Android 16 では、デベロッパー向けに優れた新しい機能と API が導入されました。以下のセクションでは、これらの機能の概要を説明し、関連する API を使い始めるうえで役立つ情報を提供します。
新しい API、変更された API、削除された API の一覧については、API 差分レポートをご覧ください。新しい API について詳しくは、Android API リファレンスをご覧ください。新しい API は、見つけやすいようにハイライト表示されています。また、プラットフォームの変更がアプリに影響する可能性がある領域も確認する必要があります。詳細については、次のページをご覧ください。
コア機能
Android には、Android システムのコア機能を拡張する新しい API が含まれています。
2025 年に 2 つの Android API をリリース
- このプレビューは、2025 年第 2 四半期にリリースが予定されている Android の次のメジャー リリースを対象としています。このリリースは、過去のすべての API リリースと同様に、targetSdkVersion に関連付けられている動作の変更を計画できます。
- エコシステム全体のデバイスのリリース スケジュールに合わせて、メジャー リリースを 1 四半期前倒し(昨年は第 3 四半期でしたが、今年は第 2 四半期)に予定しています。これにより、より多くのデバイスで Android のメジャー リリースを早期に利用できるようになります。メジャー リリースが第 2 四半期に予定されているため、アプリの準備状況を確認するために、年次互換性テストを例年より数か月早く実施する必要があります。
- 2025 年第 4 四半期に、新しいデベロッパー API も含めて、さらにリリースする予定です。2025 年にアプリに影響する可能性がある動作変更が予定されているリリースは、第 2 四半期のメジャー リリースのみです。
4 四半期のマイナー リリースでは、新しいデベロッパー API に加え、機能のアップデート、最適化、バグの修正が含まれます。アプリに影響する動作の変更は含まれません。
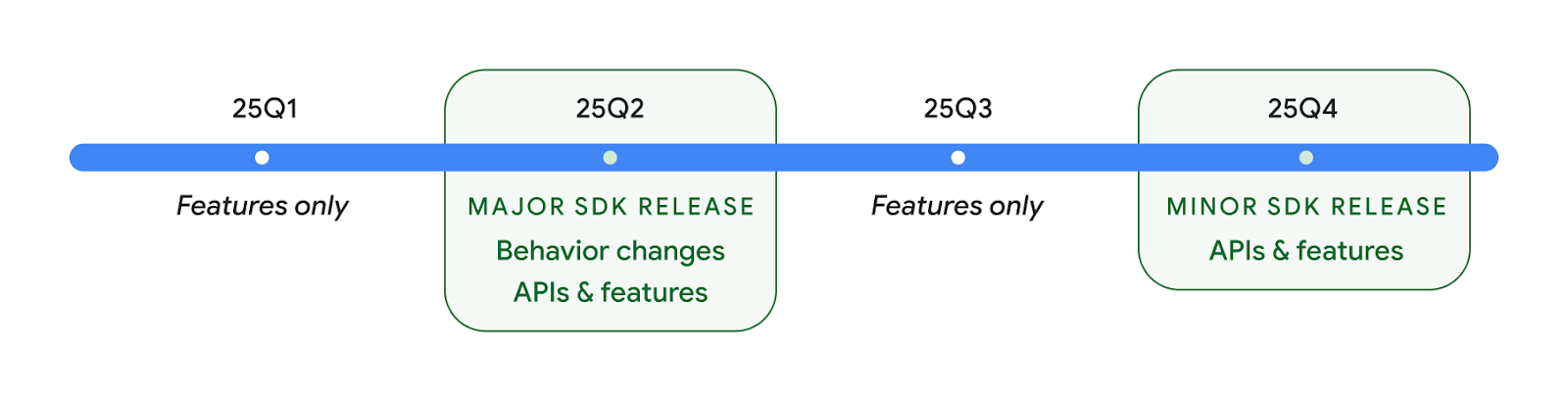
Android のリリースは引き続き四半期ごとに行われます。API リリース間の Q1 と Q3 のアップデートでは、継続的な品質を確保するために増分アップデートが提供されます。Google は、できるだけ多くのデバイスに Q2 リリースを導入できるよう、デバイス パートナーと積極的に連携しています。
メジャー リリースとマイナー リリースで新しい API を使用する
現在、API レベルのチェックでコードブロックを保護するには、VERSION_CODES で SDK_INT 定数を使用します。これは、Android のメジャー リリースで引き続きサポートされます。
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
新しい SDK_INT_FULL 定数は、新しい VERSION_CODES_FULL 列挙型を使用して、メジャー バージョンとマイナー バージョンの両方に対する API チェックに使用できます。
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
Build.getMinorSdkVersion() メソッドを使用して、マイナー SDK バージョンのみを取得することもできます。
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
これらの API は未確定であり、変更される可能性があります。ご不明な点がございましたら、フィードバックをお送りください。
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 16 では、アプリ デベロッパーとユーザーがニーズに合わせてデバイスを構成するための制御と柔軟性が向上しています。
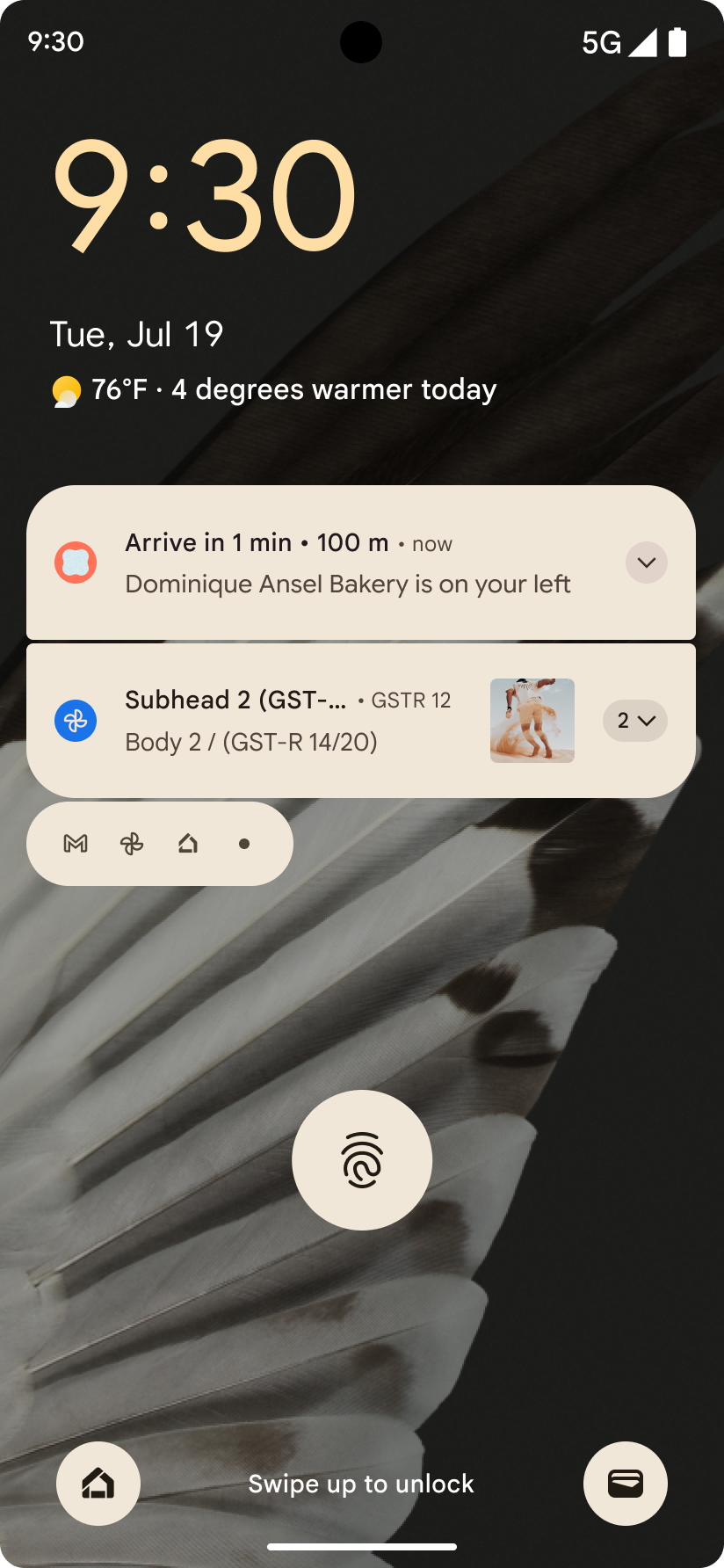
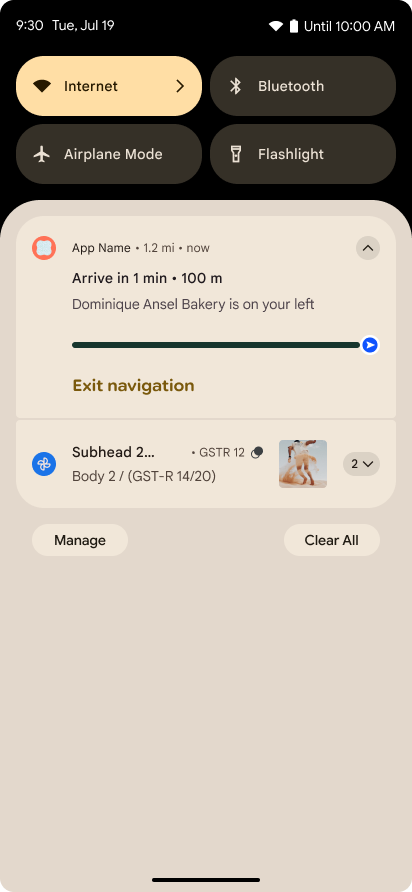
進行状況を中心とした通知
Android 16 では、ユーザーが開始した、最初から最後までのジャーニーをシームレスに追跡できるように、進行状況重視の通知が導入されています。
Notification.ProgressStyle は、進行状況重視の通知を作成できる新しい通知スタイルです。主なユースケースには、乗車シェアリング、配達、ナビゲーションなどがあります。Notification.ProgressStyle クラス内で、ポイントとセグメントを使用して、ユーザー ジャーニー内の状態とマイルストーンを指定できます。
詳細については、進行状況重視の通知のドキュメント ページをご覧ください。
予測型「戻る」のアップデート
Android 16 では、ジェスチャー ナビゲーション(ホームに戻るアニメーションなど)で予測型「戻る」システム アニメーションを有効にするための新しい API が追加されました。新しい PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER に onBackInvokedCallback を登録すると、システムが「戻る」ナビゲーションを処理するたびに、通常の「戻る」ナビゲーション フローに影響を与えることなく、アプリが通常の onBackInvoked 呼び出しを受け取ることができます。
Android 16 では、finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() と moveTaskToBackCallback も追加されています。これらのコールバックを OnBackInvokedDispatcher に登録することで、システムは、戻るジェスチャーが呼び出されたときに特定の動作をトリガーし、対応する事前アニメーションを再生できます。
リッチ ハプティクス
Android は、誕生以来、触覚アクチュエータの制御を公開してきました。
Android 11 では、デバイス定義のセマンティック プリミティブの VibrationEffect.Compositions を介して、より高度なアクチュエータがサポートできる、より複雑なハプティクス エフェクトのサポートが追加されました。
Android 16 では、ハプティクス API が追加されました。これにより、アプリはデバイスの機能の違いを抽象化しながら、ハプティクス エフェクトの振幅と周波数の曲線を定義できます。
デベロッパーの生産性とツール
生産性を向上させるための取り組みのほとんどは、Android Studio、Jetpack Compose、Android Jetpack ライブラリなどのツールを中心に行われていますが、プラットフォームでビジョンを実現するための方法も常に探しています。
ライブ壁紙のコンテンツ処理
Android 16 では、ライブ壁紙 フレームワークに新しいコンテンツ API が追加され、ユーザー主導の動的壁紙の課題に対処できるようになりました。現在、ユーザー提供のコンテンツを組み込んだライブ壁紙には、サービス固有の複雑な実装が必要です。Android 16 では、WallpaperDescription と WallpaperInstance が導入されています。WallpaperDescription を使用すると、同じサービスからライブ壁紙の個別のインスタンスを識別できます。たとえば、ホーム画面とロック画面の両方にインスタンスがある壁紙には、両方の場所に固有のコンテンツが含まれている場合があります。壁紙選択ツールと WallpaperManager は、このメタデータを使用して壁紙をユーザーに適切に表示し、多様でパーソナライズされたライブ壁紙を作成するためのプロセスを効率化します。
パフォーマンスとバッテリー
Android 16 では、アプリに関する分析情報を収集するのに役立つ API が導入されています。
システム トリガー プロファイリング
ProfilingManager は Android 15 で追加されました。これにより、アプリは、フィールドの一般公開デバイスで Perfetto を使用してプロファイリング データの収集をリクエストできるようになりました。ただし、このプロファイリングはアプリから開始する必要があるため、起動や ANR などの重要なフローは、アプリでキャプチャするのが困難または不可能です。
これを支援するため、Android 16 では ProfilingManager にシステム トリガーのプロファイリングが導入されています。アプリは、コールド スタート reportFullyDrawn や ANR などの特定のトリガーのトレースを受信する関心を登録できます。これにより、システムはアプリに代わってトレースを開始および停止します。トレース完了後、結果はアプリのデータ ディレクトリに配信されます。
ApplicationStartInfo の開始コンポーネント
ApplicationStartInfo は Android 15 で追加されました。これにより、アプリはプロセスの開始理由、開始タイプ、開始時間、スロットリングなどの有用な診断データを確認できるようになりました。Android 16 では、起動をトリガーしたコンポーネントのタイプを区別するために getStartComponent() が追加されました。これは、アプリの起動フローを最適化する際に役立ちます。
ジョブのイントロスペクションの改善
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API は、ジョブが保留中である理由を返します。ただし、ジョブが保留状態になる理由は複数考えられます。
Android 16 では、新しい API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId) が導入されます。この API は、デベロッパーが設定した明示的な制約とシステムが設定した暗黙的な制約の両方により、ジョブが保留になっている理由を複数返します。
また、最近の制約変更のリストを返す JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId) も導入されます。
特に、特定のタスクの成功率が低下している場合や、特定のジョブの完了のレイテンシに関するバグがある場合は、API を使用してジョブが実行されない理由をデバッグすることをおすすめします。たとえば、バックグラウンドでのウィジェットの更新が失敗した場合や、アプリの起動前にプリフェッチ ジョブが呼び出されなかった場合です。
また、明示的に設定された制約ではなく、システム定義の制約が原因で特定のジョブが完了していないかどうかを把握するのにも役立ちます。
リフレッシュ レートの自動調整
Android 15 で導入されたリフレッシュ レートの自動調整(ARR)により、サポートされているハードウェアのディスプレイのリフレッシュ レートを、個別の VSync ステップを使用してコンテンツのフレームレートに合わせることができます。これにより、消費電力を削減し、ジャンクを引き起こす可能性のあるモード切り替えの必要性を排除できます。
Android 16 では、hasArrSupport() と getSuggestedFrameRate(int) が導入され、getSupportedRefreshRates() が復元されるため、アプリで ARR を簡単に利用できるようになります。RecyclerView 1.4 は、スワイプやスムーズ スクロールからのセットリング時に ARR を内部でサポートしています。Google は、ARR のサポートをさらに多くの Jetpack ライブラリに追加する作業を続けています。こちらのフレームレートに関する記事では、アプリで ARR を直接使用できるようにフレームレートを設定するために使用できる API について説明しています。
ADPF のヘッドルーム API
SystemHealthManager では、ゲームやリソースを大量に消費するアプリに利用可能な CPU リソースと GPU リソースの推定値を提供するように設計された getCpuHeadroom API と getGpuHeadroom API が導入されています。これらのメソッドを使用すると、アプリやゲームでシステムの健全性を最適に改善する方法を見極めることができます。特に、サーマル スロットリングを検出する他の Android Dynamic Performance Framework(ADPF)API と組み合わせて使用すると効果的です。
対応デバイスで CpuHeadroomParams と GpuHeadroomParams を使用すると、ヘッドルームの計算に使用する時間枠をカスタマイズし、リソースの平均可用性または最小可用性を選択できます。これにより、CPU または GPU のリソース使用量を適度に削減し、ユーザー エクスペリエンスとバッテリー駆動時間を改善できます。
ユーザー補助
Android 16 では、すべてのユーザーにアプリを提供するために役立つ新しいユーザー補助 API と機能が追加されています。
Accessibility API の改善
Android 16 では、UI セマンティクスを強化する API が追加され、TalkBack などのユーザー補助サービスに依存するユーザーの整合性が向上します。
テキストのコントラストを最大化するためにテキストの輪郭を表示する
視力の弱いユーザーはコントラスト感度が低下していることが多いため、オブジェクトを背景と区別するのが困難です。このようなユーザーをサポートするため、Android 16 では高コントラスト テキストに代わるアウトライン テキストが導入されました。アウトライン テキストは、テキストの周囲に大きなコントラスト領域を描画して、読みやすさを大幅に改善します。
Android 16 には、アプリがこのモードが有効になっているかどうかを確認またはリスナーを登録できる新しい AccessibilityManager API が含まれています。これは主に、Compose などの UI ツールキットが同様のビジュアル エクスペリエンスを提供するために使用されます。UI ツールキット ライブラリを維持している場合や、アプリが android.text.Layout クラスをバイパスするカスタム テキスト レンダリングを実行している場合は、このクラスを使用して、アウトライン テキストが有効になっているかどうかを確認できます。
TtsSpan に時間の長さを追加
Android 16 では、TtsSpan を TYPE_DURATION で拡張しています。これは、ARG_HOURS、ARG_MINUTES、ARG_SECONDS で構成されています。これにより、時間の長さを直接アノテーションして、TalkBack などのサービスで正確で一貫したテキスト読み上げ出力を実現できます。
複数のラベルを持つ要素をサポートする
現在、Android では UI 要素が別の要素からユーザー補助ラベルを派生させることができますが、ウェブ コンテンツでよくあるシナリオとして、複数のラベルを関連付ける機能が追加されました。AccessibilityNodeInfo 内にリストベースの API を導入することで、Android はこれらのマルチラベル関係を直接サポートできるようになります。この変更の一環として、AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy と #getLabeledBy のサポートが終了し、代わりに #addLabeledBy、#removeLabeledBy、#getLabeledByList が使用されるようになりました。
展開可能な要素のサポートを改善しました
Android 16 では、メニューや展開可能なリストなどのインタラクティブな要素の展開状態や閉じ状態を伝達できるユーザー補助 API が追加されています。setExpandedState を使用して展開状態を設定し、CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED コンテンツ変更タイプで TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents をディスパッチすると、TalkBack などのスクリーン リーダーが状態の変化を通知し、より直感的で包括的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを提供できます。
不確定形式の ProgressBar
Android 16 では RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE が追加され、確定型と不確定型の両方の ProgressBar ウィジェットに RangeInfo を公開できるようになりました。これにより、TalkBack などのサービスが進行状況インジケータのフィードバックをより一貫して提供できるようになります。
3 つの状態のチェックボックス
Android 16 の新しい AccessibilityNodeInfo メソッド getChecked と setChecked(int) は、「チェック済み」と「未チェック」に加えて、「部分的にチェック済み」の状態をサポートするようになりました。これは、非推奨のブール値 isChecked と setChecked(boolean) に代わるものです。
補足説明
ユーザー補助サービスが ViewGroup を記述する場合は、その子ビューのコンテンツ ラベルと組み合わせます。ViewGroup に contentDescription を指定すると、ユーザー補助サービスは、フォーカス不可能な子ビューの説明もオーバーライドしていると想定します。たとえば、ドロップダウン(「フォント ファミリー」など)にラベルを付けながら、ユーザー補助用に現在の選択内容(「Roboto」など)を保持したい場合、この点が問題になることがあります。Android 16 では setSupplementalDescription が追加され、子からの情報を上書きせずに ViewGroup に関する情報を提供するテキストを指定できるようになりました。
必須のフォーム フィールド
Android 16 では、AccessibilityNodeInfo に setFieldRequired が追加され、アプリがフォーム フィールドへの入力が必須であることをユーザー補助サービスに通知できるようになりました。これは、必須の利用規約チェックボックスなど、さまざまな種類のフォームに記入するユーザーにとって重要なシナリオです。ユーザーは、必須フィールドを一貫して識別し、すばやく移動できます。
LEA 補聴器を使用した音声通話で、スマートフォンのマイクを入力として使用
Android 16 では、LE Audio 補聴器のユーザーが、音声通話で補聴器の組み込みマイクとスマートフォンのマイクを切り替えられる機能が追加されています。これは、騒がしい環境や、補聴器のマイクがうまく機能しない可能性があるその他の状況で役立ちます。
LEA 補聴器の周囲の音の調整
Android 16 では、LE Audio 補聴器のユーザーが、補聴器のマイクによって拾われる周囲の音の音量を調整できる機能が追加されました。これは、背景のノイズがうるさすぎる場合や静かすぎる場合に役立ちます。
カメラ
Android 16 では、プロのカメラユーザー向けのサポートが強化され、ハイブリッド自動露出と、色温度と色合いの正確な調整が可能になります。新しいナイトモード インジケーターにより、アプリはナイトモードのカメラ セッションへの切り替えのタイミングを把握できます。新しい Intent アクションにより、モーション フォトを簡単に撮影できるようになりました。また、HEIC エンコードと ISO 21496-1 ドラフト標準の新しいパラメータのサポートにより、UltraHDR 画像の改善も継続して行っています。
ハイブリッド自動露出
Android 16 では、Camera2 に新しいハイブリッド自動露出モードが追加されました。これにより、露出の特定の部分を手動で制御しながら、残りの部分を自動露出(AE)アルゴリズムに処理させることができます。ISO + AE と露出時間 + AE を制御できるため、完全な手動制御か自動露出に完全に依存するかのどちらかである現在のアプローチよりも柔軟性が増します。
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
色温度と色合いを正確に調整
Android 16 では、プロの動画撮影アプリをより適切にサポートするために、カメラで色温度と色合いを微調整できるようになりました。以前の Android バージョンでは、CONTROL_AWB_MODE で白色バランスの設定を制御できました。CONTROL_AWB_MODE には、白熱灯、曇り、夕暮れなど、プリセット リストに限定されたオプションが含まれていました。COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT を使用すると、COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE と COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT を使用して、相関色温度に基づいてホワイトバランスを正確に調整できます。
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
次の例は、さまざまな色温度と色合いの調整を適用した写真の外観を示しています。





カメラの夜間モードのシーン検出
夜間モードのカメラ セッションとの切り替えタイミングをアプリが把握できるように、Android 16 では EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR が追加されました。サポートされている場合は、Camera2 内の CaptureResult で使用できます。
これは、Instagram でユーザーが美しい低照度写真を撮影できるようにした方法に関するブログ投稿で、近日提供予定として簡単に言及した API です。この投稿は、夜間モードを実装する方法に関する実用的なガイドです。また、アプリ内カメラで撮影された高画質の夜間モードの写真と、アプリ内カメラから共有される写真数の増加を結びつけるケーススタディも掲載されています。
モーション フォトのキャプチャ インテント アクション
Android 16 では、カメラ アプリにモーション フォトをキャプチャして返すようリクエストする標準インテント アクション(ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE、ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE)が追加されました。
追加の EXTRA_OUTPUT を渡してイメージの書き込み先を制御するか、Intent.setClipData(ClipData) を介して Uri を渡す必要があります。ClipData を設定しないと、Context.startActivity(Intent) を呼び出すときにコピーされます。
ウルトラ HDR 画像の拡張

Android 16 では、UltraHDR 画像で鮮明な画質を実現するための取り組みを継続しています。HEIC ファイル形式の UltraHDR 画像のサポートが追加されました。これらの画像は ImageFormat タイプ HEIC_ULTRAHDR になり、既存の UltraHDR JPEG 形式と同様に埋め込みのゲインマップが含まれます。UltraHDR の AVIF サポートにも取り組んでおりますので、どうぞご期待ください。
さらに、Android 16 では、ISO 21496-1 ドラフト標準の UltraHDR に追加のパラメータを実装しています。これには、ゲインマップの計算を適用するカラースペースを取得して設定する機能や、SDR ゲインマップを含む HDR エンコード ベース画像のサポートが含まれます。
グラフィック
Android 16 には、AGSL を使用したカスタム グラフィック効果など、最新のグラフィックの改善が含まれています。
AGSL を使用したカスタム グラフィック効果
Android 16 では、RuntimeColorFilter と RuntimeXfermode が追加され、しきい値、セピア、色相飽和度などの複雑なエフェクトを作成して、描画呼び出しに適用できるようになりました。Android 13 以降では、AGSL を使用して、Shader を拡張するカスタム RuntimeShaders を作成できます。新しい API はこれをミラーリングし、ColorFilter を拡張する AGSL ベースの RuntimeColorFilter と、ソース ピクセル間と宛先ピクセル間の AGSL ベースのカスタム コンポジットとブレンドを実装できる Xfermode エフェクトを追加します。
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
接続
Android 16 では、プラットフォームがアップデートされ、アプリで最新の通信技術やワイヤレス技術を利用できるようになります。
セキュリティ強化による測距
Android 16 では、Wi-Fi 6 の 802.11az を搭載したサポート対象デバイスの Wi-Fi 位置情報で堅牢なセキュリティ機能がサポートされるようになりました。これにより、アプリは、プロトコルの精度、スケーラビリティ、動的スケジューリングの向上と、AES-256 ベースの暗号化や MITM 攻撃からの保護などのセキュリティ強化を組み合わせることができます。これにより、ノートパソコンや車のドアのロック解除など、近接型のユースケースでより安全に使用できます。802.11az は Wi-Fi 6 規格と統合されており、そのインフラストラクチャと機能を活用することで、より広範な導入とより簡単なデプロイを実現します。
汎用的な距離測定 API
Android 16 には、サポートされているハードウェアでローカル デバイスとリモート デバイス間の距離と角度を決定する方法を提供するための新しい RangingManager が含まれています。RangingManager は、BLE チャネル サウンド、BLE RSSI ベースの測距、ウルトラワイドバンド、Wi-Fi ラウンドトリップ時間など、さまざまな測距技術の使用をサポートしています。
コンパニオン デバイス マネージャーのデバイスの存在
Android 16 では、コンパニオン アプリ サービスをバインドするための新しい API が導入されています。BLE が範囲内にあり、Bluetooth が接続されている場合はサービスがバインドされ、BLE が範囲外にあるか Bluetooth が接続されていない場合はサービスがバインド解除されます。アプリは、さまざまな DevicePresenceEvent に基づいて、新しい onDevicePresenceEvent() コールバックを受け取ります。詳しくは、'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)' をご覧ください。
メディア
Android 16 には、メディア エクスペリエンスを向上させるさまざまな機能が含まれています。
写真選択ツールの改善
写真選択ツールは、メディア ライブラリ全体ではなく、ローカル ストレージとクラウド ストレージの両方から選択した画像と動画にアプリがアクセスできるようにする、安全な組み込みツールです。Google システム アップデートを介したモジュラー システム コンポーネントと Google Play 開発者サービスを組み合わせて、Android 4.4(API レベル 19)以前に対応しています。統合に必要なコードは、関連する Android Jetpack ライブラリで数行のみです。
Android 16 では、写真選択ツールが次のように改善されています。
- 埋め込み写真選択ツール: アプリがビュー階層に写真選択ツールを埋め込むことを可能にする新しい API。これにより、アプリのより統合された部分のように感じながら、プロセスの分離を活用して、アプリが過度に広範な権限を必要とせずにユーザーがメディアを選択できるようにします。埋め込みの写真選択ツールを統合する場合は、プラットフォーム バージョン間の互換性を最大限に高め、統合を簡素化するために、今後リリースされる Android Jetpack ライブラリを使用することをおすすめします。
- 写真選択ツールでの Cloud Search: Android の写真選択ツールでクラウド メディア プロバイダからの検索を可能にする新しい API。写真選択ツールの検索機能は近日提供予定です。
高度なプロフェッショナル動画
Android 16 では、プロレベルの高品質な動画の撮影とポストプロダクションに使用するように設計された Advanced Professional Video(APV)コーデックのサポートが導入されています。
APV コーデック標準には次の機能があります。
- 知覚的に損失のない動画品質(RAW 動画品質に近い)
- 複雑さが低く、スループットの高いフレーム内のみのコーディング(ピクセル ドメイン予測なし)により、編集ワークフローをより適切にサポート
- 軽量エントロピー コーディング スキームにより、2K、4K、8K 解像度のコンテンツで最大数 Gbps の高ビットレート範囲をサポート
- 没入型コンテンツと並列エンコードとデコードを可能にするフレーム タイリング
- さまざまなクロマ サンプリング形式とビット深度のサポート
- 画質の大幅な低下なしで複数のデコードと再エンコードをサポート
- マルチビュー動画と補助動画(深度、アルファ、プレビューなど)をサポートする
- HDR10/10+ とユーザー定義メタデータのサポート
APV のリファレンス実装は、OpenAPV プロジェクトで提供されています。Android 16 では、10 ビット エンコードと最大 2 Gbps のターゲット ビットレートを備えた YUV 422 カラー サンプリングを提供する APV 422-10 プロファイルのサポートが実装されます。
プライバシー
Android 16 には、アプリ デベロッパーがユーザーのプライバシーを保護するのに役立つさまざまな機能が含まれています。
ヘルスコネクトの更新
ヘルスコネクトに ACTIVITY_INTENSITY が追加されました。これは、中程度および激しいアクティビティに関する世界保健機関のガイドラインに従って定義されたデータ型です。各レコードには、開始時間、終了時間、アクティビティの強度(中程度または激しい)が必要です。
ヘルスコネクトには、医療記録をサポートする更新された API も含まれています。これにより、アプリはユーザーの明示的な同意を得て、FHIR 形式の医療記録の読み取りと書き込みを行うことができます。
Android 版プライバシー サンドボックス
Android 16 には、最新バージョンの Android 版プライバシー サンドボックスが組み込まれています。これは、ユーザーがプライバシーが保護されていることを認識できる技術を開発するための継続的な取り組みの一環です。Android 版プライバシー サンドボックスのデベロッパー ベータ版プログラムについて詳しくは、ウェブサイトをご覧ください。SDK ランタイムをご確認ください。SDK ランタイムを使用すると、SDK をサービス提供元のアプリとは別の専用のランタイム環境で実行できるため、ユーザーデータの収集と共有に関する安全対策と保証を強化できます。
セキュリティ
Android 16 には、アプリのセキュリティを強化し、アプリのデータを保護するのに役立つ機能が含まれています。
キー共有 API
Android 16 では、Android Keystore キーへのアクセスを他のアプリと共有する API が追加されています。新しい KeyStoreManager クラスは、アプリの uid による鍵へのアクセスの付与と取り消しをサポートし、アプリが共有鍵にアクセスするための API が含まれています。
デバイスのフォーム ファクタ
Android 16 では、Android のフォーム ファクタを最大限に活用するためのサポートがアプリに提供されます。
テレビの画質と音質の標準化されたフレームワーク
Android 16 の新しい MediaQuality パッケージは、オーディオ プロファイルと画像プロファイル、ハードウェア関連の設定にアクセスするための標準化された API のセットを公開します。これにより、ストリーミング アプリはプロファイルをクエリし、メディアに動的に適用できます。
- ダイナミック レンジが広い映画では、シャドウの微細なディテールを認識し、周囲光に合わせて調整するために、より高い色の精度が必要になります。そのため、明るさよりも色の精度を重視したプロファイルが適している場合があります。
- スポーツのライブ配信は、ダイナミック レンジが狭い状態でマスタリングされることが多く、日光の下で視聴されることも多いので、色の精度よりも明るさを優先するプロファイルの方が良い結果が得られます。
- 完全にインタラクティブなコンテンツでは、レイテンシを低減するために最小限の処理と高いフレームレートが必要です。そのため、多くのテレビにはゲーム プロファイルが付属しています。
この API を使用すると、アプリでプロファイルを切り替えたり、ユーザーがサポートされているテレビをコンテンツに合わせて調整したりできます。
多言語対応
Android 16 では、デバイスが異なる言語で使用される場合のユーザー エクスペリエンスを補完する機能が追加されています。
縦書きテキスト
Android 16 では、テキストの垂直方向のレンダリングと測定に対する低レベルのサポートが追加され、ライブラリ デベロッパー向けの基本的な垂直書き込みサポートが提供されます。これは、縦書きが一般的である日本語などの言語で特に便利です。Paint クラスに新しいフラグ VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG が追加されました。このフラグが Paint.setFlags を使用して設定されている場合、Paint のテキスト測定 API は水平方向の移動ではなく垂直方向の移動を報告し、Canvas はテキストを垂直方向に描画します。
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
測定単位のカスタマイズ
ユーザーは、[設定] の地域別の設定で測定単位をカスタマイズできるようになりました。ユーザー設定はロケール コードの一部として含まれるため、ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED に BroadcastReceiver を登録して、地域の設定が変更されたときに言語 / 地域の構成の変更を処理できます。
フォーマッタを使用すると、ローカル エクスペリエンスに合わせることができます。たとえば、英語(米国)の「0.5 in」は、スマートフォンを英語(デンマーク)に設定しているユーザー、または英語(米国)でスマートフォンを使用しているユーザーで、測定単位としてメートル法を設定している場合は「12,7 mm」になります。
これらの設定を確認するには、設定アプリを開いて [システム] > [言語と地域] に移動します。
