In many cases, multilingual users set their system language to one language—such as English—but they want to select other languages for specific apps, such as Dutch, Chinese, or Hindi. To help apps provide a better experience for these users, Android 13 introduces the following features for apps that support multiple languages:
System settings: A centralized location where users can select a preferred language for each app.
You can configure your app to automatically generate the files needed to support per-app language preferences and show up in the system settings. To learn more, see the instructions for enabling automatic per-app language support.
Additional APIs: These public APIs, such as the
setApplicationLocales()andgetApplicationLocales()methods inLocaleManager, let apps set a different language from the system language at runtime.These APIs automatically sync with system settings; therefore, apps that use these APIs to create custom in-app language pickers will ensure their users have a consistent user experience regardless of where they select their language preferences. The public APIs also help you reduce the amount of boilerplate code, they support split APKs, and they support Auto Backup for Apps to store app-level user language settings.
For backward compatibility with previous Android versions, equivalent APIs are also available in AndroidX. However, the backward compatible APIs work with the AppCompatActivity context, not the application context, for Android 12 (API level 32) and earlier. Access the backward compatible APIs with Appcompat 1.6.0 or higher.
Overview of implementing this feature
The following table shows recommended implementations based on different use cases.
| Use case | Recommended implementation |
|---|---|
| Your app doesn't have an in-app language picker |
|
| Your app already has an in-app language picker |
|
System settings for users
Starting in Android 13, Android includes a centralized location in system settings for setting per-app language preferences. To ensure your app's languages are configurable in system settings on devices running Android 13 or higher, enable automatic per-app language support (recommended) or configure support manually.
Enable automatic per-app language support
Starting with Android Studio Giraffe and AGP 8.1, you can configure your app to
support per-app language
preferences
automatically. Based on your project resources, AGP generates the LocaleConfig
file and adds a reference to it in the final manifest file, so you no longer
have to do it manually. AGP uses the resources in the res folders of your app
modules and any library module dependencies to determine the locales to include
in the LocaleConfig file. This means that if you add resources for a new
language to your app, you don't have to worry about updating the LocaleConfig
file.
Note that the automatic per-app language feature supports apps that run Android
13 (API level 33) or higher. To use the feature, you must set
compileSdkVersion to 33 or higher. To configure per-app language preferences
for prior versions of Android, you still need to
use the APIs and in-app language pickers.
To enable automatic per-app language support, follow these steps:
- To turn the feature on, use the
generateLocaleConfigsetting in theandroidResources {}block of the module-levelbuild.gradle.ktsfile (build.gradlefile if you're using Groovy). The feature is off by default.Kotlin
android { androidResources { generateLocaleConfig = true } }
Groovy
android { androidResources { generateLocaleConfig true } }
- Specify a default locale:
- In the app module's
resfolder, create a new file calledresources.properties. In the
resources.propertiesfile, set the default locale with theunqualifiedResLocalelabel. To format the locale names, see How to form locale names.
- In the app module's
AGP adds this default locale and any
alternative locales
you've specified, using values-* directories in the res folder, to the
auto-generated LocaleConfig file.
How to form locale names
To form locale names, combine the language code with the optional script and region codes, separating each with a dash:
- Language: Use the two- or three-letter ISO 639-1 code.
- Script (optional): Use the ISO 15924code.
- Region (optional): Use either the two-letter ISO 3166-1-alpha-2 code or three-digit UN_M.49 code.
For example if your default locale is American English:
unqualifiedResLocale=en-US
Use android:localeConfig to add supported languages to system settings
You can manually set up your app to to ensure its languages are configurable in
system settings on devices running Android 13 or higher. To do this, create a
locales_config XML file and add it your app's manifest using the
android:localeConfig attribute. Omitting the android:localeConfig manifest
entry signals that users shouldn't be able to set your app's language
independent of their system language within their system settings.
To manually add your app's supported languages to a user's system settings:
Create a file called
res/xml/locales_config.xmland specify your app's languages, including your app's ultimate fallback locale, which is the locale specified inres/values/strings.xml.See How to form locale names for the format requirements. See also the sample
locale_config.xmlfile for a list of the most commonly used locales.For example, format the
locales_config.xmlfile like this for an app that supports the following languages:- English (United States) as the ultimate fallback locale
- English (United Kingdom)
- French
- Japanese
- Chinese (Simplified, Macau)
- Chinese (Traditional, Macau)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <locale-config xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <locale android:name="en-US"/> <locale android:name="en-GB"/> <locale android:name="fr"/> <locale android:name="ja"/> <locale android:name="zh-Hans-MO"/> <locale android:name="zh-Hant-MO"/> </locale-config>In the manifest, add a line pointing to this new file:
<manifest> ... <application ... android:localeConfig="@xml/locales_config"> </application> </manifest>
You can dynamically update your app's localeConfig with
LocaleManager.setOverrideLocaleConfig to customize the set of languages
displayed in the per-app language list in Android Settings. This lets you
customize the language list per region, run A/B experiments, and provide updated
locales if your app utilizes server-side localization pushes as shown in the
following example:
Kotlin
//For setOverrideLocaleConfig val localeManager = applicationContext .getSystemService(LocaleManager::class.java) localeManager.overrideLocaleConfig = LocaleConfig( LocaleList.forLanguageTags("en-US,ja-JP,zh-Hans-SG") ) //For getOverrideLocaleConfig // The app calls the API to get the override LocaleConfig val overrideLocaleConfig = localeManager.overrideLocaleConfig // If the returned overrideLocaleConfig isn't equal to NULL, then the app calls the API to get the supported Locales val supportedLocales = overrideLocaleConfig.supportedLocales()
Java
//For setOverrideLocaleConfig mContext.getSystemService(LocaleManager.class).setOverrideLocaleConfig(new LocaleConfig(LocaleList.forLanguageTags("en-US,ja-JP,zh-Hans-SG"))); //For getOverrideLocaleConfig // The app calls the API to get the override LocaleConfig LocaleConfig overrideLocaleConfig = mContext.getSystemService(LocaleManager.class).getOverrideLocaleConfig(); // If the returned overrideLocaleConfig isn't equal to NULL, then the app calls the API to get the supported Locales LocaleList supportedLocales = overrideLocaleConfig.getSupportedLocales();
Additionally, IMEs can now use
LocaleManager.getApplicationLocales
to know the UI language of the current app to update the keyboard language as
shown:
Kotlin
val currentAppLocales: LocaleList = applicationContext.getSystemService(LocaleManager::class.java).getApplicationLocales(appPackageName)
Java
LocaleList currentAppLocales = mContext.getSystemService(LocaleManager.class).getApplicationLocales(appPackageName);
Specify supported languages in Gradle
If not already present, specify the same languages using the
resourceConfigurations
property in your app's module-level build.gradle file:
android {
...
defaultConfig {
resourceConfigurations += ["en", "en-rGB", "fr", "ja", "b+zh+Hans+MO", "b+zh+Hant+MO"]
}
}
When the resourceConfigurations property is present, the build system only includes
language resource in the APK for these specified languages, preventing
translated strings from being included from other libraries that might support
languages that your app does not support. For more information, see
specify the languages your app supports.
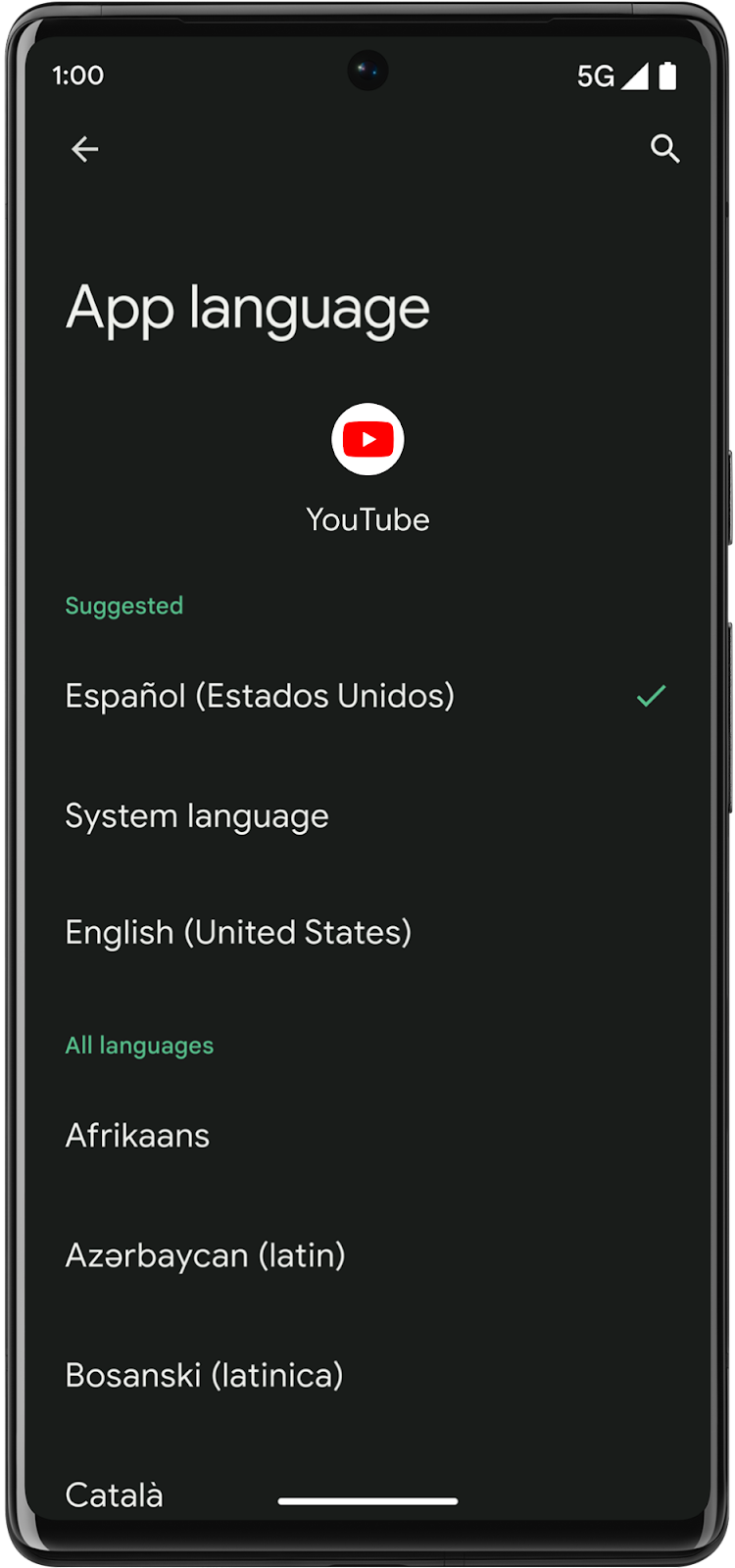
How users select an app language in system settings
Users can select their preferred language for each app through the system settings. They can access these settings in two different ways:
Access through the System settings
Settings > System > Languages & Input > App Languages > (select an app)
Access through Apps settings
Settings > Apps > (select an app) > Language
Handle in-app language pickers
For apps that already have an in-app language picker or want to use one, use the public APIs instead of custom app logic to handle setting and getting a user's preferred language for your app. If you use the public APIs for your in-app language picker, the device's system settings are automatically updated to match whichever language the user selects through your in-app experience.
For backward compatibility with previous Android versions, we strongly recommend using the AndroidX support library when implementing an in-app language picker. However, you can also implement the framework APIs directly if you need to.
Implement using the AndroidX support library
Use the setApplicationLocales() and getApplicationLocales()
methods in Appcompat 1.6.0
or higher. Note the backward compatible APIs work with the AppCompatActivity context,
not the application context, for Android 12 (API level 32) and earlier.
For example, to set a user's preferred language, you would ask the user to select a locale in the language picker, then set that value in the system:
Kotlin
val appLocale: LocaleListCompat = LocaleListCompat.forLanguageTags("xx-YY") // Call this on the main thread as it may require Activity.restart() AppCompatDelegate.setApplicationLocales(appLocale)
Java
LocaleListCompat appLocale = LocaleListCompat.forLanguageTags("xx-YY"); // Call this on the main thread as it may require Activity.restart() AppCompatDelegate.setApplicationLocales(appLocale);
Note that calling setApplicationLocales() recreates your Activity, unless
your app handles locale configuration
changes by itself.
Use AppCompatDelegate.getApplicationLocales() to retrieve the user's preferred locale. The user might have selected their app locale from system settings or from your in-app language picker.
Support Android 12 and lower
To support for devices running Android 12 (API level 32) and lower, tell
AndroidX to handle locale storage by setting an autoStoreLocales value to
true and android:enabled to false in the manifest entry for your app's
AppLocalesMetadataHolderService service, as shown in the following code
snippet:
<application
...
<service
android:name="androidx.appcompat.app.AppLocalesMetadataHolderService"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false">
<meta-data
android:name="autoStoreLocales"
android:value="true" />
</service>
...
</application>
Note that setting an autoStoreLocales value to true causes a blocking read
on the main thread and might cause a
StrictMode diskRead and
diskWrite violation if you are logging thread violations. See
AppCompatDelegate.setApplicationLocales()
for more information.
Custom storage handling
Omitting the manifest entry or setting autoStoreLocales to false signals
that you are handling your own storage. In this case, you must provide the
stored locales before onCreate in the activity lifecycle and gate calls to
AppCompatDelegate.setApplicationLocales() in Android 12 (API level 32) or
lower.
If your app has a custom locale storage location, we recommend using a one-time
handoff between your custom locale storage solution and autoStoreLocales so
users continue to enjoy your app in the language they prefer. This is especially
applicable in cases when your app is first run after a device has upgraded to
Android 13. In this case, you can provide pre-existing, user-requested locales
by retrieving the locales from your custom storage and passing the locales into
AppCompatDelegate.setApplicationLocales().
Implement using the Android framework APIs
While we strongly recommend that you use the AndroidX support library to
implement in-app language pickers, you can also use the
setApplicationLocales()
and getApplicationLocales()
methods in the Android framework for devices running Android 13.
For example, to set a user's preferred language, you would ask the user to select a locale in the language picker, then set that value in the system:
// 1. Inside an activity, in-app language picker gets an input locale "xx-YY"
// 2. App calls the API to set its locale
mContext.getSystemService(LocaleManager.class
).setApplicationLocales(new LocaleList(Locale.forLanguageTag("xx-YY")));
// 3. The system updates the locale and restarts the app, including any configuration updates
// 4. The app is now displayed in "xx-YY" language
To get a user's current preferred language to display in the language picker, your app can get the value back from the system:
// 1. App calls the API to get the preferred locale
LocaleList currentAppLocales =
mContext.getSystemService(LocaleManager.class).getApplicationLocales();
// 2. App uses the returned LocaleList to display languages to the user
Additional best practices
Take note of the following best practices.
Consider language when invoking an intent in another app
Language-focused intents might allow you to specify the language you want the
invoked app to be in. One example is the
EXTRA_LANGUAGE
feature from the Speech Recognizer API.
Consider the Accept-Language header for Chrome Custom tab
Consider adding the Accept-Language Header
through the Browser.EXTRA_HEADERS
to open a web page in your app's language when invoking a Chrome Custom tab.
If you remove per-app language preferences within system settings, reset your app locale to the system locale
If you remove your app's language preferences from system settings (by removing
android:localeConfig from your app's AndroidManifest.xml), users can't
easily reset their app language back to the system default.
For this reason, if you remove android:localeConfig, consider resetting the
app locale to the system locale using
LocaleListCompat.getEmptyLocaleList()
or
LocaleList.getEmptyLocaleList()
as seen in the following code snippet:
Kotlin
// Use the AndroidX APIs to reset to the system locale for backward and forward compatibility AppCompatDelegate.setApplicationLocales( LocaleListCompat.getEmptyLocaleList() ) // Or use the Framework APIs for Android 13 and above to reset to the system locale val context = LocalContext.current context.getSystemService(LocaleManager::class.java) .applicationLocales = LocaleList.getEmptyLocaleList()
Java
// Use the AndroidX APIs to reset to the system locale for backward and forward compatibility AppCompatDelegate.setApplicationLocales( LocaleListCompat.getEmptyLocaleList() ); // Or use the Framework APIs for Android 13 and above to reset to the system locale mContext.getSystemService(LocaleManager.class) .setApplicationLocales(LocaleList.getEmptyLocaleList());
Additional resources
See our code samples, blog articles, and videos for additional information.
- Per-App Language Preferences Part 1 blog
- Per-App Language Preferences Part 2 blog
- Sample Apps
- Building for a multilingual world video
Sample locale_config.xml file
By default, Android includes system-level translations in the Android Open
Source Project (AOSP) for a standard set of the most commonly-used locales.
The sample locale_config.xml file that's included in this section shows the
suggested format for each of these locales. Reference this sample file to help
you construct your own locale_config.xml file for the set of languages that
your app supports.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<locale-config xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<locale android:name="af"/> <!-- Afrikaans -->
<locale android:name="am"/> <!-- Amharic -->
<locale android:name="ar"/> <!-- Arabic -->
<locale android:name="as"/> <!-- Assamese -->
<locale android:name="az"/> <!-- Azerbaijani -->
<locale android:name="be"/> <!-- Belarusian -->
<locale android:name="bg"/> <!-- Bulgarian -->
<locale android:name="bn"/> <!-- Bengali -->
<locale android:name="bs"/> <!-- Bosnian -->
<locale android:name="ca"/> <!-- Catalan -->
<locale android:name="cs"/> <!-- Czech -->
<locale android:name="da"/> <!-- Danish -->
<locale android:name="de"/> <!-- German -->
<locale android:name="el"/> <!-- Greek -->
<locale android:name="en-AU"/> <!-- English (Australia) -->
<locale android:name="en-CA"/> <!-- English (Canada) -->
<locale android:name="en-GB"/> <!-- English (United Kingdom) -->
<locale android:name="en-IN"/> <!-- English (India) -->
<locale android:name="en-US"/> <!-- English (United States) -->
<locale android:name="es"/> <!-- Spanish (Spain) -->
<locale android:name="es-US"/> <!-- Spanish (United States) -->
<locale android:name="et"/> <!-- Estonian -->
<locale android:name="eu"/> <!-- Basque -->
<locale android:name="fa"/> <!-- Farsi -->
<locale android:name="fi"/> <!-- Finnish -->
<locale android:name="fil"/> <!-- Filipino -->
<locale android:name="fr"/> <!-- French (France) -->
<locale android:name="fr-CA"/> <!-- French (Canada) -->
<locale android:name="gl"/> <!-- Galician -->
<locale android:name="gu"/> <!-- Gujarati -->
<locale android:name="hi"/> <!-- Hindi -->
<locale android:name="hr"/> <!-- Croatian -->
<locale android:name="hu"/> <!-- Hungarian -->
<locale android:name="hy"/> <!-- Armenian -->
<locale android:name="in"/> <!-- Indonesian -->
<locale android:name="is"/> <!-- Icelandic -->
<locale android:name="it"/> <!-- Italian -->
<locale android:name="iw"/> <!-- Hebrew -->
<locale android:name="ja"/> <!-- Japanese -->
<locale android:name="ka"/> <!-- Georgian -->
<locale android:name="kk"/> <!-- Kazakh -->
<locale android:name="km"/> <!-- Khmer -->
<locale android:name="kn"/> <!-- Kannada -->
<locale android:name="ko"/> <!-- Korean -->
<locale android:name="ky"/> <!-- Kyrgyz -->
<locale android:name="lo"/> <!-- Lao -->
<locale android:name="lt"/> <!-- Lithuanian -->
<locale android:name="lv"/> <!-- Latvian -->
<locale android:name="mk"/> <!-- Macedonian -->
<locale android:name="ml"/> <!-- Malayalam -->
<locale android:name="mn"/> <!-- Mongolian -->
<locale android:name="mr"/> <!-- Marathi -->
<locale android:name="ms"/> <!-- Malay -->
<locale android:name="my"/> <!-- Burmese -->
<locale android:name="nb"/> <!-- Norwegian -->
<locale android:name="ne"/> <!-- Nepali -->
<locale android:name="nl"/> <!-- Dutch -->
<locale android:name="or"/> <!-- Odia -->
<locale android:name="pa"/> <!-- Punjabi -->
<locale android:name="pl"/> <!-- Polish -->
<locale android:name="pt-BR"/> <!-- Portuguese (Brazil) -->
<locale android:name="pt-PT"/> <!-- Portuguese (Portugal) -->
<locale android:name="ro"/> <!-- Romanian -->
<locale android:name="ru"/> <!-- Russian -->
<locale android:name="si"/> <!-- Sinhala -->
<locale android:name="sk"/> <!-- Slovak -->
<locale android:name="sl"/> <!-- Slovenian -->
<locale android:name="sq"/> <!-- Albanian -->
<locale android:name="sr"/> <!-- Serbian (Cyrillic) -->
<locale android:name="sr-Latn"/> <!-- Serbian (Latin) -->
<locale android:name="sv"/> <!-- Swedish -->
<locale android:name="sw"/> <!-- Swahili -->
<locale android:name="ta"/> <!-- Tamil -->
<locale android:name="te"/> <!-- Telugu -->
<locale android:name="th"/> <!-- Thai -->
<locale android:name="tr"/> <!-- Turkish -->
<locale android:name="uk"/> <!-- Ukrainian -->
<locale android:name="ur"/> <!-- Urdu -->
<locale android:name="uz"/> <!-- Uzbek -->
<locale android:name="vi"/> <!-- Vietnamese -->
<locale android:name="zh-Hans"/> <!-- Chinese (Simplified) -->
<locale android:name="zh-Hant"/> <!-- Chinese (Traditional) -->
<locale android:name="zu"/> <!-- Zulu -->
</locale-config>
