يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة ورائعة للمطوّرين. توضّح الأقسام التالية هذه الميزات لمساعدتك على البدء في استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات ذات الصلة.
للحصول على قائمة مفصّلة بواجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة والمعدَّلة والمحذوفة، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تقرير الاختلافات في واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. للحصول على تفاصيل حول واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة، يُرجى الانتقال إلى مرجع واجهات برمجة تطبيقات Android، حيث يتم تمييز واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة لتسهيل العثور عليها.عليك أيضًا مراجعة الأقسام التي قد تؤثر فيها تغييرات النظام الأساسي في تطبيقاتك. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على الصفحات التالية:
- التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثّر في التطبيقات عند استهدافها الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android
- تغييرات في السلوك تؤثر في جميع التطبيقات بغض النظر عن
targetSdkVersion
الوظيفة الأساسية
يتضمّن Android واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة توسّع الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام Android.
إصداران من واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Android في عام 2025
- هذه المعاينة مخصّصة للإصدار الرئيسي التالي من Android والمقرر إطلاقه في الربع الثاني من عام 2025. يشبه هذا الإصدار جميع إصدارات واجهة برمجة التطبيقات التي طرحناها في السابق، حيث يمكن أن نُجري تغييرات مخطّط لها في السلوك غالبًا ما تكون مرتبطة بقيمة targetSdkVersion.
- نحن نخطّط لطرح الإصدار الرئيسي في الربع الثاني من العام بدلاً من الربع الثالث كما كان الحال في الأعوام السابقة، وذلك لمواءمة الجدول الزمني لإطلاق الأجهزة في منظومتنا المتكاملة بشكل أفضل، ما يتيح لمزيد من الأجهزة الحصول على الإصدار الرئيسي من Android في وقت أقرب. مع طرح الإصدار الرئيسي في الربع الثاني من العام، عليك إجراء اختبار التوافق السنوي قبل بضعة أشهر من السنوات السابقة للتأكّد من جاهزية تطبيقاتك.
- نخطّط لطرح إصدار آخر في الربع الرابع من عام 2025 سيتضمّن أيضًا واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة للمطوّرين. سيكون الإصدار الرئيسي للربع الثاني من العام هو الإصدار الوحيد في عام 2025 الذي يتضمّن تغييرات مخطّط لها في السلوك قد تؤثّر في التطبيقات.
بالإضافة إلى واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة للمطوّرين، سيتضمّن الإصدار الثانوي للربع الرابع تحديثات ميزات وتحسينات وإصلاحات أخطاء، ولن يتضمّن أي تغييرات في السلوك تؤثّر في التطبيق.
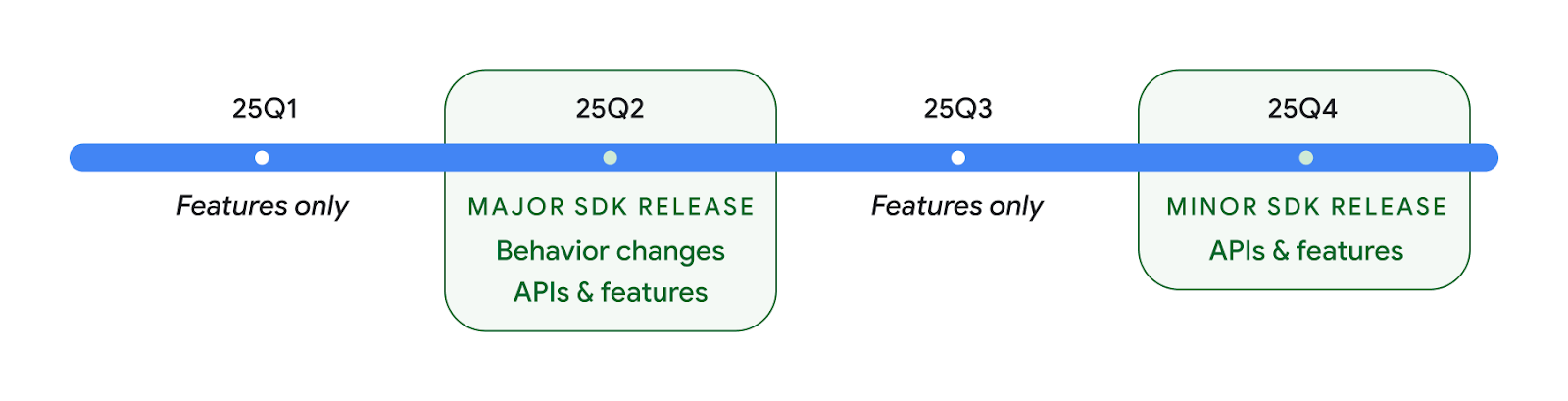
سنواصل طرح إصدارات Android كل ثلاثة أشهر. ستوفّر تحديثات الرُبع الأول والرُبع الثالث بين إصدارات واجهة برمجة التطبيقات تحديثات تدريجية للمساعدة في ضمان باستمرارية الجودة. نحن نعمل بنشاط مع شركائنا من المصنّعين لطرح الإصدار في الربع الثاني على أكبر عدد ممكن من الأجهزة.
استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة مع الإصدارات الرئيسية والثانوية
يتم حاليًا حماية كتلة رمز باستخدام عملية تحقّق من مستوى واجهة برمجة التطبيقات باستخدامCONSTANTSDK_INT معVERSION_CODES. وسيستمر
إتاحة هذا الإجراء لإصدارات Android الرئيسية.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
يمكن استخدام الثابت الجديد SDK_INT_FULL
لعمليات التحقّق من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات في كلّ من الإصدارات الرئيسية والثانوية باستخدام التعداد الجديد VERSION_CODES_FULL.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام الوسيطة
Build.getMinorSdkVersion()
للحصول على الإصدار الثانوي من حزمة SDK فقط.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
لم يتم الانتهاء من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه بعد، وهي عرضة للتغيير، لذا يُرجى إرسال ملاحظاتك إلينا إذا كانت لديك أي استفسارات.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يمنح نظام التشغيل Android 16 مطوّري التطبيقات والمستخدمين المزيد من التحكّم والمرونة في إعداد أجهزتهم بما يتناسب مع احتياجاتهم.
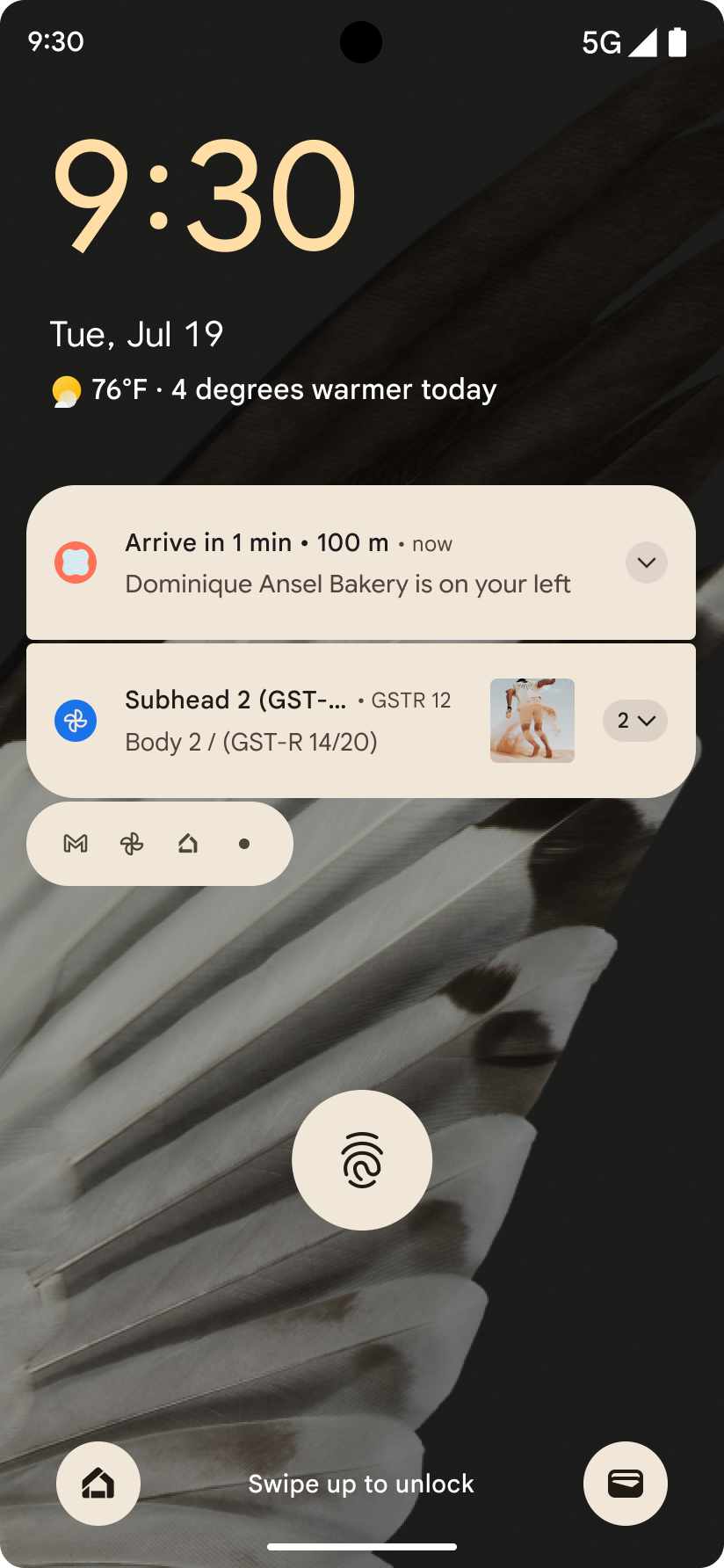
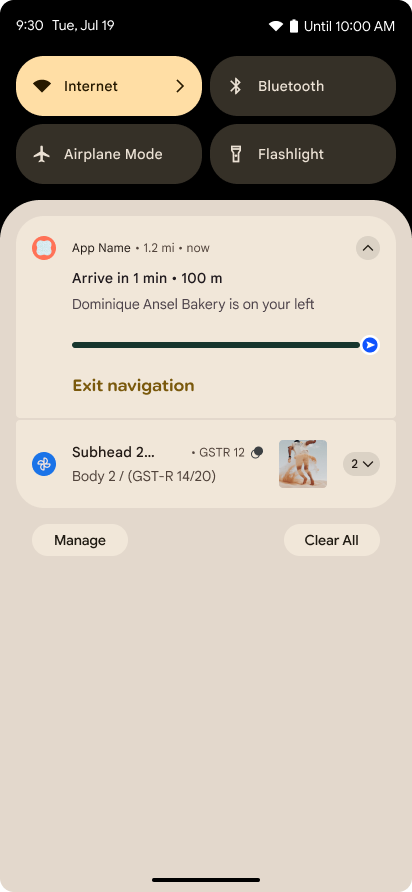
الإشعارات التي تركّز على مستوى التقدّم
يقدّم الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android إشعارات تركّز على مستوى التقدّم لمساعدة المستخدمين في تتبُّع الرحلات التي يبدأها المستخدمون من البداية إلى النهاية بسلاسة.
Notification.ProgressStyle هو أسلوب إشعار
جديد يتيح لك إنشاء إشعارات تركّز على مستوى التقدّم. تشمل حالات الاستخدام الرئيسية
خدمات النقل المشترك والتوصيل والملاحة. ضمن Notification.ProgressStyle
الفئة، يمكنك الإشارة إلى الحالات والمحطّات الرئيسية في رحلة المستخدِم باستخدام
النقاط والشريح.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على صفحة مستندات الإشعارات التي تركّز على مستوى التقدّم.
تعديلات على إيماءة الرجوع إلى الخلف التنبؤية
يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة لمساعدتك في تفعيل الصور المتحركة في النظام لإيماءة الرجوع إلى الخلف التنبؤية في أثناء التنقّل باستخدام الإيماءات، مثل الصورة المتحركة للرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية. من خلال تسجيل
onBackInvokedCallback باستخدام الرمز الجديد
PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER، يمكن لتطبيقكتلقّي طلب onBackInvoked العادي كلما تعامل النظام مع عملية الرجوع بدون التأثير في سير عملية الرجوع العادي.
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 أيضًا رمزَي
finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() و
moveTaskToBackCallback. من خلال تسجيل عمليات الاستدعاء هذه
باستخدام OnBackInvokedDispatcher، يمكن للنظام بدء
سلوكيات معيّنة وتشغيل الصور المتحركة المقابلة مسبقًا عند تنفيذ رمز الإيماءة
للرجوع.
تجاوب حسّي أكثر ثراءً
منذ إطلاقه، وفّر نظام التشغيل Android إمكانية التحكّم في المحرّك اللمسي.
أضاف نظام التشغيل Android 11 ميزة التوافق مع التأثيرات اللمسية الأكثر تعقيدًا التي يمكن أن توفّرها ملفّات
التشغيل المتقدّمة من خلال
VibrationEffect.Compositions من العناصر الأساسية
الدلالية التي يحدّدها الجهاز.
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات للتأثيرات الحسية تتيح للتطبيقات تحديد منحنيات amplitude وfrequency لتأثير حسي مع تجاهل اختلافات قدرات الجهاز.
إنتاجية المطوّرين وأدواتهم
مع أنّ معظم جهودنا لتحسين إنتاجيتك تركّز على أدوات مثل استوديو Android وJetpack Compose ومكتبات Android Jetpack، إلا أنّنا نبحث دائمًا عن طرق في النظام الأساسي لمساعدتك في تحقيق أهدافك.
التعامل مع المحتوى في الخلفيات المتحركة
في الإصدار 16 من Android، سيحصل إطار عمل الخلفيات المتحركة على واجهة برمجة تطبيقات جديدة للمحتوى بهدف
معالجة تحديات الخلفيات الديناميكية التي ينشئها المستخدمون. في الوقت الحالي، تتطلّب
خلفيات الشاشة النشطة التي تتضمّن محتوى يقدّمه المستخدم تنفيذًا معقدًا
خاصًا بالخدمة. يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 رمزَي emoji
WallpaperDescription و
WallpaperInstance. يتيح لك WallpaperDescription معرفة
حالات مختلفة من خلفية متحركة من الخدمة نفسها. على سبيل المثال، قد تتضمّن الخلفية التي تظهر على كل من الشاشة الرئيسية وشاشة القفل محتوًى فريدًا في كلا المكانَين. يستخدم أداة اختيار الخلفية وWallpaperManager هذه البيانات الوصفية لعرض
الخلفيات بشكل أفضل للمستخدمين، ما يسهّل عليك إنشاء تجارب متنوعة
ومخصَّصة للخلفيات الحية.
الأداء والبطارية
يقدّم الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تساعد في جمع إحصاءات حول تطبيقاتك.
تحديد المواصفات الشخصية لصاحب البيانات من خلال النظام
تم إضافةProfilingManager في Android 15، ما يتيح للتطبيقات طلب جمع بيانات الأداء باستخدام Perfetto على الأجهزة العامة في الميدان.
ومع ذلك، بما أنّه يجب بدء عملية وضع هذه الملفات الشخصية من التطبيق، سيكون من الصعب أو من المستحيل على التطبيقات تسجيل مسارات الأداء الحرجة، مثل عمليات بدء التشغيل أو أخطاء ANR.
للمساعدة في ذلك، يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 ميزة "الملف الشخصي الذي يبدأه النظام" لتطبيق
ProfilingManager. يمكن للتطبيقات تسجيل اهتمامها بتلقّي عمليات تتبُّع لعوامل بدء محدّدة
مثل بدء التشغيل البارد reportFullyDrawn
أو أخطاء ANR، ثم يبدأ النظام عملية تتبُّع ويوقفها نيابةً عن التطبيق. بعد اكتمال التتبُّع، يتم إرسال النتائج إلى دليل بيانات التطبيق.
بدء المكوّن في ApplicationStartInfo
تم إضافةApplicationStartInfo في الإصدار
15 من Android، ما يتيح للتطبيق الاطّلاع على أسباب
بدء العملية ونوع البدء وأوقات البدء والحدّ من السرعة وغيرها من بيانات التشخيص مفيدة. يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android رمزًا برمجيًا هو
getStartComponent()
لتمييز نوع المكوّن الذي بدأ عملية التشغيل، ما قد يكون مفيدًا في
تحسين عملية بدء تشغيل تطبيقك.
فحص أفضل للوظائف
تعرض واجهة برمجة التطبيقات JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() سبب احتمال أن تكون إحدى المهام في انتظار المراجعة. ومع ذلك، قد تكون المهمة في انتظار المراجعة لعدة أسباب.
في Android 16، نقدّم واجهة برمجة تطبيقات جديدة
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId)، وهي تعرض عدة
أسباب لتعليق إحدى المهام، وذلك بسبب القيود الصريحة التي يحدّدها المطوّر والقيود الضمنية التي يحدّدها النظام.
نقدّم أيضًا الرمز
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId) الذي يعرض قائمة
بأحدث تغييرات القيود.
ننصحك باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لمساعدتك في تصحيح الأخطاء المتعلّقة بعدم تنفيذ مهامك، خاصةً إذا لاحظت انخفاضًا في معدّلات نجاح مهام معيّنة أو إذا واجهت أخطاء تتعلّق بالوقت المستغرَق لإكمال مهام معيّنة. على سبيل المثال، تعذّر تعديل التطبيقات المصغّرة في الخلفية أو تعذّر استدعاء مهمة التحميل المُسبَق قبل بدأ التطبيق.
ويمكن أن يساعدك ذلك أيضًا في معرفة ما إذا كانت بعض المهام لا تكتمل بسبب قيود محدّدة من النظام مقارنةً بالقيود المحدّدة بوضوح.
معدّل التحديث التكيّفي
إنّ معدل إعادة التحميل التكيُّفي (ARR) الذي تم تقديمه في Android 15 يتيح لمعدل إعادة تحميل الشاشة على الأجهزة المتوافقة التكيُّف مع معدل عرض اللقطات للمحتوى باستخدام خطوات فاصل عرض اللقطات المنفصلة. ويؤدي ذلك إلى تقليل استهلاك الطاقة مع التخلص من الحاجة إلى التبديل بين الأوضاع الذي قد يؤدي إلى حدوث تقطُّع في الأداء.
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 hasArrSupport() و
getSuggestedFrameRate(int) مع استعادة
getSupportedRefreshRates() لتسهيل استفادة تطبيقاتك من ميزة ARR. يتيح RecyclerView
1.4 استخدام ميزة ARR داخليًا عند الانتقال من التمرير السريع أو
الانتقال السلس، ونحن نواصل عملنا لإضافة ميزة ARR
إلى المزيد من مكتبات Jetpack. تتناول مقالة معدّل عرض اللقطات هذه
العديد من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي يمكنك استخدامها لضبط معدّل عرض اللقطات كي يتمكّن تطبيقك من استخدام ميزة "معدل عرض الإعلانات" مباشرةً.
واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الخاصة بمساحة التحسين في ADPF
يقدّم SystemHealthManager واجهات برمجة التطبيقات
getCpuHeadroom و
getGpuHeadroom، وهي مصمّمة لتزويد الألعاب و
التطبيقات المستهلكة للموارد الكثيفة بتقديرات لموارد وحدة المعالجة المركزية ووحدة معالجة الرسومات المتاحة. توفّر هذه ال methods طريقة لك لقياس مدى قدرة تطبيقك أو لعبتك على تحسين حالة النظام على أفضل نحو، خاصةً عند استخدامها مع واجهات برمجة تطبيقات أخرى لإطار عمل Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF) التي ترصد التباطؤ المتعلّق بالحرارة.
باستخدام CpuHeadroomParams و
GpuHeadroomParams على الأجهزة المتوافقة، يمكنك
تخصيص النافذة الزمنية المستخدَمة لاحتساب الحد الأقصى للطاقة واختيار بين
متوسط أو الحد الأدنى لمستوى توفّر الموارد. ويمكن أن يساعدك ذلك في تقليل استخدام موارد وحدة المعالجة المركزية أو
وحدة معالجة الرسومات وفقًا لذلك، ما يؤدي إلى تحسين تجارب المستخدمين وتحسين
عمر البطارية.
تسهيل الاستخدام
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة لتسهيل الاستخدام يمكن أن تساعدك في توفير تطبيقك لجميع المستخدمين.
واجهات برمجة تطبيقات محسَّنة لتسهيل الاستخدام
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات إضافية لتحسين دلالات واجهة المستخدم التي تساعد في تحسين الاتساق للمستخدمين الذين يعتمدون على خدمات تسهيل الاستخدام، مثل TalkBack.
النص المفرّغ لزيادة تباين النص إلى أقصى حد
غالبًا ما يعاني المستخدمون الذين يعانون من ضعف في النظر من انخفاض في حساسية التباين، ما يجعل من الصعوبة بمكان تمييز الأجسام عن الخلفيات. لمساعدة هؤلاء المستخدمين، يقدّم الإصدار 16 من Android ميزة "النص المخطّط" الذي يحلّ محلّ ميزة "النص العالي التباين"، والذي يرسم منطقة أكبر ذات تباين أعلى حول النص لتحسين قراءته بشكل كبير.
يحتوي Android 16 على واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة AccessibilityManager للسماح لتطبيقاتك بالتحقّق أو تسجيل مستمع لتحديد ما إذا كان هذا الوضع مفعّلاً. يُستخدم هذا الأسلوب بشكل أساسي في حِزم أدوات واجهة المستخدم، مثل Compose، لتوفير تجربة مرئية مشابهة. إذا كنت تحافظ على مكتبة UI Toolkit أو كان
تطبيقك يُجري عرضًا مخصّصًا للنص يتجاوز فئة
android.text.Layout، يمكنك استخدام هذا الإجراء لمعرفة
حالات تفعيل النص المخطّط.
تمت إضافة المدة إلى TtsSpan
يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android TtsSpan TYPE_DURATION،
المكوّن من ARG_HOURS وARG_MINUTES
وARG_SECONDS. يتيح لك ذلك إضافة تعليقات توضيحية مباشرةً إلى مدّة المحتوى، ما يضمن تحويلًا دقيقًا ومتسقًا للنص إلى كلام باستخدام خدمات مثل TalkBack.
إتاحة العناصر التي تحتوي على تصنيفات متعددة
يسمح Android حاليًا لعناصر واجهة المستخدم بالحصول على تصنيف تسهيل الاستخدام من عنصر آخر، كما يتيح الآن إمكانية ربط تصنيفات متعددة، وهو سيناريو شائع في محتوى الويب. من خلال تقديم واجهة برمجة تطبيقات مستندة إلى قائمة في
AccessibilityNodeInfo، يمكن لنظام التشغيل Android إتاحة
هذه العلاقات المتعدّدة التصنيفات مباشرةً. وكجزء من هذا التغيير، أوقفنا نهائيًا استخدام
AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy و
#getLabeledBy واستبدلناهما برمزَي
#addLabeledBy و#removeLabeledBy و
#getLabeledByList.
تحسين التوافق مع العناصر القابلة للتوسيع
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تسهيل الاستخدام تتيح لك الإشارة إلى الحالة الموسّعة أو
المجمّعة للعناصر التفاعلية، مثل القوائم والقوائم القابلة للتوسيع. من خلال
ضبط الحالة الموسّعة باستخدام setExpandedState و
إرسال TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents
باستخدام نوع تغيير المحتوى CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED،
يمكنك التأكّد من أنّ برامج قراءة الشاشة، مثل TalkBack، تعلن عن
تغييرات الحالة، ما يقدّم تجربة مستخدم أكثر سهولة وشمولية.
أشرطة تقدّم غير محدّدة
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 رمز RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE، ما يتيح لك
عرض RangeInfo لكل من التطبيقات المصغّرةProgressBar المحددة وغير المحددة، ما يسمح لخدمات مثل
TalkBack بتقديم ملاحظات بشكل أكثر اتساقًا لمؤشرات التقدّم.
مربّع اختيار ثلاثي الحالات
تتيح الطريقتان الجديدتان AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked وsetChecked(int)
في Android 16 الآن حالة "تم وضع علامة جزئية" بالإضافة إلى
"تم وضع علامة" و "لم يتم وضع علامة". ويحلّ هذا النوع محلّ النوعَين المنطقيَين المتوقفَين نهائيًا
isChecked وsetChecked(boolean).
الأوصاف التكميلية
عندما تصف الخدمة المخصّصة لتسهيل الاستخدام عنصر ViewGroup، فإنّها
تضمّن تصنيفات المحتوى من عناصر العرض الثانوية. في حال تقديم contentDescription لعنصر ViewGroup، تفترض خدمات تسهيل الاستخدام أنّك تريد
أيضًا إلغاء وصف عناصر العرض الثانوية غير القابلة للتركيز. قد يتسبب ذلك في
مشاكل إذا أردت تصنيف عناصر مثل القائمة المنسدلة (على سبيل المثال، "عائلة
الخط") مع الحفاظ على الاختيار الحالي لتسهيل الاستخدام (على سبيل المثال،
"Roboto"). يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android setSupplementalDescription حتى تتمكّن من تقديم نص يقدّم معلومات عن ViewGroup بدون
إلغاء المعلومات الواردة من العناصر الفرعية.
حقول النموذج المطلوبة
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 الرمز setFieldRequired إلى
AccessibilityNodeInfo حتى تتمكّن التطبيقات من إبلاغ خدمة تسهيل الاستخدام بأنّ إدخال البيانات في حقل النموذج مطلوب. هذا سيناريو مهم
للمستخدمين الذين يملؤون العديد من أنواع النماذج، حتى الأشياء البسيطة مثل مربّع الاختيار المطلوب
لأحكام وشروط الاستخدام، ما يساعد المستخدمين في التعرّف على الحقول المطلوبة باستمرار
والتنقّل بينها بسرعة.
استخدام الهاتف كميكروفون لإجراء المكالمات الصوتية باستخدام سماعات الأذن الطبية المزودة بتقنية LEA
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 إمكانية السماح لمستخدمي سمّاعات الأذن الطبية المزوّدة بتقنية LE Audio بالتبديل بين الميكروفونات المدمجة في سمّاعات الأذن الطبية والميكروفون في الهاتف لإجراء المكالمات الصوتية. يمكن أن يكون ذلك مفيدًا في البيئات الصاخبة أو في حالات أخرى قد لا تعمل فيها ميكروفونات سماعة الأذن الطبية بشكل جيد.
عناصر التحكّم في مستوى الصوت المحيط لسماعات الأذن الطبية المتوافقة مع تقنية LEA
يتيح نظام التشغيل Android 16 لمستخدمي سمّاعات الأذن الطبية التي تتضمّن تقنية LE Audio إمكانية ضبط مستوى الصوت المحيط الذي تلتقطه ميكروفونات سمّاعة الأذن الطبية. يمكن أن يكون هذا الإجراء مفيداً في الحالات التي تكون فيها الضوضاء في الخلفية صاخبة جدًا أو منخفضة جدًا.
الكاميرا
يحسِّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 إمكانية استخدام الكاميرات الاحترافية، ما يتيح التعريض التلقائي المختلط إلى جانب التعديلات الدقيقة لدرجة حرارة الألوان ودرجة اللون. يساعد مؤشر وضع التصوير الليلي الجديد تطبيقك في معرفة الوقت المناسب للتبديل إلى جلسة تصوير في وضع التصوير الليلي أو الخروج منها. تسهّل الإجراءات الجديدة Intent التقاط صور متحركة،
ونواصل تحسين صور Ultra HDR من خلال توفير توافق مع ترميز HEIC
ومَعلمات جديدة من مسودة معيار ISO 21496-1.
التعرّض التلقائي المختلط للضوء
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 أوضاعًا جديدة مختلطة للتعريض التلقائي إلى Camera2، ما يتيح لك التحكّم يدويًا في جوانب معيّنة من التعريض مع السماح لخوارزمية التعريض التلقائي (AE) بالتعامل مع الباقي. يمكنك التحكّم في درجة ISO + التعريض التلقائي ووقت التعريض + التعريض التلقائي، ما يوفّر مزيدًا من المرونة مقارنةً بالنهج الحالي الذي يتيح لك التحكّم يدوياً بالكامل أو الاعتماد بالكامل على التعريض التلقائي.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
تعديلات دقيقة على درجة حرارة الألوان ودرجة اللون
يضيف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android ميزة ضبط درجة حرارة اللون والصبغة في الكاميرا بدقة
لتوفير دعم أفضل لتطبيقات تسجيل الفيديو الاحترافية. في الإصدارات السابقة من Android
، كان بإمكانك التحكّم في إعدادات توازن اللون الأبيض من خلال
CONTROL_AWB_MODE، الذي يحتوي على خيارات محدودة في
قائمة مُعدّة مسبقًا، مثل مصباح متوهج،
غائم، ومغيم. يتيح الرمز
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT استخدام رمزَي
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE و
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT لإجراء تعديلات دقيقة على
توازن اللون الأبيض استنادًا إلى درجة حرارة الألوان المرتبطة.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
توضّح الأمثلة التالية كيف ستبدو الصورة بعد تطبيق تعديلات مختلفة على درجة حرارة اللون والصبغة:





رصد المشاهد في "الوضع الليلي" للكاميرا
لمساعدة تطبيقك في معرفة وقت التبديل إلى جلسة الكاميرا في الوضع الليلي والخروج منها،أضافت الإصدار 16 من Android EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. إذا كان CaptureResult متاحًا، يمكنك العثور عليه في Camera2.
هذه هي واجهة برمجة التطبيقات التي ذكرناها بشكل موجز في منشور المدوّنة كيف سمحت منصة Instagram للمستخدمين بالتقاط صور رائعة في الإضاءة المنخفضة. هذه المشاركة هي دليل عملي حول كيفية استخدام وضع "الليل" بالإضافة إلى دراسة حالة تربط بين الصور العالية الجودة في وضع "الليل" داخل التطبيق وزيادة عدد الصور التي تتم مشاركتها من الكاميرا داخل التطبيق.
إجراءات Intent لالتقاط صور حيّة
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 إجراءات Intent عادية، وهي
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE و
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE، تطلب من
تطبيق الكاميرا التقاط صورة متحركة وإعادتها.
يجب إدخال EXTRA_OUTPUT إضافي للتحكّم في
مكان كتابة الصورة، أو Uri من خلال
Intent.setClipData(ClipData). إذا لم تضبط
ClipData، سيتم نسخها إليك عند الاتصال بالرقم
Context.startActivity(Intent).
تحسينات على صور UltraHDR

يواصل نظام Android 16 جهودنا لتوفير جودة صور مذهلة باستخدام صور UltraHDR. تمت إضافة إمكانية استخدام صور UltraHDR بتنسيق ملف HEIC. ستحصل هذه الصور على نوع ImageFormat
HEIC_ULTRAHDR وستحتوي على خريطة مكاسب مضمّنة مشابهة
لتنسيق UltraHDR JPEG الحالي. نحن نعمل أيضًا على إتاحة تنسيق AVIF لميزة UltraHDR، لذا يُرجى متابعتنا باستمرار.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، ينفِّذ الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android مَعلمات إضافية في ميزة "دقة HDR الفائقة" من مسودة معيار ISO 21496-1، بما في ذلك إمكانية الحصول على مساحة الألوان التي يجب تطبيق العمليات الحسابية لخريطة الكسب فيها وضبطها، بالإضافة إلى إتاحة الصور الأساسية المُشفَّرة بتقنية النطاق العالي الديناميكية (HDR) مع خرائط الكسب بتقنية النطاق العادي الديناميكية (SDR).
الرسومات
يتضمّن Android 16 أحدث التحسينات على الرسومات، مثل التأثيرات الرسومية المخصّصة باستخدام AGSL.
تأثيرات رسومية مخصّصة باستخدام AGSL
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 RuntimeColorFilter و
RuntimeXfermode، ما يتيح لك إنشاء تأثيرات معقّدة مثل
الحدّ الأدنى وتأثير "تشبيك الصورة" و"تشبع درجة اللون" وتطبيقها على طلبات الرسم. منذ الإصدار Android
13، أصبح بإمكانك استخدام AGSL لإنشاء
تأثيرات رسومية ديناميكية مخصّصة تمتد إلى Shader. تعكس واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة
هذا الإجراء، مع إضافة RuntimeColorFilter المستند إلى AGSL والتي
تُوسّع نطاق ColorFilter، وتأثير Xfermode الذي
يتيح لك تنفيذ عمليات دمج ومزج مخصّصة مستندة إلى AGSL بين وحدات البكسل المصدر
والوجهة.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
إمكانية الاتصال
يعدّل Android 16 النظام الأساسي لمنح تطبيقك إمكانية الوصول إلى أحدث التطورات في تكنولوجيات الاتصال والشبكات اللاسلكية.
تحديد المدى مع مستوى أمان محسّن
يضيف Android 16 ميزات أمان فعّالة في تحديد الموقع الجغرافي من خلال Wi-Fi على الأجهزة المتوافقة مع 802.11az لبروتوكول Wi-Fi 6، ما يتيح للتطبيقات الجمع بين الدقة العالية وقابلية التوسّع الأكبر والجدول الزمني الديناميكي للبروتوكول مع تحسينات الأمان، بما في ذلك التشفير المستنِد إلى AES-256 والحماية من هجمات MITM. يتيح ذلك استخدامه بأمان أكبر في حالات استخدام ميزة "الاقتران عن قرب"، مثل فتح قفل كمبيوتر محمول أو باب سيارة. تم دمج 802.11az مع معيار Wi-Fi 6، ما يستفيد من بنيته الأساسية و إمكاناته لاعتماده على نطاق أوسع ونشره بسهولة أكبر.
واجهات برمجة التطبيقات العامة لتحديد المدى
يتضمّن نظام Android 16 RangingManager الجديد الذي يوفّر
طُرقًا لتحديد المسافة والزاوية على الأجهزة المتوافقة بين
الجهاز المحلي
والجهاز البعيد. يتيح RangingManager استخدام مجموعة متنوعة من تكنولوجيات تحديد المسافة، مثل قياس طاقة قناة BLE وتحديد المسافة بالاستناد إلى مؤشر RSSI في BLE وUltrawideband ووقت الرحلة ذهابًا وإيابًا عبر شبكة Wi-Fi.
توفّر الجهاز المصاحب في "مدير الجهاز المصاحب"
في Android 16، يتمّ طرح واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة لربط
خدمة التطبيق المصاحب. سيتم ربط الخدمة عندما تكون تقنية BLE ضمن النطاق ويكون البلوتوث متصلاً،
وسيتم إلغاء ربط الخدمة عندما تكون تقنية BLE خارج النطاق أو عندما يتم
إيقاف البلوتوث. سيتلقّى التطبيق مكالمة مرتجعة جديدة لرمز دالة onDevicePresenceEvent() استنادًا إلى قيم مختلفة لحالة DevicePresenceEvent.
يمكنك الاطّلاع على مزيد من التفاصيل في
'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'.
الوسائط
يتضمّن Android 16 مجموعة متنوعة من الميزات التي تحسّن تجربة استخدام الوسائط.
تحسينات على أداة اختيار الصور
توفّر أداة اختيار الصور طريقة آمنة ومضمّنة للمستخدمين لمنح تطبيقك إذن الوصول إلى صور وفيديوهات محدّدة من التخزين على الجهاز والسحابة الإلكترونية بدلاً من الوصول إلى مكتبة الوسائط بأكملها. باستخدام مجموعة من مكوّنات النظام النموذجية من خلال تحديثات النظام من Google وخدمات Google Play، يمكن استخدام هذه الميزة في الإصدار Android 4.4 (المستوى 19 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأقدم. لا يتطلّب الدمج سوى بضعة أسطر من الرموز البرمجية مع مكتبة Android Jetpack المرتبطة.
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 التحسينات التالية على أداة اختيار الصور:
- أداة اختيار الصور المضمّنة: واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة تتيح للتطبيقات تضمين أداة اختيار الصور في التسلسل الهرمي للعرض ويسمح ذلك للمستخدمين بالشعور بأنّه جزء أكثر تكاملاً من التطبيق مع الاستفادة من عملية العزل التي تسمح للمستخدمين باختيار الوسائط بدون أن يحتاج التطبيق إلى أذونات واسعة النطاق. لزيادة التوافق إلى أقصى حدّ على مستوى إصدارات النظام الأساسي و تبسيط عملية الدمج، عليك استخدام مكتبة Android Jetpack القادمة إذا كنت تريد دمج أداة اختيار الصور المضمّنة.
- البحث في السحابة الإلكترونية في أداة اختيار الصور: واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة تتيح البحث من موفِّر وسائط السحابة الإلكترونية لأداة اختيار الصور على Android ستتوفّر قريبًا وظيفة البحث في أداة اختيار الصور.
فيديو احترافي متقدّم
يتيح نظام التشغيل Android 16 استخدام ترميز Advanced Professional Video (APV) المصمّم لاستخدامه في تسجيل الفيديوهات بجودة عالية على المستوى الاحترافي وعمليات ما بعد الإنتاج.
يتضمن معيار ترميز APV الميزات التالية:
- جودة فيديو بدون فقدان ملحوظ للبيانات (قريبة من جودة الفيديو الأصلي)
- ترميز داخل اللقطة فقط بدرجة منخفضة من التعقيد ومع معدل نقل بيانات مرتفع (بدون توقّع ملف هبوط حبيبات البكسل) لدعم سير عمل التعديل بشكل أفضل
- إتاحة نطاق معدل نقل بيانات مرتفع يصل إلى بضعة غيغابايت في الثانية للمحتوى بدقة 2K و4K و8K ، وذلك من خلال مخطّط ترميز معلومات منخفض الوزن
- تقسيم الإطارات للمحتوى الغامر وتفعيل الترميز والترميز الثنائي
- إتاحة تنسيقات مختلفة لتحليل الألوان ودرجات البت
- إتاحة عمليات فك ترميز وإعادة ترميز متعددة بدون تعريض الجودة المرئية للتدهّور الشديد
- إتاحة الفيديوهات المتعدّدة وأنواع الفيديوهات المساعِدة، مثل الفيديوهات التي تُظهر العمق والصور المموّهة والمعاينة
- التوافق مع تقنية HDR10/10+ والبيانات الوصفية التي يحدّدها المستخدم
يتم توفير تنفيذ مرجعي لـ APV من خلال مشروع OpenAPV. سيتيح نظام Android 16 استخدام الملف الشخصي APV 422-10 الذي يقدّم تحليل ألوان YUV 422 بالإضافة إلى ترميز 10 بت ومعدّلات نقل البيانات المستهدَفة التي تصل إلى 2 غيغابايت في الثانية.
الخصوصية
يتضمّن Android 16 مجموعة متنوّعة من الميزات التي تساعد مطوّري التطبيقات في حماية خصوصية المستخدمين.
تحديثات Health Connect
يضيف Health Connect ACTIVITY_INTENSITY، وهو نوع بيانات محدّد وفقًا لإرشادات منظمة
الصحة العالمية حول النشاط المعتدل والقوي. يتطلّب كل تسجيل معرفة وقت البدء والانتهاء وما إذا كانت شدة النشاط معتدلة أو قوية.
يحتوي Health Connect أيضًا على واجهات برمجة تطبيقات معدَّلة تتيح استخدام السجلّات الطبية. يتيح ذلك للتطبيقات قراءة السجلات الطبية وكتابتها بتنسيق FHIR بعد الحصول على موافقة صريحة من المستخدم.
"مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" على Android
يتضمّن الإصدار 16 من Android أحدث إصدار من مبادرة حماية الخصوصية على Android، وهي جزء من عملنا المستمر لتطوير تقنيات تضمن للمستخدمين اتّخاذ خطوات لحماية خصوصيتهم. يمكنك زيارة موقعنا الإلكتروني للاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات عن "مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" في الإصدار التجريبي من برنامج "مطوّرو تطبيقات Android" لمساعدتك في البدء. اطّلِع على وقت تشغيل حزمة SDK الذي يتيح تشغيل حِزم SDK في بيئة وقت تشغيل مخصّصة منفصلة عن التطبيق الذي تقدّمه، ما يوفر وسائل حماية أقوى بشأن جمع بيانات المستخدمين ومشاركتها.
الأمان
يتضمّن Android 16 ميزات تساعدك في تعزيز أمان تطبيقك وحماية بياناته.
Key sharing API
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تتيح مشاركة إمكانية الوصول إلى مفاتيح
متجر مفاتيح Android مع التطبيقات الأخرى. تتيح فئة
KeyStoreManager الجديدة
منح وإبطال إذن الوصول إلى المفاتيح
حسب uid للتطبيق، وتتضمّن واجهة برمجة تطبيقات للتطبيقات للوصول إلى مفاتيح
المشترَكة.
أشكال الأجهزة
يوفّر Android 16 لتطبيقاتك إمكانية الاستفادة إلى أقصى حد من عوامل الشكل في Android.
إطار عمل موحّد لجودة الصورة والصوت في أجهزة التلفزيون
توفّر MediaQuality
الحزمة الجديدة في Android 16 مجموعة من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الموحدة للوصول إلى الملفات الصوتية والملفات الصوتية والصور والإعدادات المتعلّقة بالأجهزة. يتيح ذلك لتطبيقات البث الاستعلام عن الملفات الشخصية
وتطبيقها على الوسائط ديناميكيًا:
- تتطلّب الأفلام التي تمّت إتقانها بنطاق ديناميكي أوسع دقة ألوان أكبر لتمييز التفاصيل الدقيقة في الظلال والتكيّف مع الإضاءة المحيطة، لذا قد يكون من المناسب استخدام ملف شخصي يفضّل دقة الألوان على السطوع.
- غالبًا ما يتم ضبط الفعاليات الرياضية المباشرة باستخدام نطاق ديناميكي ضيّق، ولكن يتم مشاهدتها غالبًا في ضوء النهار، لذا يمكن أن يقدّم الملف الشخصي الذي يفضّل السطوع على دقة الألوان نتائج أفضل.
- يتطلب المحتوى التفاعلي بالكامل الحد الأدنى من المعالجة لتقليل وقت الاستجابة، ويتطلب معدلات عرض صور أعلى، ولهذا السبب يتم شحن العديد من أجهزة التلفزيون مع ملف ألعاب.
تسمح واجهة برمجة التطبيقات للتطبيقات بالتبديل بين الملفات الشخصية والمستخدمين للاستفادة من ضبط أجهزة التلفزيون المتوافقة بما يناسب المحتوى على أفضل نحو.
التوافق مع أسواق عالمية
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 ميزات وإمكانات تكمل تجربة المستخدم عند استخدام الجهاز بلغات مختلفة.
نص عمودي
يضيف نظام Android 16 دعمًا من المستوى الأدنى لعرض النص وقياسه عموديًا بهدف
توفير دعم أساسي للكتابة العمودية لمطوّري المكتبات. ويفيد ذلك
بشكل خاص في اللغات التي تستخدم عادةً أنظمة كتابة عمودية، مثل اليابانية. تمت إضافة علامة جديدة،
VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG،
إلى فئة Paint. عند ضبط
هذا الإعداد باستخدام
Paint.setFlags، ستحدّد واجهات برمجة التطبيقات
لقياس النصوص في Paint التقدّم في الرسم بالاتجاه العمودي بدلاً من التقدّم في الرسم بالاتجاه الأفقي، وسيرسم Canvas النص
بالاتجاه العمودي.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
تخصيص نظام القياس
يمكن للمستخدمين الآن تخصيص نظام القياس في الإعدادات المفضّلة على مستوى المنطقة ضمن
الإعدادات. يتم تضمين إعدادات المستخدم المفضّلة كجزء من رمز اللغة، لذا يمكنك تسجيل BroadcastReceiver على ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED للتعامل مع تغييرات إعدادات اللغة عند تغيير الإعدادات المفضّلة على مستوى المنطقة.
يمكن أن يساعد استخدام أدوات التنسيق في مطابقة التجربة المحلية. على سبيل المثال، تمثل القيمة "0.5 بوصة" باللغة الإنجليزية (الولايات المتحدة) القيمة "12.7 مم" لمستخدم ضبط لغة هاتفه على الإنجليزية (الدنمارك) أو يستخدم هاتفه باللغة الإنجليزية (الولايات المتحدة) مع استخدام النظام المتري كنظام القياس المفضّل.
للعثور على هذه الإعدادات، افتح تطبيق "الإعدادات" وانتقِل إلى النظام > اللغات والمنطقة.
