Android activates a compatibility mode for apps that declare orientation or resizability restrictions. Compatibility mode ensures acceptable app behavior on large screen devices, foldable flip phones, and desktop environments but with suboptimal usability.
Per-app overrides enable device manufacturers, virtual device owners1, and users to change app behavior to improve app layout or prevent apps from breaking on select devices.
Android 16
Android 16 (API level 36) ignores screen orientation, aspect ratio, and app resizability restrictions to improve the layout of apps on form factors with smallest width >= 600dp.
The following per-app overrides are nonfunctional for apps that target API level 36:
- FORCE_RESIZE_APP
- FORCE_NON_RESIZE_APP
- OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO
- OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_PORTRAIT_ONLY
- OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_MEDIUM
- OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE
- OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_TO_ALIGN_WITH_SPLIT_SCREEN
- OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_EXCLUDE_PORTRAIT_FULLSCREEN
- OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION
- OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION_TO_USER
- OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_PORTRAIT
- OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_NOSENSOR
- OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_ORIENTATION_TO_REVERSE_LANDSCAPE
- OVERRIDE_ORIENTATION_ONLY_FOR_CAMERA
- OVERRIDE_USE_DISPLAY_LANDSCAPE_NATURAL_ORIENTATION
- OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION
- OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_ORIENTATION_REQUEST_WHEN_LOOP_DETECTED
- OVERRIDE_RESPECT_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION
- OVERRIDE_EXCLUDE_CAPTION_INSETS_FROM_APP_BOUNDS
Opt out
Your app can target API level 36 but opt out of the Android 16 behavior, in which case OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION_TO_USER is not applicable.
Declare manifest property
To opt out of the API level 36 behavior, declare the
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY manifest property.
To opt out for a specific activity, set the property in the <activity>
element:
<activity ...>
<property
android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY"
android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
To opt out for your entire app, set the property in the <application> element:
<application ...>
<property
android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY"
android:value="true" />
...
</application>
Reference devices
The following devices may require per-app overrides because of unusual configurations or configurations that are not well supported by apps:
- Tablets: The natural orientation of some tablets, such as Pixel Tablet,
is landscape. A device is in its natural orientation when
Display#getRotation()returnsSurface.ROTATION_0. If apps assumeROTATION_0is portrait, app layouts and camera preview can be mismatched to the device display. - Landscape foldables: Some foldable devices, such as Pixel Fold, are in portrait orientation when folded, but landscape orientation when unfolded. If apps assume the unfolded orientation is portrait, flickering loops or layout issues are likely.
- Foldable flip phones: Unfolded flip phones are typically in portrait orientation. But, when folded, the phones usually have a small display in landscape orientation. Apps must identify and accommodate the different orientations of the displays.
- External displays: Select devices can start a desktop windowing session on external, connected displays. Apps must query external displays for information such as screen size and resolution; otherwise, apps may make incorrect assumptions about the displays, which can lead to incorrect app behavior.
- Car displays: Many, but not all, car displays are landscape. Developing parked apps for car displays is similar to developing for tablets.
Common compatibility issues
Apps experience compatibility issues most often because of app orientation restrictions, resizability and aspect ratio restrictions, incorrect handling of camera preview orientation, and misused APIs.
Letterboxing
Letterboxing positions the app in the center of the screen or, on large screens, to one side or the other for convenient access. Mattes (solid‑colored bars or blurred wallpaper) fill the unused display area along the sides or top and bottom of the app.
Letterboxing happens often on large screen devices because the dimensions and aspect ratio of the device display are usually different from those of standard phones, for which most apps are designed.
Figure 1. App restricted to portrait orientation is letterboxed on landscape tablet and foldable.
Issue
App doesn't support all display configurations because the app has fixed orientation, fixed aspect ratio, or is not resizable.
Configuration settings that control app orientation and resizability include the following:
screenOrientation: Specifies a fixed orientation for an app. Apps can also set orientation at runtime by usingActivity#setRequestedOrientation().resizeableActivity: Indicates whether the system can resize apps to fit windows of varying dimensions. On Android 11 (API level 30) and lower, specifies whether apps support multi‑window mode. On Android 12 (API level 31) and higher, specifies whether apps support multi‑window mode on small screens (compact window size class). On Android 12 and higher, apps support multi‑window mode on large screens (medium or expanded window size class) regardless of this setting.maxAspectRatio: Specifies the maximum aspect ratio supported by the app. Only apps withresizeableActivityset tofalsecan setmaxAspectRatio.minAspectRatio: Specifies the minimum aspect ratio supported by the app. Only apps withresizeableActivityset tofalsecan setminAspectRatio.
App restricted to portrait orientation not usable on landscape device.
Optimization
App should support all device and multi-window mode display orientations and sizes. Remove all orientation and fixed aspect ratio restrictions from your app layouts and app manifest file.
App supports all device orientations.
Compatibility workaround
If an app with fixed orientation or fixed aspect ratio runs in a window where the app does not directly support the window size or orientation, Android letterboxes the app to preserve continuity.
Beginning with Android 12 (API level 31) and continuing with 12L (API level 32), the platform applies a variety of enhancements to letterboxed apps. Device manufacturers implement the UI enhancements. You don't need to do any additional development for your app to benefit from the improvements.
Android 12 (API level 31) introduces the following aesthetic enhancements, which can be configured by device manufacturers:
- Rounded corners: The corners of the app window have a more refined look.
- System bar transparency: Status and navigation bars, which overlay the app, are semitransparent, making icons on the bars always viewable over the letterbox background.
- Configurable aspect ratio: The aspect ratio of the app can be adjusted to improve the app's appearance.
Figure 2. Letterboxed app with UI enhancements.
12L (API level 32) adds the following functional improvements:
Configurable positioning: On large screens, device manufacturers can position the app to the left or right side of the display, making interaction easier.
Redesigned restart button: Device manufacturers can give the restart button for size compatibility mode a new look for better recognition by users.
Android 13 (API level 33) adds a user education dialog about positioning the letterboxed app on screen or including the letterbox in split‑screen mode:
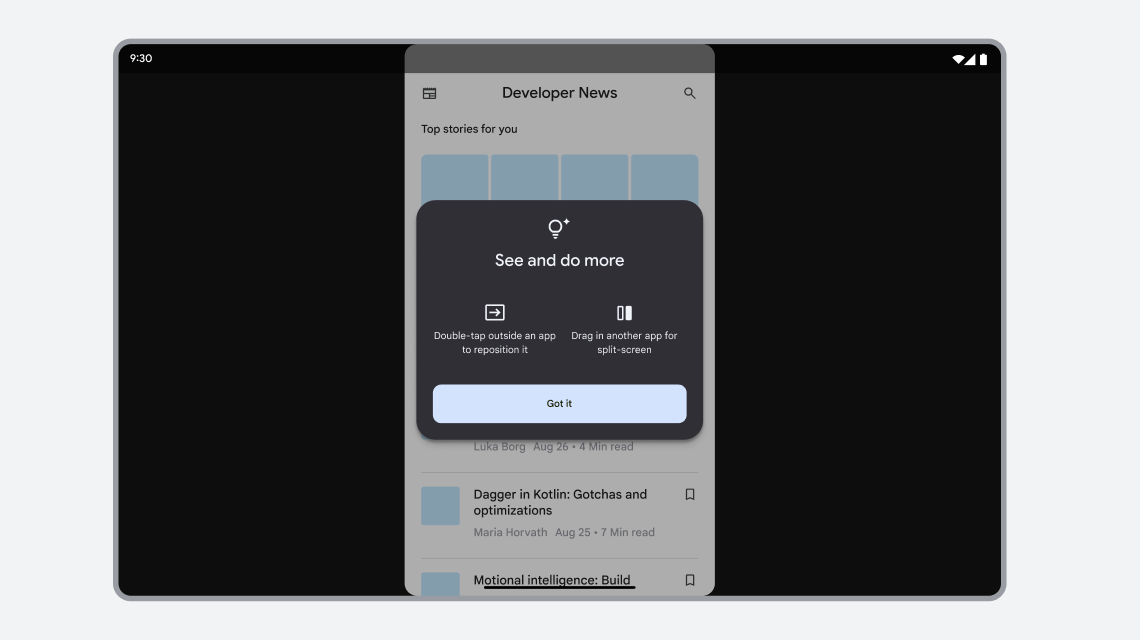
Figure 3. Letterboxed app with user education dialog.
Size compatibility mode
Size compatibility mode is letterboxing that maintains the app aspect ratio and includes a restart control. The control enables users to restart the app and redraw the display. Android invokes size compatibility mode for apps that are nonresizable. When an activity moves to a display container that is incompatible with the activity's dimensions, the system may rescale the app to fill the device display in at least one dimension.
Device configuration changes that can trigger size compatibility mode include the following:
- Device rotation
- Foldable device folding or unfolding
- Change between full screen and split-screen display modes
Issue
Size compatibility mode typically applies to activities that are restricted in orientation or aspect ratio and are configured (or determined by the system) to be nonresizable.
Your app is considered to be resizable—and won't be placed in size compatibility mode—if it meets any of the following criteria:
- Is resizable with
resizeableActivity="true" - Supports picture-in-picture (PIP) mode
- Is embedded
- Has the
FORCE_RESIZE_APPper-app override applied by the device manufacturer (properties set by the app are ignored)
If your app does not meet any of the conditions, it is considered not resizable and could be placed in size compatibility mode.
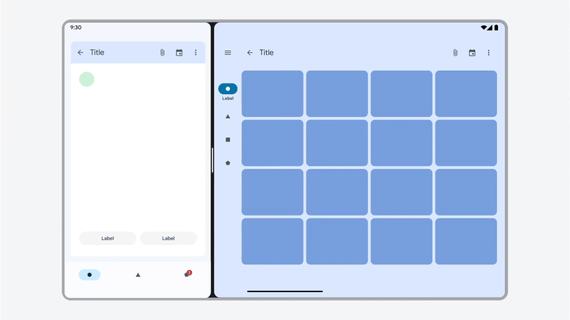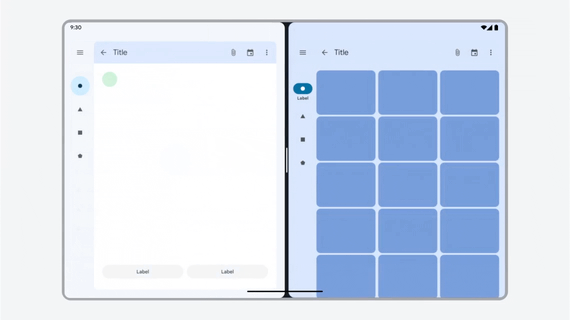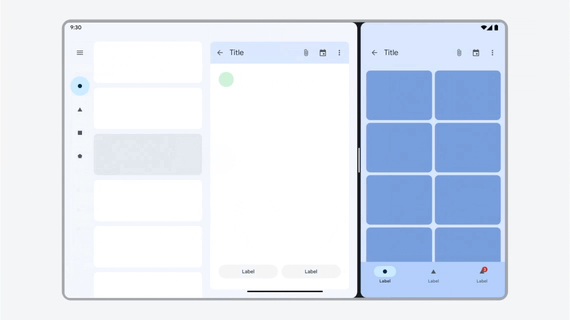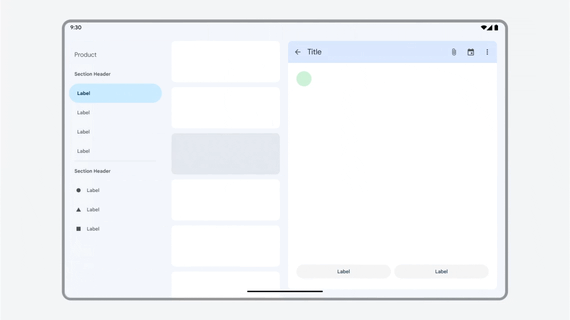
Nonresizable app crashes in multi-window mode.
Optimization
App should support all display sizes. Make your app resizable by setting the
android:resizeableActivity attribute of the <activity>
or <application> element to true in the
app manifest. Design responsive/adaptive layouts for your app. For more
information, see
Support different display sizes and Support
multi-window mode.
App works in all window sizes.
Compatibility workaround
Android places an app in size compatibility mode when the system determines the display of the letterboxed app can be improved by rescaling the app to fill the display window in at least one dimension. The system displays a restart control which recreates the app process, recreating the activity and redrawing the display. See also Processes and threads overview.
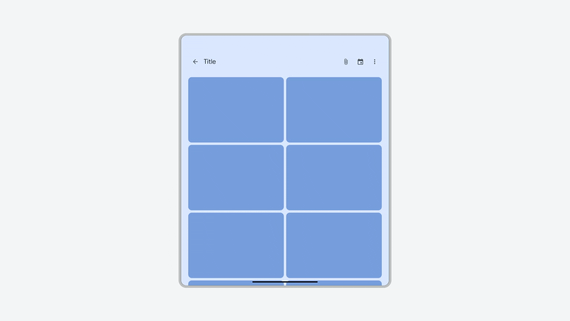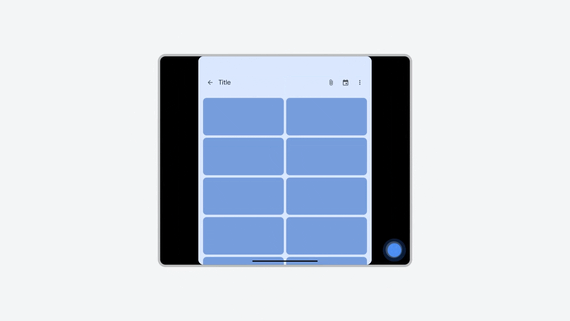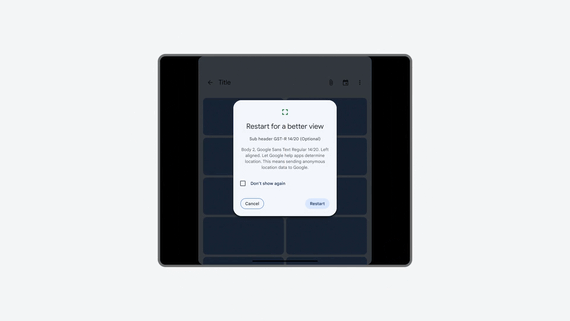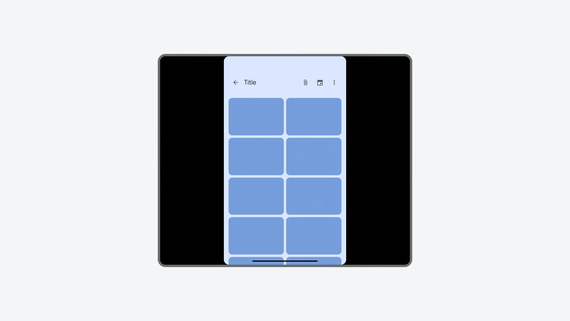
Portrait-only app letterboxed in landscape orientation, rescaled by restart control.
Display compatibility mode
Display compatibility mode prevents an app from restarting when the app moves between different displays, which can trigger a configuration change such as a color mode, touchscreen availability, or screen density change.
Display compatibility mode mode is enabled by default for games (based on the
android:appCategory flag) to improve stability and continuity.
Unlike size compatibility mode, display compatibility mode does not freeze the
app's configuration. The app can still receive all configuration updates through
APIs such as the onConfigurationChanged() callback but is spared from a
disruptive restart. This means games that properly support APIs such as
onConfigurationChanged() can still responsively update their UI even if
they are in display compatibility mode.
To opt out of display compatibility mode and handle configuration changes in
your app, declare support for the configuration changes in the app's
AndroidManifest.xml file, and handle the configuration changes in the
onConfigurationChanged() callback.
<activity
android:name=".MyGameActivity"
android:configChanges="colorMode|touchscreen|density|...">
...
</activity>
Flickering loops
When an app doesn't support all display orientations, it might repeatedly request new orientations when a configuration change occurs, creating an infinite loop that makes the display flicker or the app rotate endlessly.
Issue
On Android 12 (API level 31) and higher, device manufacturers can configure
their devices to ignore orientation restrictions specified by apps and instead
enforce compatibility modes. For example, a foldable device could ignore an
activity's android:screenOrientation="portrait"
setting when the activity is displayed on the device's landscape tablet-size,
inner screen.
If an app's orientation restrictions are ignored, the app can programmatically
set its orientation by calling
Activity#setRequestedOrientation(). The call
triggers an app restart if the app is not handling configuration changes (see
Handle configuration changes). After the
restart, the app's orientation restrictions are again ignored, the app repeats
the call to setRequestedOrientation(), the call triggers an app restart, and
so on in a self-perpetuating loop.
Another way you might encounter this is when the
natural orientation (the usual orientation as
determined by Android) of a device screen is landscape (that is, calling
Display#getRotation() returns
Surface.ROTATION_0 while the device has a landscape aspect
ratio). Historically, apps have assumed that Display.getRotation() =
Surface.ROTATION_0 means the device is in portrait orientation, but this is not
always the case, for example, on the inner screen of some foldable devices and
on some tablets.
An app in landscape orientation on a foldable inner display, might check the
screen rotation, receive a value of ROTATION_0, assume the natural orientation
of the device is portrait, and call
setRequestedOrientation(ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT
) to reconfigure the app layout. After the app restarts (in landscape
orientation), it might again check the screen rotation, receive a value of
ROTATION_0, call
setRequestedOrientation(ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT), and
continue the infinite loop.

Landscape-only app on portrait display makes repeated calls to Activity#setRequestedOrientation().
Optimization
Apps should not do the following:
- Set a default orientation with
Activity#setRequestedOrientation()in the activityonCreate()method because the orientation request can be triggered unexpectedly by unhandled configuration changes - Assume the natural orientation of the device (
ROTATION_0) is portrait - Set orientation based on signals not related to the current window size such
as
Display#getRotation(), presence of aFoldingFeature, or deprecated APIs.

App handles configuration change, does not have orientation restrictions, so does not enter a flickering loop.
Compatibility workaround
Android ignores calls to Activity#setRequestedOrientation() in the following
situations:
The activity has already relaunched from a previous call to the method or the camera compat force rotation treatment has been enabled (see Camera preview below).
Device manufacturers can apply this behavior to an app with
OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION.The activity made more than two orientation requests in one second, which indicates a loop has occurred. Of the two requests in the loop, Android uses the one that maximizes the app display area.
Device manufacturers can apply this behavior to an app with
OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_ORIENTATION_REQUEST_WHEN_LOOP_DETECTED.Virtual device owners have overridden the method call on select devices.
Camera preview
The camera preview (or viewfinder) of camera apps can be misaligned or distorted on tablets, laptops, and foldable displays.
See also Camera preview in desktop windowing.
Issue
The Android Compatibility Definition Document states that a camera image sensor "MUST be oriented so that the long dimension of the camera aligns with the screen's long dimension."
Apps often assume that device orientation and camera sensor orientation are portrait—a reasonable assumption on standard mobile phones. But the natural orientation of tablets and laptops and their camera sensors can be landscape. Also, new form factors like foldables can have multiple natural orientations and multiple camera sensors in varying orientations.
Starting an activity with a camera orientation the app does not expect or switching between different cameras or device screens (for foldables) can cause a misaligned or distorted camera preview.
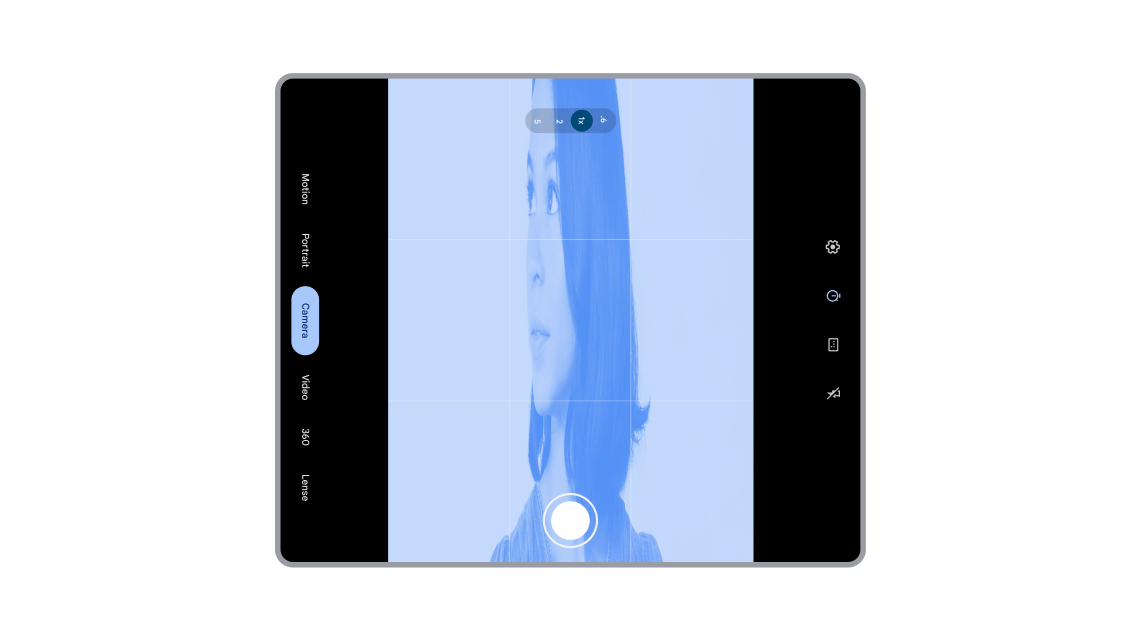
Misaligned and distorted camera preview on large screen foldable.
Optimization
Camera apps must correctly identify and manage device orientation and camera sensor orientation to present a correctly aligned and scaled camera preview. Apps must calculate device rotation, sensor rotation, and screen or window aspect ratio, and then apply the results to the camera preview. For detailed guidance, see Camera preview and Introducing Camera Viewfinder.

Camera preview correctly aligned and scaled in all device orientations.
Compatibility workaround
A device is in natural orientation when Display#getRotation()
returns Surface.ROTATION_0. The system calculates
CameraCharacteristics.SENSOR_ORIENTATION
from the device's natural orientation. Android aligns the portrait window of
portrait‑restricted apps with the natural orientation of the device, which
is what most apps expect. Android also crops the camera sensor image when the
sensor orientation is landscape and the camera preview is portrait. The specific
workarounds include the following:
Force rotate camera previews for portrait-restricted apps: Apps restricted to portrait orientation expect the device's natural orientation and the camera sensor orientation to be portrait. However, on Android 12 (API level 31) and higher, apps can run in multiple device orientations if device manufacturers ignore the orientation specification.
When a portrait-restricted app is connected to the camera, Android force rotates the app to align the app portrait window with the natural orientation of the device.
On some tablets (see reference devices), the app portrait window is rotated to full screen portrait to align with the device's natural orientation. The app occupies the full screen after force rotation.
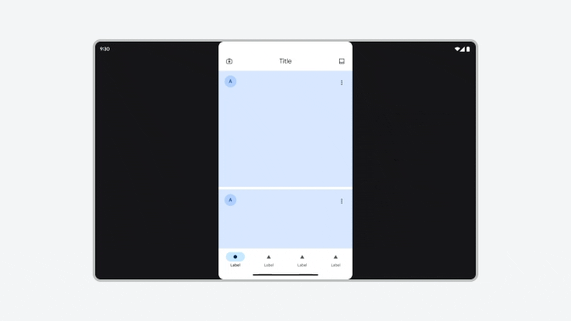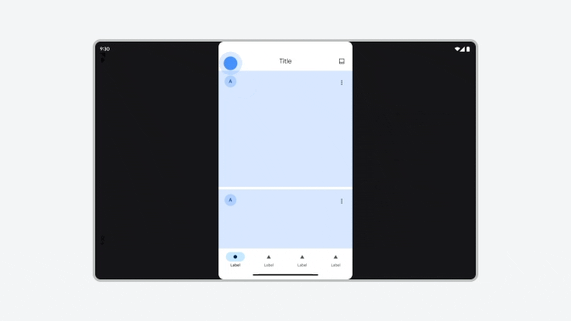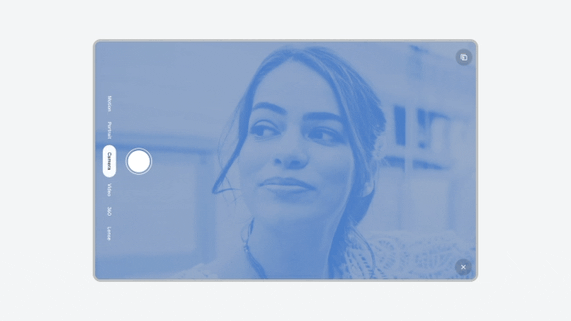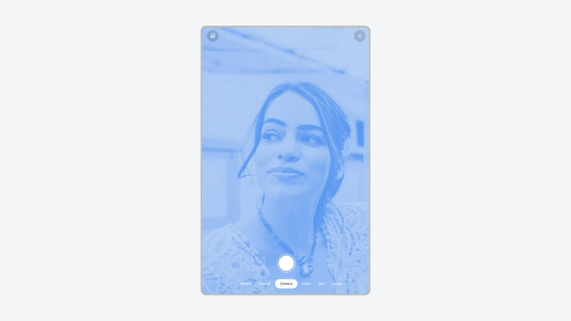
Tablet — Force rotation of portrait-restricted app.
On the landscape inner screen of foldables (see reference devices), portrait-only activities are rotated to landscape to align with the unfolded natural orientation. The app is letterboxed after force rotation.

Foldable — Force rotation of portrait-restricted app. The app is also letterboxed.
Inner front camera cropping: The inner front camera sensor on some foldables is in landscape orientation. In addition to force rotating the camera preview on the foldable inner display, Android crops the inner front (landscape) camera field of view so that the sensor captures a view opposite the device orientation.
Force refresh camera previews: The system cycles through activity methods
onStop()andonStart()(by default) oronPause()andonResume()(applied by the OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_ENABLE_REFRESH_VIA_PAUSE per-app override) after force rotation to make sure the camera preview is properly displayed.Aspect ratio scaling: The system dynamically changes the aspect ratio of the force rotated camera preview to a higher minimum aspect ratio, which ensures the camera preview is properly scaled.
App developers can override these workarounds if the apps handle camera preview correctly. See Per-app overrides.
Commonly misused APIs
As Android has added support for features like multi‑window mode and devices like foldables, legacy APIs have been deprecated and replaced by up‑to‑date APIs that work for all display sizes and device form factors. However, the deprecated APIs are still available for backward compatibility.
Some View APIs are designed for special purposes that are not always well
understood by developers.
Issue
Developers continue to use deprecated Display APIs and incorrectly assume the
APIs return the app bounds instead of device display area bounds. Or developers
mistakenly use special‑purpose view APIs to get general display metrics.
The result is miscalculations when repositioning UI elements after app window
resizing events, causing layout issues.
Deprecated and commonly misused Display APIs:
For more information, see Support multi-window mode.
Misused view APIs:
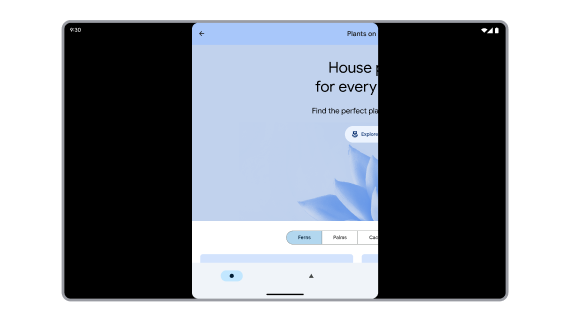
Deprecated API miscalculates app bounds. App content goes off screen.
Optimization
Never rely on physical display size for positioning UI elements. Migrate your
app to APIs based on WindowMetrics, including the following
WindowManager APIs:
Platform:
Jetpack:
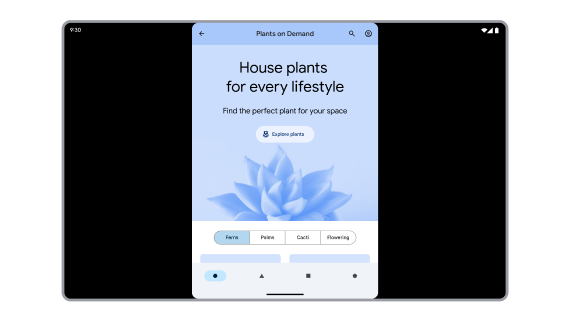
API correctly calculates app window metrics.
Compatibility workaround
Two overrides adjust the deprecated Display APIs and misused View APIs to
return the app bounds:
ALWAYS_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS for Display
APIs; OVERRIDE_SANDBOX_VIEW_BOUNDS_APIS
for View APIs. ALWAYS_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS is also applied by default to
apps that qualify for size compatibility mode.
Transparent activities
Transparent activities are the result of transparent background styles, for example:
<style name="Transparent" parent="AppTheme">
<item name="android:windowIsTranslucent">true</item>
<item name="android:windowBackground">@android:color/transparent</item>
</style>
Themes related to dialogs, such as Theme.MaterialComponents.Dialog, can
include styles that make activities transparent.
Transparent activities don't cover all the available display space, which makes them difficult to manage because the available display area can change based on configuration changes like device rotation, device folding and unfolding, and multi‑window mode.
Issue
A transparent activity should conform to the bounds of the first opaque activity below the transparent activity in the task activity stack. However, an opaque activity that launches a permission dialog can be a trampoline (an activity that launches another activity then disappears); and so, the system can't determine the bounds of the trampoline activity that launched the transparent permission dialog activity.
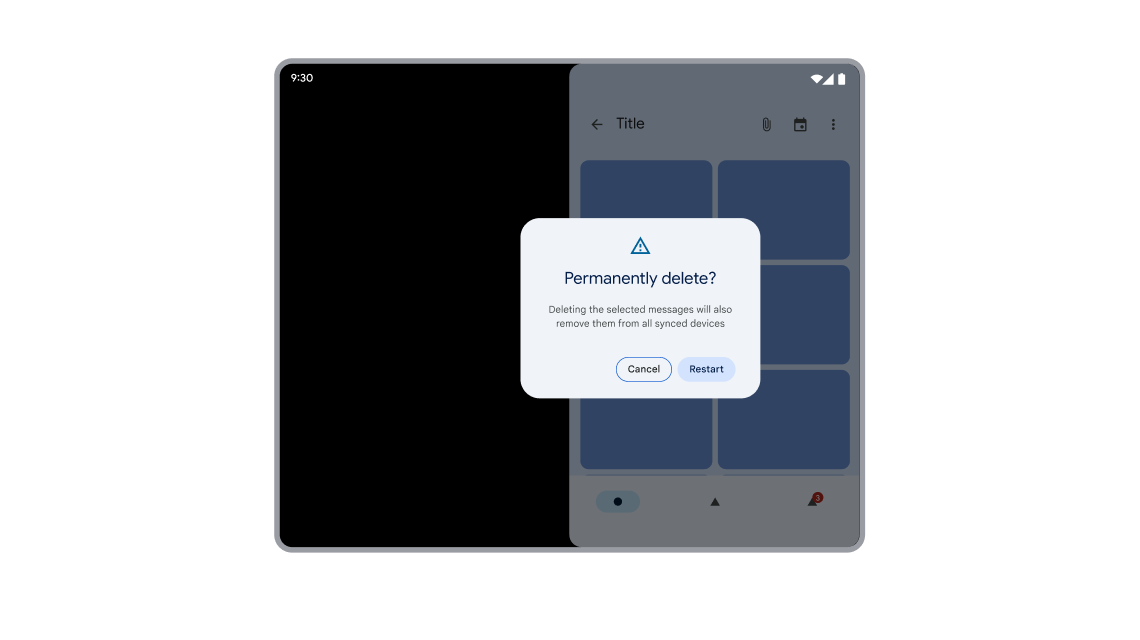
Dialog mispositioned because the activity was launched from a trampoline.
Optimization
Transparent activities inherit their constraints from the top-most opaque activity beneath them in a task's activity stack. The opaque activity must be available for the entire lifecycle of the transparent activity, from activity creation to destruction. For this reason, don't launch permission requests from trampoline activities.
If a trampoline activity launches a permission request, the user might not be able to see the permission dialog because the trampoline activity will have been destroyed before the user has had a chance to respond to the dialog, and the dimensions and position of the dialog activity might have been calculated incorrectly.
Apps should always launch permission requests from activities that remain visible until the user has made a permission decision.
Rounded corners
An activity can be transparent because of a style that specifies background transparency or because the contents of the activity don't fill the available display space. If a transparent activity fills the available display space, the system automatically applies rounded corners to the activity when configured to do so by the device manufacturer. But, if a transparent activity (like a permission dialog) doesn't fill the available space, it's up to you to decide whether or not to apply rounded corners.
Permission dialogs don't fill the available display space because the dialog layout typically uses LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT rather than LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT.
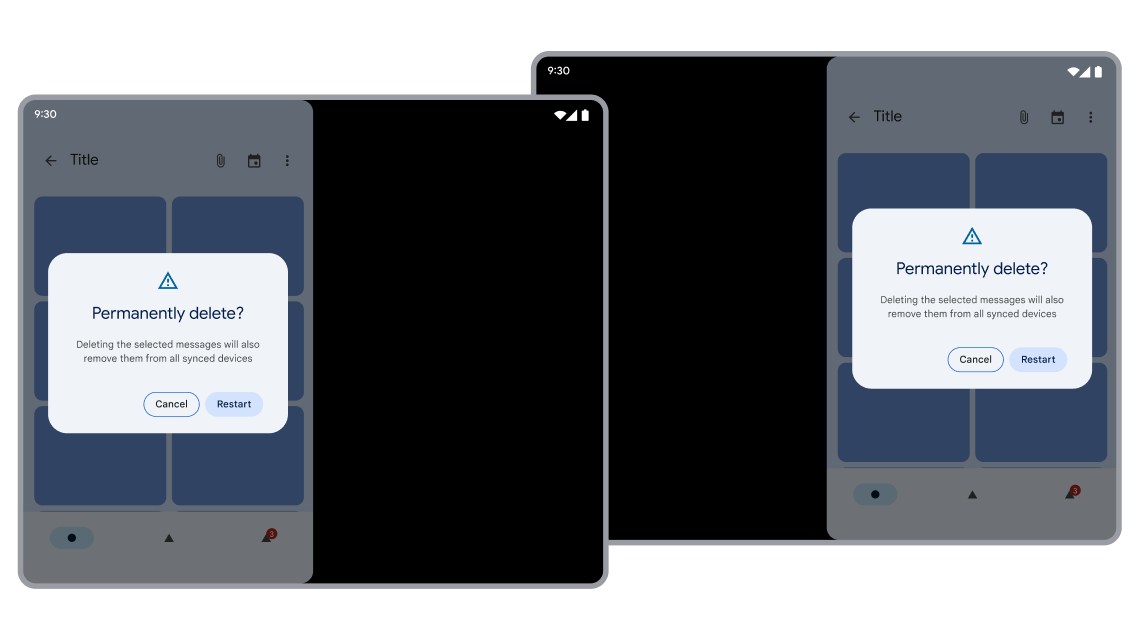
Dialog with rounded corners correctly positioned over visible launching activity.
Compatibility workaround
Keep activities that launch dialog activities visible until the user has responded to the dialog.
The system ensures that a transparent activity inherits all constraints from the first opaque activity beneath the transparent activity in the activity stack, including constraints related to:
- Size compatibility mode
- Orientation
- Aspect Ratio
Unity games
Unity games run on Android full screen or in multi‑window mode. However, many Unity games lose focus and stop drawing content when the app is placed in multi‑window mode.
Issue
Unity added a Resizable Window
option in Unity 2019.4 to support multi‑window mode on Android. However,
the initial implementation did not react to the activity lifecycle in
multi-window mode correctly, causing
UnityPlayer to suspend playback when the app loses focus. The player rendered a
black screen or the last, frozen frame of the game. Gameplay resumed only when
the user tapped the screen. Many apps using the Unity engine face this issue and
render as a black window in multi‑window mode.

Game loses focus in multi-window mode and renders as a black window.
Optimization
Upgrade Unity to 2019.4.40 or later and re‑export your game. Keep the
Resizable Window option checked in the
Android Player settings, otherwise
the game pauses when not in focus even though the game is entirely visible in
multi‑window mode.

Game renders content correctly in multi-window mode even when not in focus.
Compatibility workaround
Device manufacturers can apply the
OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_FAKE_FOCUS
per‑app override to provide a fake focus event to an app in
multi‑window mode. The override enables the activity to redraw content and
not be blacked out.
Desktop windowing
When apps run in a desktop windowing environment, they may encounter additional compatibility modes.
Apps with locked orientation are freely resizable. Even if an activity is locked to portrait orientation, users can still resize the app to landscape orientation.
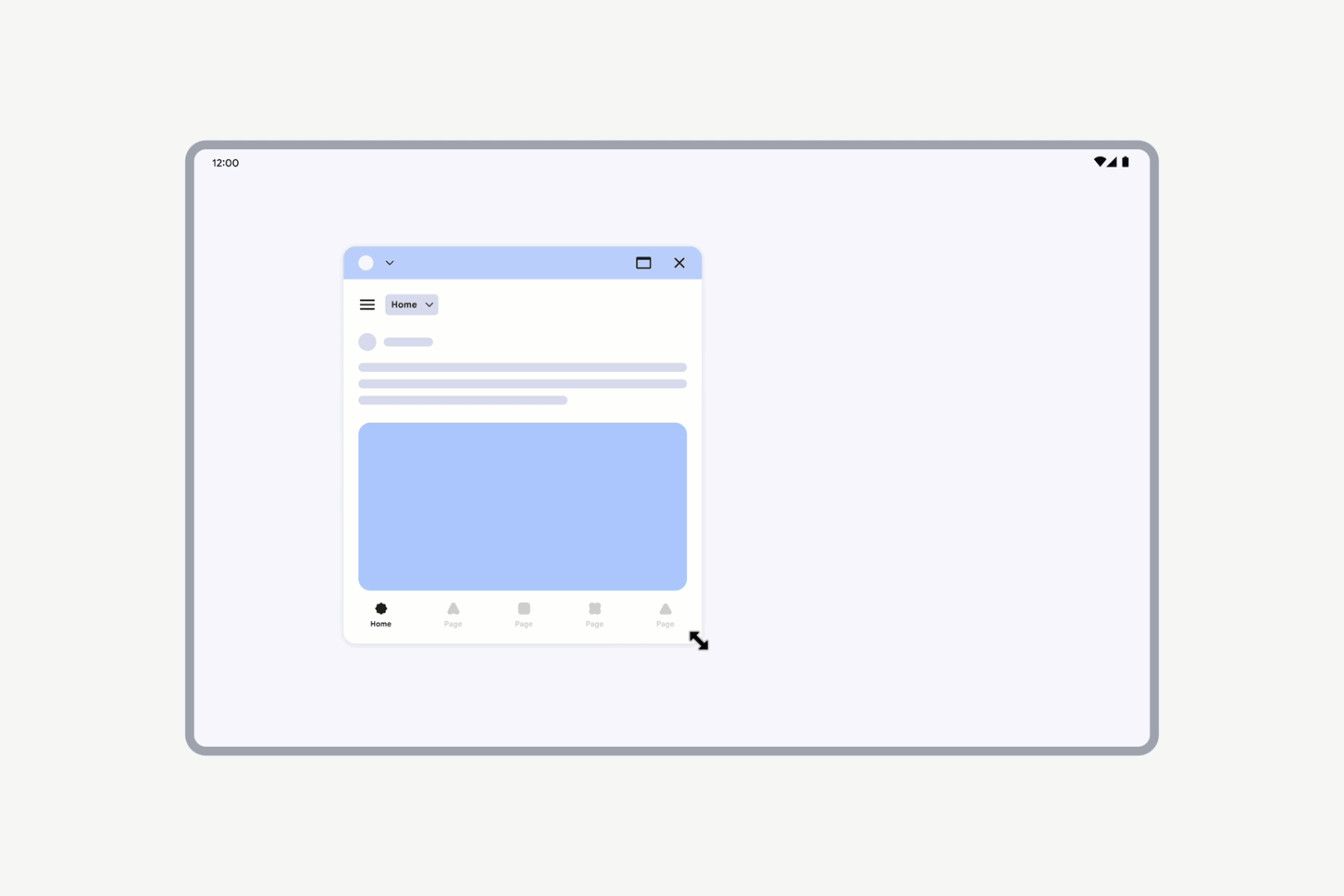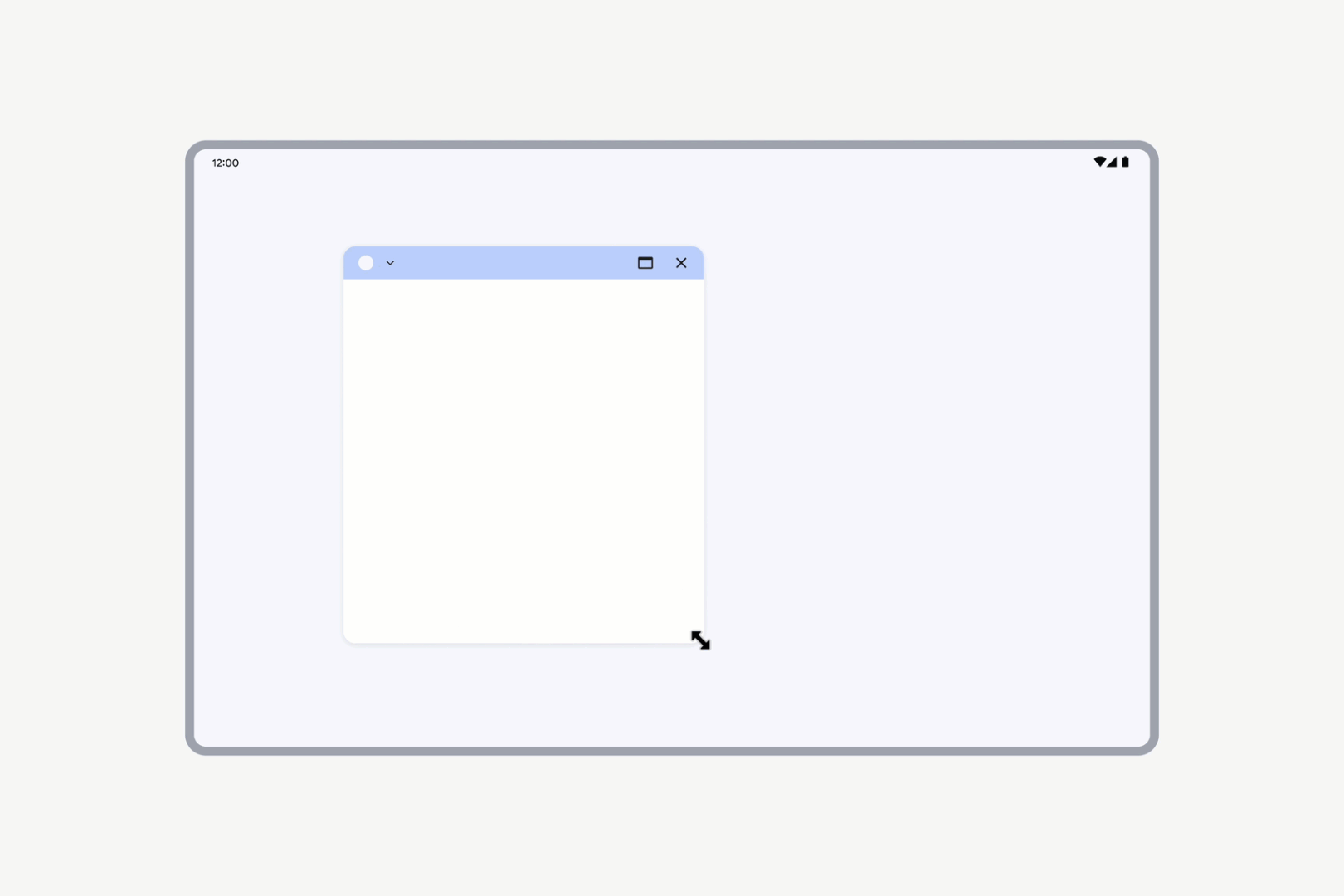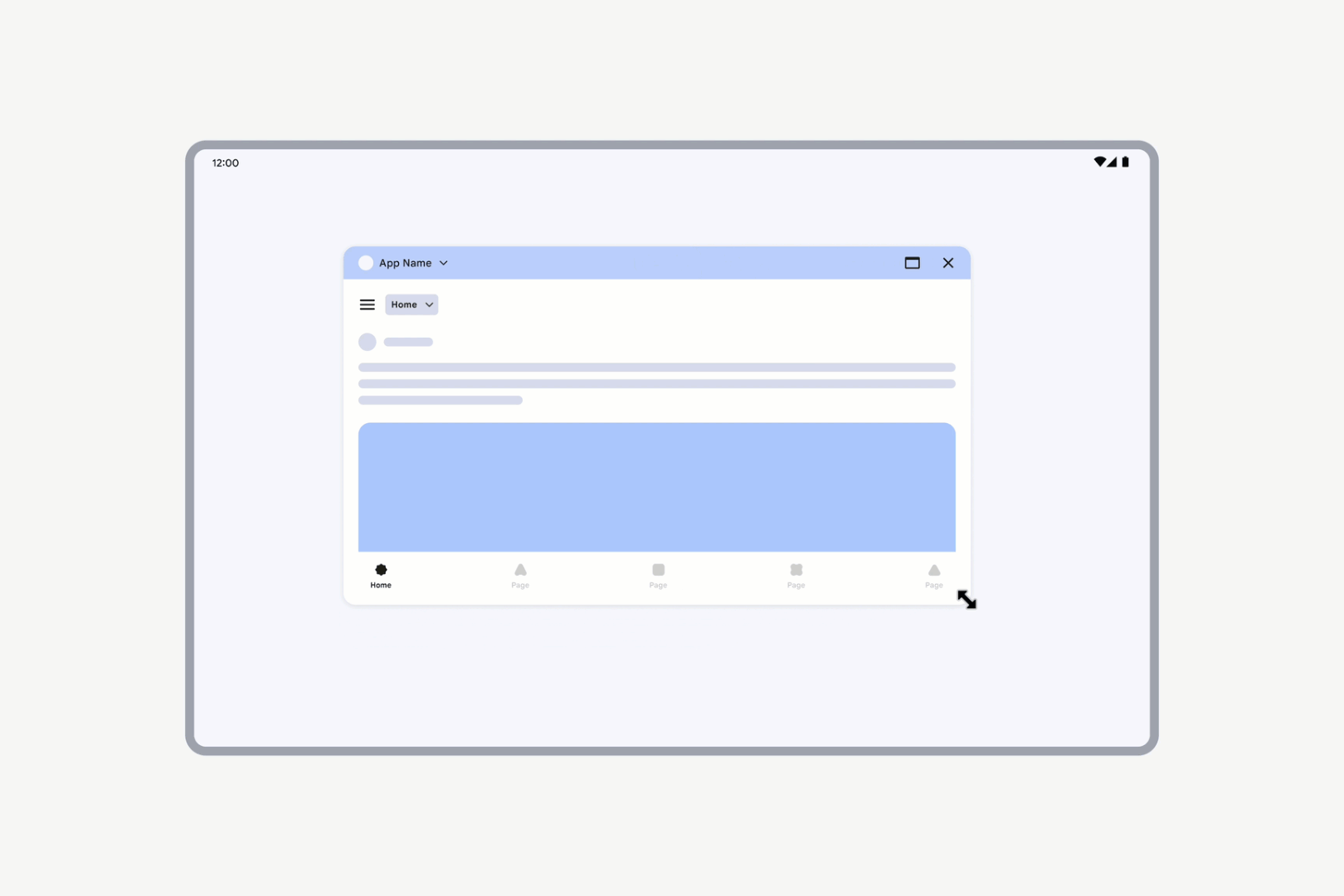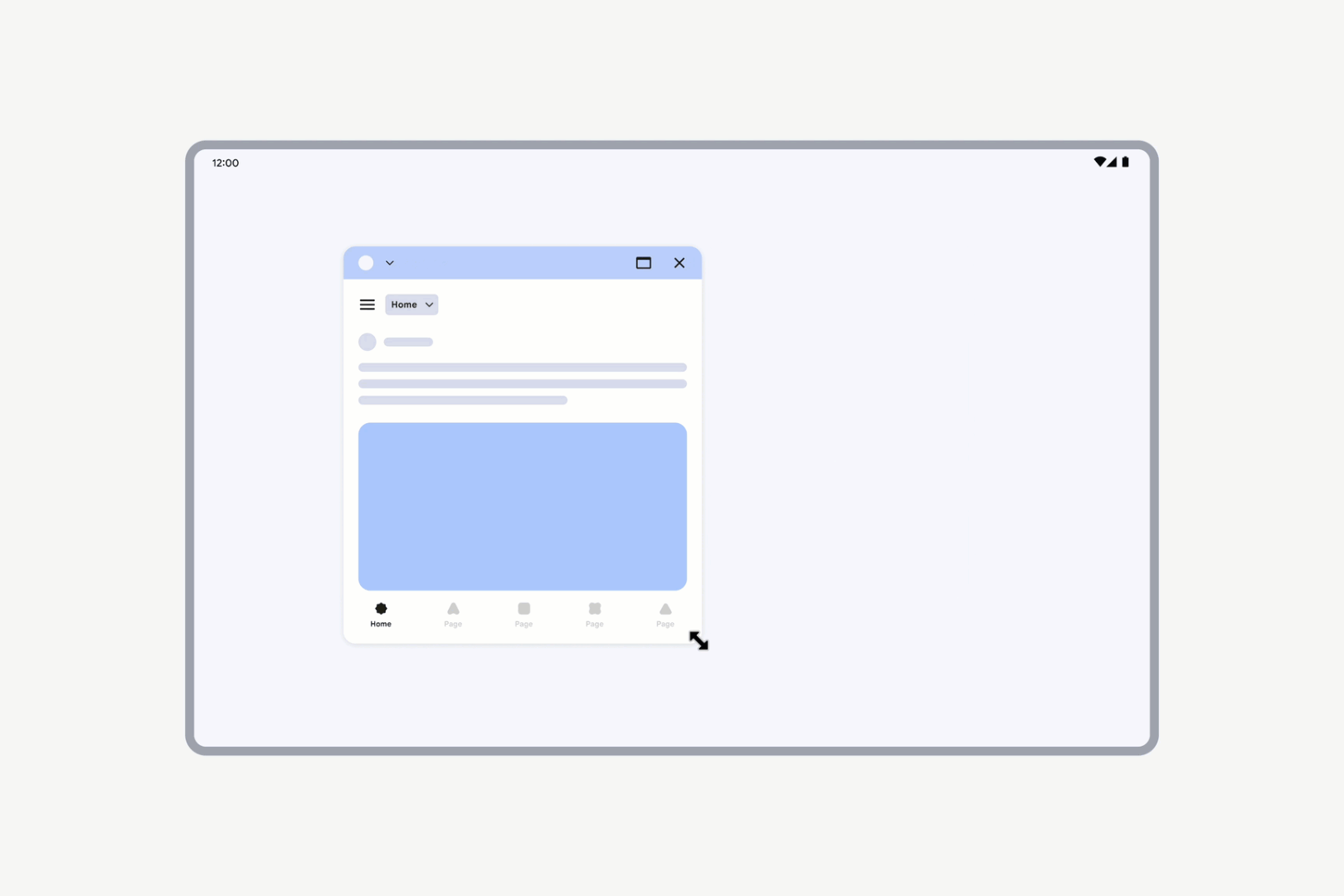
Apps with locked orientation can still be freely resized.
However, if an activity is declared as nonresizable (resizeableActivity = false), the activity UI scales while maintaining the same aspect ratio.
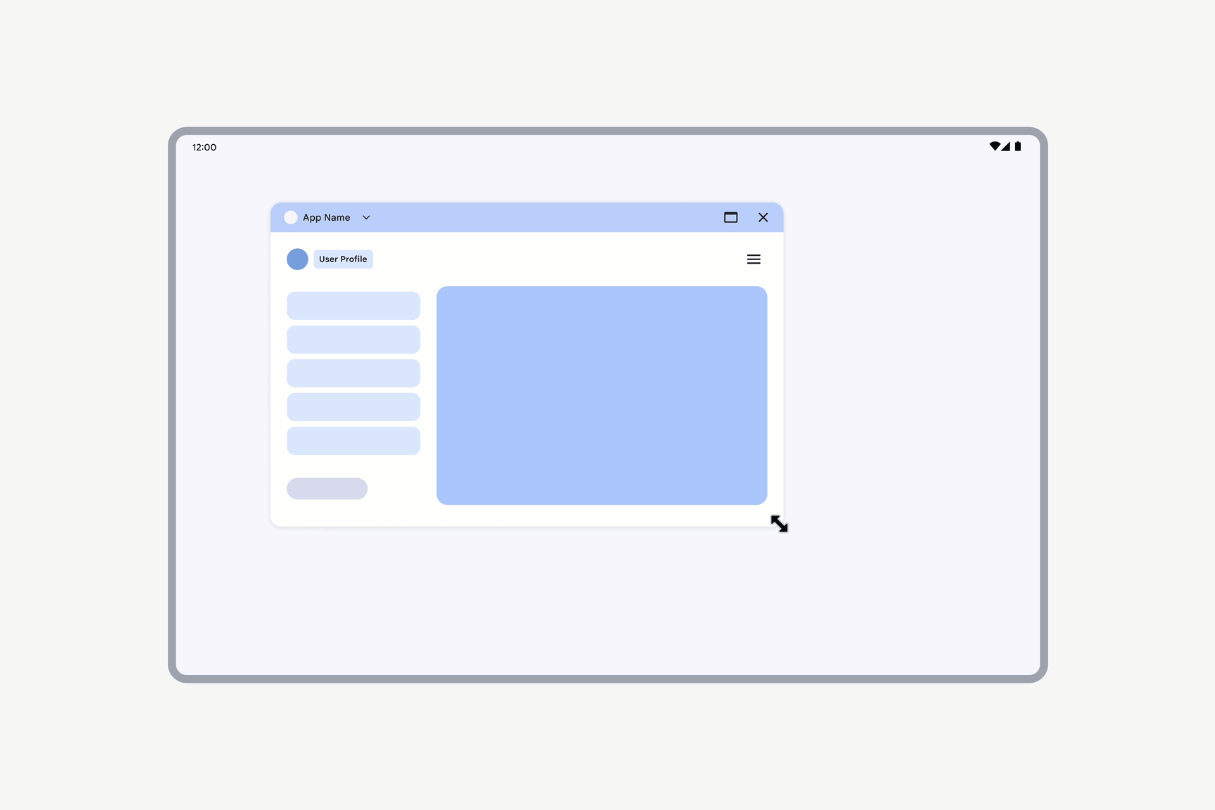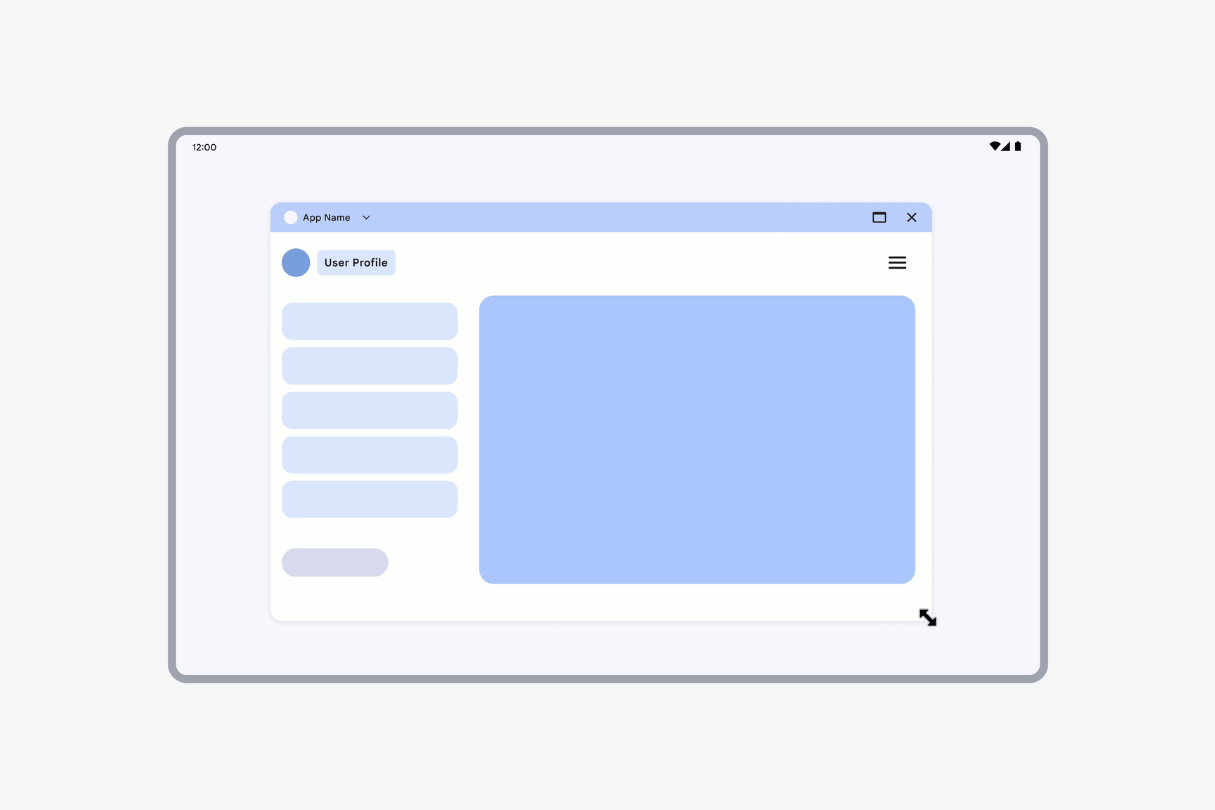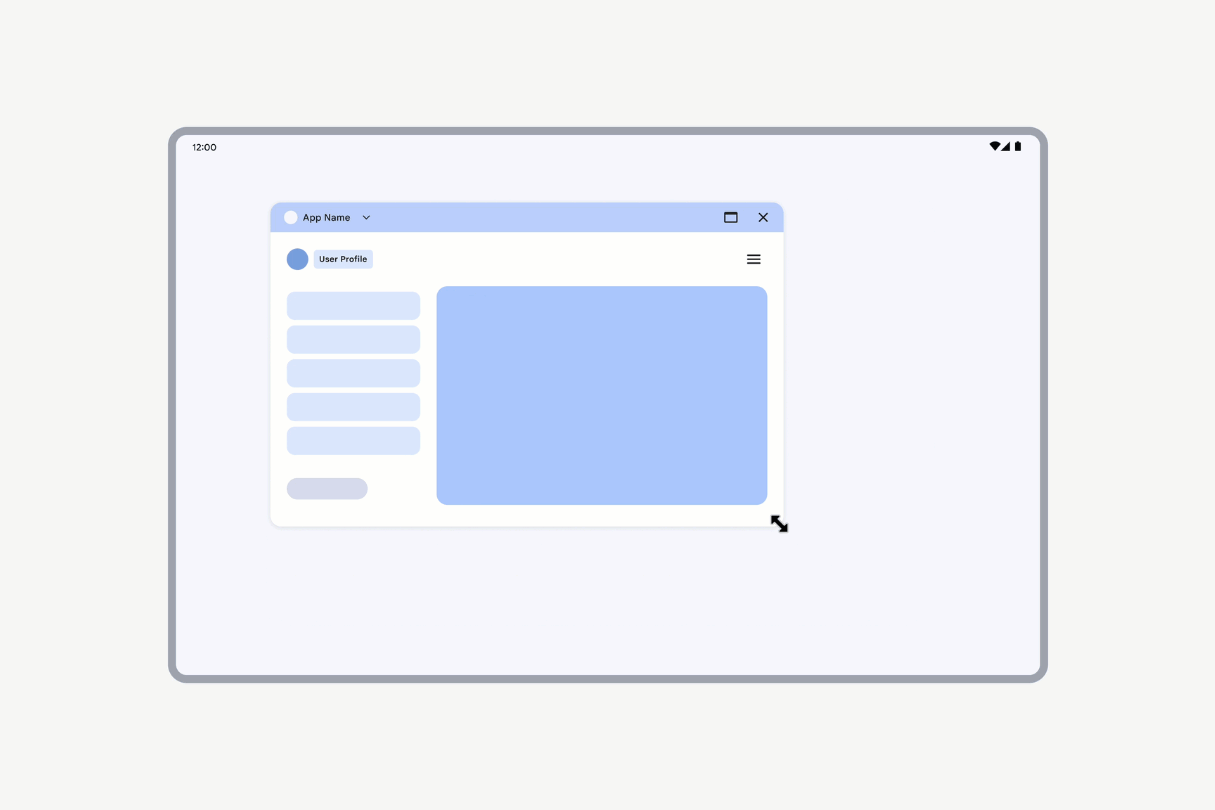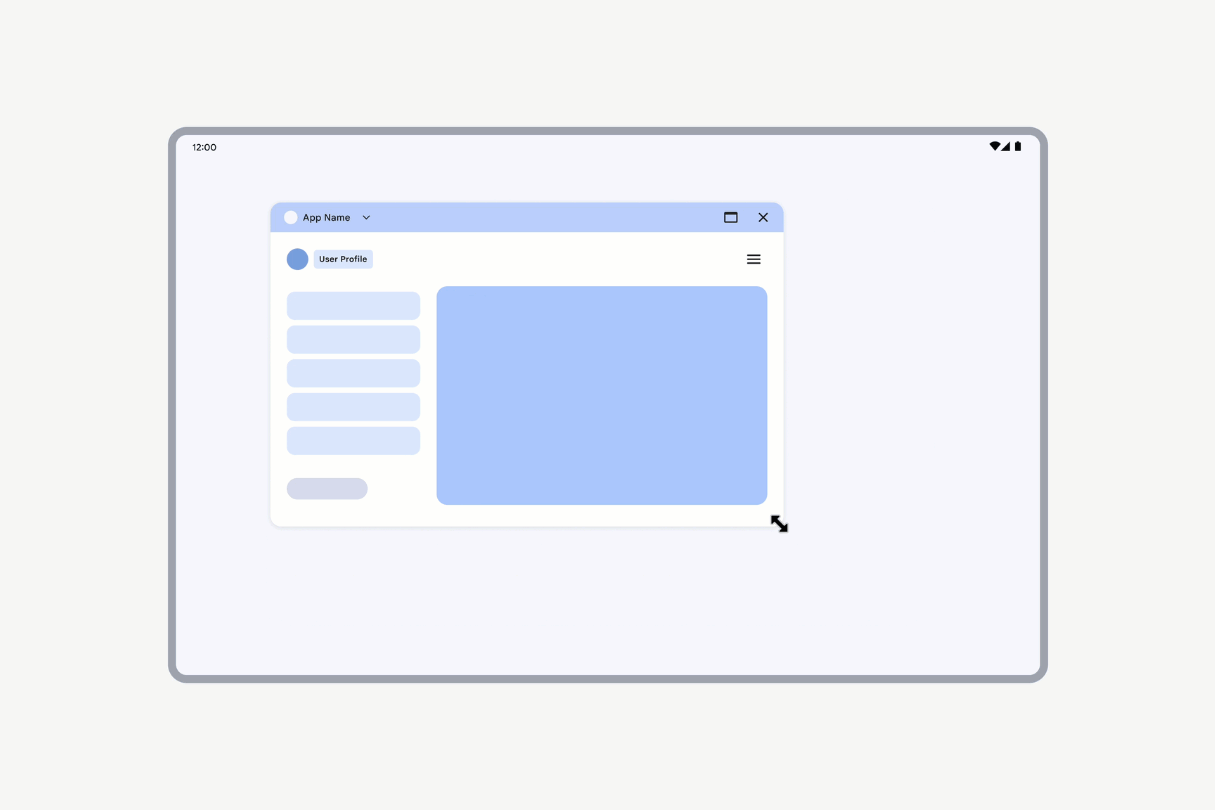
Activities declared as nonresizable have their UI scaled.
Camera preview in desktop windowing
When an app runs in desktop windowing, the display rotation and window orientation can be different from what they might encounter in fullscreen on standard phones.
Issue
Apps often assume that device orientation and camera sensor orientation are portrait, which can result in misaligned or distorted camera preview.
Optimization
Camera apps must correctly identify and manage device orientation and camera sensor orientation to present a correctly aligned and scaled camera preview. Apps must calculate device rotation, sensor rotation, and window aspect ratio, and then apply the results to the camera preview, which should also respond to window configuration changes. For detailed guidance, see Camera preview.
Compatibility workaround
When fixed-orientation apps in desktop windowing start a camera preview, the system might trigger camera compatibility treatment to avoid stretched and sideways previews.
The treatment sandboxes the environment to match the requested orientation in the following ways:
Letterbox the app window to the requested orientation: This is to avoid stretching issues due to inappropriate scaling.
Sandbox the display rotation: The treatment simulates the device placed in the requested orientation. As the most common incorrect assumption for camera previews is that the app is running on a portrait device, display rotation is sandboxed to 0 degrees for apps requesting portrait orientation, and 90 degrees for devices requesting landscape orientation.
Camera cropping: If the display rotation has changed, this is reflected on the camera feed: if a device is in landscape orientation and the treatment is triggered for an app requesting portrait orientation, camera field of view is cropped to resemble that of a portrait-oriented camera.
Rotate and crop the camera feed: The system cycles through activity methods
onStop()andonStart()(by default) oronPause()andonResume()(applied by the OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_ENABLE_REFRESH_VIA_PAUSE per-app override) after the treatment is applied to make sure the camera preview is properly displayed.
App developers can override these workarounds if the apps handle camera preview correctly. See Per-app overrides.
Resizing
When a simulated requested orientation treatment is active, resizing the window scales the viewfinder UI while keeping its aspect ratio. The rest of the app window can be freely resized.
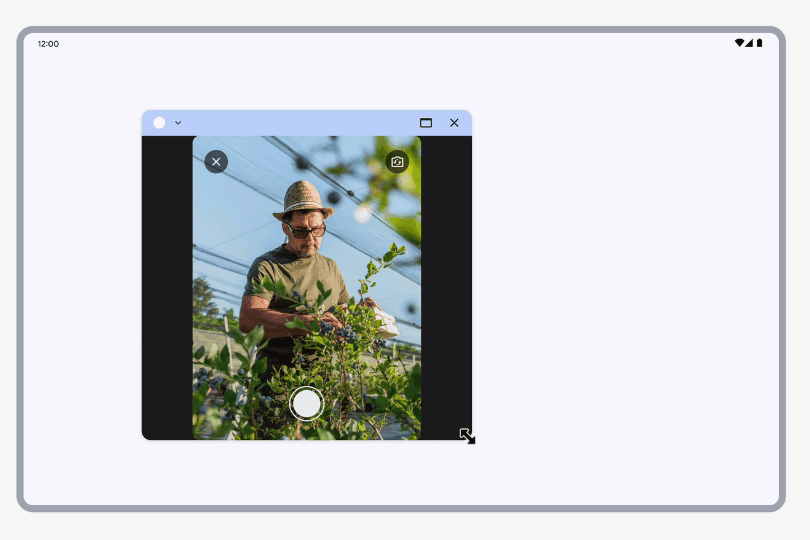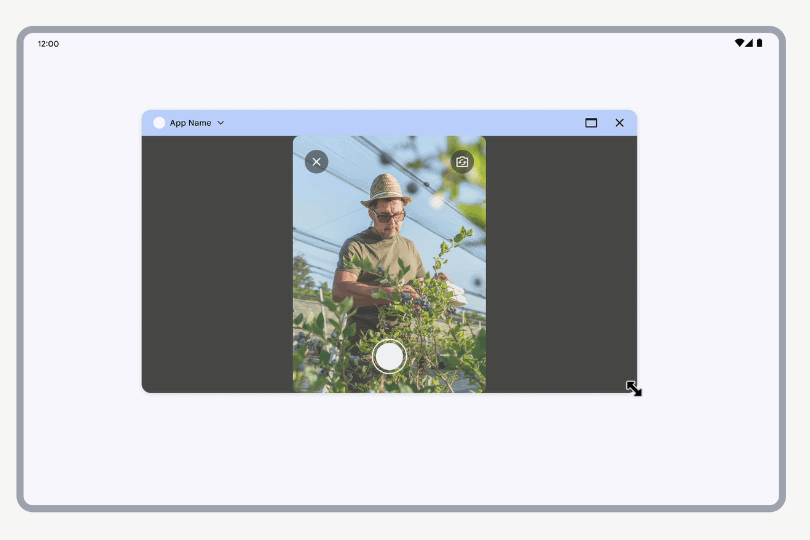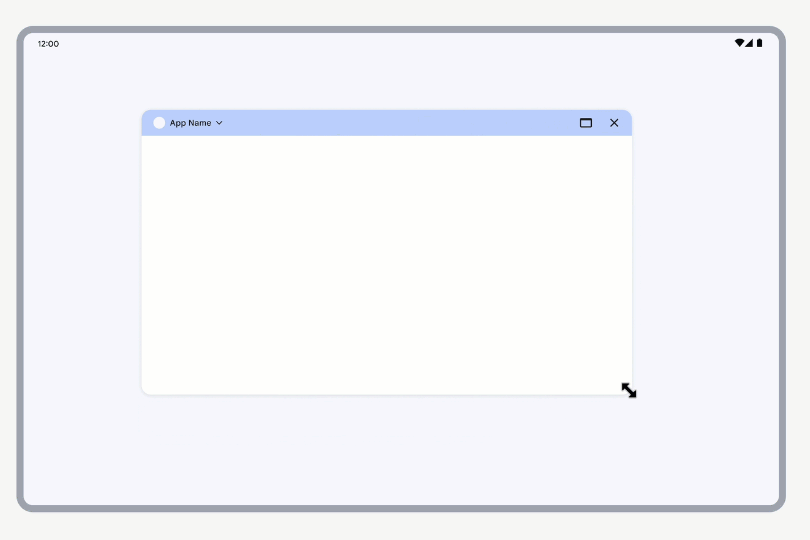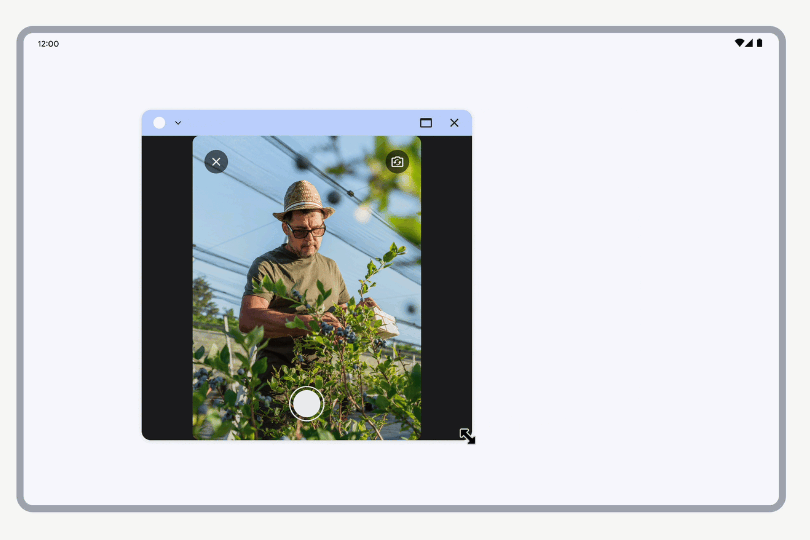
Resizing a window with a camera viewfinder
Test your app for compatibility issues
To test your app and understand how it behaves on different form factors, take advantage of the following resources:
- Device streaming: To test your app on production devices (including reference devices) hosted in Google data centers, see Android Device Streaming, powered by Firebase
- Emulators in Android Studio: For information on creating emulators for reference devices, see Create and manage virtual devices
- Android Studio resizable emulator: For information on accessing virtual devices, see Run apps on the Android Emulator
Is letterboxed
Verify that each activity can use all of the display space available to the app. First, declare the following code in your test folder:
Kotlin
fun isLetterboxed(activity: AppCompatActivity): Boolean { if (isInMultiWindowMode) return false val wmc = WindowMetricsCalculator.getOrCreate() val currentBounds = wmc.computeCurrentWindowMetrics(this).bounds val maxBounds = wmc.computeMaximumWindowMetrics(this).bounds val isScreenPortrait = maxBounds.height() > maxBounds.width() return if (isScreenPortrait) { currentBounds.height() < maxBounds.height() } else { currentBounds.width() < maxBounds.width() } }
Java
public boolean isLetterboxed(AppCompatActivity activity) { if (activity.isInMultiWindowMode()) { return false; } WindowMetricsCalculator wmc = WindowMetricsCalculator.getOrCreate(); Rect currentBounds = wmc.computeCurrentWindowMetrics(activity).getBounds(); Rect maxBounds = wmc.computeMaximumWindowMetrics(activity).getBounds(); boolean isScreenPortrait = maxBounds.height() > maxBounds.width(); return (isScreenPortrait) ? currentBounds.height() < maxBounds.height() : currentBounds.width() < maxBounds.width(); }
Then run a test to assert the behavior and make sure the target activity is not letterboxed:
Kotlin
@get:Rule val activityRule = ActivityScenarioRule(MainActivity::class.java) @Test fun activity_launched_notLetterBoxed() { activityRule.scenario.onActivity { assertFalse(it.isLetterboxed()) } }
Java
@Rule public ActivityScenarioRule<MainActivity> rule = new ActivityScenarioRule<>(MainActivity.class); @Test public void activity_launched_notLetterBoxed() { try (ActivityScenario<MainActivity> scenario = ActivityScenario.launch(MainActivity.class)) { scenario.onActivity( activity -> { assertFalse(activity.isLetterboxed()); }); } }
Ideally, run this kind of test only until it passes and asserts that your app's activities take up the entire display space available to the app. Test your app on all device types to ensure consistent behavior.
Per-app overrides
Android provides overrides that change the configured behavior of apps. For
example, the FORCE_RESIZE_APP override instructs the
system to bypass size compatibility mode and resize the app to fit display
dimensions even if resizeableActivity="false" is
specified in the app manifest.
Device manufacturers apply overrides to select apps—or all apps—on specific devices. On Android 14 (API level 34) and higher, users can apply overrides to apps through device settings. On Android 16 (API level 36) and higher, virtual device owners apply overrides on select devices the virtual device owners manage.
User per-app overrides
On Android 14 and higher, a settings menu enables users to change the aspect ratio of apps. Large screen devices such as the reference devices implement the menu.
The menu contains a list of all apps installed on the device. Users choose an app and then set the app aspect ratio to 3:4, 1:1, full screen, or other value configured by the device manufacturer. Users can also reset the aspect ratio to the app default, which is specified in the app manifest.
Apps can opt out of the compatibility override by setting the following PackageManager.Property tags:
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_USER_ASPECT_RATIO_OVERRIDE
To opt out of the user aspect ratio compatibility override, add the property to your app manifest and set the value to
false:<application> <property android:name="android.window. PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_USER_ASPECT_RATIO_OVERRIDE" android:value="false" /> </application>Your app will be excluded from the list of apps in device settings. Users won't be able to override the app's aspect ratio.
Setting the property to
truehas no effect.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_USER_ASPECT_RATIO_FULLSCREEN_OVERRIDE
To opt out of the full-screen option of the user aspect ratio compatibility override, add the property to your app manifest and set the value to
false:<application> <property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_USER_ASPECT_RATIO_FULLSCREEN_OVERRIDE" android:value="false" /> </application>The full-screen option is removed from the list of aspect ratio options in device settings. Users won't be able to apply the full-screen override to your app.
Setting this property to
truehas no effect.
Optimize your app for all screens: Don't set aspect ratio restrictions in your app. Use window size classes to support different layouts based on the amount of available display space.
Device per-app overrides
Device manufacturers and virtual device owners (select trusted and privileged apps) apply overrides on a per‑app basis on specific devices, including tablets, foldables, ChromeOS devices, and car displays. The reference devices may apply some of the overrides to a variety of apps by default.
Apps can opt out of most overrides (see the Per-app overrides table below).
You can test your app with overrides enabled or disabled using the compatibility framework (see Compatibility framework tools). When enabled, overrides apply to the entire app.
You can also use the Android Debug Bridge (adb) to enable or disable overrides and determine which overrides apply to your app.
Enable or disable overrides as follows:
adb shell am compat enable/disable <override name/id> <package>
For the reference devices, check which overrides apply to your app:
adb shell dumpsys platform_compat | grep <package name>
The following table lists available overrides along with guidance on how to optimize your app so the app does not need to rely on overrides. You can add property flags to your app manifest to opt out of some overrides.
| Per-app overrides | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Name | ID | Description |
| Input Compat | OVERRIDE_MOUSE_TO_TOUCH | 413207127 | Converts MotionEvent instances from a mouse device into touch events by rewriting the MotionEvent source and tool type when they're delivered to the application. |
| Resizability | FORCE_RESIZE_APP | 174042936 | Bypasses size compatibility mode for app on configuration changes. |
| FORCE_NON_RESIZE_APP | 181136395 | Forces app into size compatibility mode on configuration changes. | |
| Aspect ratio | OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO | 174042980 | Gatekeeper override that must be enabled to apply any other aspect ratio overrides. |
| OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_PORTRAIT_ONLY | 203647190 | If enabled (the default), limits override scope to portrait-only activities. | |
| OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_SMALL | 349045028 | Changes the minimum aspect ratio to 4:3. | |
| OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_MEDIUM | 180326845 | Changes the minimum aspect ratio to 3:2. | |
| OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE | 180326787 | Changes the minimum aspect ratio to 16:9. | |
| OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_TO_ALIGN_WITH_SPLIT_SCREEN | 208648326 | Changes the minimum aspect ratio to fit 50% of the display size (or split-screen aspect ratio). | |
| OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_EXCLUDE_PORTRAIT_FULLSCREEN | 218959984 | Disables the minimum aspect ratio override so that apps are full screen when device is portrait. | |
| Orientation | OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION | 265464455 | Enables overriding any orientation. |
| OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION_TO_USER | 310816437 | Overrides orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions. | |
| OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_PORTRAIT | 265452344 | Overrides the orientation to be portrait when an activity has an undefined orientation. | |
| OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_NOSENSOR | 265451093 | Overrides the orientation to be nosensor (use the natural orientation of device) when an activity has an undefined orientation. |
|
| OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_ORIENTATION_TO_REVERSE_LANDSCAPE | 266124927 | Rotates landscape-only apps 180 degrees. | |
| OVERRIDE_ORIENTATION_ONLY_FOR_CAMERA | 265456536 | Limits orientation override scope to when app is connected to the camera. | |
| OVERRIDE_USE_DISPLAY_LANDSCAPE_NATURAL_ORIENTATION | 255940284 | Sets the display to fixed landscape natural orientation when a task is full screen (including when letterboxed). | |
| OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION | 254631730 | Ignores orientation requests from app to avoid rotation infinite loops. | |
| OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_ORIENTATION_REQUEST_WHEN_LOOP_DETECTED | 273509367 | Ignores repeated orientation requests while an activity is relaunching. If Android detects an app is requesting at least two new orientations within one second, the system considers this a rotation infinite loop and applies the override. | |
| OVERRIDE_RESPECT_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION | 236283604 | Prevents letterboxing by disabling the device manufacturer ignore orientation request setting. | |
| Sandbox APIs | NEVER_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS | 184838306 | Prevents changing the behavior of any display APIs. |
| ALWAYS_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS | 185004937 | Forces the Display APIs in the app to return app bounds. Display APIs return logical display area bounds, but sometimes the app assumes Display APIs return app bounds, which leads to UI issues. |
|
| OVERRIDE_SANDBOX_VIEW_BOUNDS_APIS | 237531167 | Forces the View APIs used in the app to return app bounds. View APIs return logical display area bounds, but sometimes the app assumes View APIs return app bounds, which leads to UI issues. |
|
| Camera compat | OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_FORCE_ROTATION | 263959004 | Turns off force rotation. By default, all fixed-orientation camera apps are force rotated when the camera preview is open. |
| OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_SIMULATE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION | 398195815 | Turns off simulating requested orientation treatment for camera compatibility. By default, fixed-orientation camera apps are adjusted based on their requested orientation when the camera preview is open. | |
| OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_REFRESH | 264304459 | Removes the default hard refresh applied when a camera preview is force rotated. | |
| OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_ENABLE_REFRESH_VIA_PAUSE | 264301586 | Switches the hard refresh to a soft refresh when a camera preview is force rotated, which helps preserve state during the force rotation. By default, Android applies a hard refresh when the camera preview is force rotated. The hard refresh can cause issues with apps losing state or blacking out depending on how the apps cached their previous state. | |
| OVERRIDE_CAMERA_LANDSCAPE_TO_PORTRAIT | 250678880 | Crops the image buffer of the inner front camera. If the override is disabled, the inner front camera cropping is removed and the field of view of the camera preview is increased. By default on some foldables (see reference devices), the system crops the camera preview of all camera apps when using the inner front camera. | |
| Miscellaneous | OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_FAKE_FOCUS | 263259275 | Prevents the app from being blacked out when the app loses focus in split-screen mode. App waits for focus before drawing the app content, which can cause the app to freeze or be blacked out. The override enables Android to send a fake focus event to the app, which signals to the app to begin drawing content again. |
OVERRIDE_MOUSE_TO_TOUCH
Enables the compatibility treatment that converts MotionEvent instances from a mouse or touchpad to touch events by rewriting the MotionEvent source to SOURCE_TOUCHSCREEN and MotionEvent tool type to TOOL_TYPE_FINGER when the motion events are delivered to the application.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Not applicable. The problem should be solved in the application logic.
How to optimize apps
Your app should handle input events from mouse and touchpad, including touchpad gesture and mouse wheel scrolling. See Keyboard, mouse, and trackpad.
How to disable or opt out of override
Declare FEATURE_PC in a <uses-feature> element in the application's manifest.
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.type.pc"
android:required="false" />
Note: Set android:required="false" so the PC feature is optional and Google Play doesn't exclude the application on non-PC devices.
Property flags to adjust override
None.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_MOUSE_TO_TOUCH <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_MOUSE_TO_TOUCH <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
FORCE_RESIZE_APP
Forces the packages to which the override is applied to be resizable and able to enter multi‑window mode. Applies to all displays sizes.
How apps can achieve same result as override
In the app manifest, set the android:resizeableActivity
attribute to true.
How to optimize apps
Use responsive/adaptive layouts to enable apps to adapt to all display sizes and aspect ratios. See Support different display sizes.
How to disable or opt out of override
Set the property flag PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESIZEABLE_ACTIVITY_OVERRIDES to
false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESIZEABLE_ACTIVITY_OVERRIDES"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override and make app resizable:
adb shell am compat enable FORCE_RESIZE_APP <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable FORCE_RESIZE_APP <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
FORCE_NON_RESIZE_APP
Forces the packages to which the override is applied to be nonresizable and enter size compatibility mode on configuration changes. Applies to all display sizes.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set both the android:resizeableActivity attribute and
android.supports_size_changes metadata flag to false in the app manifest,
and declare either an orientation or aspect ratio restriction.
How to optimize apps
All apps that behave well if resized should either have
android:resizeableActivity or android.supports_size_changes set to true.
Other apps should be improved to behave well when resized. See
android:resizeableActivity.
How to disable or opt out of override
Set the property flag PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESIZEABLE_ACTIVITY_OVERRIDES to
false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESIZEABLE_ACTIVITY_OVERRIDES"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override and make app nonresizable:
adb shell am compat enable FORCE_NON_RESIZE_APP <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable FORCE_NON_RESIZE_APP <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO
The gatekeeper for all overrides that force a given minimum aspect ratio.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set android:minAspectRatio at the activity or app level.
How to optimize apps
Don't set aspect ratio restrictions in your app. Make sure your app supports
different display sizes. Use window size
classes to support different layouts based on the amount of space your app has
on the screen. See the
Compose WindowSizeClass API and View
WindowSizeClass API.
How to disable or opt out of override
Specify an aspect ratio restriction or set the property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_OVERRIDE to false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_OVERRIDE"
android:value="false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_PORTRAIT_ONLY
Restricts app settings that force a given minimum aspect ratio for activities
with portrait‑only orientation. Enabled by default and only takes effect
if OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO is also enabled.
How apps can achieve same result as override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to optimize apps
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to disable or opt out of override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
Property flags to adjust override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_PORTRAIT_ONLY <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_PORTRAIT_ONLY <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_SMALL
Sets the activity's minimum aspect ratio to a small value (4:3).
How apps can achieve same result as override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to optimize apps
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to disable or opt out of override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
Property flags to adjust override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_SMALL <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_SMALL <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_MEDIUM
Sets the activity's minimum aspect ratio to a medium value (3:2).
How apps can achieve same result as override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to optimize apps
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to disable or opt out of override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
Property flags to adjust override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_MEDIUM <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_MEDIUM <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE
Sets the activity's minimum aspect ratio to a large value (16:9).
How apps can achieve same result as override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to optimize apps
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to disable or opt out of override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
Property flags to adjust override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE <package>`
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_TO_ALIGN_WITH_SPLIT_SCREEN
Enables the use of split-screen aspect ratio. Allows an app to use all the available space in split-screen mode, avoiding letterboxing.
How apps can achieve same result as override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to optimize apps
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to disable or opt out of override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
Property flags to adjust override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_TO_ALIGN_WITH_SPLIT_SCREEN <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_TO_ALIGN_WITH_SPLIT_SCREEN <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_EXCLUDE_PORTRAIT_FULLSCREEN
Disables the minimum aspect ratio override in portrait full screen to use all available screen space.
How apps can achieve same result as override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to optimize apps
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
How to disable or opt out of override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
Property flags to adjust override
See OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_EXCLUDE_PORTRAIT_FULLSCREEN <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_EXCLUDE_PORTRAIT_FULLSCREEN <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION
Enables the following overrides to override any orientation:
- OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_PORTRAIT
- OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_NOSENSOR
- OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_ORIENTATION_TO_REVERSE_LANDSCAPE
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set the activity:screenOrientation manifest attribute,
or use the Activity#setRequestedOrientation() API.
How to optimize apps
Your app should support all orientations. An orientation change is a
configuration change, which can be handled either of two ways: letting the
system destroy and recreate the app, or managing the configuration changes
yourself. If you manage configuration changes yourself, the app state can be
retained by using ViewModel. In very limited cases, you can decide to lock the
orientation on small displays only, although doing so might not scale as well as
letting the user rotate the app as needed. On Android 12L and higher versions,
fixed orientation can be overridden by device configuration. For more
information about handling configuration changes and supporting all
orientations, see Handle configuration changes,
ViewModel overview, and App orientation restricted on
phones but not on large screen devices.
How to disable or opt out of override
Set the property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_ORIENTATION_OVERRIDE
to false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_ORIENTATION_OVERRIDE"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION_TO_USER
Enables app to fill the available display space. Overrides any orientation,
resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions specified in the app manifest. Also
ignores any calls to
Activity#setRequestedOrientation() or
Activity#getRequestedOrientation().
How apps can achieve same result as override
Do not set the
android:screenOrientationmanifest attribute, or set the attribute to"user".Set the
android:resizeableActivitymanifest attribute totrue.On small screens, to support app resizing while disabling multi‑window mode with
android:resizeableActivity=false, set theandroid.supports_size_changesmetadata flag totrue. Do not setminAspectRatioandmaxAspectRatio.
How to optimize apps
Enable your app to support all orientations; don't set a screenOrientation
specification in your app's manifest. Support app resizability,
multi‑window mode, and all display aspect ratios by setting the
android:resizeableActivity attribute in your app's manifest to true. See
Support different display sizes.
How to disable or opt out of override
Property flags to adjust override
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION_TO_USER <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION_TO_USER <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_PORTRAIT
Enables portrait orientation for all activities in the package. Unless OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION is enabled, the override is used only when no other fixed orientation has been specified by the activity.
How apps can achieve same result as override
How to optimize apps
How to disable or opt out of override
Property flags to adjust override
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_PORTRAIT <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_PORTRAIT <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_NOSENSOR
Enables nosensor orientation for all activities in the package. Unless OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION is enabled, the override is used only when no other fixed orientation has been specified by the activity.
How apps can achieve same result as override
How to optimize apps
How to disable or opt out of override
Property flags to adjust override
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_NOSENSOR <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_NOSENSOR <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_ORIENTATION_TO_REVERSE_LANDSCAPE
Enables reverseLandscape orientation for all activities in the package. Unless OVERRIDE_ANY_ORIENTATION is enabled, the override is used only when no other fixed orientation has been specified by the activity.
How apps can achieve same result as override
How to optimize apps
How to disable or opt out of override
Property flags to adjust override
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_ORIENTATION_TO_REVERSE_LANDSCAPE <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_ORIENTATION_TO_REVERSE_LANDSCAPE <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_ORIENTATION_ONLY_FOR_CAMERA
Limits OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_PORTRAIT, OVERRIDE_UNDEFINED_ORIENTATION_TO_NOSENSOR, and OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_ORIENTATION_TO_REVERSE_LANDSCAPE overrides to take effect only when camera connection is active.
How apps can achieve same result as override
How to optimize apps
How to disable or opt out of override
Property flags to adjust override
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_ORIENTATION_ONLY_FOR_CAMERA <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_ORIENTATION_ONLY_FOR_CAMERA <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_USE_DISPLAY_LANDSCAPE_NATURAL_ORIENTATION
Restricts display orientation to landscape natural orientation when the following conditions are met:
- Activity is full screen
- Opt out component property
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_DISPLAY_ORIENTATION_OVERRIDEisn't enabled - Device manufacturer ignore orientation request setting is enabled for the display
- Natural orientation of the display is landscape
How apps can achieve same result as override
Not applicable. The problem should be solved in the application logic.
How to optimize apps
How to disable or opt out of override
Set the property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_DISPLAY_ORIENTATION_OVERRIDE
to false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_DISPLAY_ORIENTATION_OVERRIDE"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_USE_DISPLAY_LANDSCAPE_NATURAL_ORIENTATION <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_USE_DISPLAY_LANDSCAPE_NATURAL_ORIENTATION <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION
Enables compat policy that skips updating app orientation in response to app
calling Activity#setRequestedOrientation() when app
is relaunching or has an active camera compat treatment.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_IGNORE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION
to true.
How to optimize apps
How to disable or opt out of override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_IGNORE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION
to false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_IGNORE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_ORIENTATION_REQUEST_WHEN_LOOP_DETECTED
Enables the compatibility policy that ignores an app's requested orientation in
response to the app calling
Activity#setRequestedOrientation() more than twice
in one second if an activity is not letterboxed for fixed orientation.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Not applicable. The problem should be solved in the application logic.
How to optimize apps
How to disable or opt out of override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_IGNORING_ORIENTATION_REQUEST_WHEN_LOOP_DETECTED to
false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_IGNORING_ORIENTATION_REQUEST_WHEN_LOOP_DETECTED"
android:value="false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_ORIENTATION_REQUEST_WHEN_LOOP_DETECTED <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_IGNORE_ORIENTATION_REQUEST_WHEN_LOOP_DETECTED <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_RESPECT_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION
Excludes packages from ignore orientation request behavior that can be enabled by device manufacturers for a display area or the whole display.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Not applicable. The problem should be solved in the application logic.
How to optimize apps
How to disable or opt out of override
No opt-out. Disabling the override can be dangerous if the app is not compatible with a device that has the device manufacturer ignore orientation request setting enabled. Contact Android Developer Relations to disable the override.
Property flags to adjust override
No property flags for this override.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_RESPECT_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_RESPECT_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
NEVER_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS
Forces packages to never have Display API sandboxing applied
for a letterboxed or size compatibility mode activity. The Display APIs
continue to provide display area bounds.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Declare activities resizable by either setting the
android:resizeableActivity manifest attribute to true
or the android.supports_size_changes metadata flag to true.
How to optimize apps
Apps that declare they are fully resizable should never rely upon display size
to position UI elements. Migrate your app to up‑to‑date APIs that
provide WindowMetrics. If you are using Jetpack Compose, take advantage of the
WindowSizeClass API to draw the UI based on how much screen
area the app has on the current display. See
Use window size classes.
How to disable or opt out of override
No opt-out. Migrate from deprecated APIs.
Property flags to adjust override
No property flags for this override.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable NEVER_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable NEVER_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
ALWAYS_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS
Forces packages to always have Display API sandboxing applied
regardless of windowing mode. The Display APIs always provide the app bounds.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Declare activities nonresizable by either setting the
android:resizeableActivity attribute to false or the
android.supports_size_changes metadata flag to false.
How to optimize apps
Apps that declare they are fully resizable should never rely on display size to
position UI elements. Migrate your app from deprecated APIs to
up‑to‑date APIs that provide WindowMetrics. See
WindowMetricsCalculator.
How to disable or opt out of override
No opt-out. Migrate from deprecated APIs.
Property flags to adjust override
No property flags for this override.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable ALWAYS_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable ALWAYS_SANDBOX_DISPLAY_APIS <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_SANDBOX_VIEW_BOUNDS_APIS
Forces packages to sandbox the following View APIs to activity bounds:
How apps can achieve same result as override
Resolve the issue in application code by using APIs that provide the bounds of the app window and offsets relative to the app window rather than the bounds of the device display and offsets relative to the device display.
How to optimize apps
Apps should use View APIs, taking into account the possibility of letterboxing
and multi-window mode being applied to the app. See
WindowMetricsCalculator.
How to disable or opt out of override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_SANDBOXING_VIEW_BOUNDS_APIS
to false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_SANDBOXING_VIEW_BOUNDS_APIS"
android:value="false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_SANDBOX_VIEW_BOUNDS_APIS <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_SANDBOX_VIEW_BOUNDS_APIS <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_FORCE_ROTATION
Disables force rotation. Improves the user experience on some apps.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ALLOW_FORCE_ROTATION
to false.
How to optimize apps
Do not rely on cached camera sensor orientation or device information. For camera compatibility guidance, see Introducing Camera Viewfinder and Support resizable surfaces in your camera app.
How to disable or opt out of override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ALLOW_FORCE_ROTATION
to true.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ALLOW_FORCE_ROTATION"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override, which removes force rotation:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_FORCE_ROTATION <package>
To remove the override, which allows force rotation to happen:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_FORCE_ROTATION <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_SIMULATE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION
Disables simulating requested orientation treatment for camera. Improves the user experience on some apps.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ALLOW_SIMULATE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION
to false.
How to optimize apps
Do not rely on cached camera sensor orientation or device information. For camera compatibility guidance, see Introducing Camera Viewfinder and Support resizable surfaces in your camera app.
How to disable or opt out of override
As this property disables the compatibility treatment, you can improve the user experience by taking into account dynamic display rotation changes, sensor orientation of the device, and window and preview size.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ALLOW_SIMULATE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override, which removes simulating requested orientation:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_SIMULATE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION <package>
To remove the override, which allows simulating requested orientation to happen:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_SIMULATE_REQUESTED_ORIENTATION <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_REFRESH
Disables activity refresh after force rotation. Improves the user experience when refresh causes state loss in apps.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ALLOW_REFRESH
to false.
How to optimize apps
See OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_FORCE_ROTATION.
How to disable or opt out of override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ALLOW_REFRESH
to true.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ALLOW_REFRESH"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override, which removes activity refresh:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_REFRESH <package>
To remove the override, which allows activity refresh:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_REFRESH <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_ENABLE_REFRESH_VIA_PAUSE
Makes the packages it is applied to do activity refresh using an onResume()
→ onPause() → onResume() cycle rather than onResume() →
onStop() → onResume() after camera compatibility force rotation.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ENABLE_REFRESH_VIA_PAUSE
to true.
How to optimize apps
See OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_FORCE_ROTATION.
How to disable or opt out of override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ENABLE_REFRESH_VIA_PAUSE
to false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_CAMERA_COMPAT_ENABLE_REFRESH_VIA_PAUSE"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_ENABLE_REFRESH_VIA_PAUSE <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_ENABLE_REFRESH_VIA_PAUSE <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_CAMERA_LANDSCAPE_TO_PORTRAIT
Forces camera output to be cropped to the opposite orientation when portrait camera orientation doesn't align with the natural device orientation. Many apps don't handle this situation and display stretched images otherwise.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_TO_PORTRAIT
to true.
How to optimize apps
See OVERRIDE_CAMERA_COMPAT_DISABLE_FORCE_ROTATION.
How to disable or opt out of override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_TO_PORTRAIT
to false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.camera.PROPERTY_COMPAT_OVERRIDE_LANDSCAPE_TO_PORTRAIT"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override, which applies inner front camera cropping:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_LANDSCAPE_TO_PORTRAIT <package>
To remove the override, which removes inner front camera cropping:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_CAMERA_LANDSCAPE_TO_PORTRAIT <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_DISABLE_MEDIA_PROJECTION_SINGLE_APP_OPTION
Prevents apps from opting out of app screen sharing (see
Media projection). Implemented when apps misuse the
createConfigForDefaultDisplay() API to force
full‑screen capture and jeopardize user privacy by exposing the contents
of notifications, which are captured with full‑screen but not app screen
sharing, and all apps regardless of windowing mode.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Allow the default media projection behavior (implemented in Android 14, API
level 34, with createScreenCaptureIntent()),
which enables users to decide whether to share the full screen or a single app
window regardless of windowing mode. Or call
createScreenCaptureIntent(MediaProjectionConfig)
with a MediaProjectionConfig argument returned from a
call to createConfigForUserChoice().
How to optimize apps
Allow users to select whether to share the entire device display or an app window during media projection, which as of Android 14 is the default behavior.
Make your app resizable (resizeableActivity="true") to
support multi‑window mode.
How to disable or opt out of override
Because of the seriousness of user privacy, your app cannot disable or opt out of this override.
Property flags to adjust override
None.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override, which cancels the app's opt out of partial screen sharing (that is, enables partial screen sharing):
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_DISABLE_MEDIA_PROJECTION_SINGLE_APP_OPTION <package>
To remove the override, which allows the app's opt out of partial screen sharing:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_DISABLE_MEDIA_PROJECTION_SINGLE_APP_OPTION <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_FAKE_FOCUS
Enables sending fake focus for unfocused apps in split‑screen mode. Some game engines wait to get focus before drawing the content of the app; and so, fake focus helps apps avoid staying blacked out when they are resumed and do not yet have focus.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ENABLE_FAKE_FOCUS to
true.
How to optimize apps
You can avoid this issue if your app handles multiple orientations and configuration changes well. Make your app large screen ready by following the Large screen app quality guidelines.
If you run the Unity game engine, upgrade to version 2019.4.40 or later and re‑export your game. Keep the Resizable Window option checked in the Android Player settings.
How to disable or opt out of override
Set property flag
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ENABLE_FAKE_FOCUS to
false.
Property flags to adjust override
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ENABLE_FAKE_FOCUS"
android:value="true|false"/>
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_FAKE_FOCUS <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_ENABLE_COMPAT_FAKE_FOCUS <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
OVERRIDE_EXCLUDE_CAPTION_INSETS_FROM_APP_BOUNDS
When the override is enabled, the activity receives configuration coupled with caption bar insets. Normally, caption bar insets are decoupled from configuration.
How apps can achieve same result as override
Enable edge‑to‑edge display or update the app's target SDK to API level 35 or higher. See the following:
- Compose: About window insets
- Views: Display content edge-to-edge in views
- Configuration: Behavior changes: Apps targeting Android 15 or higher
How to optimize apps
You can avoid this issue if your app enables edge‑to‑edge display or targets API level 35 or higher.
How to disable or opt out of override
Enable edge‑to‑edge display or target API level 35 or higher.
Property flags to adjust override
None.
adb commands to test override
To apply the override:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_EXCLUDE_CAPTION_INSETS_FROM_APP_BOUNDS <package>
To remove the override:
adb shell am compat disable OVERRIDE_EXCLUDE_CAPTION_INSETS_FROM_APP_BOUNDS <package>
Note: The commands only temporarily apply or remove the override.
Additional resources
- Large screen app quality guidelines
- Core app quality guidelines
-
A virtual device owner is a trusted or privileged app that manages a virtual device. Virtual device owners create virtual devices to render apps and then project the apps to remote devices, such as personal computers, virtual reality devices, or car infotainment systems. The virtual device owner is on a local device, such as a phone. ↩
