Historically, Android has only supported 4 KB memory page sizes, which has optimized system memory performance for the average amount of total memory that Android devices have typically had. Beginning with Android 15, AOSP supports devices that are configured to use a page size of 16 KB (16 KB devices). If your app uses any NDK libraries, either directly or indirectly through an SDK, then you will need to rebuild your app for it to work on these 16 KB devices.
As device manufacturers continue to build devices with larger amounts of physical memory (RAM), many of these devices will adopt 16 KB (and eventually greater) page sizes to optimize the device's performance. Adding support for 16 KB page size devices enables your app to run on these devices and helps your app benefit from the associated performance improvements. Without recompiling, apps won't work on 16 KB devices in future Android releases.
To help you add support for your app, we've provided guidance on how to check if your app is impacted, how to rebuild your app (if applicable), and how to test your app in a 16 KB environment using emulators (including Android 15 system images for the Android Emulator).
Benefits and performance gains
Devices configured with 16 KB page sizes use slightly more memory on average, but also gain various performance improvements for both the system and apps:
- Lower app launch times while the system is under memory pressure: 3.16% lower on average, with more significant improvements (up to 30%) for some apps that we tested
- Reduced power draw during app launch: 4.56% reduction on average
- Faster camera launch: 4.48% faster hot starts on average, and 6.60% faster cold starts on average
- Improved system boot time: improved by 8% (approximately 950 milliseconds) on average
These improvements are based on our initial testing, and results on actual devices will likely differ. We'll provide additional analysis of potential gains for apps as we continue our testing.
Check if your app is impacted
If your app uses any native code, then you should rebuild your app with support for 16 KB devices. If you are unsure if your app uses native code, you can use the APK Analyzer to identify whether any native code is present and then check the alignment of ELF segments for any shared libraries that you find. Android Studio also provides features that help you to automatically detect alignment issues.
If your app only uses code written in the Java programming language or in Kotlin, including all libraries or SDKs, then your app already supports 16 KB devices. Nevertheless, we recommend that you test your app in a 16 KB environment to verify that there are no unexpected regressions in app behavior.
Does your app use native code?
Your app makes use of native code if any of the following apply:
- Your app uses any C/C++ (native) code. If your app uses the Android NDK, then your app uses native code.
- Your app links with any third-party native libraries or dependencies (such as SDKs) that use them.
- Your app is built by a third-party app builder that uses native libraries on device.
Identify native libraries using APK Analyzer
APK Analyzer is a tool that lets you evaluate various aspects of a built APK. To check whether your app uses native code (regardless of whether it is 16 KB compatible):
- Open Android Studio, then click File > Open and choose any project.
From the menu bar, click Build > Analyze APK...
Choose the APK you want to analyze.
Look within the
libfolder, which hosts shared object (.so) files if any are present. If any shared object files are present, your app uses native code. The Alignment column displays warning messages for any files that have alignment issues. If no shared object files are present or there is nolibfolder, then your app doesn't use native code.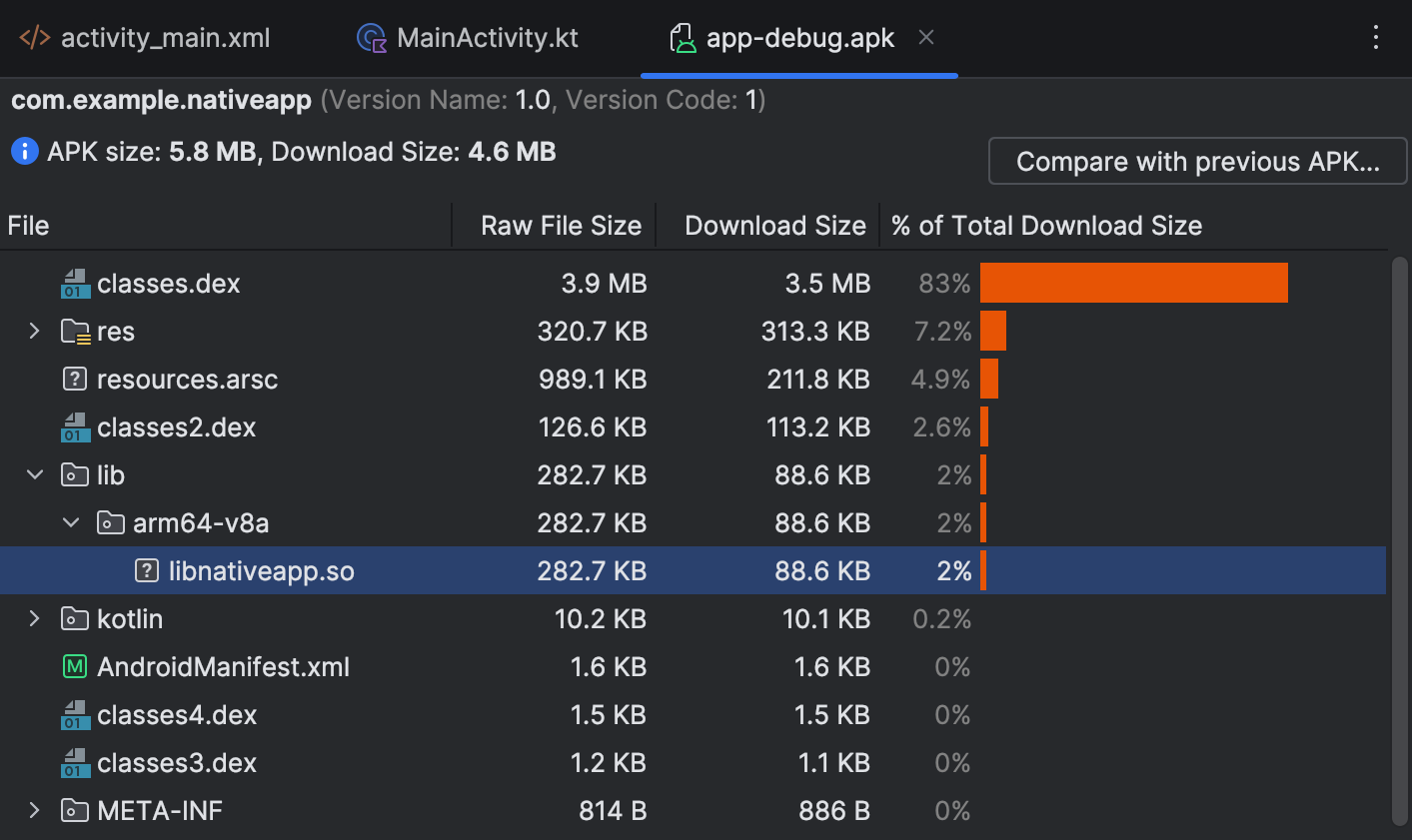
Detect alignment issues with automated checks
Android Studio warns you proactively if your prebuilt libraries or APKs aren't 16 KB compliant. Use the APK Analyzer tool to review which libraries need to be updated or if any code changes are required.
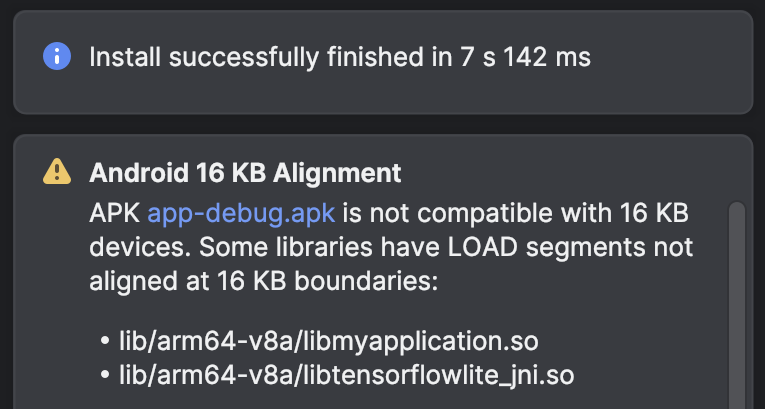
Lint in Android Studio also highlights native libraries that aren't 16 KB aligned.
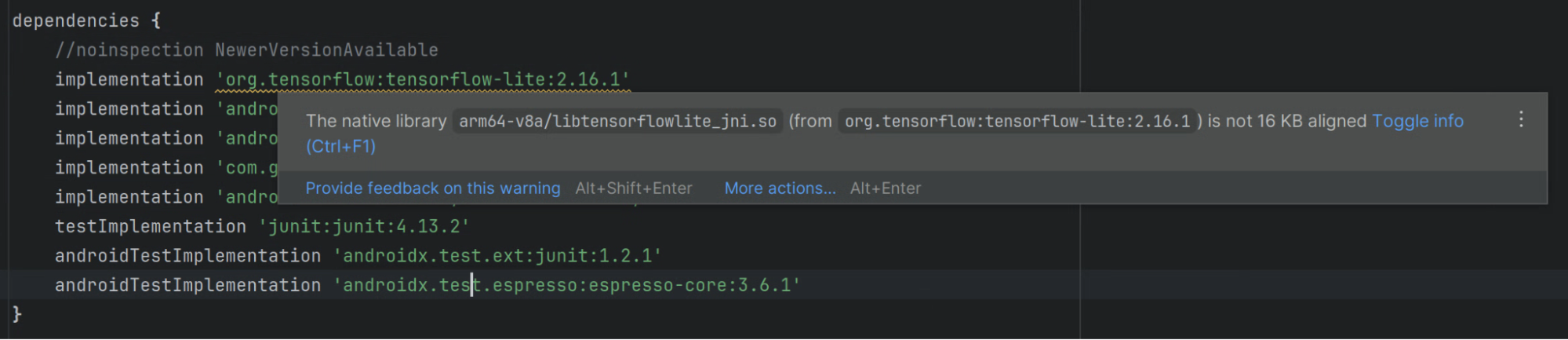
Check the alignment of ELF segments for shared libraries
For any shared libraries, verify that the shared libraries' ELF segments are
aligned properly using 16 KB ELF alignment. If you are developing on either
Linux or macOS, you can use the check_elf_alignment.sh script as described in
the following section. You can also use the command-line tools directly.
Use the check_elf_alignment.sh script (Linux or macOS)
Follow these steps to check the alignment of ELF segments using the
check_elf_alignment.sh script:
Save the
check_elf_alignment.shscript to a file.Run the script on your app's APK file:
check_elf_alignment.sh APK_NAME.apkThe script outputs either
ALIGNEDorUNALIGNEDfor all thearm64-v8ashared libraries.If any
arm64-v8aorx86_64shared libraries areUNALIGNED, you'll need to update the packaging for those libraries, then recompile your app and retest by following the steps in this section.
Use command-line tools directly
Follow these steps to check the alignment of ELF segments using command-line tools directly:
- Make sure both Android SDK Build-Tools version 35.0.0 or higher and the
Android NDK are installed using the SDK Manager in Android Studio or
sdkmanagercommand-line tool. Extract your app's APK file:
Linux or macOS
unzip APK_NAME.apk -d /tmp/my_apk_outWindows (PowerShell)
Expand-Archive -Path .\APK_NAME.apk -DestinationPath ~\tmp\my_apk_outIn the temporary directory that you extracted your APK file to, check the contents of the
libdirectory for shared object (.so) files. These are the same shared object files that you would've seen while identifying native libraries using APK Analyzer. Run the following command on each shared object file:Linux or macOS
SDK_ROOT_LOCATION/Android/sdk/ndk/NDK_VERSION/toolchains/llvm/prebuilt/darwin-x86_64/bin/llvm-objdump -p SHARED_OBJECT_FILE.so | grep LOADWindows (PowerShell)
SDK_ROOT_LOCATION\Android\sdk\ndk\NDK_VERSION\toolchains\llvm\prebuilt\windows-x86_64\bin\llvm-objdump.exe -p SHARED_OBJECT_FILE.so | Select-String -Pattern "LOAD"Where
SDK_ROOT_LOCATIONis the path to the directory where you've installed the Android SDK,SHARED_OBJECT_FILEis the name of the shared object file that you're checking, andNDK_VERSIONis the version of the Android NDK that you have installed (for example,28.0.12433566). The output will look something like the following for each file you check:LOAD off 0x0000000000000000 vaddr 0x0000000000000000 paddr 0x0000000000000000 align 2**14 LOAD off 0x0000000000042a90 vaddr 0x0000000000043a90 paddr 0x0000000000043a90 align 2**14 LOAD off 0x0000000000046230 vaddr 0x0000000000048230 paddr 0x0000000000048230 align 2**14Check the output lines to ensure that the load segments don't have values less than
2**14. If any load segments are2**13,2**12, or lower values, you'll need to update the packaging for those libraries, then recompile your app and retest by following the steps in this section.Next, run the
zipaligncommand-line tool on your app's APK file:Linux or macOS
SDK_ROOT_LOCATION/Android/sdk/build-tools/35.0.0/zipalign -v -c -P 16 4 APK_NAME.apkWindows (PowerShell)
SDK_ROOT_LOCATION\Android\sdk\build-tools\35.0.0\zipalign.exe -v -c -P 16 4 APK_NAME.apkWhere
SDK_ROOT_LOCATIONis the path to the directory where you've installed the Android SDK, andAPK_NAMEis the name of your app's APK file. The last line of the output will say "Verification successful" if all of the shared libraries are aligned correctly.If the verification failed, some shared libraries need to be realigned, so you'll need to update the packaging for those libraries, then recompile your app and retest by following the steps in this section.
Build your app with support for 16 KB devices
If your app uses native code, then complete the steps that are outlined in the following sections to make sure that your app supports 16 KB devices:
- Update the packaging of your shared libraries
- Compile your app using 16 KB ELF alignment
- Fix code and resolve runtime issues
- Check SDKs for 16 KB support
Update the packaging of your shared libraries
Upgrade to AGP version 8.5.1 or higher and use uncompressed shared libraries.
Use bundletool to verify zip alignment
To see the alignment of your bundle, use:
bundletool dump config --bundle=<my .aab> | grep alignment
If you see PAGE_ALIGNMENT_16K then you know your bundle requests 16 KB
zip alignment. If you see PAGE_ALIGNMENT_4K, this instructs the APK built from
this AAB to have 4 KB aligned .so files in the zip file.
AGP version 8.5.1 or higher
16 KB devices require apps that ship with uncompressed shared libraries to align them on a 16 KB zip-aligned boundary. To do this, you need to upgrade to Android Gradle Plugin (AGP) version 8.5.1 or higher. Refer to the Android Gradle plugin Upgrade Assistant section for details on the upgrade process.
AGP version 8.5 or lower
If you can't upgrade AGP to version 8.5.1 or higher, then the alternative is to switch to use compressed shared libraries. Update your Gradle configuration to have Gradle compress your shared libraries when packaging your app to avoid app installation issues with unaligned shared libraries.
Groovy
In your build.gradle file, add the following option:
android {
...
packagingOptions {
jniLibs {
useLegacyPackaging true
}
}
}
Kotlin
In your build.gradle.kts file, add the following option:
android {
...
packagingOptions {
jniLibs {
useLegacyPackaging = true
}
}
}
Compile your app using 16 KB ELF alignment
16 KB devices require the shared libraries' ELF segments to be aligned properly using 16 KB ELF alignment in order for your app to run.
For game developers, if your game runs on top of Unity game engine, refer to the Unity guide. If your game runs on top of Unreal game engine, refer to the Unreal guide. For native game engines, continue with this guide.
To compile your app using 16 KB ELF alignment, complete the steps in one of the following sections depending on the version of the Android NDK that you're using.
Android NDK r28 and higher
NDK version r28 and higher compile 16 KB-aligned by default.
Android NDK r27
To support compiling 16 KB-aligned shared libraries with Android NDK
version r27 and higher, you need to update your ndk-build, build.gradle,
build.gradle.kts, or linker flags as follows:
ndk-build
In your Application.mk:
APP_SUPPORT_FLEXIBLE_PAGE_SIZES := true
Groovy
In your build.gradle file, set the argument
-DANDROID_SUPPORT_FLEXIBLE_PAGE_SIZES=ON:
android {
...
defaultConfig {
...
// This block is different from the one you use to link Gradle
// to your CMake or ndk-build script.
externalNativeBuild {
// For ndk-build, instead use the ndkBuild block.
cmake {
// Passes optional arguments to CMake.
arguments "-DANDROID_SUPPORT_FLEXIBLE_PAGE_SIZES=ON"
}
}
}
}
Kotlin
In your build.gradle.kts file, set the argument
-DANDROID_SUPPORT_FLEXIBLE_PAGE_SIZES=ON:
android {
...
defaultConfig {
...
// This block is different from the one you use to link Gradle
// to your CMake or ndk-build script.
externalNativeBuild {
// For ndk-build, instead use the ndkBuild block.
cmake {
// Passes optional arguments to CMake.
arguments += listOf("-DANDROID_SUPPORT_FLEXIBLE_PAGE_SIZES=ON")
}
}
}
}
Other build systems
Specify the following linker flags:
-Wl,-z,max-page-size=16384
Android NDK r26 and lower
Always update your NDK. This should only be used as a last resort, and no support is guaranteed.
To support compiling 16 KB-aligned shared libraries with Android NDK
version r26 or lower, you need to update your ndk-build or cmake
configuration as follows:
ndk-build
Update your Android.mk to enable 16 KB ELF alignment:
LOCAL_LDFLAGS += "-Wl,-z,max-page-size=16384"
CMake
Update your CMakeLists.txt to enable 16 KB ELF alignment:
target_link_options(${CMAKE_PROJECT_NAME} PRIVATE "-Wl,-z,max-page-size=16384")
Android NDK r22 and lower is not compatible
Always update your NDK. This should only be used as a last resort, and no support is guaranteed.
In addition to steps for NDK r26 and lower, common-page-size=16384 can
workaround bugs in old GNU ld and LLVM lld linkers. This only works
if the ELF also has present a .relro_padding section. This depends on the
version of the linker and the specific program that is written. There is no
support for these NDK versions, and if it does not work, update the NDK version
before reporting any issue.
Fix code and resolve runtime issues
Even if your app is 16 KB-aligned, your app can encounter errors if places in your code assume that a device is using a specific page size. To avoid this, complete the following steps:
Remove any hard-coded dependencies that reference the
PAGE_SIZEconstant or instances in your code logic that assume that a device's page size is 4 KB (4096).Use
getpagesize()orsysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE)instead.Look for usages of
mmap()and other APIs that require page-aligned arguments and replace with alternatives where necessary.
In some cases, if your app uses PAGE_SIZE as a convenient value that isn't
tied to the underlying page size, then this won't cause your app to break when
used in 16 KB mode. However, if this value is passed to the kernel with
mmap without MAP_FIXED, the kernel still uses an entire page, which wastes
some memory. For these reasons, PAGE_SIZE is undefined when 16 KB mode is
enabled on NDK r27 and higher.
If your app uses PAGE_SIZE in this way and never directly passes this value to
the kernel, then instead of using PAGE_SIZE, create a new variable with a new
name to reflect that it is used for other purposes and does not reflect a real
memory page.
Check SDKs for 16 KB support
Many SDKs are compatible with 16 KB page sizes, especially if you build them yourself or get recent prebuilts. However, because some SDK prebuilts or SDK versions aren't 16 KB compatible, you should check the website for each SDK provider to determine which version to use with 16 KB.
Test your app in a 16 KB environment
After you build your app with support for 16 KB devices, you'll want to test your app in a 16 KB environment to see whether your app experiences any regressions. To do this, follow these steps:
Set up the Android 15 SDK or higher.
Set up one of the following testing environments:
Start up your test device, then run the following command to verify that it's using a 16 KB environment:
adb shell getconf PAGE_SIZEThe command should return a value of
16384.Run the following
zipaligncommand to verify that your app is 16 KB-aligned, where APK_NAME is the name of your app's APK file:zipalign -c -P 16 -v 4 APK_NAME.apkThoroughly test your app, focusing on any areas that might be affected by changing code instances that reference specific page sizes.
Set up the Android Emulator with a 16-KB-based system image
To set up a 16 KB environment using the Android Emulator, follow these steps:
- In Android Studio, click Tools > SDK Manager.
In the SDK Platforms tab, check Show Package Details, then expand the Android VanillaIceCream or higher section and select one or both of the following emulator system images, depending on the virtual devices you want to create:
- Google APIs Experimental 16 KB Page Size ARM 64 v8a System Image
- Google APIs Experimental 16 KB Page Size Intel x86_64 Atom System Image
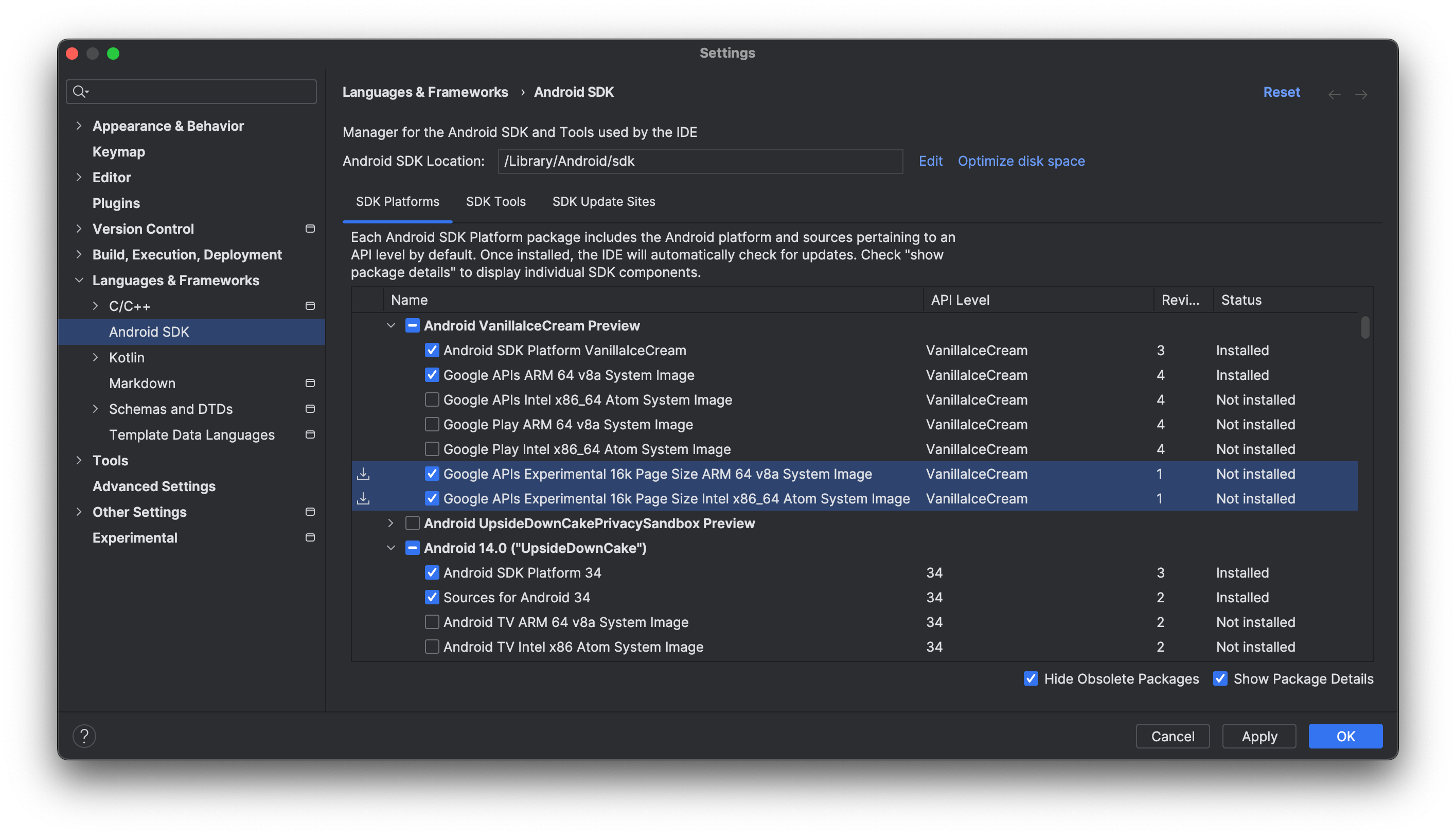
Click Apply > OK to download whichever system images you selected.
Follow the steps to set up a virtual device for Android 15, and when prompted to select a system image, select the 16 KB system image that you downloaded. If it's not recommended automatically, you can find the 16 KB system image in the Other Images tab.
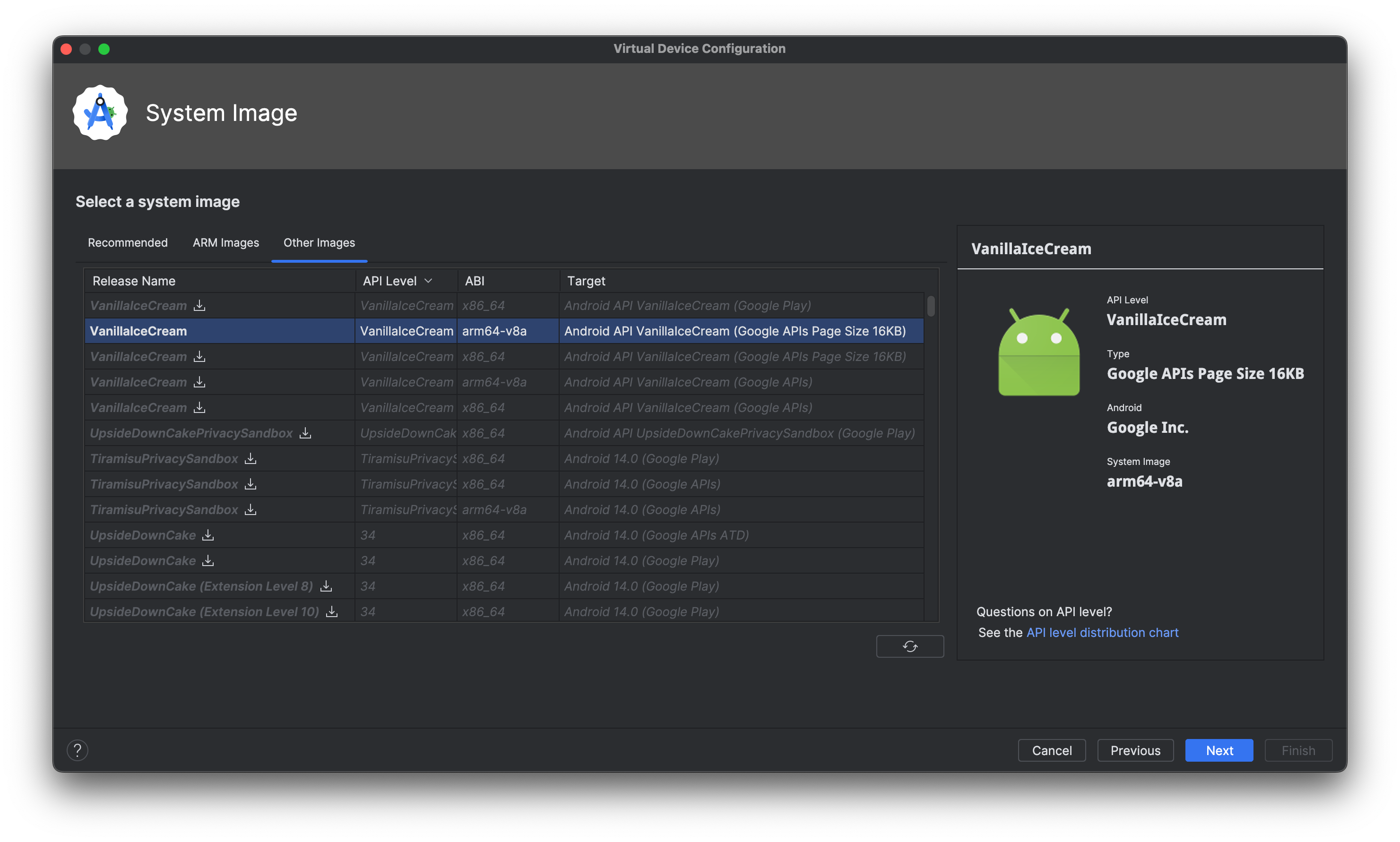
Launch the emulator
After you finish setting up the Android Emulator and virtual devices, launch the emulator from the target device menu, or from the command line.
Enable 16 KB mode on a device using developer options
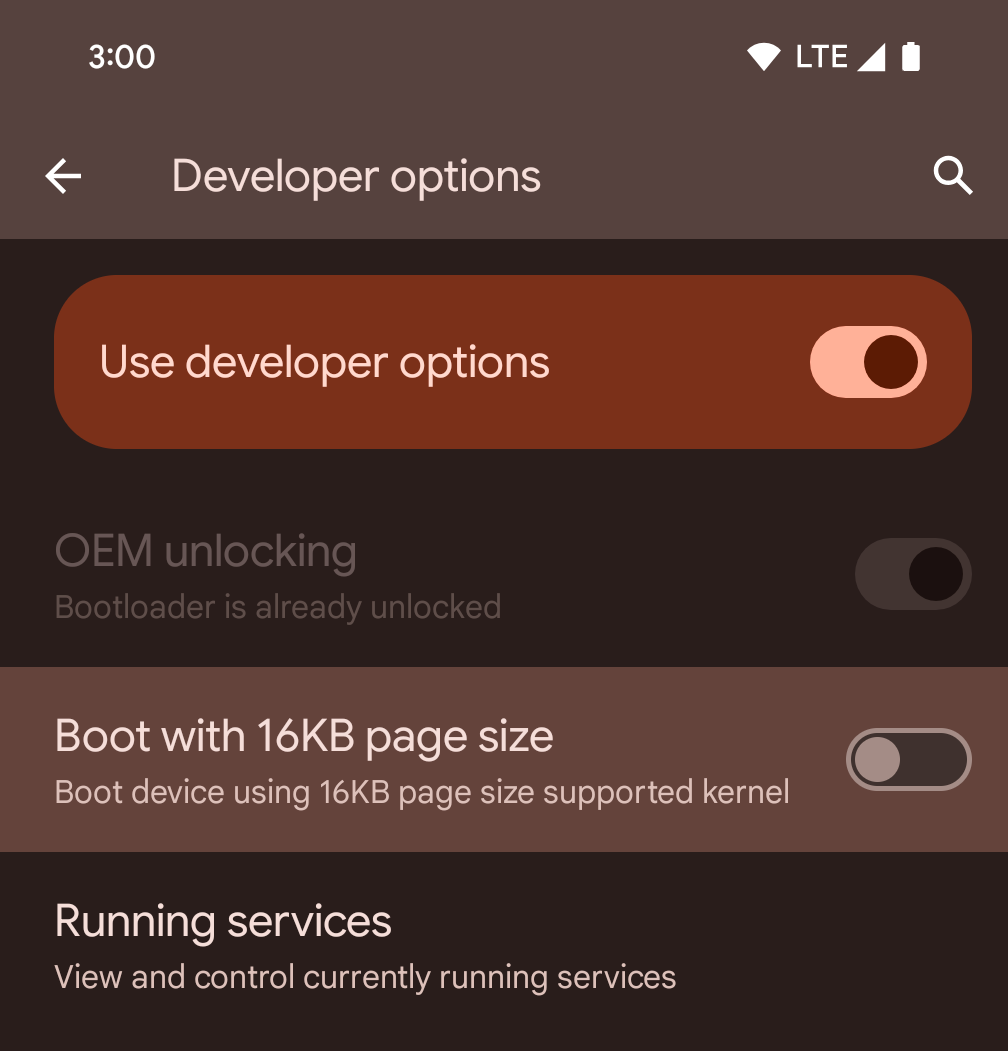
Toggle the Boot with 16KB page size developer option to boot a device in 16 KB mode.
In QPR versions of Android 15, you can use the developer option that's available on certain devices to boot the device in 16 KB mode and perform on-device testing. Before using the developer option, go to Settings > System > Software updates and apply any updates that are available.
This developer option is available on the following devices:
Pixel 8 and 8 Pro (with Android 15 QPR1 or higher)
Pixel 8a (with Android 15 QPR1 or higher)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro, and 9 Pro XL (with Android 15 QPR2 Beta 2 or higher)
16 KB backcompat mode
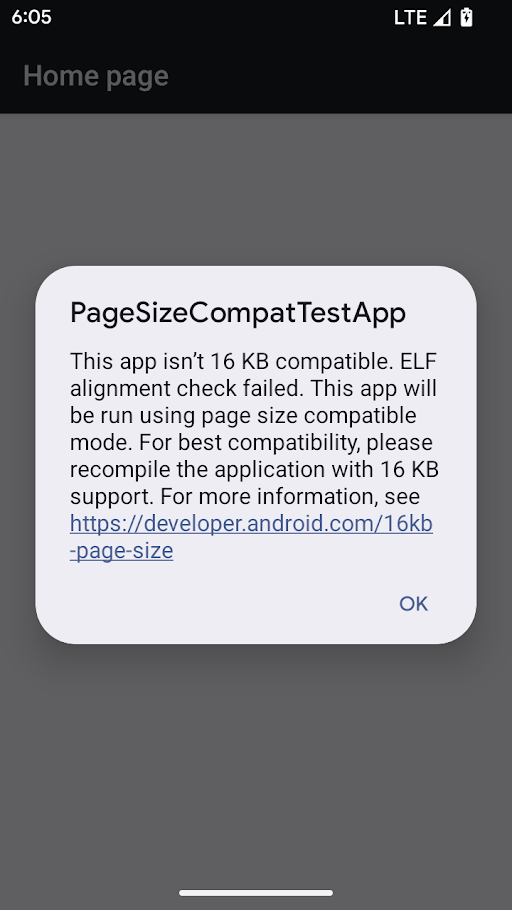
Warning in page size compat mode
The 16 KB backcompat option is available when a device is running with a 16 KB kernel. The package manager runs an app in 16 KB backcompat mode when the following conditions are met:
- If the app has ELF files (with an
.soextension) with a LOAD segment alignment of 4 KB. - If the zipped APK has uncompressed ELF files that are 4 KB ZIP aligned.
If the package manager has enabled 16 KB backcompat mode for an app, the app displays a warning when it's first launched saying that it's running in 16 KB backcompat mode.
16 KB backcompat mode allows some apps to work, but for best reliability and stability, apps should still be 16 KB aligned.
On the app info page, under Advanced, toggle the setting Run app with page size compat mode to enable or disable the 16 KB backcompat mode for specific app. This setting is visible only when the device is running with 16 KB page size.
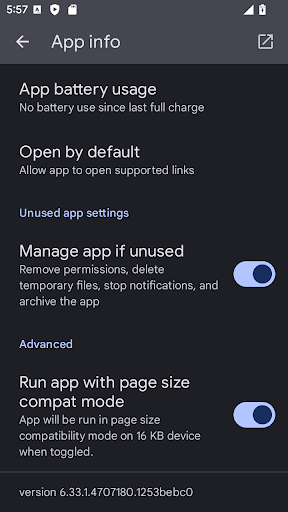
Page size compat mode setting
To force 16 KB backcompat on for every app on the device:
adb shell setprop bionic.linker.16kb.app_compat.enabled true
adb shell setprop pm.16kb.app_compat.disabled false
To force 16 KB backcompat off for every app on the device:
adb shell setprop bionic.linker.16kb.app_compat.enabled false
adb shell setprop pm.16kb.app_compat.disabled true
Set the android:pageSizeCompat property to enabled or disabled to turn on or
off backcompat mode for a specific app in its AndroidManifest.xml. When this
property is set, the app won't display backcompat mode warnings when it
launches.
Google Play compatibility requirement
As device manufacturers equip devices with more RAM to optimize performance, many will adopt larger page sizes like 16 KB. To prepare for the launch of these upcoming devices, Google Play is introducing a new compatibility requirement: starting November 1st, 2025, all new apps and updates to existing apps submitted to Google Play and targeting devices running Android 15 (API level 35) and higher must support 16 KB page sizes.
To read more about this compatibility requirement, see this blog post.

