If you're using a View-based layout, there are three main choices for
implementing toggles. We recommend using the
SwitchMaterial component
from the Material
Components library:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<com.google.android.material.switchmaterial.SwitchMaterial
android:id="@+id/material_switch"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/material_switch"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Legacy apps might still use the older
SwitchCompat AppCompat
component, as shown in the following example:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.SwitchCompat
android:id="@+id/switchcompat"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/switchcompat"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
The following example shows
AppCompatToggleButton,
which is another legacy component that has a noticeably different UI:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/toggle_button_label"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@id/toggle"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle="packed"
app:layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf="@id/toggle"
android:text="@string/toggle_button" />
<androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatToggleButton
android:id="@+id/toggle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/toggle_button_label"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
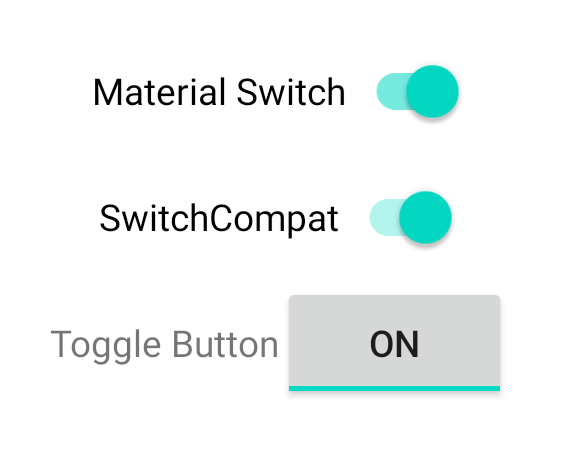
These three components offer the same behavior but look different. The
differences between the SwitchMaterial and SwitchCompat are subtle, but
AppCompatToggleButton is noticeably different:
Handle state changes
SwitchMaterial, SwitchCompat, and AppCompatToggleButton are all subclasses
of CompoundButton, which
gives them a common mechanism for handling checked state changes. You implement
an instance of
CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener
and add it to the button, as shown in the following example:
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) val binding: SwitchLayoutBinding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(layoutInflater) setContentView(binding.root) binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener { _, isChecked -> if (isChecked) { // The switch is checked. } else { // The switch isn't checked. } } } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); SwitchLayoutBinding binding = SwitchLayoutBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater()); setContentView(binding.getRoot()); binding.materialSwitch.setOnCheckedChangeListener((buttonView, isChecked) -> { if (isChecked) { // The switch is checked. } else { // The switch isn't checked. } }); } }
CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener is a single abstract method interface
(or SAM interface), so you can implement it as a lambda. The lambda is called
whenever the checked state changes, and the value of the isChecked boolean
that is passed to the lambda indicates the new checked state.

