Android 16 プラットフォームには、アプリに影響を与える可能性のある動作変更が含まれています。下記の動作変更は、targetSdkVersion に関係なく、Android 16 上で稼働するすべてのアプリに適用されます。該当する場合は、アプリをテストし、必要に応じて修正して、これらの変更に対応する必要があります。
Android 16 をターゲットとするアプリにのみ影響する動作変更のリストも必ずご確認ください。
コア機能
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、Android システムのさまざまなコア機能を変更または拡張する以下の変更が含まれています。
JobScheduler の割り当ての最適化
Android 16 以降では、次の要素に基づいて、通常のジョブと迅速なジョブの実行ランタイム割り当てを調整しています。
- アプリケーションが属するアプリ スタンバイ バケット: Android 16 では、アクティブなスタンバイ バケットは、十分なランタイム割り当てによって適用されるようになります。
- アプリが最上位の状態のときにジョブの実行が開始された場合: Android 16 では、アプリがユーザーに表示されている間に開始され、アプリが非表示になった後も継続されるジョブは、ジョブの実行時間割り当てに準拠します。
- フォアグラウンド サービスの実行中にジョブが実行されている場合: Android 16 では、フォアグラウンド サービスと同時に実行されているジョブは、ジョブの実行時間割り当てに準拠します。ジョブをユーザー開始型データ転送に活用している場合は、代わりにユーザー開始型データ転送ジョブの使用を検討してください。
この変更は、WorkManager、JobScheduler、DownloadManager を使用してスケジュール設定されたタスクに影響します。ジョブが停止した理由をデバッグするには、WorkInfo.getStopReason() を呼び出してジョブが停止した理由をロギングすることをおすすめします(JobScheduler ジョブの場合は JobParameters.getStopReason() を呼び出します)。
アプリの状態が使用できるリソースに与える影響については、電源管理のリソース制限をご覧ください。バッテリーを最適化するためのベスト プラクティスについて詳しくは、タスク スケジューリング API のバッテリー使用量を最適化するをご覧ください。
また、Android 16 で導入された新しい JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API を活用して、ジョブが実行されなかった理由を把握することをおすすめします。
テスト
アプリの動作をテストするには、アプリが Android 16 デバイスで実行されている場合に限り、特定のジョブ割り当ての最適化のオーバーライドを有効にできます。
「トップ状態はジョブ ランタイム割り当てに準拠する」の適用を無効にするには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
「フォアグラウンド サービスと同時に実行されるジョブはジョブ ランタイム割り当てに準拠する」の適用を無効にするには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
特定のアプリ スタンバイ バケットの動作をテストするには、次の adb コマンドを使用してアプリのアプリ スタンバイ バケットを設定します。
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
アプリが属するアプリ スタンバイ バケットを把握するには、次の adb コマンドを使用して、アプリのアプリ スタンバイ バケットを取得します。
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
空のジョブが破棄された停止理由
An abandoned job occurs when the JobParameters object associated with the job
has been garbage collected, but JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) has not been called to signal job completion. This indicates that
the job may be running and being rescheduled without the app's awareness.
Apps that rely on JobScheduler, don't maintain a strong reference to the
JobParameters object, and timeout will now be granted the new job stop reason
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, instead of STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
If there are frequent occurrences of the new abandoned stop reason, the system will take mitigation steps to reduce job frequency.
Apps should use the new stop reason to detect and reduce abandoned jobs.
If you're using WorkManager, AsyncTask, or DownloadManager, you aren't impacted because these APIs manage the job lifecycle on your app's behalf.
JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground のサポートを完全に終了
The JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean)
method indicates the importance of a job while the scheduling app is in the
foreground or when temporarily exempted from background restrictions.
This method has been deprecated since Android 12 (API level 31). Starting in Android 16, it no longer functions effectively and calling this method will be ignored.
This removal of functionality also applies to
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). Starting in Android
16, if the method is called, the method returns false.
順序付きブロードキャストの優先度のスコープがグローバルではなくなった
Android apps are allowed to define priorities on broadcast receivers to control
the order in which the receivers receive and process the broadcast. For
manifest-declared receivers, apps can use the
android:priority attribute to define the priority and for
context-registered receivers, apps can use the
IntentFilter#setPriority() API to define the priority. When
a broadcast is sent, the system delivers it to receivers in order of their
priority, from highest to lowest.
In Android 16, broadcast delivery order using the android:priority attribute
or IntentFilter#setPriority() across different processes will not be
guaranteed. Broadcast priorities will only be respected within the same
application process rather than across all processes.
Also, broadcast priorities will be automatically confined to the range
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Only system components will be
allowed to set SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY as broadcast
priority.
Your app might be impacted if it does either of the following:
- Your application has declared multiple processes with the same broadcast intent, and has expectations around receiving those intents in a certain order based on the priority.
- Your application process interacts with other processes and has expectations around receiving a broadcast intent in a certain order.
If the processes need to coordinate with each other, they should communicate using other coordination channels.
ART の内部変更
Android 16 には、Android ランタイム(ART)の最新のアップデートが含まれています。これにより、Android ランタイム(ART)のパフォーマンスが向上し、追加の Java 機能をサポートしています。Google Play システム アップデートにより、Android 12(API レベル 31)以降を搭載した 10 億台を超えるデバイスでもこれらの改善を利用できます。
これらの変更がリリースされると、ART の内部構造に依存するライブラリとアプリコードは、Android 16 を搭載したデバイスや、Google Play システム アップデートを通じて ART モジュールを更新する以前の Android バージョンで正しく動作しない可能性があります。
内部構造(SDK 以外のインターフェースなど)に依存すると、常に互換性の問題が発生する可能性がありますが、内部 ART 構造を利用するコード(またはコードを含むライブラリ)に依存しないようにすることが特に重要です。ART の変更は、デバイスが実行しているプラットフォーム バージョンに関連付けられておらず、Google Play システム アップデートを通じて 10 億台を超えるデバイスに配信されるためです。
すべてのデベロッパーは、Android 16 でアプリを徹底的にテストして、アプリに影響があるかどうかを確認する必要があります。また、既知の問題をチェックして、アプリが内部 ART 構造に依存していることが判明したライブラリに依存しているかどうかを確認します。影響を受けるアプリコードまたはライブラリの依存関係がある場合は、可能な限り公開 API の代替手段を探し、新しいユースケース用の公開 API をリクエストしてください。リクエストは、Issue Tracker で機能リクエストを作成して行います。
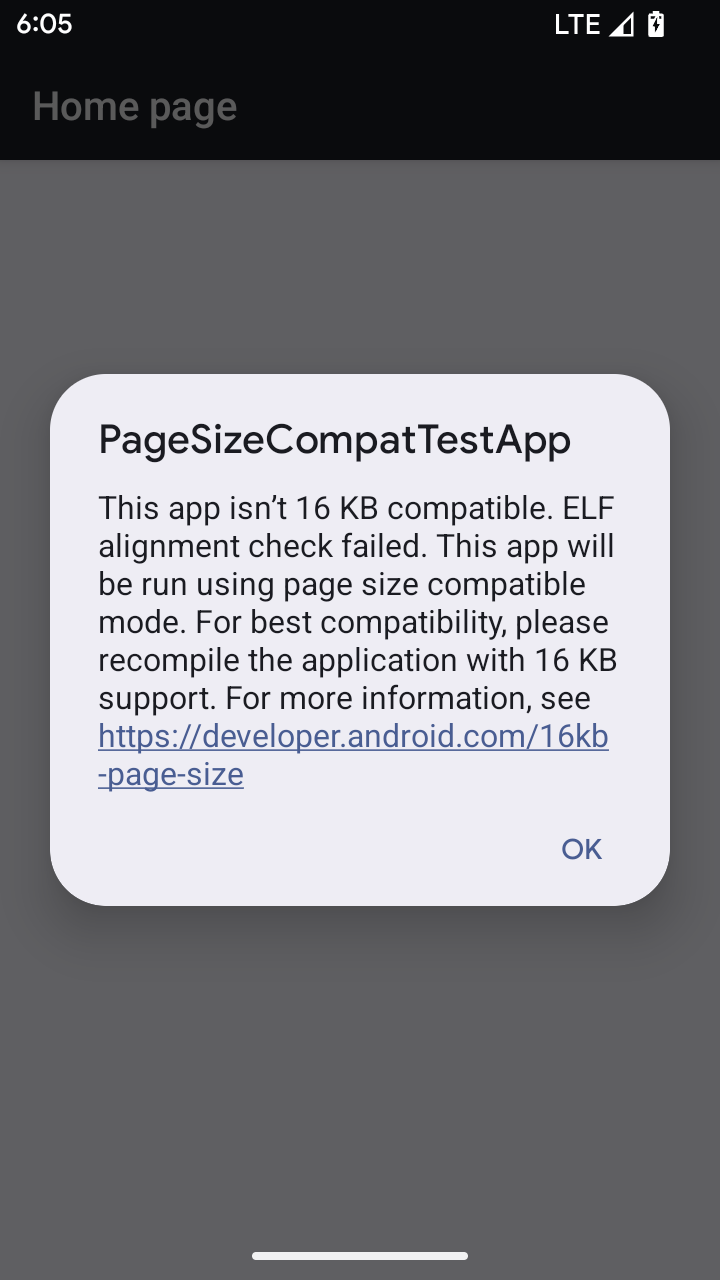
16 KB ページサイズの互換モード
Android 15 introduced support for 16 KB memory pages to optimize performance of the platform. Android 16 adds a compatibility mode, allowing some apps built for 4 KB memory pages to run on a device configured for 16 KB memory pages.
When your app is running on a device with Android 16 or higher, if Android
detects that your app has 4 KB aligned memory pages, it automatically uses
compatibility mode and display a notification dialog to the user. Setting the
android:pageSizeCompat property in the AndroidManifest.xml to enable the
backwards compatibility mode will prevent the display of the dialog when your
app launches. To use the android:pageSizeCompat property, compile your app
using the Android 16 SDK.
For best performance, reliability, and stability, your app should still be 16 KB aligned. Check out our recent blog post on updating your apps to support 16 KB memory pages for more details.
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、より一貫性のある直感的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現するための以下の変更が含まれています。
妨げになるユーザー補助の読み上げの非推奨化
Android 16 deprecates accessibility announcements, characterized by the use of
announceForAccessibility or the dispatch of
TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT accessibility events. These can create
inconsistent user experiences for users of TalkBack and Android's screen reader,
and alternatives better serve a broader range of user needs across a variety of
Android's assistive technologies.
Examples of alternatives:
- For significant UI changes like window changes, use
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)andsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - To inform the user of changes to critical UI, use
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. These should be used sparingly as they may generate announcements every time a View is updated. - To notify users about errors, send an
AccessibilityEventof typeAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORand setAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence), or useTextView#setError(CharSequence).
The reference documentation for the deprecated
announceForAccessibility API includes more details about
suggested alternatives.
3 ボタン ナビゲーションのサポート
Android 16 brings predictive back support to the 3-button navigation for apps that have properly migrated to predictive back. Long-pressing the back button initiates a predictive back animation, giving you a preview of where the back swipe takes you.
This behavior applies across all areas of the system that support predictive back animations, including the system animations (back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity).
テーマ別アプリアイコンの自動生成
Beginning with Android 16 QPR 2, Android automatically applies themes to app icons to create a cohesive home screen experience. This occurs if an app does not provide its own themed app icon. Apps can control the design of their themed app icon by including a monochrome layer within their adaptive icon and previewing what their app icon will look like in Android Studio.
デバイスのフォーム ファクタ
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、仮想デバイスの所有者がディスプレイに投影するアプリに対して、次の変更が加えられています。
仮想デバイス所有者のオーバーライド
A virtual device owner is a trusted or privileged app that creates and manages a virtual device. Virtual device owners run apps on a virtual device and then project the apps to the display of a remote device, such as a personal computer, virtual reality device, or car infotainment system. The virtual device owner is on a local device, such as a mobile phone.
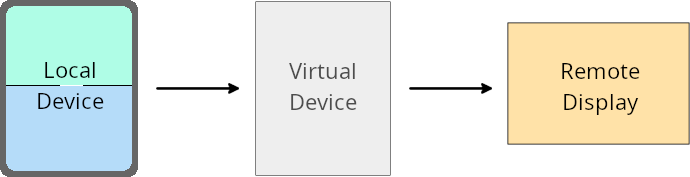
Per-app overrides
On devices running Android 16 (API level 36), virtual device owners can override app settings on select virtual devices that the virtual device owners manage. For example, to improve app layout, a virtual device owner can ignore orientation, aspect ratio, and resizability restrictions when projecting apps onto an external display.
Common breaking changes
The Android 16 behavior might impact your app's UI on large screen form factors such as car displays or Chromebooks, especially layouts that were designed for small displays in portrait orientation. To learn how to make your app adaptive for all device form factors, see About adaptive layouts.
References
セキュリティ
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、システム セキュリティを強化し、アプリとユーザーを悪意のあるアプリから保護するための変更が含まれています。
インテント リダイレクト攻撃に対するセキュリティの強化
Android 16 では、一般的な Intent リダイレクト攻撃に対するデフォルトのセキュリティが提供され、互換性とデベロッパーの変更が最小限で済みます。
Intent リダイレクト エクスプロイトに対するデフォルトのセキュリティ強化ソリューションを導入します。ほとんどの場合、インテントを使用するアプリで互換性の問題が発生することはありません。Google は開発プロセス全体で指標を収集し、どのアプリで破損が発生する可能性があるかをモニタリングしています。
Android のインテント リダイレクトは、脆弱なアプリに関連して新しいコンポーネントの起動に使用されるインテントの内容を攻撃者が部分的または完全に制御できる場合に発生します。一方、被害者のアプリは(「トップレベル」の)インテントの Extras フィールドで信頼できないサブレベルのインテントを起動します。これにより、攻撃者のアプリが被害者のアプリのコンテキストで非公開コンポーネントを起動し、特権アクションをトリガーしたり、機密データへの URI アクセス権を取得したりする可能性があります。これにより、データ窃盗や任意のコード実行につながるおそれがあります。
インテント リダイレクト処理をオプトアウトする
Android 16 では、アプリが起動時のセキュリティ保護をオプトアウトできる新しい API が導入されています。これは、デフォルトのセキュリティ動作が正当なアプリのユースケースを妨げる特定のケースで必要になることがあります。
Android 16(API レベル 36)以降の SDK を対象にコンパイルするアプリの場合
Intent オブジェクトで removeLaunchSecurityProtection() メソッドを直接使用できます。
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Android 15(API レベル 35)以下を対象にコンパイルするアプリの場合
推奨はされませんが、リフレクションを使用して removeLaunchSecurityProtection() メソッドにアクセスできます。
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
コンパニオン アプリに検出タイムアウトが通知されなくなった
Android 16 では、コンパニオン デバイスのペア設定フロー中に新しい動作が導入され、悪意のあるアプリからユーザーの位置情報のプライバシーを保護します。Android 16 で実行されているすべてのコンパニオン アプリは、RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT を使用して検出タイムアウトを直接通知されなくなりました。代わりに、タイムアウト イベントが視覚的なダイアログでユーザーに通知されます。ユーザーがダイアログを閉じると、アプリは RESULT_USER_REJECTED で関連付けの失敗をアラートします。
検索時間も元の 20 秒から延長され、検索中にユーザーがいつでもデバイス検出を停止できるようになりました。検索開始から 20 秒以内に 1 台以上のデバイスが検出されると、CDM は追加のデバイスの検索を停止します。
接続
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、周辺機器との接続性を改善するために、Bluetooth スタックに次の変更が加えられています。
債券損失の処理を改善
Starting in Android 16, the Bluetooth stack has been updated to improve security and user experience when a remote bond loss is detected. Previously, the system would automatically remove the bond and initiate a new pairing process, which could lead to unintentional re-pairing. We have seen in many instances apps not taking care of the bond loss event in a consistent way.
To unify the experience, Android 16 improved the bond loss handling to the system. If a previously bonded Bluetooth device could not be authenticated upon reconnection, the system will disconnect the link, retain local bond information, and display a system dialog informing users of the bond loss and directing them to re-pair.
