The Media Quality framework is being introduced in Android 16 for Android TV with the objective of establishing a standardized API for Picture Quality (PQ) and Audio Quality (AQ) adjustments. The primary goal is to provide a unified approach to these adjustments across different Android TV devices. This standardized framework aims to simplify development for app developers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and system-on-chip (SoC) vendors by offering a consistent set of Android APIs. For SoC vendors specifically, it allows the Android framework to handle PQ and AQ configuration, reducing the overhead of collaborating with different application developers.
Ultimately, for Google and Android platform, it helps reduce fragmentation, improve quality and scalability, provide new features, and lay the foundation for a Unified AQ/PQ UI and improved user experience.
The Media Quality framework supports various use cases to enhance the TV-watching experience. It is worth noting that profiles and settings can be managed per package name (app), and per input ID. Additionally, profiles can be created by system apps, or by other apps that are in the allowlist. Profiles can be updated or removed only by the owner of the profiles. Specifically, the framework manages Picture and Sound Profiles. Examples of picture parameters include brightness, contrast, sharpness. Examples of sound parameters include bass and treble. These profiles can be applied in various contexts, including setting global default profiles, streaming profiles via MediaCodec, setting app default profiles for specific media apps, and setting TV input picture profiles for specific inputs like HDMI. The framework also supports status changes, allowing different parameter sets for states like HDR, managing active picture profiles for ongoing processing, and handling ambient backlight features.
The Android team is working with our ecosystem partners to support Media Quality framework.
Components
The Media Quality Framework is composed of several key components that work together across the application, framework, and hardware layers.
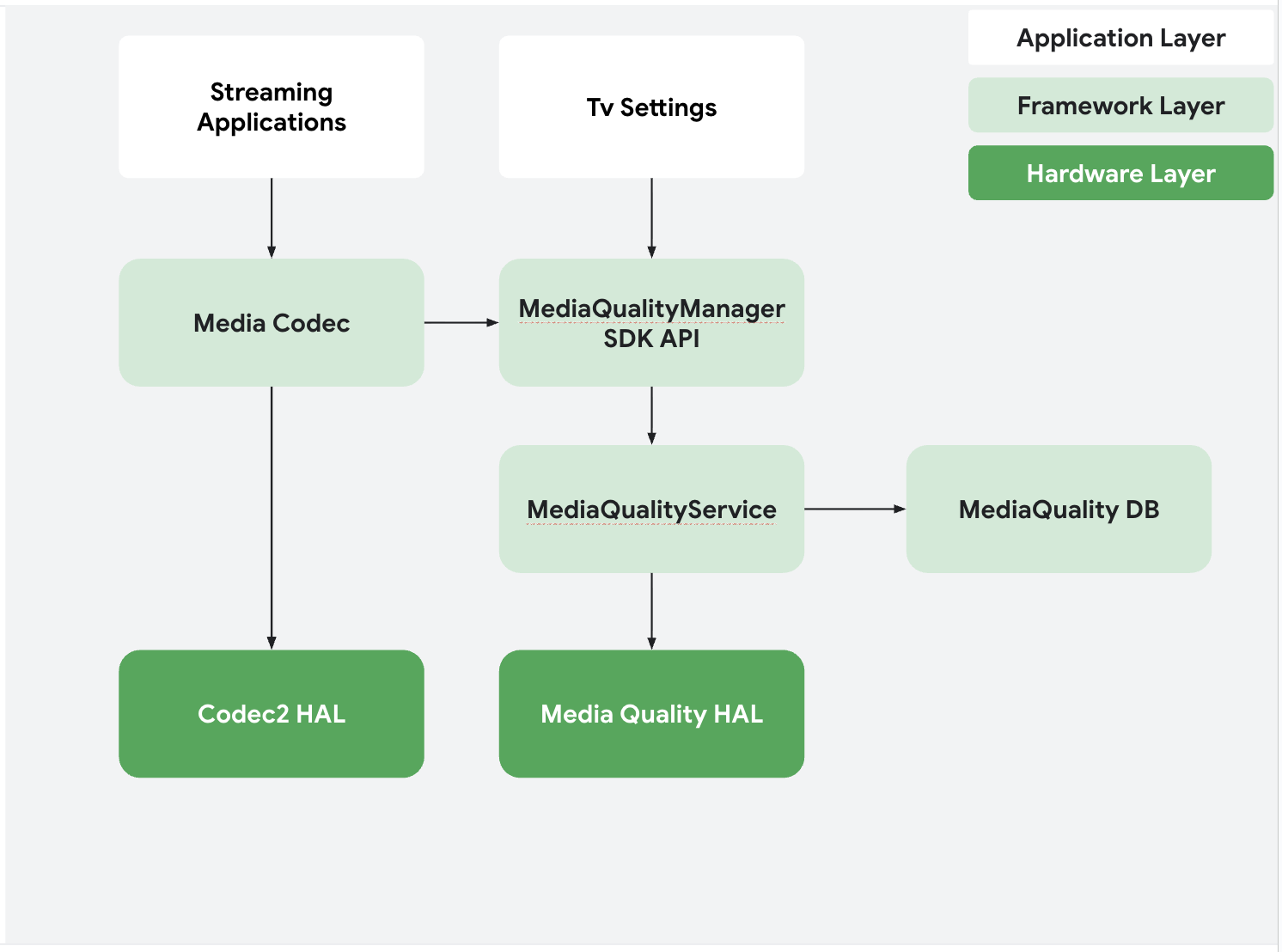
Figure 1. Interactions between Media Quality Framework components
- Media Quality Manager (SDK API): The application-facing SDK API that allows apps to manage picture and sound profiles.
- Media Quality Service: A system service that contains the core business logic, managing profiles, permissions, and communication with the HAL.
- Media Quality Database: A SQLite database that stores all picture and sound profiles.
- Media Quality Contract: Defines the standardized parameters and data structures used for communication between apps and the framework.
- Media Quality HAL: The Hardware Abstraction Layer that SoC vendors implement to communicate picture and sound profile changes to the underlying hardware.
Features
The Media Quality Framework supports a wide range of features to provide a flexible and powerful system for managing media quality.
Profile Management
- App-managed profiles: Apps can create, update, and delete their own profiles for a customized experience.
- Default profiles: System apps can set default profiles for specific apps or TV inputs (e.g., HDMI 1).
- Global default profile: A system-wide fallback profile that is applied when no specific profile is set.
Overall Workflow
The following diagrams illustrate the call sequences for common media quality operations.
Create and Apply a Picture Profile

Figure 2. Sequence diagram for creating a picture profile
- A system app calls
setPictureProfileAllowList()to grant a media app permission to create profiles. - The media app registers a
PictureProfileCallbackto receive notifications about profile changes. - The media app calls
createPictureProfile()with aPictureProfileobject. - The
MediaQualityServiceprocesses the request, saves the profile to the database, and notifies the app of success or failure via the registered callback (onPictureProfileAdded()oronError()).
Set a Per-Stream Picture Profile
This workflow demonstrates how an application can apply a specific profile to its video content during playback.
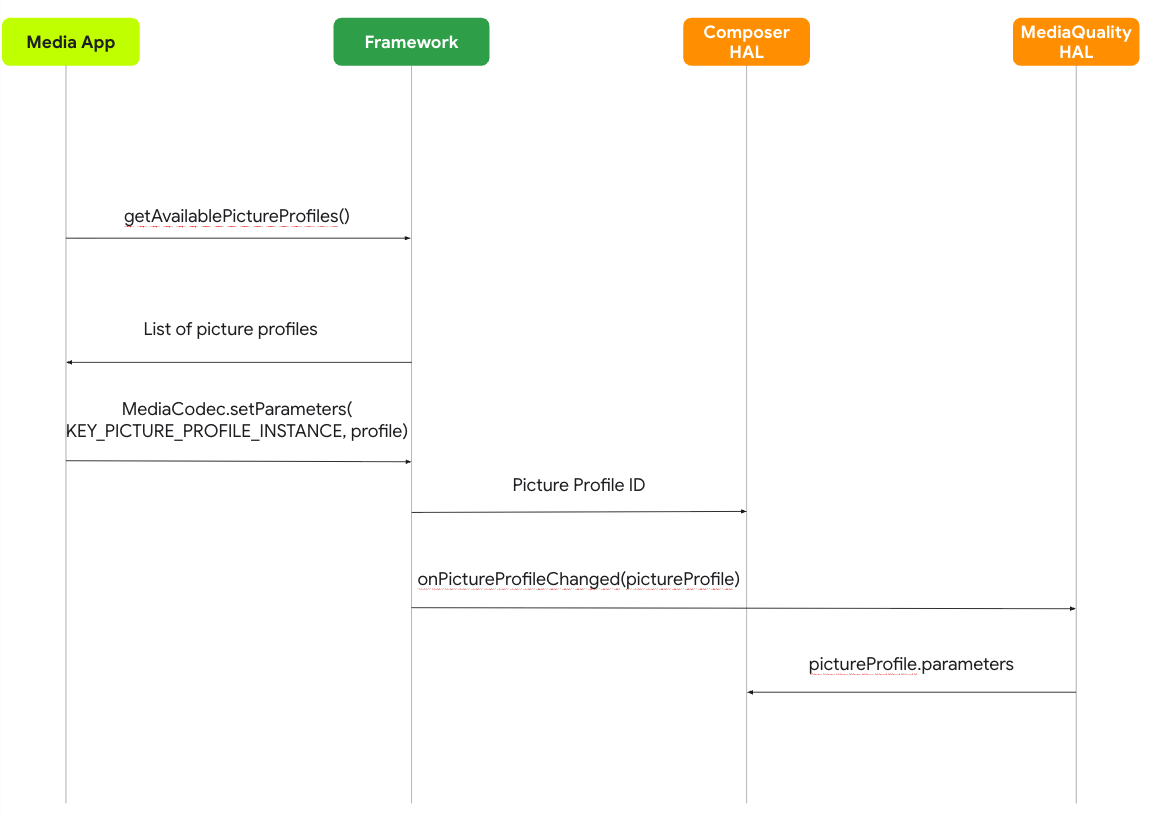
Figure 3. Sequence diagram for setting a per-stream picture profile
- The media app queries the
MediaQualityManagerto get a list of available picture profiles. - The app then uses
MediaCodec.setParametersto select and set the desired profile for the stream. - The framework communicates this choice to the Media Quality (MQ) HAL, passing along the profile ID and its parameters.
- Finally, the MQ HAL sends these parameters to the Composer HAL, which renders the video stream with the specified picture profile.
Set a Global Default Profile
Only system apps can set the global default profile, which serves as a fallback for any content that does not have a specific profile assigned.
- The system app retrieves a list of available picture profiles from the framework.
- The app then selects one of these profiles to be the new global default by calling
setDefaultPictureProfile(id). - The framework sends that profile's parameters to the Media Quality HAL, which then applies the changes.
Media Quality SDK API
The Media Quality SDK API provides the necessary tools for apps to interact with the framework. The main entry point is the android.media.quality package.
android.media.quality
This package contains the primary classes for managing media quality.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
MediaQualityManager |
The central class for interacting with the MQF. |
PictureProfile |
A data class representing a complete set of picture parameters for a specific mode. |
SoundProfile |
A data class for sound parameters. |
MediaQualityContract |
A class containing constants for all pre-defined parameter keys. |
MediaQualityManager
Key methods include:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
createPictureProfile(PictureProfile profile) |
Creates a new picture profile. Requires special permissions or for the app to be on the allowlist. |
updatePictureProfile(PictureProfile profile) |
Updates an existing picture profile. Can only be called by the profile's creator. |
removePictureProfile(String profileId) |
Deletes a profile. Can only be called by the profile's creator. |
getAvailablePictureProfiles() |
Returns a list of all available picture profiles. |
setDefaultPictureProfile(String profileId) |
Sets the global default picture profile. Requires MANAGE_GLOBAL_PICTURE_QUALITY_SERVICE permission. |
registerPictureProfileCallback(PictureProfileCallback cb) |
Registers a callback to listen for profile changes. |
PictureProfile Object
The PictureProfile object encapsulates all the information for a given picture mode.
public final class PictureProfile {
private String id;
private int type; // System or Application
private String name; // e.g., "Movie", "Game"
private String inputId; // e.g., "HDMI1"
private String packageName; // e.g., "com.google.android.youtube"
private PersistableBundle parameters; // Bundle containing all PQ parameters
}
Media Quality HAL
The Media Quality HAL is an AIDL-based interface defined in hardware/interfaces/tv/mediaquality/aidl/. SoC vendors must implement this interface to enable the Media Quality Framework on their devices. The HAL serves as the communication bridge between the MediaQualityService in the Android framework and the underlying hardware, responsible for applying picture and sound adjustments.
The HAL manages picture and sound profiles using AIDL parcelables. This involves receiving profile changes from the framework and notifying the framework of any adjustments made at the hardware level.
Modules
The HAL interface is composed of several key AIDL files:
| HAL File | Description |
|---|---|
IMediaQuality.aidl |
The main interface for the Media Quality service, used for setting listeners and discovering hardware capabilities. |
IPictureProfileChangedListener.aidl |
A listener interface that the framework uses to notify the HAL (specifically, a component like the composer HAL) of changes to a picture profile. |
IPictureProfileAdjustmentListener.aidl |
A listener interface that the HAL uses to notify the framework of adjustments made at the hardware level, for example, when a user changes a setting directly via a hardware remote. |
PictureParameter.aidl |
An AIDL union that defines all the standard picture parameters, such as contrast and sharpness, that can be adjusted. |
PictureProfile.aidl |
The AIDL parcelable that represents a PictureProfile object at the HAL layer, containing a profile ID and its associated parameters. |
ISoundProfileChangedListener.aidl |
A listener interface that the framework uses to notify the HAL of changes to a sound profile. |
ISoundProfileAdjustmentListener.aidl |
A listener interface that the HAL uses to notify the framework of sound adjustments made at the hardware level. |
