Android 14 mang đến cho nhà phát triển các tính năng và API mới hữu ích. Nội dung dưới đây giúp bạn tìm hiểu các tính năng cho ứng dụng cũng như làm quen với các API liên quan.
Để biết danh sách chi tiết về các API đã thêm, sửa đổi và xoá, hãy đọc báo cáo điểm khác biệt về API. Để biết thông tin chi tiết về các API đã thêm, hãy truy cập vào tài liệu tham khảo về API cho Android. Đối với Android 14, hãy tìm các API đã được thêm vào API cấp 34. Để tìm hiểu những thay đổi của nền tảng có thể tác động đến ứng dụng của bạn, hãy nhớ tham khảo các thay đổi về hành vi của Android 14 đối với ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 14 và tất cả ứng dụng.
Quốc tế hoá
Lựa chọn ưu tiên về ngôn ngữ cho mỗi ứng dụng
Android 14 mở rộng các tính năng về ngôn ngữ cho mỗi ứng dụng từng ra mắt trong Android 13 (API cấp 33), cũng như bổ sung thêm những tính năng sau:
Tự động tạo
localeConfigcủa ứng dụng: Bắt đầu từ Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 và AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, bạn có thể định cấu hình ứng dụng của mình để tự động hỗ trợ lựa chọn ưu tiên về ngôn ngữ cho mỗi ứng dụng. Dựa trên các tài nguyên của dự án, trình bổ trợ Android cho Gradle sẽ tạo tệpLocaleConfigvà thêm mục tham chiếu đến tệp đó trong tệp kê khai cuối cùng, do đó, bạn không còn phải tạo hoặc cập nhật tệp theo cách thủ công nữa. AGP sẽ sử dụng các tài nguyên trong thư mụcrescủa mô-đun ứng dụng và mọi phần phụ thuộc của mô-đun thư viện để xác định ngôn ngữ cần đưa vào tệpLocaleConfig.Bản cập nhật động cho
localeConfigcủa ứng dụng: Sử dụng các phương thứcsetOverrideLocaleConfig()vàgetOverrideLocaleConfig()trongLocaleManagerđể tự động cập nhật danh sách ngôn ngữ được hỗ trợ của ứng dụng trong phần cài đặt hệ thống của thiết bị. Hãy sử dụng khả năng hoạt này để tuỳ chỉnh danh sách ngôn ngữ được hỗ trợ cho mỗi khu vực, chạy kiểm thử A/B hoặc cung cấp danh sách ngôn ngữ được cập nhật nếu ứng dụng sử dụng tính năng thông báo đẩy phía máy chủ để bản địa hoá.Chế độ hiển thị ngôn ngữ ứng dụng cho trình chỉnh sửa phương thức nhập (IME): IME có thể sử dụng phương thức
getApplicationLocales()để kiểm tra ngôn ngữ của ứng dụng và so khớp ngôn ngữ IME với ngôn ngữ đó.
API Biến tố ngữ pháp
Có đến 3 tỷ người sử dụng ngôn ngữ có phân biệt giống ngữ pháp: ngôn ngữ mà các danh mục ngữ pháp (chẳng hạn như danh từ, động từ, tính từ và giới từ) sẽ phản ánh theo giống của người và đối tượng mà bạn nói đến hoặc nói về. Theo truyền thống, nhiều ngôn ngữ có phân biệt giống ngữ pháp sử dụng giống đực làm giống mặc định hoặc chung.
Việc xưng hô sai ngữ pháp với người dùng, chẳng hạn như xưng hô với phụ nữ theo ngữ pháp giống đực, có thể ảnh hưởng tiêu cực đến hiệu suất và thái độ của họ. Ngược lại, giao diện người dùng có ngôn ngữ phản ánh chính xác giống ngữ pháp của người dùng có thể cải thiện mức độ tương tác, cũng như mang lại trải nghiệm tự nhiên và phù hợp hơn cho người dùng.
To help you build a user-centric UI for gendered languages, Android 14 introduces the Grammatical Inflection API, which lets you add support for grammatical gender without refactoring your app.
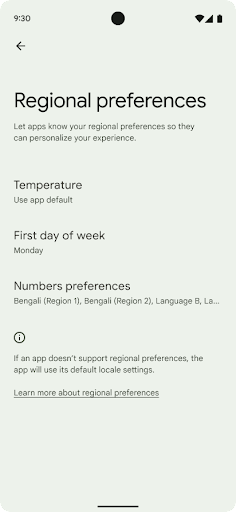
Lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực
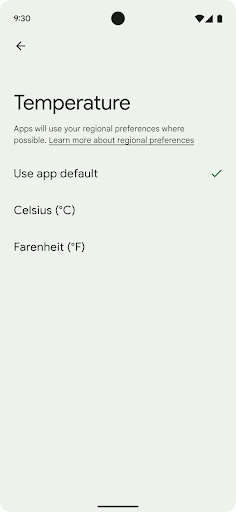
Các lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực cho phép người dùng cá nhân hoá đơn vị nhiệt độ, ngày đầu tiên trong tuần và hệ thống đánh số. Có thể người Châu Âu sinh sống ở Hoa Kỳ sẽ thích dùng đơn vị nhiệt độ bằng độ C thay vì độ F và muốn ứng dụng coi thứ Hai là đầu tuần thay vì mặc định ở Hoa Kỳ là Chủ nhật.
Các trình đơn Cài đặt Android mới cho những lựa chọn ưu tiên này là một nơi tập trung và dễ thấy để người dùng thay đổi các lựa chọn ưu tiên cho ứng dụng. Các lựa chọn ưu tiên này cũng được duy trì thông qua tính năng sao lưu và khôi phục. Một số API và ý định (ví dụ: getTemperatureUnit và getFirstDayOfWeek) cấp cho ứng dụng quyền đọc các lựa chọn ưu tiên của người dùng, nhờ đó, ứng dụng của bạn có thể điều chỉnh cách trình bày thông tin. Bạn cũng có thể đăng ký BroadcastReceiver trên ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED để xử lý các thay đổi về cấu hình ngôn ngữ khi các lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực được thay đổi.
Để tìm các chế độ cài đặt này, hãy mở ứng dụng Cài đặt rồi chuyển đến Hệ thống > Ngôn ngữ và phương thức nhập > Lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực.
Hỗ trợ tiếp cận
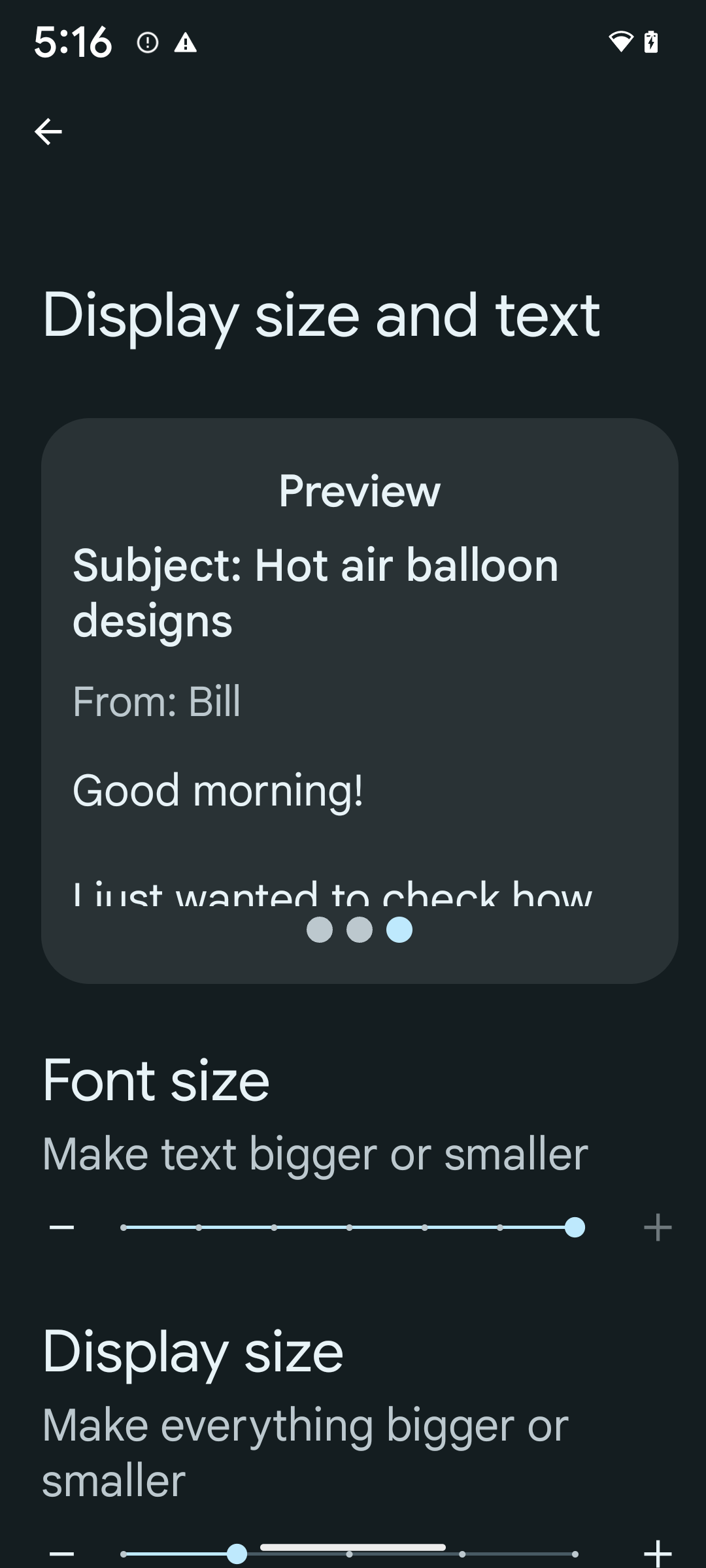
Điều chỉnh tỷ lệ phông chữ phi tuyến tính lên đến 200%
Starting in Android 14, the system supports font scaling up to 200%, providing users with additional accessibility options.
To prevent large text elements on screen from scaling too large, the system applies a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling strategy means that large text doesn't scale at the same rate as smaller text. Nonlinear font scaling helps preserve the proportional hierarchy between elements of different sizes while mitigating issues with linear text scaling at high degrees (such as text being cut off or text that becomes harder to read due to an extremely large display sizes).
Test your app with nonlinear font scaling
If you already use scaled pixels (sp) units to define text sizing, then these additional options and scaling improvements are applied automatically to the text in your app. However, you should still perform UI testing with the maximum font size enabled (200%) to ensure that your app applies the font sizes correctly and can accommodate larger font sizes without impacting usability.
To enable 200% font size, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Accessibility > Display size and text.
- For the Font size option, tap the plus (+) icon until the maximum font size setting is enabled, as shown in the image that accompanies this section.
Use scaled pixel (sp) units for text-sizes
Remember to always specify text sizes in sp units. When your app uses sp units, Android can apply the user's preferred text size and scale it appropriately.
Don't use sp units for padding or define view heights assuming implicit padding: with nonlinear font scaling sp dimensions might not be proportional, so 4sp + 20sp might not equal 24sp.
Convert scaled pixel (sp) units
Use TypedValue.applyDimension() to convert from sp units
to pixels, and use TypedValue.deriveDimension() to
convert pixels to sp. These methods apply the appropriate nonlinear scaling
curve automatically.
Avoid hardcoding equations using
Configuration.fontScale or
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Because font scaling is
nonlinear, the scaledDensity field is no longer accurate. The fontScale
field should be used for informational purposes only because fonts are no longer
scaled with a single scalar value.
Use sp units for lineHeight
Always define android:lineHeight using sp units instead
of dp, so the line height scales along with your text. Otherwise, if your text
is sp but your lineHeight is in dp or px, it doesn't scale and looks cramped.
TextView automatically corrects the lineHeight so that your intended
proportions are preserved, but only if both textSize and lineHeight are
defined in sp units.
Camera và nội dung nghe nhìn
Ultra HDR cho hình ảnh

Android 14 adds support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) images that retain more of the information from the sensor when taking a photo, which enables vibrant colors and greater contrast. Android uses the Ultra HDR format, which is fully backward compatible with JPEG images, allowing apps to seamlessly interoperate with HDR images, displaying them in Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) as needed.
Rendering these images in the UI in HDR is done automatically by the framework
when your app opts in to using HDR UI for its Activity Window, either through a
manifest entry or at runtime by calling
Window.setColorMode(). You can also capture compressed Ultra
HDR still images on supported devices. With more colors recovered
from the sensor, editing in post can be more flexible. The
Gainmap associated with Ultra HDR images can be used to render
them using OpenGL or Vulkan.
Thu phóng, Lấy nét, Xem nhanh và nhiều tính năng khác trong các tiện ích camera
Android 14 nâng cấp và cải thiện tiện ích máy ảnh, cho phép các ứng dụng xử lý trong thời gian dài hơn, nhờ đó hình ảnh được cải thiện bằng cách sử dụng các thuật toán chuyên sâu về điện toán như chụp ảnh ở điều kiện ánh sáng yếu trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ. Các tính năng này mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm mạnh mẽ hơn nữa khi sử dụng các tính năng của tiện ích máy ảnh. Sau đây là một số ví dụ về những điểm cải tiến này:
- Tính năng ước tính độ trễ xử lý ảnh tĩnh động cung cấp thông tin ước tính độ trễ chụp ảnh tĩnh chính xác hơn nhiều dựa trên điều kiện môi trường và cảnh hiện tại. Gọi
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()để lấy đối tượngStillCaptureLatencycó hai phương thức ước tính độ trễ. Phương thứcgetCaptureLatency()trả về độ trễ ước tính giữaonCaptureStartedvàonCaptureProcessStarted(), còn phương thứcgetProcessingLatency()trả về độ trễ ước tính giữaonCaptureProcessStarted()và khung hình đã xử lý cuối cùng. - Hỗ trợ các lệnh gọi lại tiến trình chụp để ứng dụng có thể hiển thị tiến trình hiện tại của các thao tác xử lý ảnh chụp tĩnh, chạy trong thời gian dài. Bạn có thể kiểm tra xem tính năng này có dùng được với
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailablehay không. Nếu có, bạn sẽ triển khai lệnh gọi lạionCaptureProcessProgressed(), trong đó tiến trình (từ 0 đến 100) được truyền vào dưới dạng tham số. Siêu dữ liệu dành riêng cho tiện ích, chẳng hạn như
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHđể điều chỉnh mức độ của một hiệu ứng tiện ích, chẳng hạn như mức độ làm mờ nền bằngEXTENSION_BOKEH.Tính năng Xem sau cho tính năng Chụp ảnh tĩnh trong các tiện ích máy ảnh, cung cấp hình ảnh được xử lý ít hơn và nhanh hơn so với hình ảnh cuối cùng. Nếu một tiện ích tăng độ trễ xử lý, thì bạn có thể cung cấp hình ảnh sau khi xem làm phần giữ chỗ để cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng và sau đó chuyển sang hình ảnh cuối cùng. Bạn có thể kiểm tra xem tính năng này có dùng được với
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailablehay không. Sau đó, bạn có thể truyềnOutputConfigurationđếnExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Hỗ trợ
SurfaceViewcho phép đường dẫn kết xuất bản xem trước được tối ưu hoá và tiết kiệm điện năng hơn.Hỗ trợ tính năng nhấn để lấy nét và thu phóng trong quá trình sử dụng tiện ích.
Thu phóng trong cảm biến
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
Âm thanh qua cổng USB không bị suy hao
Android 14 hỗ trợ các định dạng âm thanh không suy hao để mang lại trải nghiệm âm thanh chất lượng cao qua tai nghe có dây USB. Bạn có thể truy vấn một thiết bị USB để biết các thuộc tính bộ trộn ưu tiên, đăng ký trình nghe cho các thay đổi trong các thuộc tính bộ trộn ưu tiên và định cấu hình các thuộc tính bộ trộn bằng cách sử dụng lớp AudioMixerAttributes. Lớp này đại diện cho định dạng, chẳng hạn như mặt nạ kênh, tốc độ lấy mẫu và hành vi của bộ trộn âm thanh. Lớp này cho phép gửi trực tiếp âm thanh mà không cần trộn, điều chỉnh âm lượng hoặc xử lý hiệu ứng.
Năng suất và công cụ dành cho nhà phát triển
Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực
Android 14 thêm Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực làm API nền tảng, với khả năng hỗ trợ bổ sung cho các thiết bị Android 4.4 (API cấp 19) thông qua Thư viện Jetpack bằng Dịch vụ Google Play. Mục đích của Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực là giúp người dùng đăng nhập dễ dàng hơn bằng các API truy xuất và lưu trữ thông tin xác thực thông qua các trình cung cấp thông tin xác thực do người dùng định cấu hình. Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức đăng nhập, bao gồm tên người dùng và mật khẩu, khoá truy cập và các giải pháp đăng nhập liên kết (chẳng hạn như Đăng nhập bằng Google) trong một API duy nhất.
Khẩu khoá truy cập mang lại nhiều lợi thế. Ví dụ: khoá truy cập được xây dựng dựa trên các tiêu chuẩn của ngành, có thể hoạt động trên nhiều hệ điều hành và hệ sinh thái trình duyệt, cũng như có thể được sử dụng với cả trang web và ứng dụng.
Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem tài liệu về Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực và khoá truy cập cũng như bài đăng trên blog về Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực và khoá truy cập.
Health Connect
Health Connect là một kho lưu trữ trên thiết bị dành cho dữ liệu sức khoẻ và thể chất của người dùng. Tính năng này cho phép người dùng chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa các ứng dụng mà họ yêu thích, với một nơi duy nhất để kiểm soát dữ liệu họ muốn chia sẻ với các ứng dụng này.
Trên các thiết bị chạy phiên bản Android trước Android 14, bạn có thể tải Health Connect xuống dưới dạng ứng dụng trên Cửa hàng Google Play. Kể từ Android 14, Health Connect là một phần của nền tảng và nhận được bản cập nhật thông qua bản cập nhật hệ thống của Google Play mà không cần tải xuống riêng. Nhờ đó, Health Connect có thể được cập nhật thường xuyên và các ứng dụng của bạn có thể dựa vào Health Connect có sẵn trên các thiết bị chạy Android 14 trở lên. Người dùng có thể truy cập vào Health Connect từ phần Cài đặt trong thiết bị của họ, với các chế độ kiểm soát quyền riêng tư được tích hợp vào phần cài đặt hệ thống.
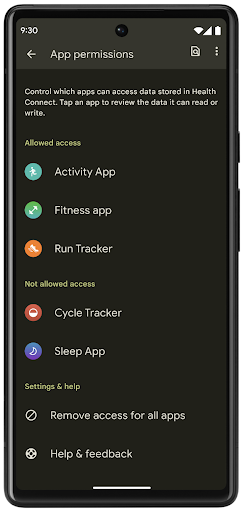
Health Connect có một số tính năng mới trong Android 14, chẳng hạn như tuyến đường tập thể dục, cho phép người dùng chia sẻ tuyến đường tập thể dục của họ và có thể được trực quan hoá trên bản đồ. Tuyến đường được xác định là danh sách các vị trí được lưu trong một khoảng thời gian và ứng dụng của bạn có thể chèn các tuyến đường vào các phiên tập thể dục, liên kết các tuyến đường đó với nhau. Để đảm bảo người dùng có toàn quyền kiểm soát dữ liệu nhạy cảm này, người dùng phải cho phép chia sẻ từng tuyến đường với các ứng dụng khác.
Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem tài liệu về Health Connect và bài đăng trên blog về Tính năng mới trong Android Health.
Nội dung cập nhật OpenJDK 17
Android 14 tiếp tục công cuộc làm mới các thư viện cốt lõi của Android để phù hợp với các tính năng trong bản phát hành OpenJDK LTS mới nhất, bao gồm cả bản cập nhật thư viện và tính năng hỗ trợ ngôn ngữ Java 17 cho các nhà phát triển ứng dụng và nền tảng.
Bao gồm các tính năng và điểm cải tiến sau đây:
- Cập nhật tính năng hỗ trợ Java 17 cho khoảng 300 lớp
java.base. - Khối văn bản (Text Blocks) ra mắt các giá trị cố định dạng chuỗi nhiều dòng bằng ngôn ngữ lập trình Java.
- So khớp mẫu cho instanceof, cho phép một đối tượng được xem là có một kiểu cụ thể trong
instanceofmà không cần thêm bất cứ biến nào. - Lớp kín (sealed classes) cho phép bạn hạn chế các lớp và giao diện có thể mở rộng hoặc triển khai các lớp đó.
Nhờ các bản cập nhật hệ thống Google Play (Project Mainline), hơn 600 triệu thiết bị được phép nhận các bản cập nhật Android Runtime (ART) mới nhất có các thay đổi này. Đây là một phần trong cam kết của chúng tôi nhằm cung cấp cho các ứng dụng một môi trường nhất quán, bảo mật hơn trên các thiết bị, đồng thời cung cấp các tính năng và chức năng mới cho người dùng độc lập với các bản phát hành nền tảng.
Java và OpenJDK là các nhãn hiệu hoặc nhãn hiệu đã đăng ký của Oracle và/hoặc các đơn vị liên kết với Oracle.
Những điểm cải tiến cho các cửa hàng ứng dụng
Android 14 introduces several PackageInstaller APIs that
allow app stores to improve their user experience.
Request install approval before downloading
Installing or updating an app might require user approval.
For example, when an installer making use of the
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES permission attempts to install a
new app. In prior Android versions, app stores can only request user approval
after APKs are written to the install session and the
session is committed.
Starting with Android 14, the requestUserPreapproval()
method lets installers request user approval before committing the install
session. This improvement lets an app store defer downloading any APKs until
after the installation has been approved by the user. Furthermore, once a user
has approved installation, the app store can download and install the app in the
background without interrupting the user.
Claim responsibility for future updates
The setRequestUpdateOwnership() method allows an installer
to indicate to the system that it intends to be responsible for future updates
to an app it is installing. This capability enables update ownership
enforcement, meaning that only the update owner is permitted
to install automatic updates to the app. Update ownership enforcement helps to
ensure that users receive updates only from the expected app store.
Any other installer, including those making use of the
INSTALL_PACKAGES permission, must receive explicit user
approval in order to install an update. If a user decides to proceed with an
update from another source, update ownership is lost.
Update apps at less-disruptive times
App stores typically want to avoid updating an app that is actively in use because this leads to the app's running processes being killed, which potentially interrupts what the user was doing.
Starting with Android 14, the InstallConstraints API
gives installers a way to ensure that their app updates happen at an opportune
moment. For example, an app store can call the
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() method to
make sure that an update is only committed when the user is no longer
interacting with the app in question.
Seamlessly install optional splits
With split APKs, features of an app can be delivered in separate APK files,
rather than as a monolithic APK. Split APKs allow app stores to optimize the
delivery of different app components. For example, app stores might optimize
based on the properties of the target device. The
PackageInstaller API has supported splits since its
introduction in API level 22.
In Android 14, the setDontKillApp() method allows an
installer to indicate that the app's running processes shouldn't be killed when
new splits are installed. App stores can use this feature to seamlessly install
new features of an app while the user is using the app.
Gói siêu dữ liệu ứng dụng
Starting in Android 14, the Android package installer lets you specify app metadata, such as data safety practices, to include on app store pages such as Google Play.
Phát hiện thời điểm người dùng chụp ảnh màn hình thiết bị
To create a more standardized experience for detecting screenshots, Android 14 introduces a privacy-preserving screenshot detection API. This API lets apps register callbacks on a per-activity basis. These callbacks are invoked, and the user is notified, when the user takes a screenshot while that activity is visible.
Trải nghiệm người dùng
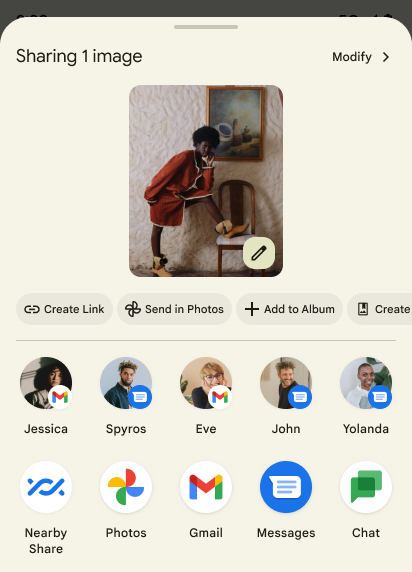
Các thao tác tuỳ chỉnh trên Trang chia sẻ nội dung và cách cải thiện thứ hạng
Android 14 updates the system sharesheet to support custom app actions and more informative preview results for users.
Add custom actions
With Android 14, your app can add custom actions to the system sharesheet it invokes.
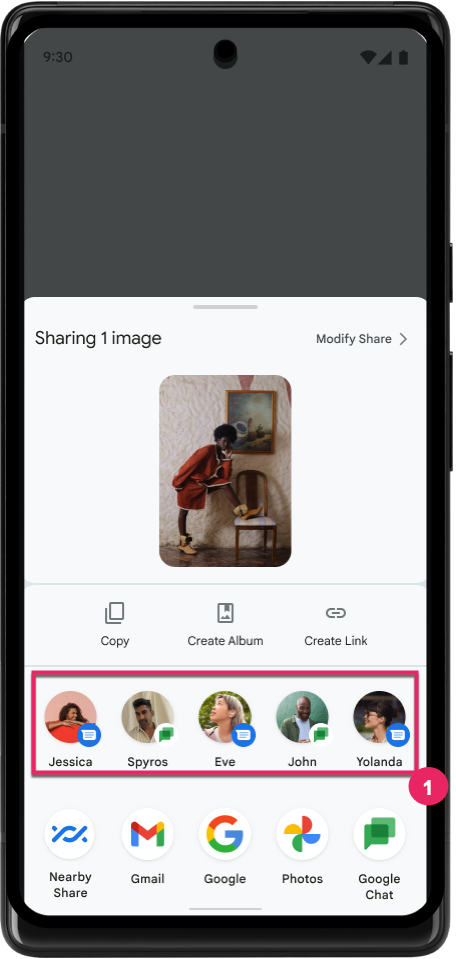
Improve ranking of Direct Share targets
Android 14 uses more signals from apps to determine the ranking of the direct share targets to provide more helpful results for the user. To provide the most useful signal for ranking, follow the guidance for improving rankings of your Direct Share targets. Communication apps can also report shortcut usage for outgoing and incoming messages.
Hỗ trợ ảnh động tích hợp sẵn và ảnh động tuỳ chỉnh cho tính năng Xem trước thao tác quay lại
Android 13 introduced the predictive back-to-home animation behind a developer option. When used in a supported app with the developer option enabled, swiping back shows an animation indicating that the back gesture exits the app back to the home screen.
Android 14 includes multiple improvements and new guidance for Predictive Back:
- You can set
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueto opt in to predictive back system animations per-Activity instead of for the entire app. - We've added new system animations to accompany the back-to-home animation from Android 13. The new system animations are cross-activity and cross-task, which you get automatically after migrating to Predictive Back.
- We've added new Material Component animations for Bottom sheets, Side sheets, and Search.
- We've created design guidance for creating custom in-app animations and transitions.
- We've added new APIs to support custom in-app transition animations:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Use
overrideActivityTransitioninstead ofoverridePendingTransitionfor transitions that respond as the user swipes back.
With this Android 14 preview release, all features of Predictive Back remain behind a developer option. See the developer guide to migrate your app to predictive back, as well as the developer guide to creating custom in-app transitions.
Chế độ ghi đè cho mỗi ứng dụng của nhà sản xuất thiết bị có màn hình lớn
Per-app overrides enable device manufacturers to change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the FORCE_RESIZE_APP override instructs the system to resize the app to fit display dimensions (avoiding size compatibility mode) even if resizeableActivity="false" is set in the app manifest.
Overrides are intended to improve the user experience on large screens.
New manifest properties enable you to disable some device manufacturer overrides for your app.
Chế độ ghi đè cho mỗi ứng dụng của người dùng trên màn hình lớn
Tính năng ghi đè cho mỗi ứng dụng thay đổi hành vi của ứng dụng trên thiết bị có màn hình lớn. Ví dụ: chế độ ghi đè của nhà sản xuất thiết bị OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE đặt tỷ lệ khung hình của ứng dụng thành 16:9 bất kể cấu hình của ứng dụng.
Android 14 QPR1 cho phép người dùng áp dụng chế độ ghi đè cho mỗi ứng dụng thông qua trình đơn cài đặt mới trên các thiết bị có màn hình lớn.
Chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng
Tính năng chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng cho phép người dùng chia sẻ một cửa sổ ứng dụng thay vì toàn bộ màn hình thiết bị trong khi ghi nội dung trên màn hình.
Khi chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng, thanh trạng thái, thanh điều hướng, thông báo và các thành phần khác trên giao diện người dùng của hệ thống sẽ bị loại trừ khỏi màn hình được chia sẻ. Chỉ nội dung của ứng dụng đã chọn mới được chia sẻ.
Tính năng chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng giúp cải thiện năng suất và quyền riêng tư bằng cách cho phép người dùng chạy nhiều ứng dụng nhưng chỉ giới hạn việc chia sẻ nội dung ở một ứng dụng.
Tính năng Trả lời thông minh dựa trên LLM trong Gboard trên Pixel 8 Pro
On Pixel 8 Pro devices with the December Feature Drop, developers can try out higher-quality smart replies in Gboard powered by on-device Large Language Models (LLMs) running on Google Tensor.
This feature is available as a limited preview for US English in WhatsApp, Line, and KakaoTalk. It requires using a Pixel 8 Pro device with Gboard as your keyboard.
To try it out, first enable the feature in Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent.
Next, open a conversation in a supported app to see LLM-powered Smart Reply in Gboard's suggestion strip in response to incoming messages.
Đồ hoạ
Các đường dẫn nay truy vấn được và nội suy được
Android's Path API is a powerful and flexible mechanism for
creating and rendering vector graphics, with the ability to stroke or fill a
path, construct a path from line segments or quadratic or cubic curves, perform
boolean operations to get even more complex shapes, or all of these
simultaneously. One limitation is the ability to find out what is actually in a
Path object; the internals of the object are opaque to callers after creation.
To create a Path, you call methods such as
moveTo(), lineTo(), and
cubicTo() to add path segments. But there has been no way to
ask that path what the segments are, so you must retain that information at
creation time.
Starting in Android 14, you can query paths to find out what's inside of them.
First, you need to get a PathIterator object using the
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Next, you can call PathIterator to iterate through the segments
one by one, retrieving all of the necessary data for each segment. This example
uses PathIterator.Segment objects, which packages up the data
for you:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator also has a non-allocating version of next() where you can pass
in a buffer to hold the point data.
One of the important use cases of querying Path data is interpolation. For
example, you might want to animate (or morph) between two different paths. To
further simplify that use case, Android 14 also includes the
interpolate() method on Path. Assuming the two paths have
the same internal structure, the interpolate() method creates a new Path
with that interpolated result. This example returns a path whose shape is
halfway (a linear interpolation of .5) between path and otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
The Jetpack graphics-path library enables similar APIs for earlier versions of Android as well.
Lưới tuỳ chỉnh có chương trình đổ bóng đỉnh và mảnh
Android has long supported drawing triangle meshes with custom shading, but the input mesh format has been limited to a few predefined attribute combinations. Android 14 adds support for custom meshes, which can be defined as triangles or triangle strips, and can, optionally, be indexed. These meshes are specified with custom attributes, vertex strides, varying, and vertex and fragment shaders written in AGSL.
The vertex shader defines the varyings, such as position and color, while the
fragment shader can optionally define the color for the pixel, typically by
using the varyings created by the vertex shader. If color is provided by the
fragment shader, it is then blended with the current Paint
color using the blend mode selected when
drawing the mesh. Uniforms can be passed
into the fragment and vertex shaders for additional flexibility.
Trình kết xuất vùng đệm phần cứng cho Canvas
To assist in using Android's Canvas API to draw with
hardware acceleration into a HardwareBuffer, Android 14
introduces HardwareBufferRenderer. This API is
particularly useful when your use case involves communication with the system
compositor through SurfaceControl for low-latency
drawing.
