เช่นเดียวกับรุ่นก่อนๆ Android 16 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้จะมีผลกับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ขึ้นไปเท่านั้น หากแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ขึ้นไป คุณควรแก้ไขแอปให้รองรับลักษณะการทำงานเหล่านี้ในกรณีที่เกี่ยวข้อง
นอกจากนี้ โปรดตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่มีผลกับแอปทั้งหมด
ที่ทำงานบน Android 16 ไม่ว่า targetSdkVersion ของแอปจะเป็นอย่างไร
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งมีจุดประสงค์ เพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกันและใช้งานง่ายยิ่งขึ้น
การเลือกไม่ใช้แบบไร้ขอบจะสิ้นสุดลง
Android 15 enforced edge-to-edge for apps targeting Android 15 (API
level 35), but your app could opt-out by setting
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement to true. For apps
targeting Android 16 (API level 36),
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement is deprecated and disabled, and your
app can't opt-out of going edge-to-edge.
- If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 15 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementcontinues to work. - If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 16 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementis disabled.
For testing in Android 16, ensure your app supports edge-to-edge and
remove any use of R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement so that your app
also supports edge-to-edge on an Android 15 device. To support edge-to-edge,
see the Compose and Views guidance.
ต้องย้ายข้อมูลหรือเลือกไม่ใช้เพื่อใช้การคาดการณ์การย้อนกลับ
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher and running on an
Android 16 or higher device, the predictive back system animations
(back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity) are enabled by default.
Additionally, onBackPressed is not called and
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK is not dispatched anymore.
If your app intercepts the back event and you haven't migrated to predictive
back yet, update your app to use supported back navigation APIs, or
temporarily opt out by setting the
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback attribute to false in the
<application> or <activity> tag of your app's AndroidManifest.xml file.
เลิกใช้งานและปิดใช้ Elegant Font API
แอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) จะมีแอตทริบิวต์
elegantTextHeight
TextView ตั้งค่าเป็น true โดยค่าเริ่มต้น ซึ่งจะแทนที่แบบอักษรแบบย่อด้วยแบบอักษรที่อ่านง่ายกว่ามาก คุณลบล้างค่านี้ได้โดยตั้งค่าแอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight เป็น false
Android 16 จะเลิกใช้งานแอตทริบิวต์
elegantTextHeight
และระบบจะละเว้นแอตทริบิวต์เมื่อแอปกำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 เราจะเลิกใช้ "UI
fonts" ที่ควบคุมโดย API เหล่านี้ ดังนั้นคุณควรปรับเลย์เอาต์ใดๆ เพื่อให้การแสดงข้อความในภาษาอาหรับ ลาว เมียนมาร์ ทมิฬ คุชราต กันนาดา มาลายาลัม โอเดีย เตลูกู หรือไทยมีความสอดคล้องกันและพร้อมใช้งานในอนาคต
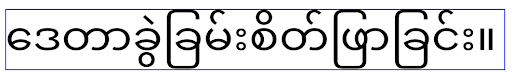 ลักษณะการทำงานของ
ลักษณะการทำงานของ elegantTextHeight สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android
14 (API ระดับ 34) และต่ำกว่า หรือสำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35)
ซึ่งลบล้างค่าเริ่มต้นโดยการตั้งค่าแอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight
เป็น false ลักษณะการทํางานของ
ลักษณะการทํางานของ elegantTextHeight สําหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android
16 (API ระดับ 36) หรือสําหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) ที่ไม่ได้
ลบล้างค่าเริ่มต้นโดยการตั้งค่าแอตทริบิวต์ elegantTextHeight
เป็น falseฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งจะแก้ไขหรือ ขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการจัดกำหนดเวลางานแบบอัตราคงที่
Prior to targeting Android 16, when scheduleAtFixedRate
missed a task execution due to being outside a valid
process lifecycle, all missed executions immediately
execute when the app returns to a valid lifecycle.
When targeting Android 16, at most one missed execution of
scheduleAtFixedRate is immediately executed when the app
returns to a valid lifecycle. This behavior change is expected to improve app
performance. Test this behavior in your app to check if your app is impacted.
You can also test by using the app compatibility framework
and enabling the STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat flag.
รูปแบบของอุปกรณ์
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้สำหรับแอปเมื่อ แสดงบนอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
เลย์เอาต์แบบปรับขนาดได้
เนื่องจากตอนนี้แอป Android ทำงานบนอุปกรณ์หลากหลายประเภท (เช่น โทรศัพท์ แท็บเล็ต อุปกรณ์พับได้ เดสก์ท็อป รถยนต์ และทีวี) และโหมดการจัดหน้าต่างบนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ (เช่น การแยกหน้าจอและการจัดหน้าต่างบนเดสก์ท็อป) นักพัฒนาแอปจึงควรสร้างแอป Android ที่ปรับให้เข้ากับขนาดหน้าจอและหน้าต่างได้ทุกขนาด ไม่ว่าอุปกรณ์จะวางแนวใดก็ตาม กระบวนทัศน์ต่างๆ เช่น การจำกัดการวางแนวและความสามารถในการปรับขนาด มีข้อจำกัดมากเกินไปในโลกที่มีอุปกรณ์หลายเครื่องในปัจจุบัน
ไม่สนใจข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และสัดส่วนภาพ
สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) Android 16 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง วิธีที่ระบบจัดการข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และสัดส่วนภาพ ในจอแสดงผลที่มีความกว้างน้อยที่สุดมากกว่าหรือเท่ากับ 600dp ข้อจำกัดจะไม่มีผลอีกต่อไป นอกจากนี้ แอปยังจะแสดงเต็มหน้าต่างแสดงผลโดยไม่คำนึงถึงสัดส่วนภาพหรือการวางแนวที่ผู้ใช้ต้องการ และจะไม่มีการใช้แถบดำด้านข้าง
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะทำให้แพลตฟอร์มมีลักษณะการทำงานที่เป็นมาตรฐานใหม่ Android กำลังเปลี่ยนไปใช้โมเดลที่คาดหวังให้แอปปรับให้เข้ากับการวางแนว ขนาดการแสดงผล และสัดส่วนภาพต่างๆ ข้อจำกัดต่างๆ เช่น การวางแนวคงที่หรือการปรับขนาดที่จำกัด จะขัดขวางความสามารถในการปรับตัวของแอป ดังนั้นเราขอแนะนำให้ทำให้แอปของคุณปรับเปลี่ยนได้เพื่อมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ดีที่สุดแก่ผู้ใช้
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังทดสอบลักษณะการทำงานนี้ได้โดยใช้เฟรมเวิร์กความเข้ากันได้ของแอปและ
เปิดใช้UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat flag
การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งผลกับส่วนอื่นในระบบที่พบบ่อย
การไม่สนใจข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และสัดส่วนภาพอาจส่งผลต่อ UI ของแอปในอุปกรณ์บางเครื่อง โดยเฉพาะองค์ประกอบที่ออกแบบมาสำหรับเลย์เอาต์ขนาดเล็กที่ล็อกไว้ในแนวนอน เช่น ปัญหาต่างๆ อย่างเลย์เอาต์ที่ยืดออก รวมถึงภาพเคลื่อนไหวและคอมโพเนนต์ที่อยู่นอกหน้าจอ การคาดเดาเกี่ยวกับสัดส่วนภาพหรือการวางแนวอาจทำให้เกิดปัญหาด้านภาพกับแอป ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาดังกล่าวและปรับปรุงลักษณะการทำงานแบบปรับเปลี่ยนได้ของแอป
การอนุญาตให้หมุนอุปกรณ์จะส่งผลให้มีการสร้างกิจกรรมใหม่มากขึ้น ซึ่งอาจส่งผล ให้สถานะของผู้ใช้สูญหายหากไม่ได้เก็บรักษาไว้อย่างถูกต้อง ดูวิธีบันทึกสถานะ UI อย่างถูกต้องในบันทึกสถานะ UI
รายละเอียดการติดตั้งใช้งาน
ระบบจะละเว้นแอตทริบิวต์ในไฟล์ Manifest และ API รันไทม์ต่อไปนี้ในอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ ในโหมดเต็มหน้าจอและโหมดหลายหน้าต่าง
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
ระบบจะละเว้นค่าต่อไปนี้สำหรับ screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation() และ getRequestedOrientation()
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
ในส่วนของการปรับขนาดจอแสดงผล android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio และ android:maxAspectRatio จะไม่มีผล
สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) ระบบจะละเว้นข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และสัดส่วนภาพของแอปบนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่โดยค่าเริ่มต้น แต่แอปทุกแอปที่ยังไม่พร้อมอย่างเต็มที่สามารถลบล้างลักษณะการทำงานนี้ชั่วคราวได้โดยการเลือกไม่ใช้ (ซึ่งจะส่งผลให้แอปมีลักษณะการทำงานก่อนหน้าคืออยู่ในโหมดความเข้ากันได้)
ข้อยกเว้น
ข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว ความสามารถในการปรับขนาด และสัดส่วนภาพของ Android 16 จะไม่ มีผลในกรณีต่อไปนี้
- เกม (อิงตามธง
android:appCategory) - ผู้ใช้เลือกใช้ลักษณะการทำงานเริ่มต้นของแอปอย่างชัดแจ้งในการตั้งค่าสัดส่วนภาพของอุปกรณ์
- หน้าจอที่มีขนาดเล็กกว่า
sw600dp
เลือกไม่ใช้ชั่วคราว
หากต้องการเลือกไม่ใช้กิจกรรมที่เฉพาะเจาะจง ให้ประกาศPROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITYพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ของไฟล์ Manifest ดังนี้
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
หากส่วนต่างๆ ของแอปยังไม่พร้อมสำหรับ Android 16 คุณสามารถเลือกไม่ใช้ ทั้งหมดได้โดยใช้พร็อพเพอร์ตี้เดียวกันที่ระดับแอปพลิเคชัน
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
สุขภาพและการออกกำลังกาย
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับข้อมูลสุขภาพ และการออกกำลังกาย
สิทธิ์ด้านสุขภาพและการออกกำลังกาย
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher,
BODY_SENSORS permissions use more granular permissions
under android.permissions.health, which Health Connect
also uses. As of Android 16, any API previously requiring BODY_SENSORS
or BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND requires the corresponding
android.permissions.health permission instead. This affects the following data
types, APIs, and foreground service types:
HEART_RATE_BPMfrom Health Services on Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEfrom Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyandheartRateBpmfromProtoLayouton Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHwhere the respectiveandroid.permission.healthpermission is needed in place ofBODY_SENSORS
If your app uses these APIs, it should request the respective granular permissions:
- For while-in-use monitoring of Heart Rate, SpO2, or Skin Temperature:
request the granular permission under
android.permissions.health, such asREAD_HEART_RATEinstead ofBODY_SENSORS. - For background sensor access: request
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDinstead ofBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
These permissions are the same as those that guard access to reading data from Health Connect, the Android datastore for health, fitness, and wellness data.
Mobile apps
Mobile apps migrating to use the READ_HEART_RATE and other granular
permissions must also declare an activity to display
the app's privacy policy. This is the same requirement as Health Connect.
การเชื่อมต่อ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ในสแต็กบลูทูธ เพื่อปรับปรุงการเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ต่อพ่วง
เจตนาใหม่ในการจัดการการสูญเสียพันธะและการเปลี่ยนแปลงการเข้ารหัส
การจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงที่ดีขึ้นทำให้ Android 16 เปิดตัว Intent ใหม่ 2 รายการเพื่อให้แอปรับรู้ถึงการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงและการเปลี่ยนแปลงการเข้ารหัสได้ดียิ่งขึ้น
ตอนนี้แอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 ทําสิ่งต่อไปนี้ได้
- รับ Intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGเมื่อตรวจพบการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงระยะไกล ซึ่งช่วยให้สามารถแสดงความคิดเห็นที่เป็นประโยชน์ต่อผู้ใช้มากขึ้นและดำเนินการที่เหมาะสม - รับ Intent
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEเมื่อใดก็ตามที่สถานะการเข้ารหัสของลิงก์มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง ซึ่งรวมถึงการเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะการเข้ารหัส การเปลี่ยนแปลงอัลกอริทึมการเข้ารหัส และการเปลี่ยนแปลงขนาดคีย์การเข้ารหัส แอปต้องถือว่าการเชื่อมโยงได้รับการคืนค่าหากลิงก์ได้รับการเข้ารหัสเรียบร้อยแล้วเมื่อได้รับ IntentACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEในภายหลัง
การปรับให้เข้ากับการใช้งาน OEM ที่หลากหลาย
แม้ว่า Android 16 จะเปิดตัว Intent ใหม่เหล่านี้ แต่การใช้งานและการออกอากาศอาจแตกต่างกันไปตามผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ (OEM) แต่ละราย นักพัฒนาแอปควรออกแบบการจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงให้ปรับให้เข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่อาจเกิดขึ้นเหล่านี้ได้อย่างราบรื่น เพื่อให้แอปมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่สอดคล้องกันและเชื่อถือได้ในอุปกรณ์ทุกเครื่อง
เราขอแนะนําลักษณะการทํางานของแอปดังต่อไปนี้
หากมีการออกอากาศ Intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGให้ทำดังนี้ระบบจะตัดการเชื่อมต่อลิงก์ ACL (การเชื่อมต่อแบบไม่ใช้การเชื่อมต่อแบบแอซิงโครนัส) แต่ระบบจะเก็บข้อมูลการเชื่อมโยงสำหรับอุปกรณ์ไว้ (ตามที่อธิบายไว้ที่นี่)
แอปของคุณควรใช้ Intent นี้เป็นสัญญาณหลักในการจับสัญญาณการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงและแนะนำผู้ใช้ให้ยืนยันว่าอุปกรณ์ระยะไกลอยู่ในระยะสัญญาณก่อนที่จะเริ่มการลืมอุปกรณ์หรือการจับคู่อีกครั้ง
หากอุปกรณ์ตัดการเชื่อมต่อหลังจากได้รับ
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGแอปของคุณควรระมัดระวังเกี่ยวกับการเชื่อมต่ออีกครั้ง เนื่องจากอุปกรณ์อาจไม่ได้จับคู่กับระบบแล้วหากไม่ได้ออกอากาศ Intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGลิงก์ ACL จะยังคงเชื่อมต่ออยู่ และระบบจะนำข้อมูลการเชื่อมโยงของอุปกรณ์ออก เช่นเดียวกับลักษณะการทำงานใน Android 15
ในกรณีนี้ แอปของคุณควรใช้กลไกการจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงที่มีอยู่ต่อไปเช่นเดียวกับใน Android รุ่นก่อนหน้า เพื่อตรวจหาและจัดการเหตุการณ์การสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยง
วิธีใหม่ในการนำการจับคู่บลูทูธออก
All apps targeting Android 16 are now able to unpair bluetooth devices using a
public API in CompanionDeviceManager. If a companion device is
being managed as a CDM association, then the app can trigger
bluetooth bond removal by using the new removeBond(int) API
on the associated device. The app can monitor the bond state changes by
listening to the bluetooth device broadcast event
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
ความปลอดภัย
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงด้านความปลอดภัยต่อไปนี้
การล็อกดาวน์เวอร์ชัน MediaStore
For apps targeting Android 16 or higher, MediaStore#getVersion() will now
be unique to each app. This eliminates identifying properties from the version
string to prevent abuse and usage for fingerprinting techniques. Apps shouldn't
make any assumptions around the format of this version. Apps should already
handle version changes when using this API and in most cases shouldn't need to
change their current behavior, unless the developer has attempted to infer
additional information that is beyond the intended scope of this API.
ความตั้งใจที่ปลอดภัยยิ่งขึ้น
The Safer Intents feature is a multi-phase security initiative designed to improve the security of Android's intent resolution mechanism. The goal is to protect apps from malicious actions by adding checks during intent processing and filtering intents that don't meet specific criteria.
In Android 15 the feature focused on the sending app, now with Android 16, shifts control to the receiving app, allowing developers to opt-in to strict intent resolution using their app manifest.
Two key changes are being implemented:
Explicit Intents Must Match the Target Component's Intent Filter: If an intent explicitly targets a component, it should match that component's intent filter.
Intents Without an Action Cannot Match any Intent Filter: Intents that don't have an action specified shouldn't be resolved to any intent filter.
These changes only apply when multiple apps are involved and don't affect intent handling within a single app.
Impact
The opt-in nature means that developers must explicitly enable it in their app manifest for it to take effect. As a result, the feature's impact will be limited to apps whose developers:
- Are aware of the Safer Intents feature and its benefits.
- Actively choose to incorporate stricter intent handling practices into their apps.
This opt-in approach minimizes the risk of breaking existing apps that may rely on the current less-secure intent resolution behavior.
While the initial impact in Android 16 may be limited, the Safer Intents initiative has a roadmap for broader impact in future Android releases. The plan is to eventually make strict intent resolution the default behavior.
The Safer Intents feature has the potential to significantly enhance the security of the Android ecosystem by making it more difficult for malicious apps to exploit vulnerabilities in the intent resolution mechanism.
However, the transition to opt-out and mandatory enforcement must be carefully managed to address potential compatibility issues with existing apps.
Implementation
Developers need to explicitly enable stricter intent matching using the
intentMatchingFlags attribute in their app manifest.
Here is an example where the feature is opt-in for the entire app,
but disabled/opt-out on a receiver:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
More on the supported flags:
| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Enforces stricter matching for incoming intents |
| none | Disables all special matching rules for incoming intents. When specifying multiple flags, conflicting values are resolved by giving precedence to the "none" flag |
| allowNullAction | Relaxes the matching rules to allow intents without an action to match. This flag to be used in conjunction with "enforceIntentFilter" to achieve a specific behavior |
Testing and Debugging
When the enforcement is active, apps should function correctly if the intent
caller has properly populated the intent.
However, blocked intents will trigger warning log messages like
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" and "Access blocked:"
with the tag "PackageManager."
This indicates a potential issue that could impact the app and requires
attention.
Logcat filter:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
การกรอง Syscall ของ GPU
เพื่อเพิ่มความปลอดภัยของพื้นผิว Mali GPU เราจึงบล็อก IOCTL ของ Mali GPU ที่เลิกใช้งานแล้วหรือมีไว้สำหรับการพัฒนา GPU เท่านั้นในบิลด์เวอร์ชันที่ใช้งานจริง นอกจากนี้ IOCTL ที่ใช้สำหรับการสร้างโปรไฟล์ GPU ยังถูกจำกัดไว้สำหรับกระบวนการเชลล์หรือแอปพลิเคชันที่แก้ไขข้อบกพร่องได้ ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับนโยบายระดับแพลตฟอร์มได้ที่การปรับปรุง SAC
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะมีผลในอุปกรณ์ Pixel ที่ใช้ GPU ของ Mali (Pixel 6-9) Arm
ได้จัดหมวดหมู่ IOCTL อย่างเป็นทางการใน
Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst ของรุ่น r54p2 เราจะดูแลรายการนี้ต่อไปในการเผยแพร่ไดรเวอร์ในอนาคต
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ไม่ส่งผลต่อ API กราฟิกที่รองรับ (รวมถึง Vulkan และ OpenGL) และคาดว่าจะไม่ส่งผลต่อนักพัฒนาแอปหรือแอปพลิเคชันที่มีอยู่ เครื่องมือสร้างโปรไฟล์ GPU เช่น Streamline Performance Analyzer และ Android GPU Inspector จะไม่ได้รับผลกระทบ
การทดสอบ
หากเห็นการปฏิเสธ SELinux ที่คล้ายกับข้อความต่อไปนี้ แสดงว่าแอปพลิเคชันของคุณอาจได้รับผลกระทบจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
หากแอปพลิเคชันของคุณต้องใช้ IOCTL ที่ถูกบล็อก โปรดรายงานข้อบกพร่องและมอบหมายให้ android-partner-security@google.com
คำถามที่พบบ่อย
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนโยบายนี้มีผลกับ OEM ทุกรายไหม การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะเป็นแบบเลือกใช้ แต่พร้อมให้บริการแก่ OEM ทุกรายที่ต้องการใช้วิธีการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งนี้ ดูวิธีการใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลงได้ใน เอกสารประกอบการใช้งาน
การเปลี่ยนแปลงในฐานของโค้ด OEM เป็นข้อบังคับในการใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้ หรือฟีเจอร์นี้จะมาพร้อมกับการเปิดตัว AOSP ใหม่โดยค่าเริ่มต้น การเปลี่ยนแปลงระดับแพลตฟอร์มจะมาพร้อมกับการเผยแพร่ AOSP ใหม่โดยค่าเริ่มต้น ผู้ให้บริการ อาจเลือกใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ในโค้ดเบสของตนหากต้องการใช้
SoC มีหน้าที่รับผิดชอบในการอัปเดตรายการ IOCTL ให้เป็นปัจจุบันอยู่เสมอใช่ไหม เช่น หากอุปกรณ์ของฉันใช้ GPU ของ ARM Mali ฉันจะต้องติดต่อ ARM เพื่อขอรับการเปลี่ยนแปลงไหม SoC แต่ละรายการต้องอัปเดตรายการ IOCTL ต่ออุปกรณ์เมื่อเผยแพร่ไดรเวอร์ เช่น ARM จะอัปเดตรายการ IOCTL ที่เผยแพร่เมื่อมีการอัปเดตไดรเวอร์ อย่างไรก็ตาม OEM ควรตรวจสอบว่าได้รวมการอัปเดตไว้ใน SEPolicy และเพิ่ม IOCTL ที่กำหนดเองที่เลือกไว้ลงในรายการตามที่จำเป็น
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะมีผลกับอุปกรณ์ Pixel ทุกรุ่นที่วางจำหน่ายโดยอัตโนมัติ หรือผู้ใช้ต้องดำเนินการบางอย่างเพื่อเปิด/ปิดการตั้งค่าเพื่อใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้จะมีผลกับอุปกรณ์ Pixel ทั้งหมดในตลาดที่ใช้ GPU Mali (Pixel 6-9) ผู้ใช้ไม่จำเป็นต้องดำเนินการใดๆ เพื่อใช้การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้
การใช้นโยบายนี้จะส่งผลต่อประสิทธิภาพของไดรเวอร์เคอร์เนลไหม เราได้ทดสอบนโยบายนี้ใน GPU ของ Mali โดยใช้ GFXBench และไม่พบการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่วัดได้ ในประสิทธิภาพของ GPU
จำเป็นไหมที่รายการ IOCTL จะต้องสอดคล้องกับเวอร์ชันปัจจุบันของไดรเวอร์ในพื้นที่ผู้ใช้และเคอร์เนล ได้ รายการ IOCTL ที่อนุญาตต้องซิงค์กับ IOCTL ที่ไดรเวอร์ทั้งใน Userspace และเคอร์เนลรองรับ หากมีการอัปเดต IOCTL ในพื้นที่ผู้ใช้หรือ ไดรเวอร์เคอร์เนล จะต้องอัปเดตรายการ IOCTL ของ SEPolicy ให้ตรงกัน
ARM ได้จัดหมวดหมู่ IOCTL เป็น "จำกัด" / "การวัด" แต่เราต้องการใช้ IOCTL บางรายการในกรณีการใช้งานจริง และ/หรือปฏิเสธรายการอื่นๆ OEM/SoC แต่ละรายมีหน้าที่รับผิดชอบในการตัดสินใจว่าจะจัดหมวดหมู่ IOCTL ที่ใช้ตามการกำหนดค่าของไลบรารี Mali ในพื้นที่ผู้ใช้ได้อย่างไร คุณใช้รายการของ ARM เพื่อช่วยในการตัดสินใจได้ แต่กรณีการใช้งานของ OEM/SoC แต่ละรายอาจแตกต่างกัน
ความเป็นส่วนตัว
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงด้านความเป็นส่วนตัวต่อไปนี้
สิทธิ์เข้าถึงเครือข่ายภายใน
Devices on the LAN can be accessed by any app that has the INTERNET permission.
This makes it easy for apps to connect to local devices but it also has privacy
implications such as forming a fingerprint of the user, and being a proxy for
location.
The Local Network Protections project aims to protect the user's privacy by gating access to the local network behind a new runtime permission.
Release plan
This change will be deployed between two releases, 25Q2 and 26Q2 respectively. It is imperative that developers follow this guidance for 25Q2 and share feedback because these protections will be enforced at a later Android release. Moreover, they will need to update scenarios which depend on implicit local network access by using the following guidance and prepare for user rejection and revocation of the new permission.
Impact
At the current stage, LNP is an opt-in feature which means only the apps that opt in will be affected. The goal of the opt-in phase is for app developers to understand which parts of their app depend on implicit local network access such that they can prepare to permission guard them for the next release.
Apps will be affected if they access the user's local network using:
- Direct or library use of raw sockets on local network addresses (e.g. mDNS or SSDP service discovery protocol)
- Use of framework level classes that access the local network (e.g. NsdManager)
Traffic to and from a local network address requires local network access permission. The following table lists some common cases:
| App Low Level Network Operation | Local Network Permission Required |
|---|---|
| Making an outgoing TCP connection | yes |
| Accepting incoming TCP connections | yes |
| Sending a UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
| Receiving an incoming UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
These restrictions are implemented deep in the networking stack, and thus they apply to all networking APIs. This includes sockets created in native or managed code, networking libraries like Cronet and OkHttp, and any APIs implemented on top of those. Trying to resolve services on the local network (i.e. those with a .local suffix) will require local network permission.
Exceptions to the rules above:
- If a device's DNS server is on a local network, traffic to or from it (at port 53) doesn't require local network access permission.
- Applications using Output Switcher as their in-app picker won't need local network permissions (more guidance to come in 2025Q4).
Developer Guidance (Opt-in)
To opt into local network restrictions, do the following:
- Flash the device to a build with 25Q2 Beta 3 or later.
- Install the app to be tested.
Toggle the Appcompat flag in adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Reboot The device
Now your app's access to the local network is restricted and any attempt to access the local network will lead to socket errors. If you are using APIs that perform local network operations outside of your app process (ex: NsdManager), they won't be impacted during the opt-in phase.
To restore access, you must grant your app permission to NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Ensure the app declares the
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESpermission in its manifest. - Go to Settings > Apps > [Application Name] > Permissions > Nearby devices > Allow.
Now your app's access to the local network should be restored and all your scenarios should work as they did prior to opting the app in.
Once enforcement for local network protection begins, here is how the app network traffic will be impacted.
| Permission | Outbound LAN Request | Outbound/Inbound Internet Request | Inbound LAN Request |
|---|---|---|---|
| Granted | Works | Works | Works |
| Not Granted | Fails | Works | Fails |
Use the following command to toggle-off the App-Compat flag
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Errors
Errors arising from these restrictions will be returned to the calling socket whenever it invokes send or a send variant to a local network address.
Example errors:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Local Network Definition
A local network in this project refers to an IP network that utilizes a broadcast-capable network interface, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet, but excludes cellular (WWAN) or VPN connections.
The following are considered local networks:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- Directly-connected routes
- Stub networks like Thread
- Multiple-subnets (TBD)
Additionally, both multicast addresses (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) and the IPv4 broadcast address (255.255.255.255) are classified as local network addresses.
รูปภาพที่เป็นของแอป
เมื่อแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมาย SDK 36 ขึ้นไปในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 16 ขึ้นไปแสดงข้อความแจ้งขอสิทธิ์เข้าถึงรูปภาพและวิดีโอ ผู้ใช้ที่เลือกจำกัดการเข้าถึงสื่อที่เลือกไว้จะเห็นรูปภาพทั้งหมดที่แอปเป็นเจ้าของซึ่งเลือกไว้ล่วงหน้าในเครื่องมือเลือกรูปภาพ ผู้ใช้สามารถยกเลิกการเลือกรายการที่เลือกไว้ล่วงหน้ารายการใดก็ได้ ซึ่งจะเป็นการเพิกถอนสิทธิ์เข้าถึงรูปภาพและวิดีโอเหล่านั้นของแอป

