The Android platform offers a spell checker framework that lets you implement and access spell checking in your app. The framework is one of the Text Service APIs.
To use the framework in your app, you create an Android service that generates a spell checker session object. Based on text you provide, the session object returns spelling suggestions generated by the spell checker.
Spell checker lifecycle
The following diagram shows the lifecycle of the spell checker service:
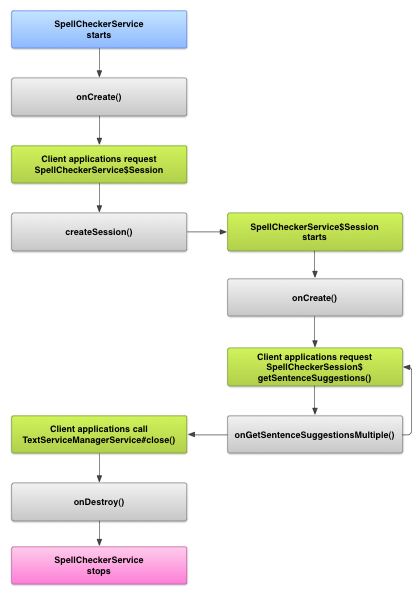
To initiate spell checking, your app starts its implementation of the spell checker service. Clients in your app, such as activities or individual UI elements, request a spell checker session from the service, then use the session to get suggestions for text. As a client terminates its operation, it closes its spell checker session. If necessary, your app can shut down the spell checker service at any time.
Implement a spell checker service
To use the spell checker framework in your app, add a spell checker service component that includes the session object definition. You can also add an optional activity to your app that controls settings. Add an XML metadata file that describes the spell checker service, and add the appropriate elements to your manifest file.
Spell checker classes
Define the service and session object with the following classes:
-
- A subclass of
SpellCheckerService- The
SpellCheckerServiceimplements both theServiceclass and the spell checker framework interface. Within your subclass, implement the following method:createSession()- A factory method that returns a
SpellCheckerService.Sessionobject to a client that wants to check spelling.
- A subclass of
-
- An implementation of
SpellCheckerService.Session- An object that the spell checker service provides to clients to let them pass text to the spell checker and receive suggestions. Within this class, implement the following methods:
onCreate()- Called by the system in response to
createSession(). In this method, you can initialize theSpellCheckerService.Sessionobject based on the current locale and other details. onGetSentenceSuggestionsMultiple()- Performs the actual spell checking. This method returns an array of
SentenceSuggestionsInfocontaining suggestions for the sentences passed to it.
Optionally, you can implement
onCancel(), which handles requests to cancel spell checking;onGetSuggestions(), which handles a word suggestion request; oronGetSuggestionsMultiple(), which handles batches of word suggestion requests. - An implementation of
Spell checker manifest and metadata
In addition to code, provide the appropriate manifest file and a metadata file for the spell checker.
The manifest file defines the app, the service, and the activity for controlling settings, as shown in the following example:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.android.samplespellcheckerservice" > <application android:label="@string/app_name" > <service android:label="@string/app_name" android:name=".SampleSpellCheckerService" android:permission="android.permission.BIND_TEXT_SERVICE" > <intent-filter > <action android:name="android.service.textservice.SpellCheckerService" /> </intent-filter> <meta-data android:name="android.view.textservice.scs" android:resource="@xml/spellchecker" /> </service> <activity android:label="@string/sample_settings" android:name="SpellCheckerSettingsActivity" > <intent-filter > <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
Components that want to use the service must request the permission
BIND_TEXT_SERVICE
to ensure that only the system binds to the service. The service's definition
also specifies the spellchecker.xml metadata file, which is
described in the next section.
The metadata file spellchecker.xml contains the following
XML:
<spell-checker xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:label="@string/spellchecker_name" android:settingsActivity="com.example.SpellCheckerSettingsActivity"> <subtype android:label="@string/subtype_generic" android:subtypeLocale="en” /> <subtype android:label="@string/subtype_generic" android:subtypeLocale="fr” /> </spell-checker>
The metadata specifies the activity that the spell checker uses to control settings. It also defines subtypes for the spell checker. In this case, the subtypes define locales that the spell checker can handle.
Access the spell checker service from a client
apps that use
TextView and
EditText
views automatically benefit from spell checking, because TextView
automatically uses a spell checker:
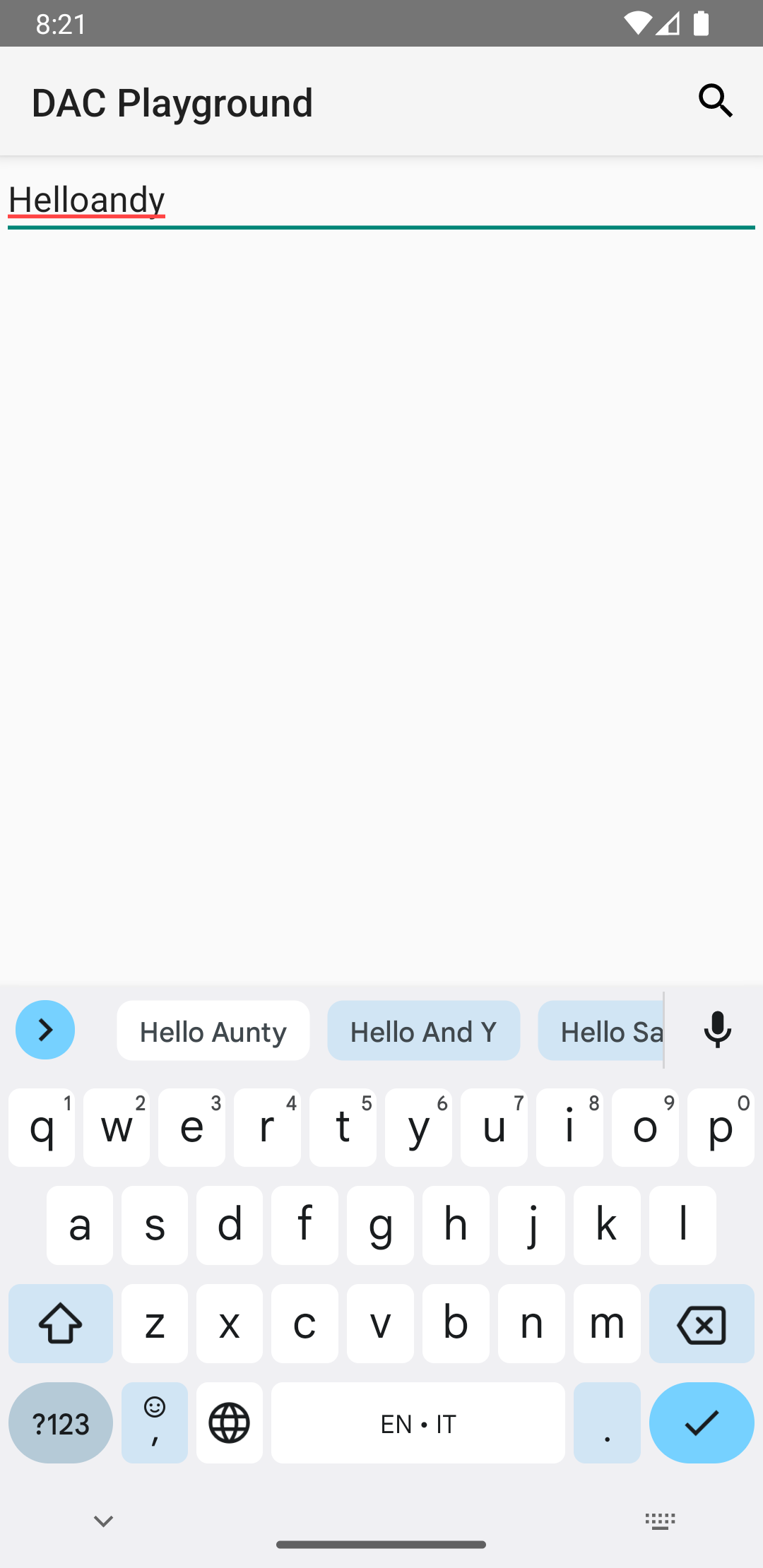
EditText.
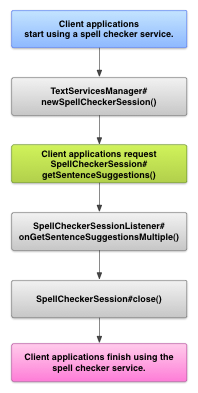
However, you might want to interact directly with a spell checker service in other cases. The following diagram shows the flow of control for interacting with a spell checker service:
The LatinIME input method editor in the Android Open Source Project contains an example of spell checking.
