때로 서로 관련이 있는 세 개 이상의 테이블 집합을 쿼리해야 할 수도 있습니다. 이 경우 테이블 간에 중첩된 관계를 정의합니다.
음악 스트리밍 앱의 예에서 모든 사용자, 각 사용자의 모든 재생목록, 각 사용자의 각 재생목록에 있는 모든 노래를 쿼리하려 한다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 사용자는 재생목록과 일대다 관계가 있으며 재생목록은 노래와 다대다 관계가 있습니다. 다음 코드 예에서는 이러한 항목을 나타내는 클래스뿐만 아니라 재생목록과 노래 간의 다대다 관계에 관한 상호 참조 테이블을 보여줍니다.
Kotlin
@Entity
data class User(
@PrimaryKey val userId: Long,
val name: String,
val age: Int
)
@Entity
data class Playlist(
@PrimaryKey val playlistId: Long,
val userCreatorId: Long,
val playlistName: String
)
@Entity
data class Song(
@PrimaryKey val songId: Long,
val songName: String,
val artist: String
)
@Entity(primaryKeys = ["playlistId", "songId"])
data class PlaylistSongCrossRef(
val playlistId: Long,
val songId: Long
)
자바
@Entity
public class User {
@PrimaryKey public long userId;
public String name;
public int age;
}
@Entity
public class Playlist {
@PrimaryKey public long playlistId;
public long userCreatorId;
public String playlistName;
}
@Entity
public class Song {
@PrimaryKey public long songId;
public String songName;
public String artist;
}
@Entity(primaryKeys = {"playlistId", "songId"})
public class PlaylistSongCrossRef {
public long playlistId;
public long songId;
}
먼저 데이터 클래스 및 @Relation 주석을 사용하여 평소처럼 집합 내 두 테이블 간의 관계를 모델링합니다. 다음 예는 Playlist 항목 클래스와 Song 항목 클래스 간의 다대다 관계를 모델링하는 PlaylistWithSongs 클래스를 보여줍니다.
Kotlin
data class PlaylistWithSongs(
@Embedded val playlist: Playlist,
@Relation(
parentColumn = "playlistId",
entityColumn = "songId",
associateBy = Junction(PlaylistSongCrossRef::class)
)
val songs: List<Song>
)
Java
public class PlaylistWithSongs {
@Embedded public Playlist playlist;
@Relation(
parentColumn = "playlistId",
entityColumn = "songId",
associateBy = Junction(PlaylistSongCrossRef.class)
)
public List<Song> songs;
}
이 관계를 나타내는 데이터 클래스를 정의한 후 집합의 다른 테이블과 첫 번째 관계 클래스 간의 관계를 모델링하여 새 관계 내부에 기존 관계를 '중첩'하는 또 다른 데이터 클래스를 만듭니다. 다음 예는 User 항목 클래스와 PlaylistWithSongs 관계 클래스 간의 일대다 관계를 모델링하는 UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs 클래스를 보여줍니다.
Kotlin
data class UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs(
@Embedded val user: User
@Relation(
entity = Playlist::class,
parentColumn = "userId",
entityColumn = "userCreatorId"
)
val playlists: List<PlaylistWithSongs>
)
Java
public class UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs {
@Embedded public User user;
@Relation(
entity = Playlist.class,
parentColumn = "userId",
entityColumn = "userCreatorId"
)
public List<PlaylistWithSongs> playlists;
}
UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs 클래스는 세 가지의 모든 항목 클래스(User, Playlist, Song) 간의 관계를 간접적으로 모델링합니다. 이는 그림 1에 설명되어 있습니다.
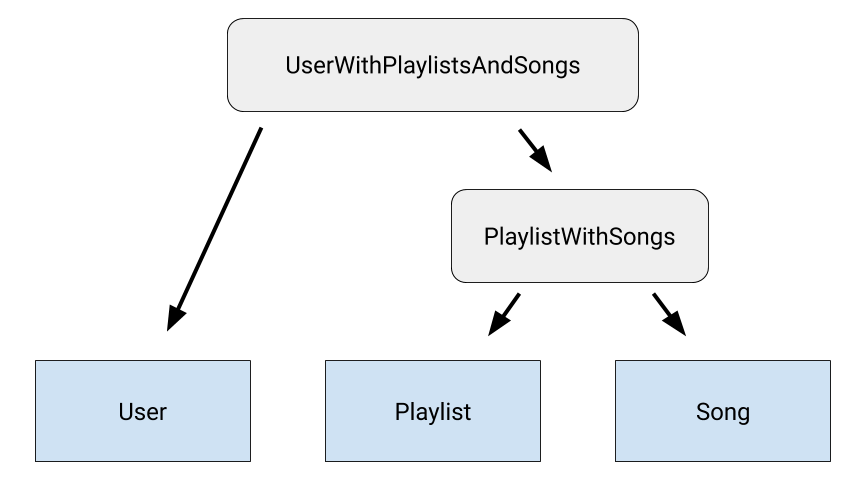
집합에 테이블이 더 많이 있다면 나머지 각 테이블 간의 관계를 모델링하는 클래스 및 이전의 모든 테이블 간의 관계를 모델링하는 관계 클래스를 만듭니다. 이렇게 하면 쿼리하려는 모든 테이블 간에 중첩된 관계 체인이 생성됩니다.
마지막으로 DAO 클래스에 메서드를 추가하여 앱에 필요한 쿼리 함수를 노출합니다. 이 메서드를 사용하려면 Room에서 여러 쿼리를 실행해야 하므로 전체 작업이 원자적으로 실행되도록 @Transaction 주석을 추가해야 합니다.
Kotlin
@Transaction
@Query("SELECT * FROM User")
fun getUsersWithPlaylistsAndSongs(): List<UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs>
Java
@Transaction
@Query("SELECT * FROM User")
public List<UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs> getUsersWithPlaylistsAndSongs();
