Scroll modifiers
The
verticalScroll
and
horizontalScroll
modifiers provide the simplest way to allow the user to scroll an element when
the bounds of its contents are larger than its maximum size constraints. With
the verticalScroll and horizontalScroll modifiers you don't need to
translate or offset the contents.
@Composable private fun ScrollBoxes() { Column( modifier = Modifier .background(Color.LightGray) .size(100.dp) .verticalScroll(rememberScrollState()) ) { repeat(10) { Text("Item $it", modifier = Modifier.padding(2.dp)) } } }

The ScrollState
allows you to change the scroll position or get its current state. To create it
with default parameters, use
rememberScrollState().
@Composable private fun ScrollBoxesSmooth() { // Smoothly scroll 100px on first composition val state = rememberScrollState() LaunchedEffect(Unit) { state.animateScrollTo(100) } Column( modifier = Modifier .background(Color.LightGray) .size(100.dp) .padding(horizontal = 8.dp) .verticalScroll(state) ) { repeat(10) { Text("Item $it", modifier = Modifier.padding(2.dp)) } } }
Scrollable modifier
The
scrollable
modifier differs from the scroll modifiers in that scrollable detects the
scroll gestures and captures the deltas, but does not offset its contents
automatically. This is instead delegated to the user through
ScrollableState
, which is required for this modifier to work correctly.
When constructing ScrollableState you must provide a consumeScrollDelta
function which will be invoked on each scroll step (by gesture input, smooth
scrolling or flinging) with the delta in pixels. This function must return the
amount of scrolling distance consumed, to ensure the event is properly
propagated in cases where there are nested elements that have the scrollable
modifier.
The following snippet detects the gestures and displays a numerical value for an offset, but does not offset any elements:
@Composable private fun ScrollableSample() { // actual composable state var offset by remember { mutableStateOf(0f) } Box( Modifier .size(150.dp) .scrollable( orientation = Orientation.Vertical, // Scrollable state: describes how to consume // scrolling delta and update offset state = rememberScrollableState { delta -> offset += delta delta } ) .background(Color.LightGray), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center ) { Text(offset.toString()) } }

Nested scrolling
Nested scrolling is a system where multiple scrolling components contained within each other work together by reacting to a single scroll gesture and communicating their scrolling deltas (changes).
The nested scrolling system allows coordination between components that are scrollable and hierarchically linked (most often by sharing the same parent). This system links scrolling containers and allows interaction with the scrolling deltas that are being propagated and shared between.
Compose provides multiple ways of handling nested scrolling between composables. A typical example of nested scrolling is a list inside another list, and a more complex case is a collapsing toolbar.
Automatic nested scrolling
Simple nested scrolling requires no action on your part. Gestures that initiate a scrolling action are propagated from children to parents automatically, such that when the child can't scroll any further, the gesture is handled by its parent element.
Automatic nested scrolling is supported and provided out of the box by some of
Compose's components and modifiers:
verticalScroll,
horizontalScroll,
scrollable,
Lazy APIs and TextField. This means that when the user scrolls an inner
child of nested components, the previous modifiers propagate the scrolling
deltas to the parents that have nested scrolling support.
The following example shows elements with a
verticalScroll
modifier applied to them inside a container that also has a verticalScroll
modifier applied to it.
@Composable private fun AutomaticNestedScroll() { val gradient = Brush.verticalGradient(0f to Color.Gray, 1000f to Color.White) Box( modifier = Modifier .background(Color.LightGray) .verticalScroll(rememberScrollState()) .padding(32.dp) ) { Column { repeat(6) { Box( modifier = Modifier .height(128.dp) .verticalScroll(rememberScrollState()) ) { Text( "Scroll here", modifier = Modifier .border(12.dp, Color.DarkGray) .background(brush = gradient) .padding(24.dp) .height(150.dp) ) } } } } }
Using the nestedScroll modifier
If you need to create an advanced coordinated scroll between multiple elements,
the
nestedScroll
modifier gives you more flexibility by defining a nested scrolling hierarchy. As
mentioned in the previous section, some components have built-in nested scroll
support. However, for composables that aren't scrollable automatically, such as
Box or Column, scroll deltas on such components won't propagate in the
nested scroll system and the deltas won't reach the NestedScrollConnection nor
the parent component. To resolve this, you can use nestedScroll to confer such
support to other components, including custom components.
Nested scrolling cycle
Nested scroll cycle is the flow of scroll deltas that are dispatched up and down
the hierarchy tree through all components (or nodes) that are part of the nested
scrolling system, for example by using scrollable components and modifiers, or
nestedScroll.
Phases of nested scrolling cycle
When a trigger event (for example, a gesture) is detected by a scrollable component, before the actual scrolling action is even triggered, the generated deltas are sent to the nested scroll system and go through three phases: pre-scroll, node consumption, and post-scroll.
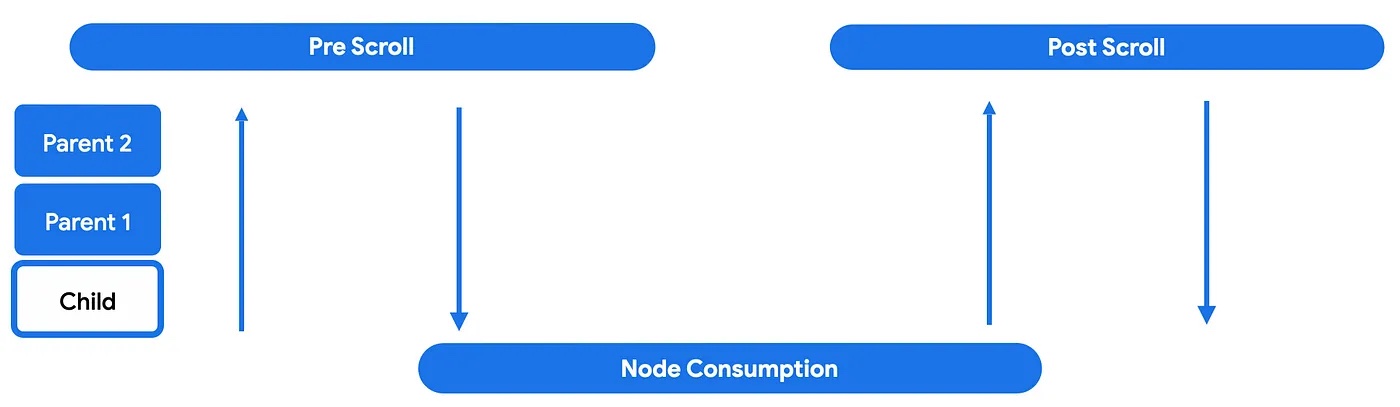
In the first, pre-scroll phase, the component that received the trigger event deltas will dispatch those events up, through the hierarchy tree, to the topmost parent. The delta events will then bubble down, meaning that deltas will be propagated from the root-most parent down towards the child that started the nested scroll cycle.
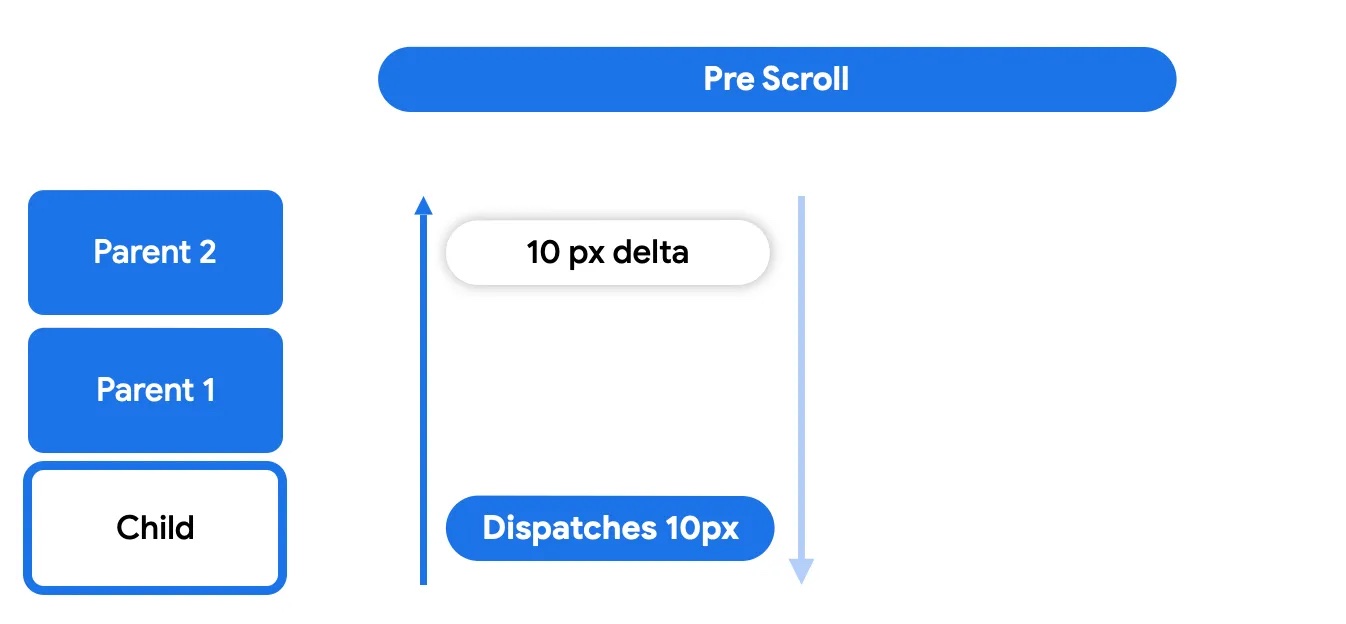
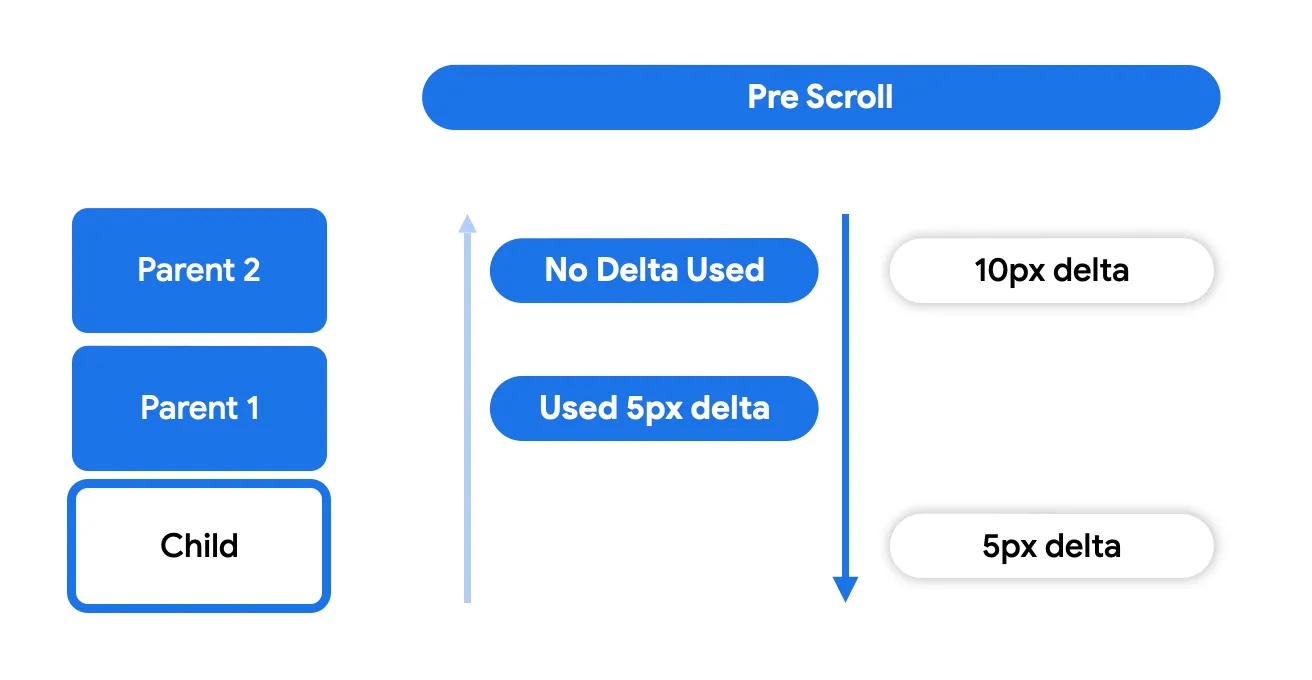
This gives the nested scroll parents (composables using nestedScroll or
scrollable modifiers) the opportunity to do something with the delta before the
node itself can consume it.
In the node consumption phase, the node itself will use whatever delta was not used by its parents. This is when the scrolling movement is actually done and is visible.
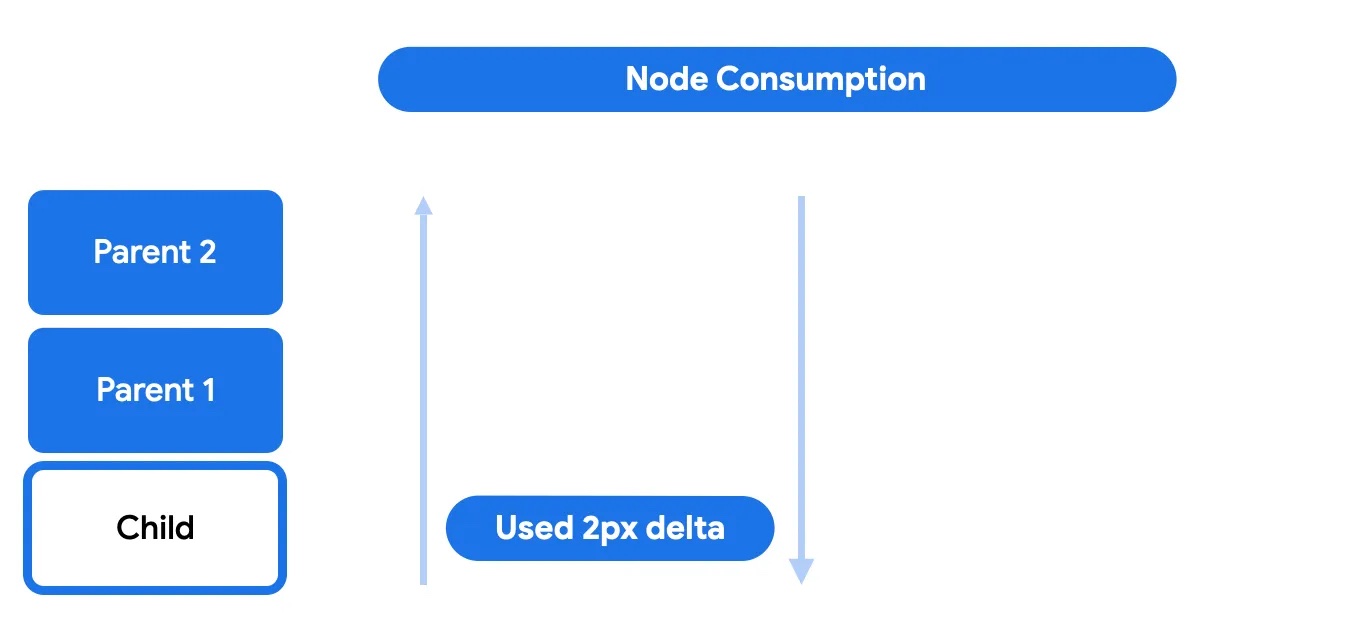
During this phase, the child may choose to consume all or part of the remaining scroll. Anything left will be sent back up to go through the post-scroll phase.
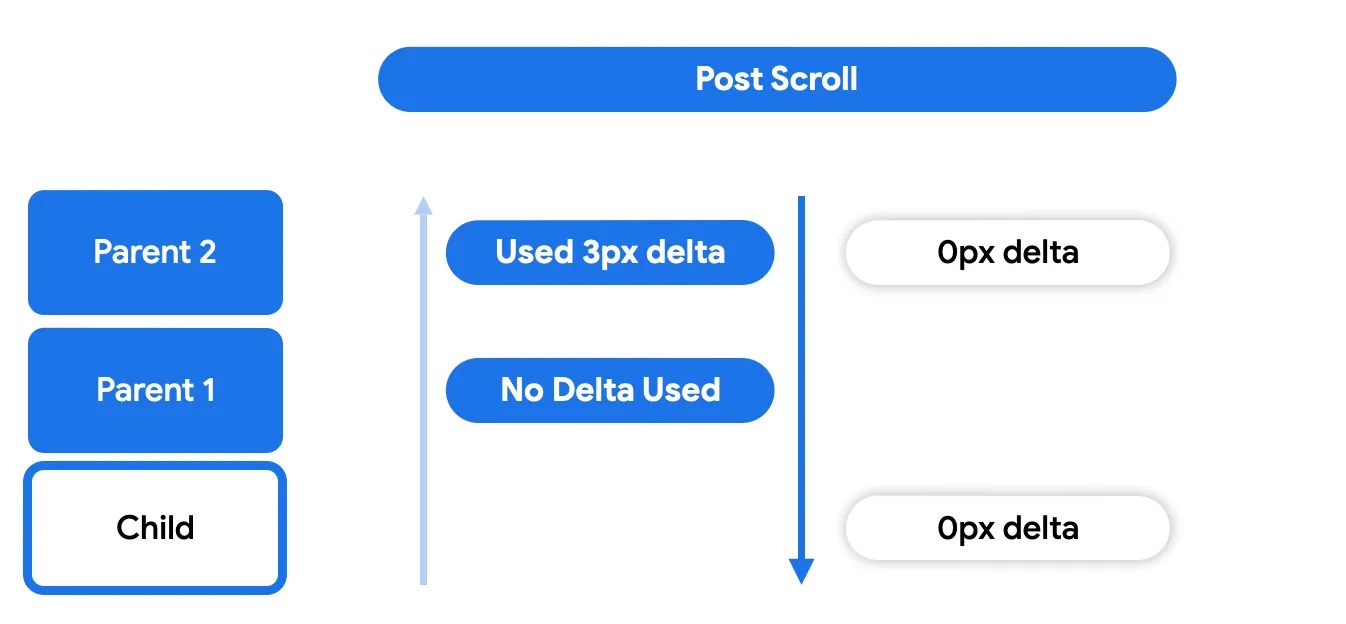
Finally, in the post-scroll phase, anything that the node itself didn't consume will be sent up again to its ancestors for consumption.
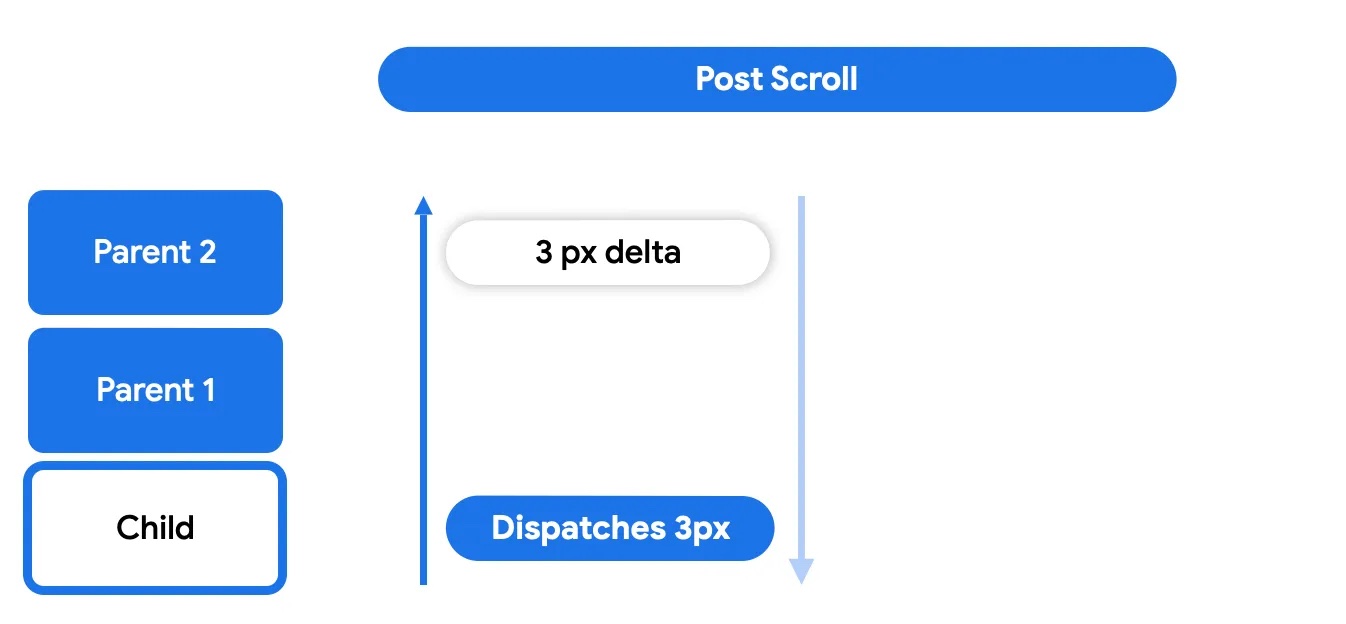
The post-scroll phase works in a similar way as the pre-scroll phase, where any of the parents may choose to consume or not.
Similarly to scroll, when a drag gesture finishes, the user's intention may be translated into a velocity that is used to fling (scroll using an animation) the scrollable container. The fling is also part of the nested scroll cycle, and the velocities generated by the drag event go through similar phases: pre-fling, node consumption, and post-fling. Note that fling animation is only associated with touch gesture and won't be triggered by other events, such as a11y or hardware scroll.
Participate in the nested scrolling cycle
Participation in the cycle means intercepting, consuming, and reporting the consumption of deltas along the hierarchy. Compose provides a set of tools to influence how the nested scrolling system works and how to interact directly with it, for example when you need to do something with the scroll deltas before a scrollable component even starts scrolling.
If the nested scroll cycle is a system acting on a chain of nodes, the
nestedScroll
modifier is a way of intercepting and inserting into these changes, and
influencing the data (scroll deltas) that are propagated in the chain. This
modifier can be placed anywhere in the hierarchy, and it communicates with
nested scroll modifier instances up the tree so it can share information through
this channel. The building blocks of this modifier are NestedScrollConnection
and NestedScrollDispatcher.
NestedScrollConnection
provides a way to respond to the phases of the nested scroll cycle and influence
the nested scroll system. It's composed of four callback methods, each
representing one of the consumption phases: pre/post-scroll and pre/post-fling:
val nestedScrollConnection = object : NestedScrollConnection { override fun onPreScroll(available: Offset, source: NestedScrollSource): Offset { println("Received onPreScroll callback.") return Offset.Zero } override fun onPostScroll( consumed: Offset, available: Offset, source: NestedScrollSource ): Offset { println("Received onPostScroll callback.") return Offset.Zero } }
Each callback also gives information about the delta being propagated:
available delta for that particular phase, and consumed delta consumed in
the previous phases. If at any point you want to stop propagating deltas up the
hierarchy, you can use the nested scroll connection to do so:
val disabledNestedScrollConnection = remember { object : NestedScrollConnection { override fun onPostScroll( consumed: Offset, available: Offset, source: NestedScrollSource ): Offset { return if (source == NestedScrollSource.SideEffect) { available } else { Offset.Zero } } } }
All callbacks provide information on the
NestedScrollSource
type.
NestedScrollDispatcher
initializes the nested scroll cycle. Using a dispatcher and calling its methods
triggers the cycle. Scrollable containers have a built-in dispatcher that sends
deltas captured during gestures into the system. For this reason, most use cases
of customizing nested scrolling involve using NestedScrollConnection instead
of a dispatcher, to react to already existing deltas rather than send new ones.
See
NestedScrollDispatcherSample
for more usages.
Resize an image on scroll
As the user scrolls, you can create a dynamic visual effect where the image changes size based on the scroll position.
Resize an image based on scroll position
This snippet demonstrates resizing an image within a LazyColumn based on
vertical scroll position. The image shrinks as the user scrolls down, and grows
as they scroll up, remaining within the defined minimum and maximum size bounds:
@Composable fun ImageResizeOnScrollExample( modifier: Modifier = Modifier, maxImageSize: Dp = 300.dp, minImageSize: Dp = 100.dp ) { var currentImageSize by remember { mutableStateOf(maxImageSize) } var imageScale by remember { mutableFloatStateOf(1f) } val nestedScrollConnection = remember { object : NestedScrollConnection { override fun onPreScroll(available: Offset, source: NestedScrollSource): Offset { // Calculate the change in image size based on scroll delta val delta = available.y val newImageSize = currentImageSize + delta.dp val previousImageSize = currentImageSize // Constrain the image size within the allowed bounds currentImageSize = newImageSize.coerceIn(minImageSize, maxImageSize) val consumed = currentImageSize - previousImageSize // Calculate the scale for the image imageScale = currentImageSize / maxImageSize // Return the consumed scroll amount return Offset(0f, consumed.value) } } } Box(Modifier.nestedScroll(nestedScrollConnection)) { LazyColumn( Modifier .fillMaxWidth() .padding(15.dp) .offset { IntOffset(0, currentImageSize.roundToPx()) } ) { // Placeholder list items items(100, key = { it }) { Text( text = "Item: $it", style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyLarge ) } } Image( painter = ColorPainter(Color.Red), contentDescription = "Red color image", Modifier .size(maxImageSize) .align(Alignment.TopCenter) .graphicsLayer { scaleX = imageScale scaleY = imageScale // Center the image vertically as it scales translationY = -(maxImageSize.toPx() - currentImageSize.toPx()) / 2f } ) } }
Key points about the code
- This code uses a
NestedScrollConnectionto intercept scroll events. onPreScrollcalculates the change in image size based on the scroll delta.- The
currentImageSizestate variable stores the current size of the image, constrained betweenminImageSizeandmaxImageSize. imageScalederives from thecurrentImageSize. - The
LazyColumnoffsets based on thecurrentImageSize. - The
Imageuses agraphicsLayermodifier to apply the calculated scale. - The
translationYwithin thegraphicsLayerensures the image remains centered vertically as it scales.
Result
The preceding snippet results in a scaling image effect on scroll:
Nested scrolling interop
When you try to nest scrollable View elements in scrollable composables, or
the other way around, you might encounter issues. Most noticeable ones would
happen when you scroll the child and reach its start or end bounds and expect
the parent to take the scrolling over. However, this expected behaviour either
might not happen or might not work as expected.
This issue is a result of the expectations built in scrollable composables.
Scrollable composables have a "nested-scroll-by-default" rule, which means that
any scrollable container must participate in the nested scroll chain, both as a
parent via
NestedScrollConnection,
and as a child via
NestedScrollDispatcher.
The child would then drive a nested scroll for the parent when the child is at
the bound. As an example, this rule allows Compose Pager and Compose LazyRow
to work well together. However, when interoperability scrolling is being done
with ViewPager2 or RecyclerView, since these don’t implement
NestedScrollingParent3,
the continuous scrolling from child to parent is not possible.
To enable nested scrolling interop API between scrollable View elements and
scrollable composables, nested in both directions, you can use the nested
scrolling interop API to mitigate these issues, in the following scenarios.
A cooperating parent View containing a child ComposeView
A cooperating parent View is one that already implements
NestedScrollingParent3
and therefore is able to receive scrolling deltas from a cooperating nested
child composable. ComposeView would act as a child in this case and would
need to (indirectly) implement
NestedScrollingChild3.
One example of a cooperating parent is
androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout.
If you need nested scrolling interoperability between scrollable View parent
containers and nested scrollable child composables, you can use
rememberNestedScrollInteropConnection().
rememberNestedScrollInteropConnection()
allows and remembers the
NestedScrollConnection
that enables nested scroll interoperability between a View parent that
implements
NestedScrollingParent3
and a Compose child. This should be used in conjunction with a
nestedScroll
modifier. Since nested scrolling is enabled by default on the Compose side, you
can use this connection to enable both nested scroll on the View side and add
the necessary glue logic between Views and composables.
A frequent use case is using CoordinatorLayout, CollapsingToolbarLayout and
a child composable, shown in this example:
<androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout android:id="@+id/app_bar" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="100dp" android:fitsSystemWindows="true"> <com.google.android.material.appbar.CollapsingToolbarLayout android:id="@+id/collapsing_toolbar_layout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:fitsSystemWindows="true" app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|exitUntilCollapsed"> <!--...--> </com.google.android.material.appbar.CollapsingToolbarLayout> </com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout> <androidx.compose.ui.platform.ComposeView android:id="@+id/compose_view" app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"/> </androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout>
In your Activity or Fragment, you need to set up your child composable and the
required
NestedScrollConnection:
open class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) findViewById<ComposeView>(R.id.compose_view).apply { setContent { val nestedScrollInterop = rememberNestedScrollInteropConnection() // Add the nested scroll connection to your top level @Composable element // using the nestedScroll modifier. LazyColumn(modifier = Modifier.nestedScroll(nestedScrollInterop)) { items(20) { item -> Box( modifier = Modifier .padding(16.dp) .height(56.dp) .fillMaxWidth() .background(Color.Gray), contentAlignment = Alignment.Center ) { Text(item.toString()) } } } } } } }
A parent composable containing a child AndroidView
This scenario covers the implementation of nested scrolling interop API on the
Compose side - when you have a parent composable containing a child
AndroidView. The AndroidView implements
NestedScrollDispatcher,
since it acts as a child to a Compose scrolling parent, as well as
NestedScrollingParent3
, since it acts as a parent to a View scrolling child. Compose parent will
then be able to receive nested scroll deltas from a nested scrollable child
View.
The following example shows how you can achieve nested scrolling interop in this scenario, along with a Compose collapsing toolbar:
@Composable
private fun NestedScrollInteropComposeParentWithAndroidChildExample() {
val toolbarHeightPx = with(LocalDensity.current) { ToolbarHeight.roundToPx().toFloat() }
val toolbarOffsetHeightPx = remember { mutableStateOf(0f) }
// Sets up the nested scroll connection between the Box composable parent
// and the child AndroidView containing the RecyclerView
val nestedScrollConnection = remember {
object : NestedScrollConnection {
override fun onPreScroll(available: Offset, source: NestedScrollSource): Offset {
// Updates the toolbar offset based on the scroll to enable
// collapsible behaviour
val delta = available.y
val newOffset = toolbarOffsetHeightPx.value + delta
toolbarOffsetHeightPx.value = newOffset.coerceIn(-toolbarHeightPx, 0f)
return Offset.Zero
}
}
}
Box(
Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.nestedScroll(nestedScrollConnection)
) {
TopAppBar(
modifier = Modifier
.height(ToolbarHeight)
.offset { IntOffset(x = 0, y = toolbarOffsetHeightPx.value.roundToInt()) }
)
AndroidView(
{ context ->
LayoutInflater.from(context)
.inflate(R.layout.view_in_compose_nested_scroll_interop, null).apply {
with(findViewById<RecyclerView>(R.id.main_list)) {
layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(context, VERTICAL, false)
adapter = NestedScrollInteropAdapter()
}
}.also {
// Nested scrolling interop is enabled when
// nested scroll is enabled for the root View
ViewCompat.setNestedScrollingEnabled(it, true)
}
},
// ...
)
}
}
private class NestedScrollInteropAdapter :
Adapter<NestedScrollInteropAdapter.NestedScrollInteropViewHolder>() {
val items = (1..10).map { it.toString() }
override fun onCreateViewHolder(
parent: ViewGroup,
viewType: Int
): NestedScrollInteropViewHolder {
return NestedScrollInteropViewHolder(
LayoutInflater.from(parent.context)
.inflate(R.layout.list_item, parent, false)
)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: NestedScrollInteropViewHolder, position: Int) {
// ...
}
class NestedScrollInteropViewHolder(view: View) : ViewHolder(view) {
fun bind(item: String) {
// ...
}
}
// ...
}
This example shows how you can use the API with a scrollable modifier:
@Composable
fun ViewInComposeNestedScrollInteropExample() {
Box(
Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.scrollable(rememberScrollableState {
// View component deltas should be reflected in Compose
// components that participate in nested scrolling
it
}, Orientation.Vertical)
) {
AndroidView(
{ context ->
LayoutInflater.from(context)
.inflate(android.R.layout.list_item, null)
.apply {
// Nested scrolling interop is enabled when
// nested scroll is enabled for the root View
ViewCompat.setNestedScrollingEnabled(this, true)
}
}
)
}
}
And finally, this example shows how nested scrolling interop API is used with
BottomSheetDialogFragment
to achieve a successful drag and dismiss behaviour:
class BottomSheetFragment : BottomSheetDialogFragment() {
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater,
container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View {
val rootView: View = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_bottom_sheet, container, false)
rootView.findViewById<ComposeView>(R.id.compose_view).apply {
setContent {
val nestedScrollInterop = rememberNestedScrollInteropConnection()
LazyColumn(
Modifier
.nestedScroll(nestedScrollInterop)
.fillMaxSize()
) {
item {
Text(text = "Bottom sheet title")
}
items(10) {
Text(
text = "List item number $it",
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
)
}
}
}
return rootView
}
}
}
Note that
rememberNestedScrollInteropConnection()
will install a
NestedScrollConnection
in the element you attach it to. NestedScrollConnection is responsible for
transmitting the deltas from the Compose level to the View level. This enables
the element to participate in nested scrolling, but it doesn't enable
scrolling of elements automatically. To composables that aren't scrollable
automatically, such as Box or Column, scroll deltas on such components won't
propagate in the nested scroll system and the deltas won't reach the
NestedScrollConnection provided by rememberNestedScrollInteropConnection(),
therefore those deltas won't reach the parent View component. To resolve this,
make sure you also set scrollable modifiers to these types of nested
composables. You can refer to the previous section on Nested
scrolling for more detailed
information.
A non-cooperating parent View containing a child ComposeView
A non-cooperating View is one that does not implement the necessary
NestedScrolling interfaces on the View side. Note that this means that
nested scrolling interoperability with these Views doesn't work out of the
box. Non-cooperating Views are RecyclerView and ViewPager2.
Additional resources
Recommended for you
- Note: link text is displayed when JavaScript is off
- Understand gestures
- Migrate
CoordinatorLayoutto Compose - Using Views in Compose
