Many apps need to be able to precisely control exactly what's drawn on the screen. This might be as small as putting a box or a circle on the screen in just the right place, or it might be an elaborate arrangement of graphic elements in many different styles.
Basic drawing with modifiers and DrawScope
The core way to draw something custom in Compose is with modifiers, such as
Modifier.drawWithContent,
Modifier.drawBehind, and
Modifier.drawWithCache.
For example, to draw something behind your composable, you can use the
drawBehind modifier to start executing drawing commands:
Spacer( modifier = Modifier .fillMaxSize() .drawBehind { // this = DrawScope } )
If all you need is a composable that draws, you can use the
Canvas composable. The Canvas composable is a
convenient wrapper around Modifier.drawBehind. You place the Canvas in
your layout the same way you would with any other Compose UI element. Within the
Canvas, you can draw elements with precise control over their style and
location.
All drawing modifiers expose a DrawScope, a scoped drawing environment
that maintains its own state. This lets you set the parameters for a group of
graphical elements. The DrawScope provides several useful fields, like size,
a Size object specifying the current dimensions of the DrawScope.
To draw something, you can use one of the many draw functions on DrawScope. For
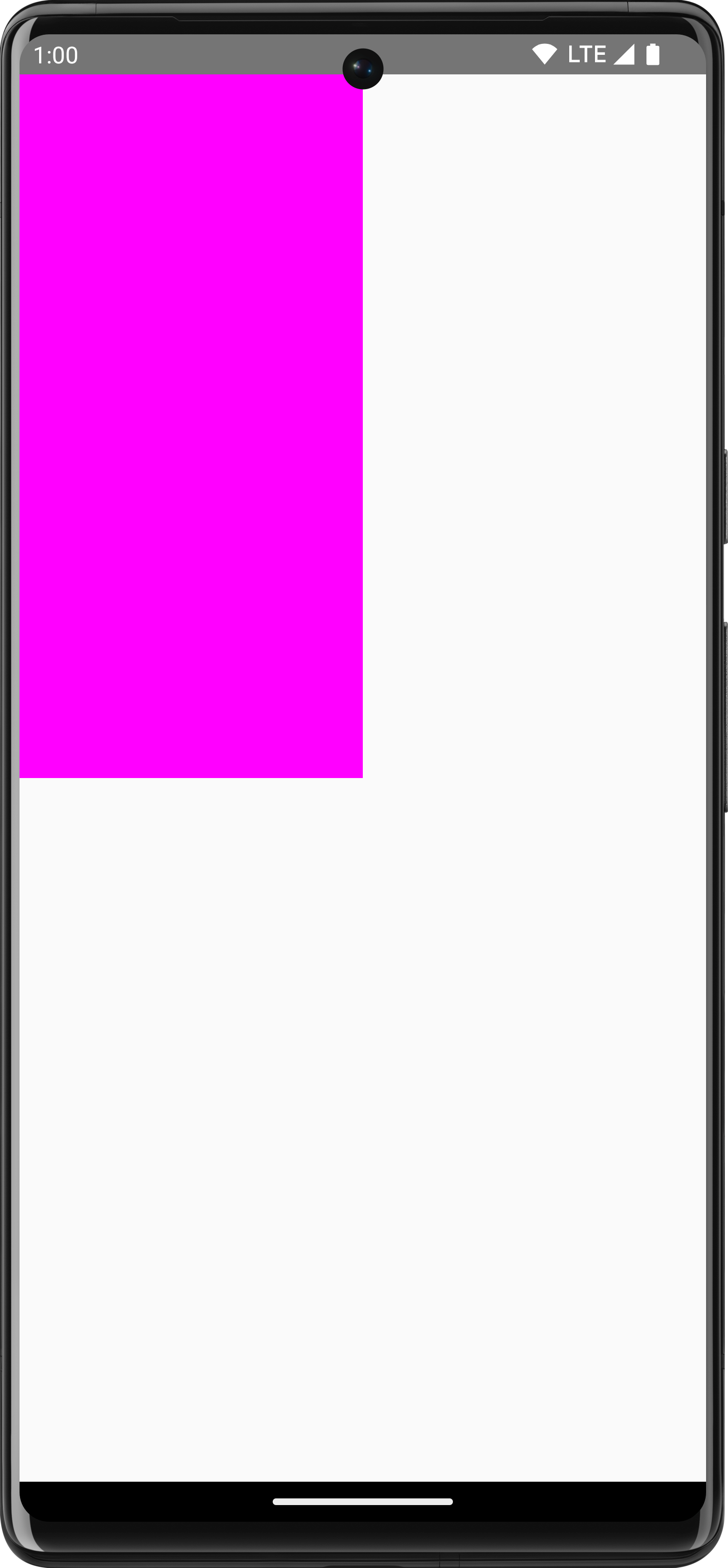
example, the following code draws a rectangle in the top left corner of the
screen:
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { val canvasQuadrantSize = size / 2F drawRect( color = Color.Magenta, size = canvasQuadrantSize ) }
To learn more about different drawing modifiers, see the Graphics Modifiers documentation.
Coordinate system
To draw something on screen, you need to know the offset (x and y) and size of
your item. With many of the draw methods on DrawScope, the position and size
are provided by default parameter values. The default parameters generally
position the item at the [0, 0] point on the canvas, and provide a default
size that fills the entire drawing area, as in the example above - you can see
the rectangle is positioned in the top left. To adjust the size and position of
your item, you need to understand the coordinate system in Compose.
The origin of the coordinate system ([0,0]) is at the top leftmost pixel in the
drawing area. x increases as it moves right and y increases as it moves
downwards.
![A grid showing the coordinate system showing the top left [0, 0] and bottom right [width, height]](/static/develop/ui/compose/images/graphics/introduction/compose_coordinate_system_drawing.png)
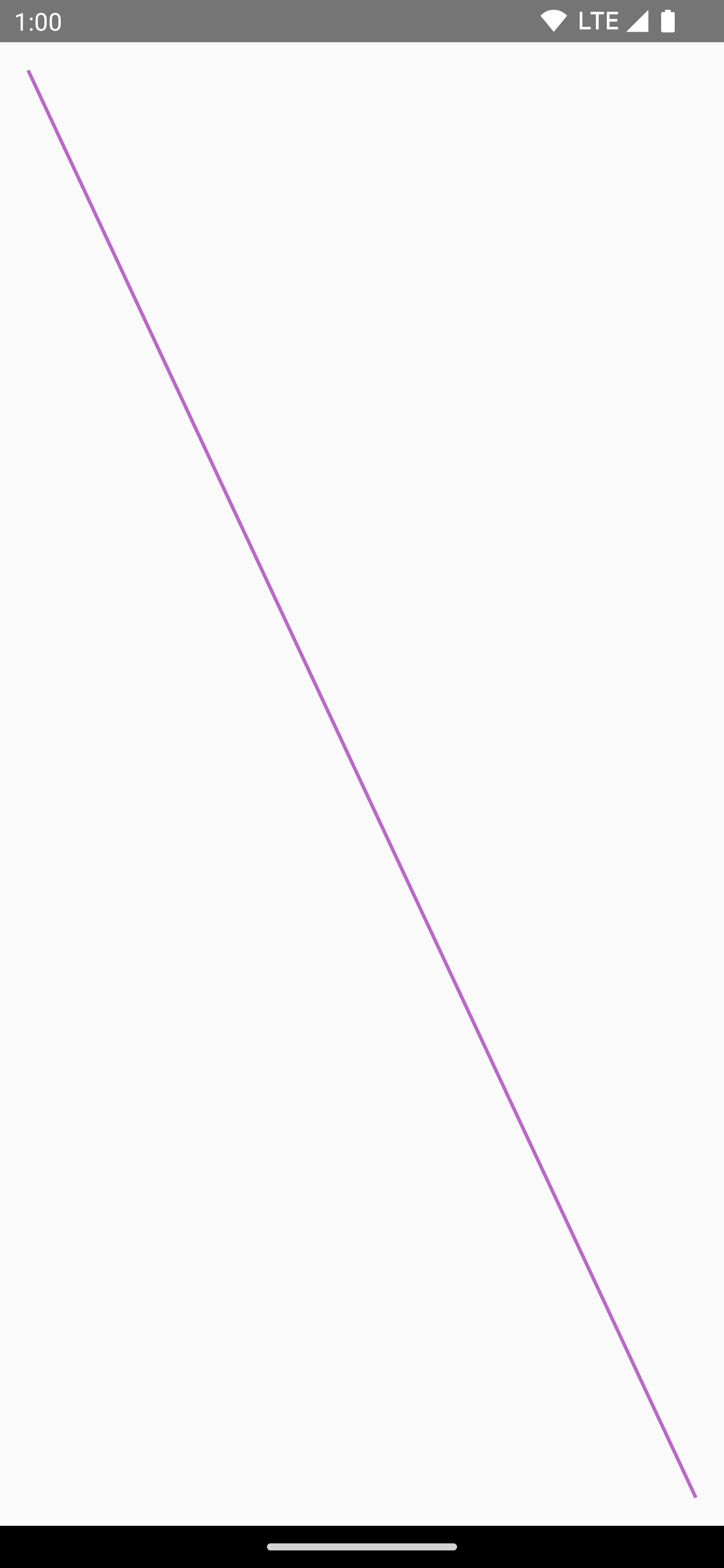
For example, if you want to draw a diagonal line from the top-right corner of
the canvas area to the bottom-left corner, you can use the
DrawScope.drawLine() function, and specify a start and end offset with
the corresponding x and y positions:
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { val canvasWidth = size.width val canvasHeight = size.height drawLine( start = Offset(x = canvasWidth, y = 0f), end = Offset(x = 0f, y = canvasHeight), color = Color.Blue ) }
Basic transformations
DrawScope offers transformations to change where or how the drawing commands
are executed.
Scale
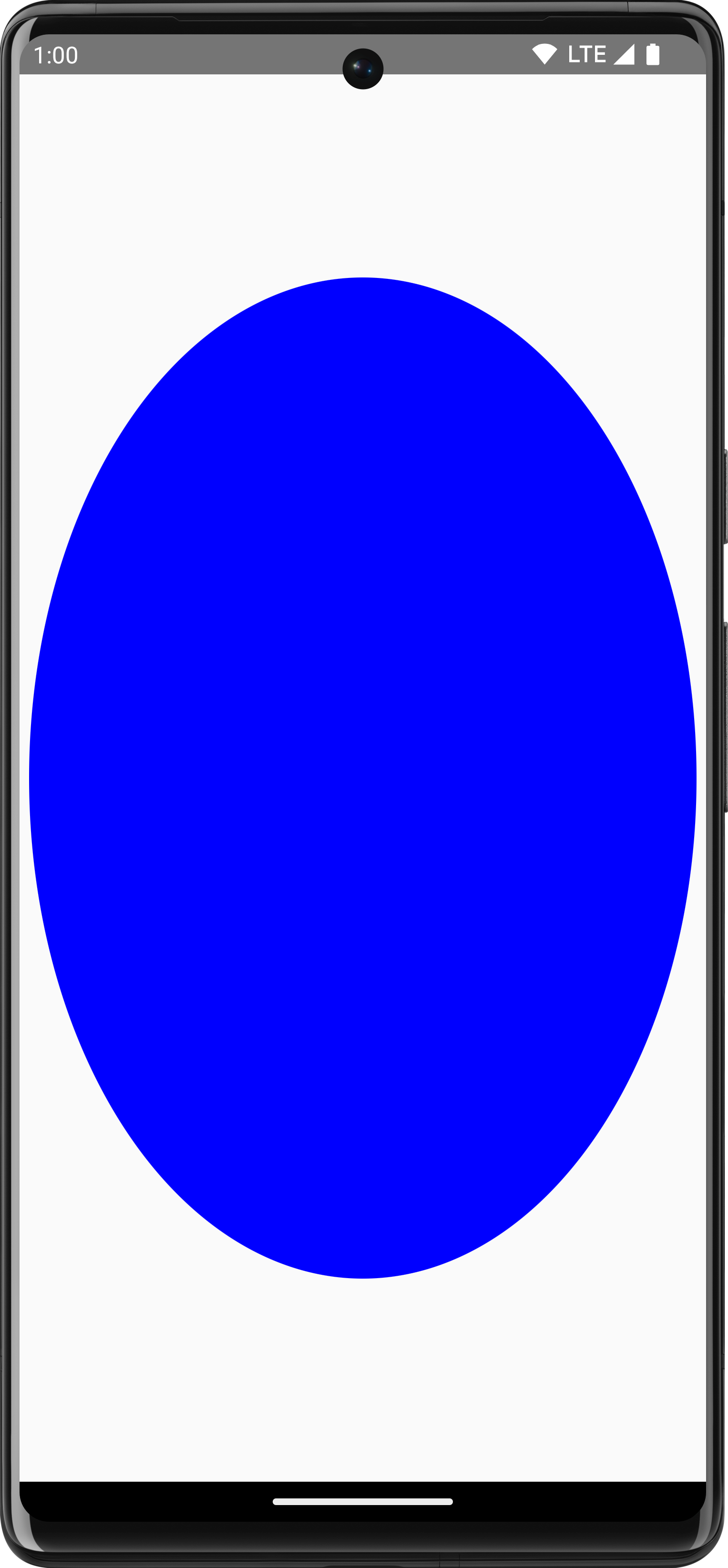
Use
DrawScope.scale()
to increase the size of your drawing operations by a factor. Operations like
scale() apply to all drawing operations within the corresponding lambda. For
example, the following code increases the scaleX 10 times and scaleY 15
times:
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { scale(scaleX = 10f, scaleY = 15f) { drawCircle(Color.Blue, radius = 20.dp.toPx()) } }
Translate
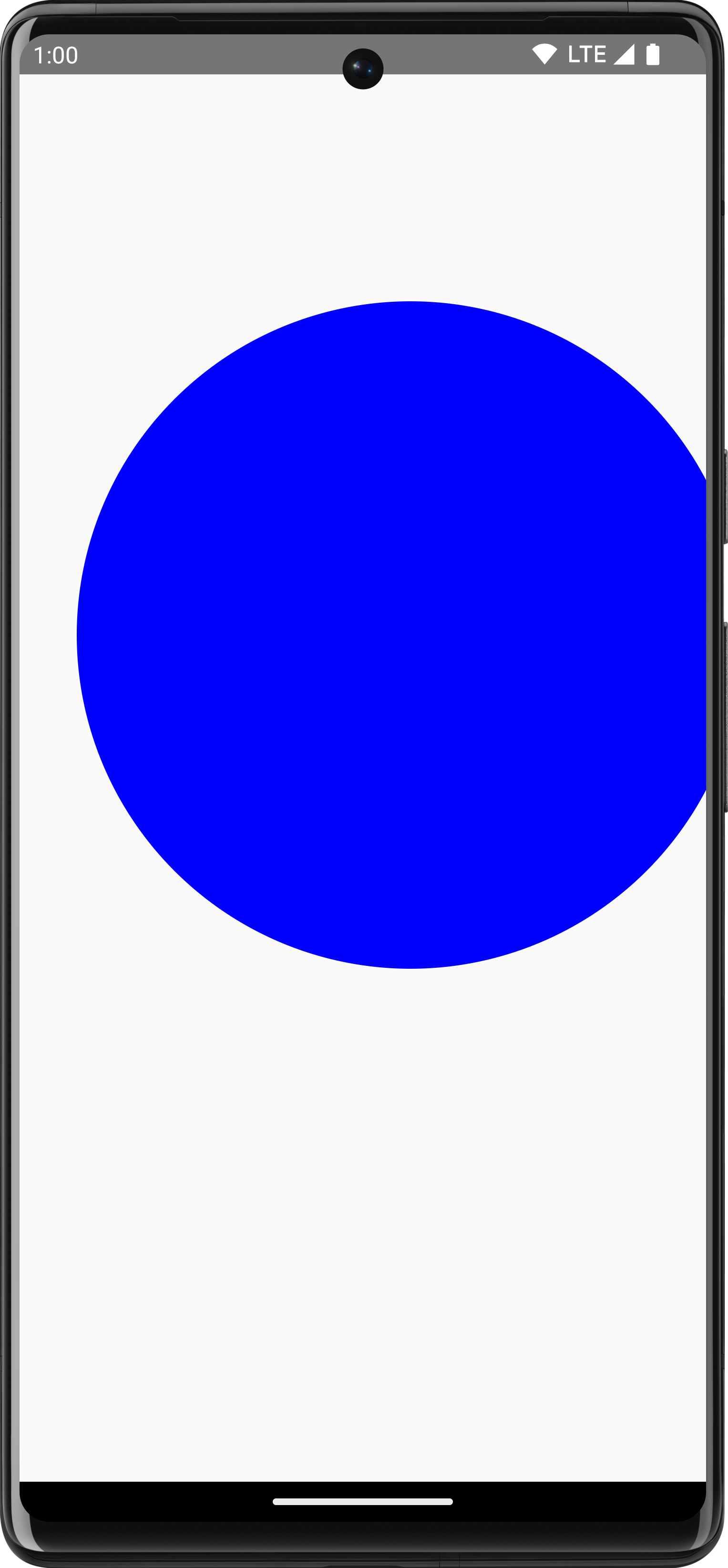
Use
DrawScope.translate()
to move your drawing operations up, down, left, or right. For example, the
following code moves the drawing 100 px to the right and 300 px up:
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { translate(left = 100f, top = -300f) { drawCircle(Color.Blue, radius = 200.dp.toPx()) } }
Rotate
Use
DrawScope.rotate()
to rotate your drawing operations around a pivot point. For example, the
following code rotates a rectangle 45 degrees:
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { rotate(degrees = 45F) { drawRect( color = Color.Gray, topLeft = Offset(x = size.width / 3F, y = size.height / 3F), size = size / 3F ) } }
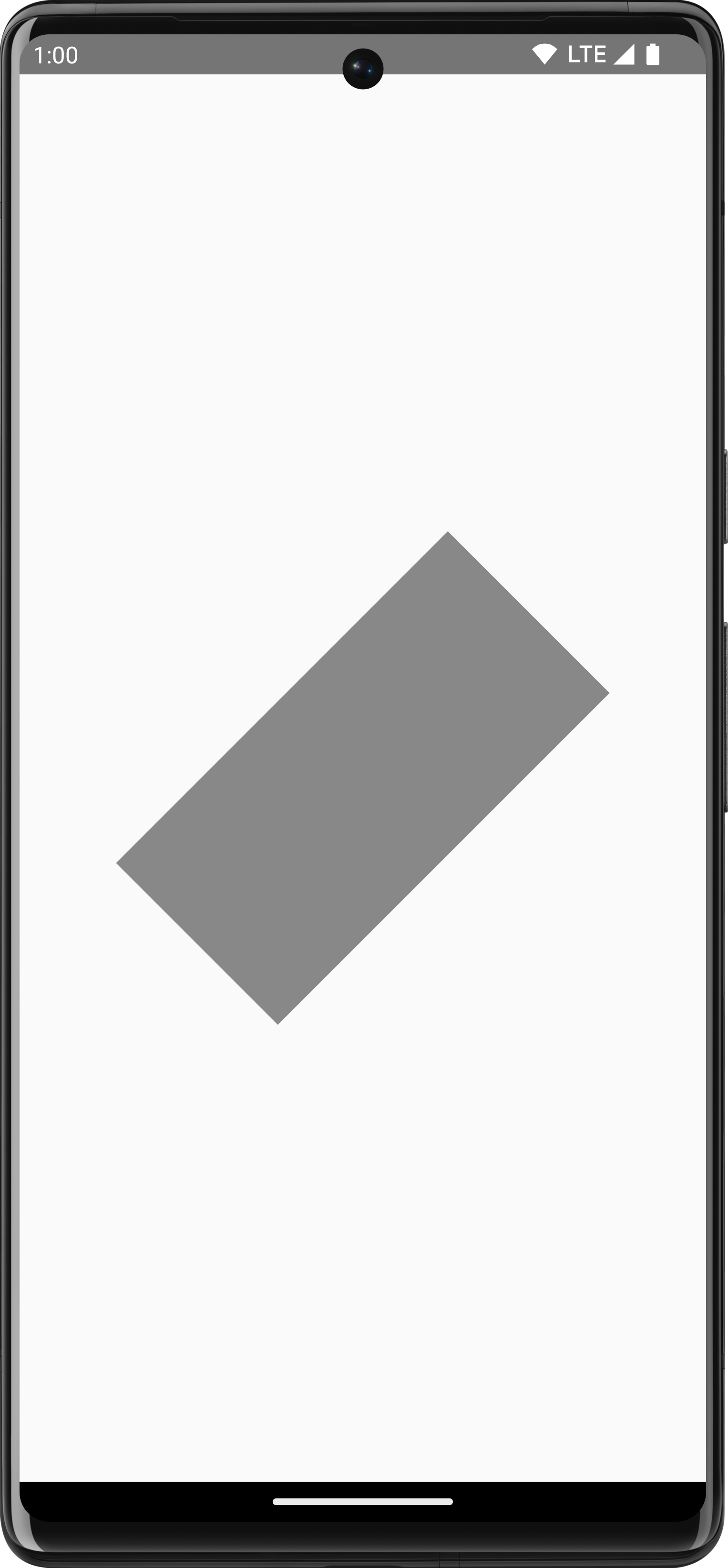
rotate() to apply a rotation to the current drawing scope, which rotates the rectangle by 45 degrees.
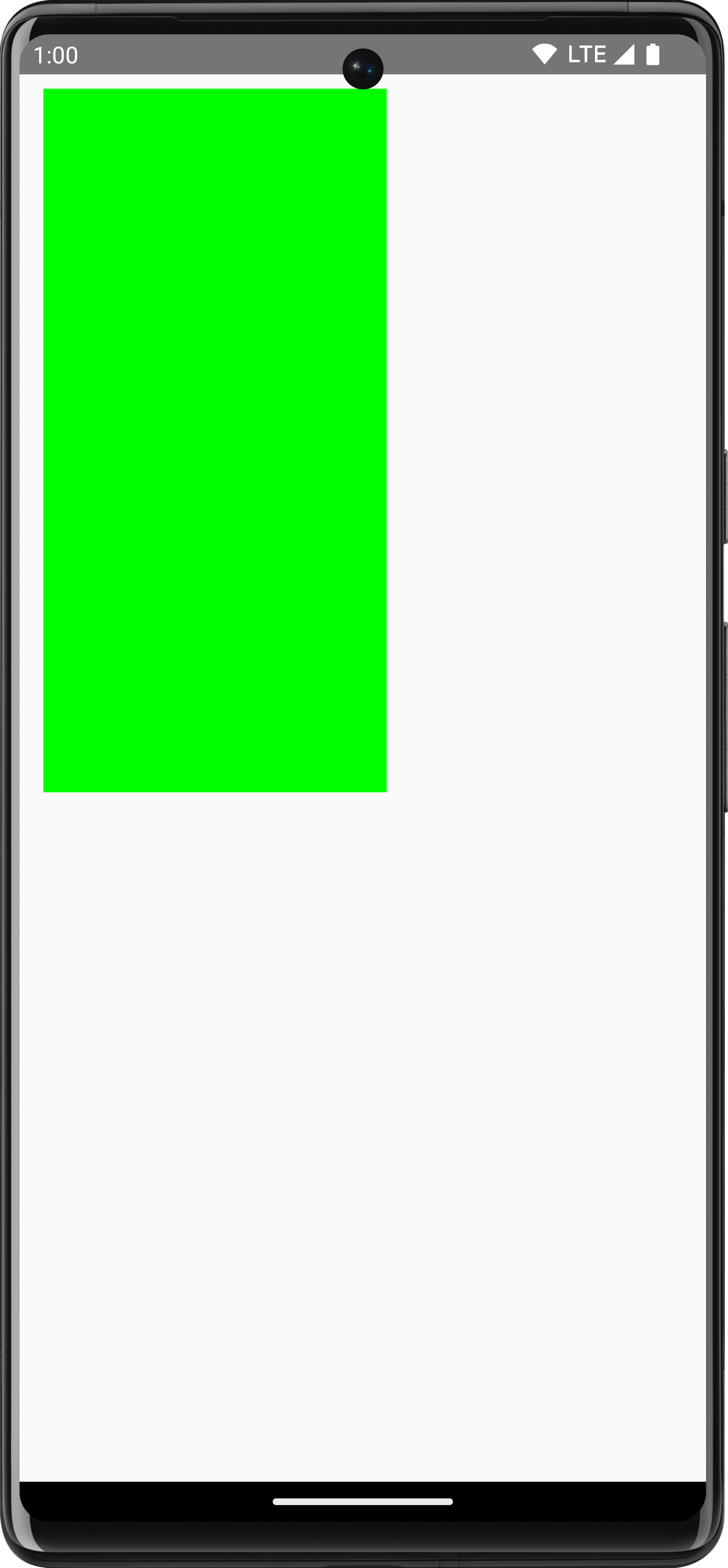
Inset
Use DrawScope.inset() to adjust the default parameters of the current
DrawScope, changing the drawing boundaries and translating the drawings
accordingly:
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { val canvasQuadrantSize = size / 2F inset(horizontal = 50f, vertical = 30f) { drawRect(color = Color.Green, size = canvasQuadrantSize) } }
This code effectively adds padding to the drawing commands:
Multiple transformations
To apply multiple transformations to your drawings, use the
DrawScope.withTransform() function, which creates and
applies a single transformation that combines all your desired changes. Using
withTransform() is more efficient than making nested calls to individual
transformations, because all the transformations are performed together in a
single operation, instead of Compose needing to calculate and save each of the
nested transformations.
For example, the following code applies both a translation and a rotation to the rectangle:
Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { withTransform({ translate(left = size.width / 5F) rotate(degrees = 45F) }) { drawRect( color = Color.Gray, topLeft = Offset(x = size.width / 3F, y = size.height / 3F), size = size / 3F ) } }
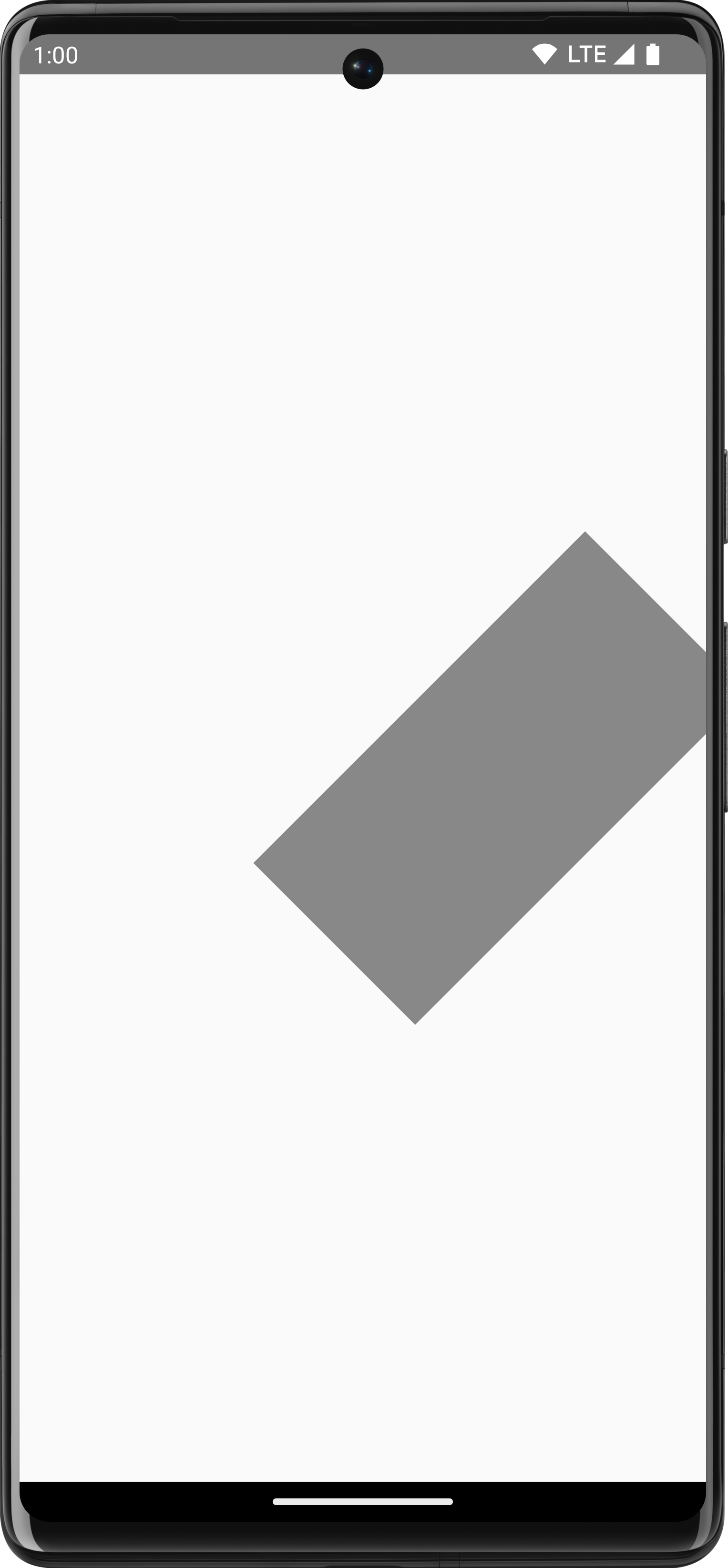
withTransform to apply both a rotation and a translation, rotating the rectangle and shifting it to the left.Common drawing operations
Draw text
To draw text in Compose, you can typically use the Text composable. However,
if you are in a DrawScope or you want to draw your text manually with
customization, you can use the
DrawScope.drawText()
method.
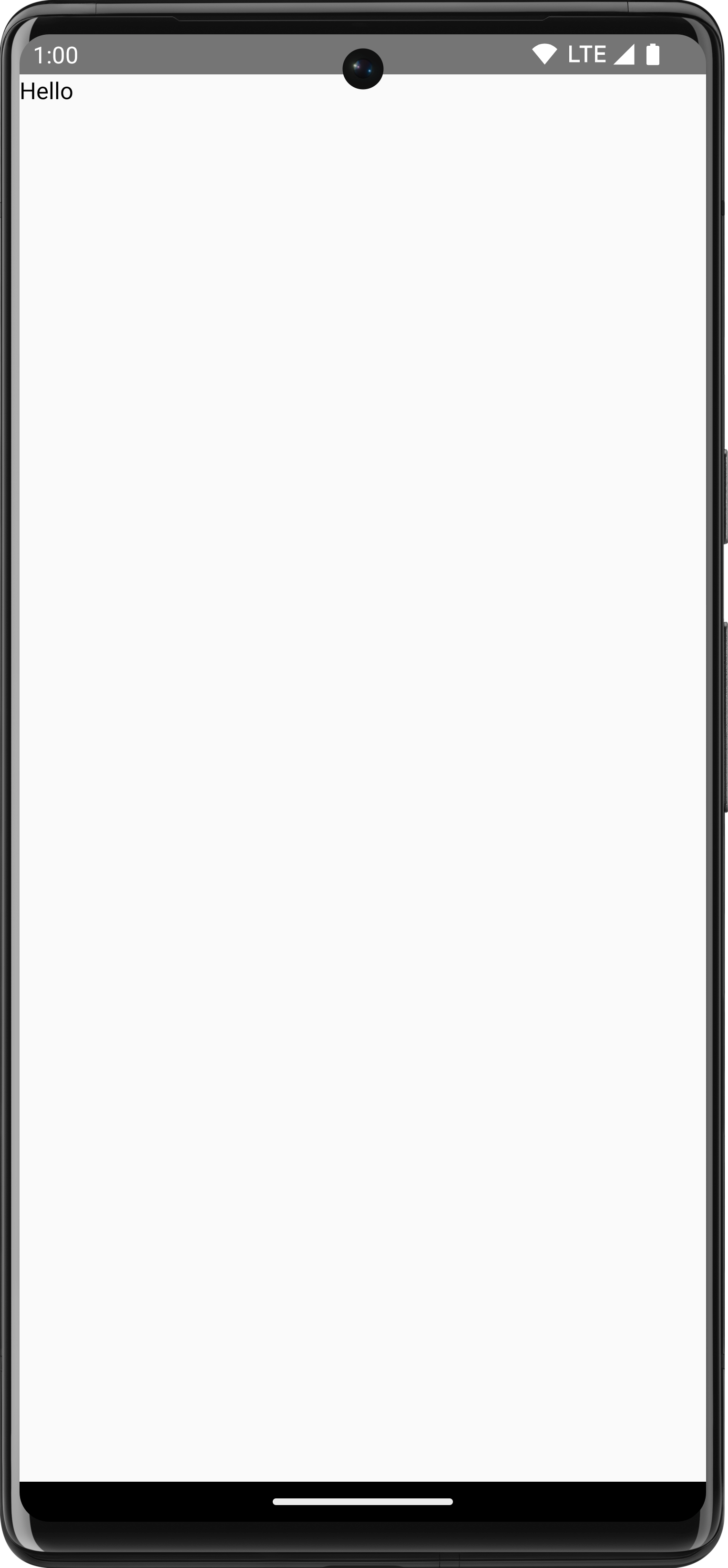
To draw text, create a TextMeasurer using rememberTextMeasurer
and call drawText with the measurer:
val textMeasurer = rememberTextMeasurer() Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { drawText(textMeasurer, "Hello") }
Measure text
Drawing text works a bit differently from other drawing commands. Normally, you give the drawing command the size (width and height) to draw the shape/image as. With text, there are a few parameters that control the size of the rendered text, such as font size, font, ligatures, and letter spacing.
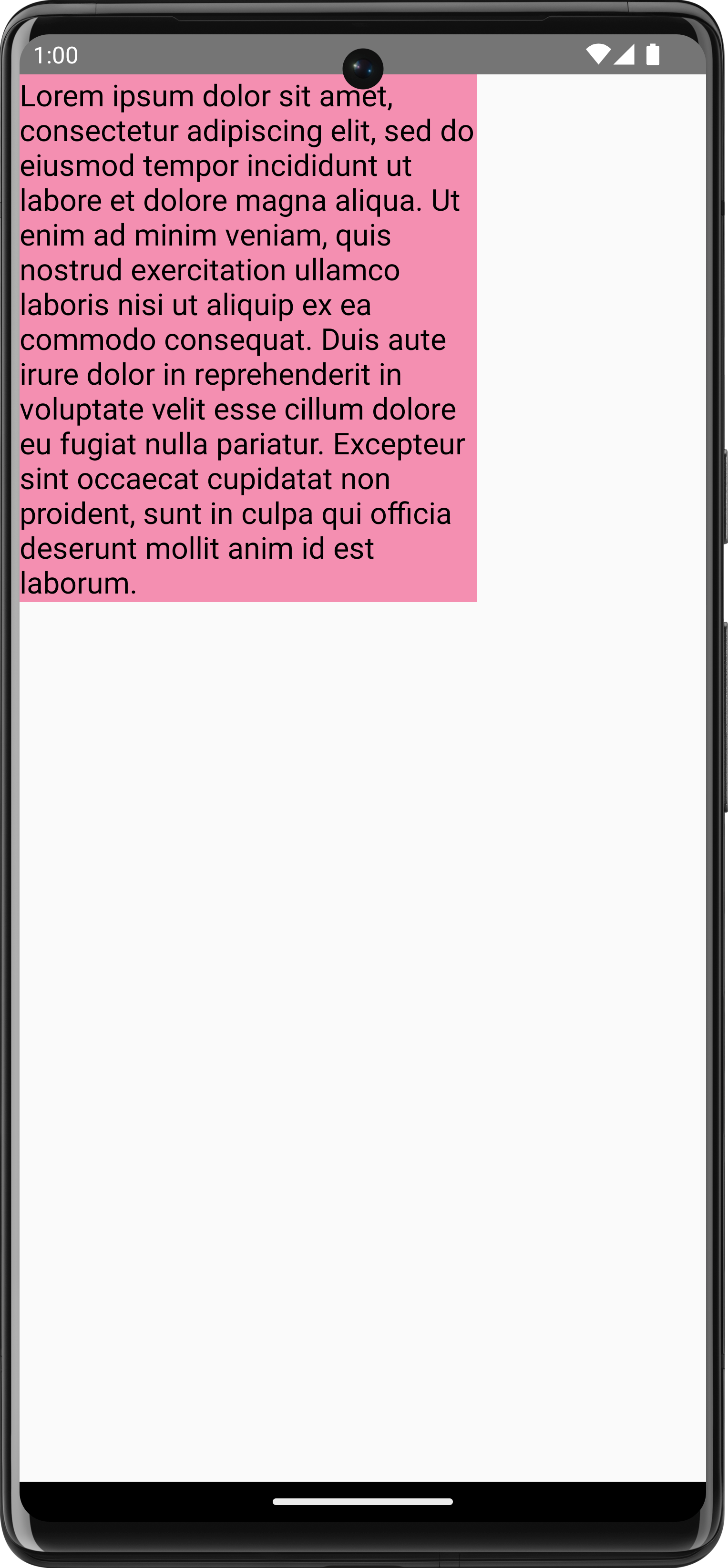
With Compose, you can use a TextMeasurer to get access to the measured
size of text, depending on the above factors. If you want to draw a background
behind the text, you can use the measured information to get the size of the
area that the text takes up:
val textMeasurer = rememberTextMeasurer() Spacer( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val measuredText = textMeasurer.measure( AnnotatedString(longTextSample), constraints = Constraints.fixedWidth((size.width * 2f / 3f).toInt()), style = TextStyle(fontSize = 18.sp) ) onDrawBehind { drawRect(pinkColor, size = measuredText.size.toSize()) drawText(measuredText) } } .fillMaxSize() )
This code snippet produces a pink background on the text:
Adjusting the constraints, font size, or any property that affects measured size
results in a new size reported. You can set a fixed size for both the width
and height, and the text then follows the set TextOverflow. For
example, the following code renders text in ⅓ of the height and ⅓ of the width
of the composable area, and sets the TextOverflow to TextOverflow.Ellipsis:
val textMeasurer = rememberTextMeasurer() Spacer( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val measuredText = textMeasurer.measure( AnnotatedString(longTextSample), constraints = Constraints.fixed( width = (size.width / 3f).toInt(), height = (size.height / 3f).toInt() ), overflow = TextOverflow.Ellipsis, style = TextStyle(fontSize = 18.sp) ) onDrawBehind { drawRect(pinkColor, size = measuredText.size.toSize()) drawText(measuredText) } } .fillMaxSize() )
The text is now drawn in the constraints with an ellipsis at the end:
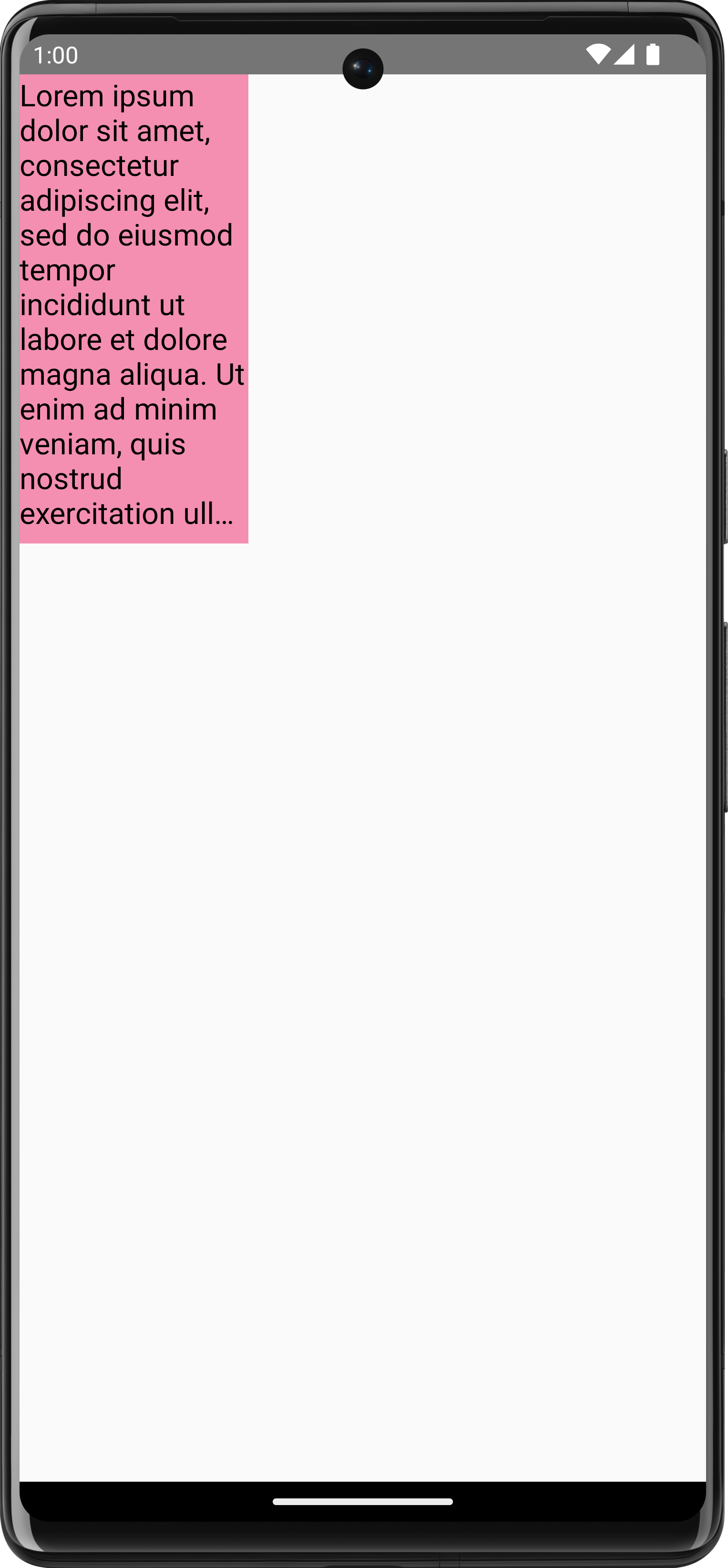
TextOverflow.Ellipsis with fixed constraints on measuring text.Draw image
To draw an ImageBitmap with DrawScope, load up the image using
ImageBitmap.imageResource() and then call drawImage:
val dogImage = ImageBitmap.imageResource(id = R.drawable.dog) Canvas(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(), onDraw = { drawImage(dogImage) })
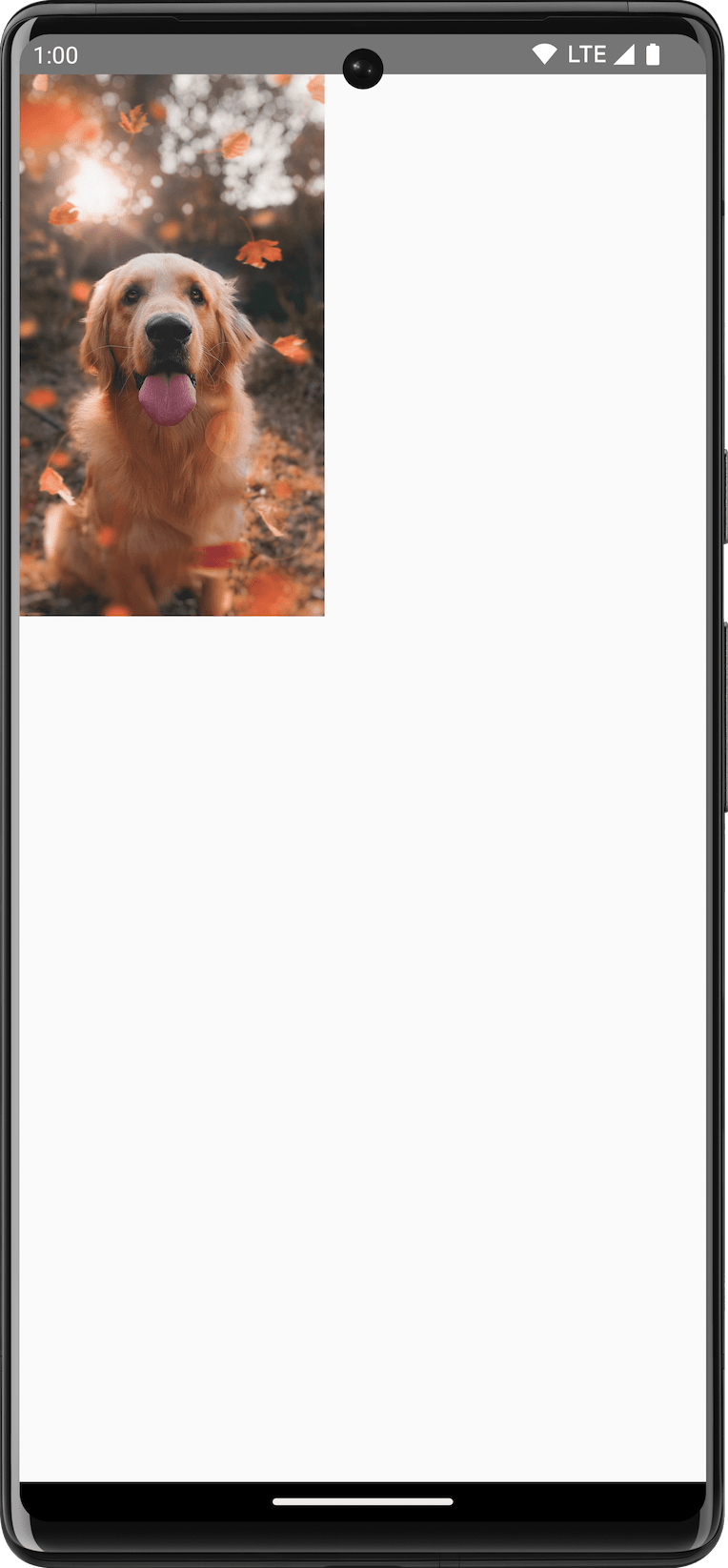
ImageBitmap on Canvas.Draw basic shapes
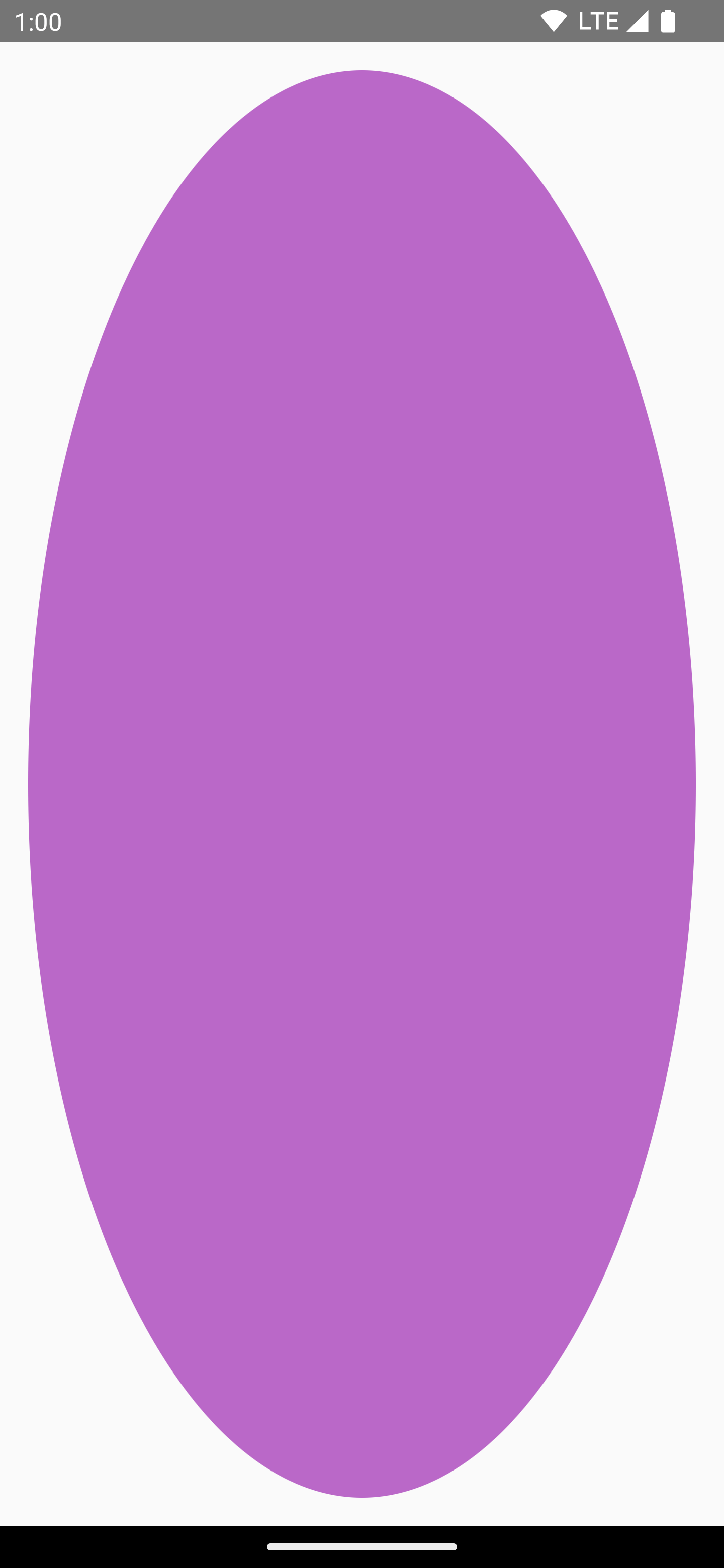
There are many shape drawing functions on DrawScope. To draw a shape, use one
of the predefined draw functions, such as drawCircle:
val purpleColor = Color(0xFFBA68C8) Canvas( modifier = Modifier .fillMaxSize() .padding(16.dp), onDraw = { drawCircle(purpleColor) } )
API |
Output |

|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
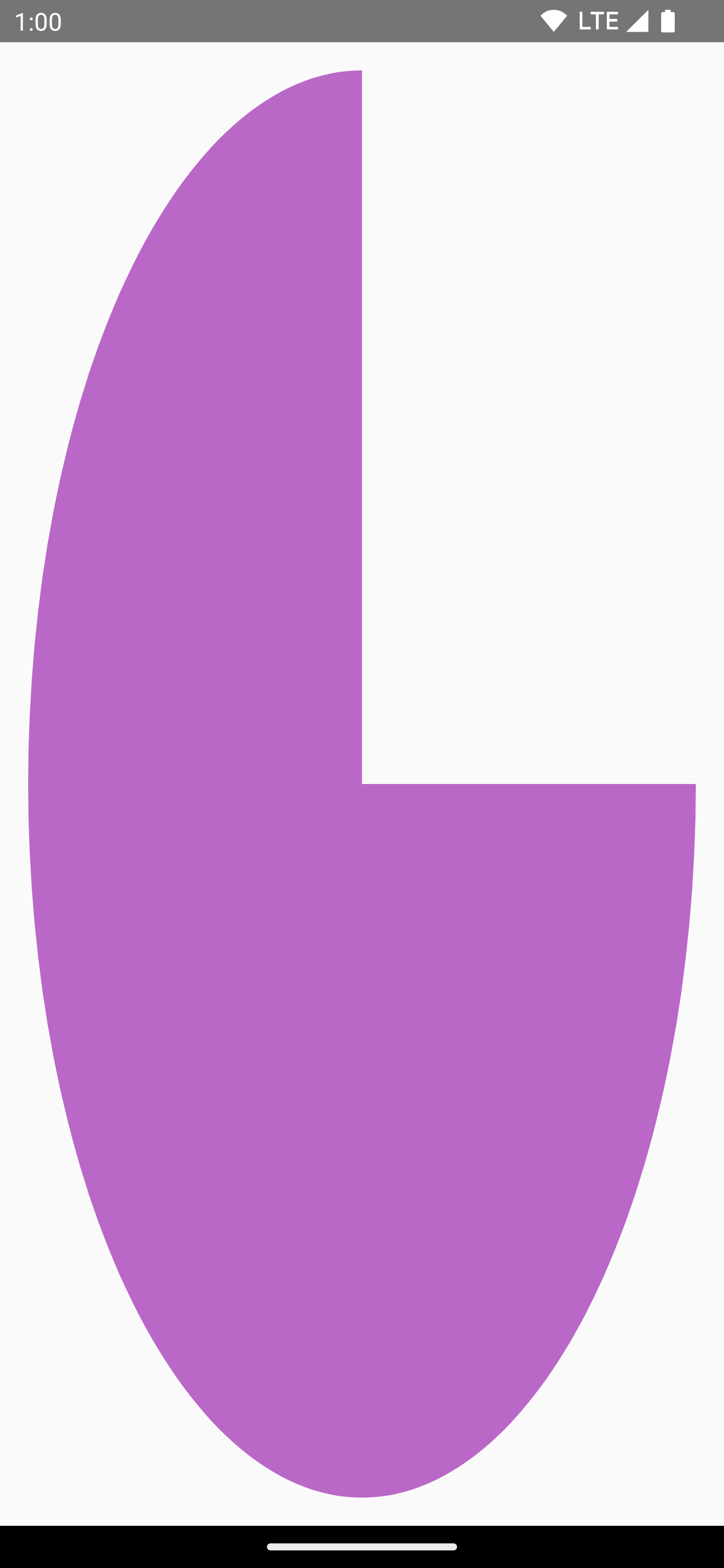
|
|
|
Draw path
A path is a series of mathematical instructions that result in a drawing once
executed. DrawScope can draw a path using the DrawScope.drawPath() method.
For example, say you wanted to draw a triangle. You can generate a path with
functions such as lineTo() and moveTo() using the size of the drawing area.
Then, call drawPath() with this newly created path to get a triangle.
Spacer( modifier = Modifier .drawWithCache { val path = Path() path.moveTo(0f, 0f) path.lineTo(size.width / 2f, size.height / 2f) path.lineTo(size.width, 0f) path.close() onDrawBehind { drawPath(path, Color.Magenta, style = Stroke(width = 10f)) } } .fillMaxSize() )
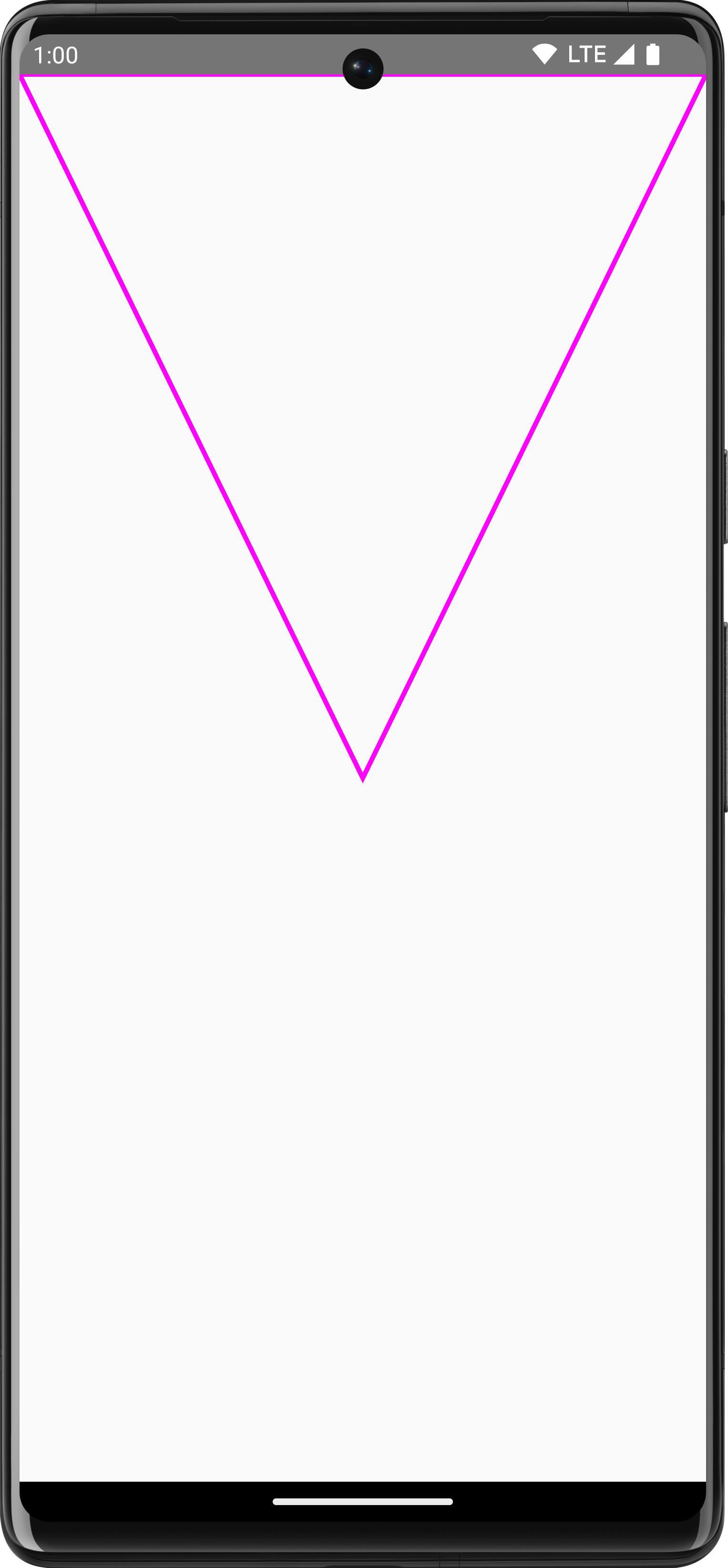
Path in Compose.Accessing Canvas object
With DrawScope, you don't have direct access to a Canvas object. You can use
DrawScope.drawIntoCanvas() to get
access to the Canvas object itself that you can call functions on.
For example, if you have a custom Drawable that you'd like to draw onto the
canvas, you can access the canvas and call Drawable#draw(), passing in the
Canvas object:
val drawable = ShapeDrawable(OvalShape()) Spacer( modifier = Modifier .drawWithContent { drawIntoCanvas { canvas -> drawable.setBounds(0, 0, size.width.toInt(), size.height.toInt()) drawable.draw(canvas.nativeCanvas) } } .fillMaxSize() )
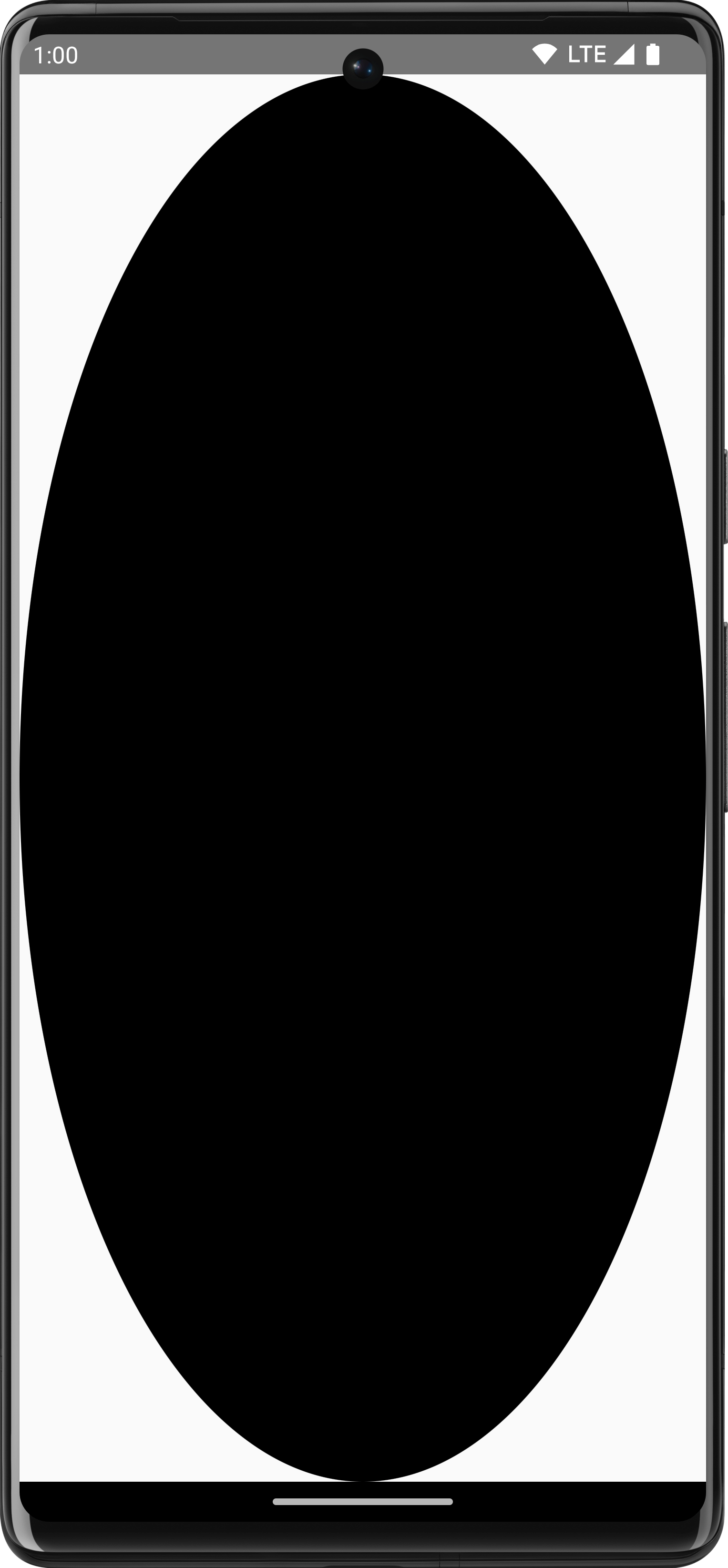
Drawable.Learn more
For more information on Drawing in Compose, take a look at the following resources:
- Graphics Modifiers - Learn about the different types of drawing modifiers.
- Brush - Learn how to customize the painting of your content.
- Custom Layouts and Graphics in Compose - Android Dev Summit 2022 - Learn how to build a custom UI in Compose with Layouts and Graphics.
- JetLagged Sample - Compose Sample that shows how to draw a custom graph.
Recommended for you
- Note: link text is displayed when JavaScript is off
- Graphics Modifiers
- Graphics in Compose
- Alignment lines in Jetpack Compose
