Bring your app to vehicles running either Android Auto or Android Automotive OS. Use one app architecture that works for both cases so every user can enjoy your app.
Android Auto
Android Auto provides a driver-optimized app experience for users who have an Android phone with the Android Auto app and a compatible car or aftermarket stereo system. Users can use your app directly on their car's display by connecting their phone. You enable Android Auto to connect with your phone app by creating services that Android Auto uses to display a driver-optimized interface to the driver. To learn more, see Android Auto overview.
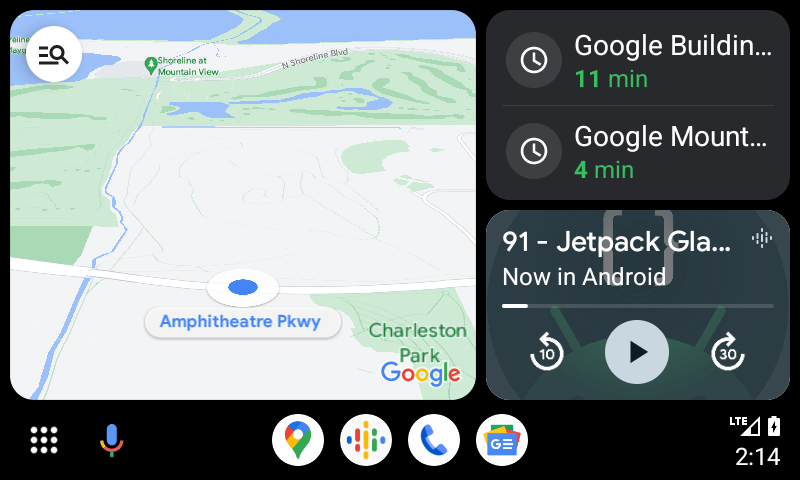
Figure 1: Android Auto—powered by a phone and running on a car.
Android Automotive OS
Android Automotive OS is an Android-based infotainment system that is built into vehicles. The car's system is a standalone Android-powered device that is optimized for driving. With Android Automotive OS, users install your app directly onto the car instead of their phones. To learn more, see Android Automotive OS overview.
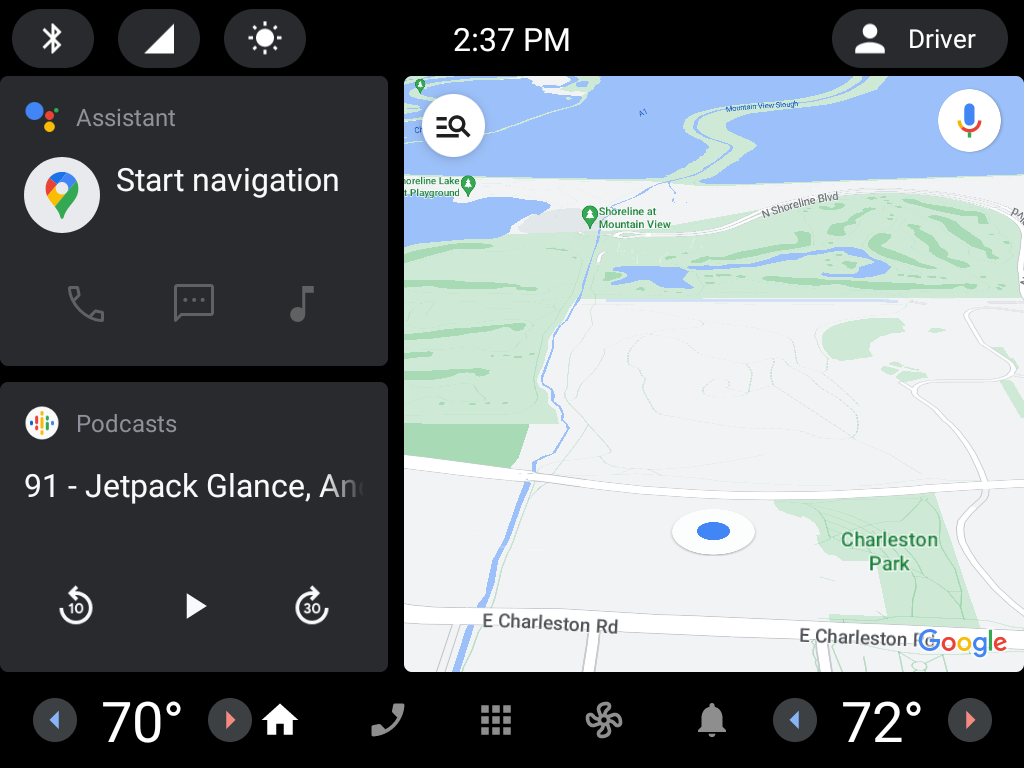
Figure 2: Android Automotive OS running on an emulator.
Supported app categories
Due to considerations unique to cars, Android Auto and Android Automotive OS only support certain types of apps as described in the following table:
| Category | Description | Platforms | Usage | Publishing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Media - audio |
Media apps let users browse and play music, radio, audiobooks, and other audio content in the car. See Build media apps for cars for more information. Important: the Media category does not include video content - see the separate Video category for details on apps that play videos.
Built using: Media apps can also be built using the Android for Cars App Library templates, as a part of our Early Access Program for Android Auto. See Build a templated media app for additional information specific to media apps. |
Android Auto and Android Automotive OS Important: Templated media apps are currently only supported on Android Auto |
While driving or parked |
All track types Important: Media apps using Car App Library templates can only be published to Internal Testing tracks and Closed Testing tracks as a part of our Early Access Program |
| Communication - messaging notifications |
Messaging notifications let users receive incoming notifications, read messages aloud using text-to-speech, and send replies using voice input in the car. See Extend messaging notifications for Android Auto for more information.
Built using: |
Android Auto | While driving or parked | All track types |
| Communication - templated messaging labs |
Templated messaging apps expand upon the capabilities of messaging notifications to let users browse conversation history, read historical messages aloud using text-to-speech, and send replies using voice input in the car. Built using: The Android for Cars App Library. See Build templated messaging experiences for Android Auto for additional information specific to messaging apps. |
Android Auto | While driving or parked | Internal Testing and Closed Testing tracks |
| Communication - calling labs |
Calling apps let users make and receive calls on their car screen. Built using: The Telecom Jetpack Library and the Android for Cars App Library. See Build calling experiences for Android Auto for additional information specific to calling apps. |
Android Auto | While driving or parked | Internal Testing and Closed Testing tracks |
| Navigation |
Navigation apps, including providers of driver and delivery services, help users get where they want to go by providing turn-by-turn directions. Built using: The Android for Cars App Library. See Build a navigation app for additional information specific to navigation apps. |
Android Auto and Android Automotive OS | While driving or parked | All track types |
| Point of Interest (POI) |
POI apps let the user discover and navigate to points of interest and take relevant actions, such as parking, charging, and fuel apps. Built using: The Android for Cars App Library. See Build a point of interest app for additional information specific to POI apps. |
Android Auto and Android Automotive OS | While driving or parked | All track types |
| Internet of Things (IOT) |
IOT apps let users take relevant actions on connected devices from within the car. Examples include controlling the state of certain devices, such as opening a garage door, flipping home light switches, or enabling home security. Built using: The Android for Cars App Library. See Build an internet of things app for additional information specific to IOT apps. |
Android Auto and Android Automotive OS | While driving or parked | All track types |
| Weather |
Weather apps let users see relevant weather information related to their current location or along their route. Weather apps can also provide navigation capabilities. Built using: The Android for Cars App Library. See Build a weather app for additional information specific to weather apps. |
Android Auto and Android Automotive OS | While driving or parked | All track types |
| Parked app categories | ||||
| Video |
Video apps let users view streaming videos while the car is parked. The core purpose of these apps is to display streaming videos. Built using: Views and/or Compose. See Build video apps for Android Automotive OS for more information. |
Android Automotive OS |
Primarily while parked Video apps can support limited use while driving as described in Support audio while driving. |
All track types |
| Games labs |
Game apps let users play games while the car is parked. The core purpose of these apps is to play games. Built using: Views and/or Compose. See Build games for cars for more information. |
Android Auto and Android Automotive OS | Only while parked | Internal Testing and Closed Testing tracks |
| Browsers labs |
Browser apps let users access web pages while the car is parked. Built using: Views and/or Compose. See Build browsers for Android Automotive OS for more information. |
Android Automotive OS | Only while parked | Internal Testing tracks |
Integrate with Google apps and services
You can build your own apps for use in vehicles that support Android for Cars, including Android Auto and Google Built-in. The following resources contain additional guidance relating to implementation:
Your app can launch navigation in Google Maps built-in through Google Maps for Automotive intents.
Navigation apps can achieve interoperability with Google Assistant through three different formats of intents. See Implement navigation app intents. To learn more about implementing turn-by-turn navigation apps compatible with Android Automotive OS and Android Auto, see Build a Navigation app.
Google Assistant can launch any app that is installed in the vehicle with voice commands like "Hey Google, open Example app."
The
PackageManagerclass lets you retrieve information about installed application packages on a device and then take further actions, such as getting the launchable intent for a package and launching that intent.
To test your apps, use the testing tools to run Android Auto and Android Automotive OS on your development machine. See Test Android Apps for Cars for details.
For app design guidelines, see Android for Cars
Additional resources
To learn more about Android for Cars, see the following additional resources.
