single-SIM mode may always have two physical slots, but in single-SIM mode it will have only one logical slot.
- Card ID: unique ID used to identify a UiccCard.
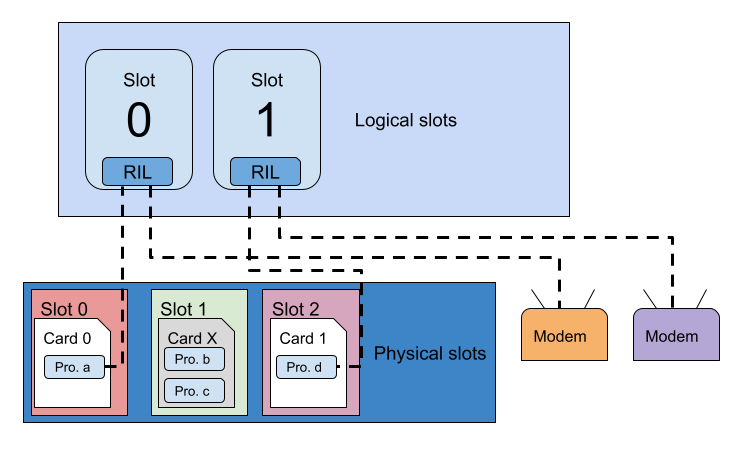
In the preceding diagram:
- The device has two logical slots.
- In physical slot 0 there is a physical UICC card with an active profile.
- In physical slot 2 is an eUICC with an active profile.
- Physical slot 1 is not currently in use.
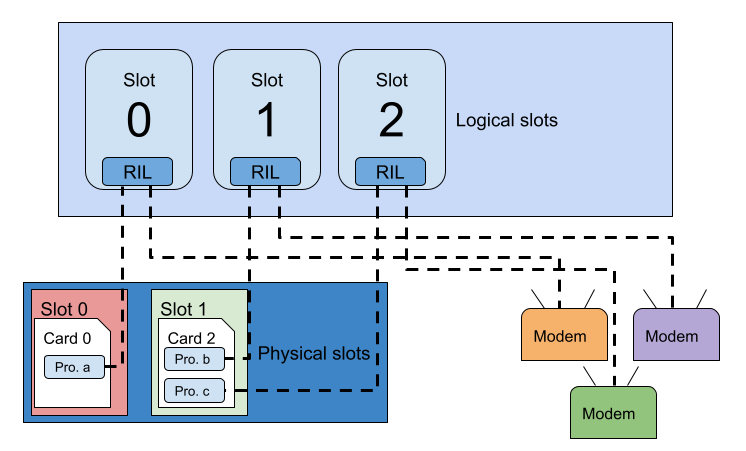
In the preceding diagram:
- The device has three logical slots.
- In physical slot 0 there is a physical UICC card with an active profile.
- In physical slot 1 is an eUICC that has two downloaded profiles, both active using MEP (Multiple Enabled Profiles).
Open Mobile API (OMAPI) reader support
On Android 11 and higher, Open Mobile API (OMAPI) supports checking for eSE, SD, and UICC support hardware on devices with the following flags:
Use these values with
getSystemAvailableFeatures()
or
hasSystemFeature()
to check for device support.
