Use the steps in this guide to access your app’s asset packs from your C and C++ code.
Sample integration code is available on GitHub.
Build for Native
Use the following steps to build Play Asset Delivery into your project’s Android App Bundle. You don't need to use Android Studio to perform these steps.
Update the version of the Android Gradle plugin in your project’s
build.gradlefile to4.0.0or later.In the top-level directory of your project, create a directory for the asset pack. This directory name is used as the asset pack name. Asset pack names must start with a letter and can only contain letters, numbers, and underscores.
In the asset pack directory, create a
build.gradlefile and add the following code. Make sure to specify the name of the asset pack and only one delivery type:// In the asset pack’s build.gradle file: plugins { id 'com.android.asset-pack' } assetPack { packName = "asset-pack-name" // Directory name for the asset pack dynamicDelivery { deliveryType = "[ install-time | fast-follow | on-demand ]" } }
In the project’s app
build.gradlefile, add the name of every asset pack in your project as shown below:// In the app build.gradle file: android { ... assetPacks = [":asset-pack-name", ":asset-pack2-name"] }
In the project’s
settings.gradlefile, include all asset packs in your project as shown below:// In the settings.gradle file: include ':app' include ':asset-pack-name' include ':asset-pack2-name'
In the asset pack directory, create the following subdirectory:
src/main/assets.Place assets in the
src/main/assetsdirectory. You can create subdirectories in here as well. The directory structure for your app should now look like the following:build.gradlesettings.gradleapp/asset-pack-name/build.gradleasset-pack-name/src/main/assets/your-asset-directories
Build the Android App Bundle with Gradle. In the generated app bundle, the root-level directory now includes the following:
asset-pack-name/manifest/AndroidManifest.xml: Configures the asset pack’s identifier and delivery modeasset-pack-name/assets/your-asset-directories: Directory that contains all assets delivered as part of the asset pack
Gradle generates the manifest for each asset pack and outputs the
assets/directory for you.(Optional) Configure your app bundle to support different texture compression formats.
Integrate with Play Asset Delivery Library
You implement this API according to the delivery type of the asset pack you wish to access. These steps are shown in the following flowchart.
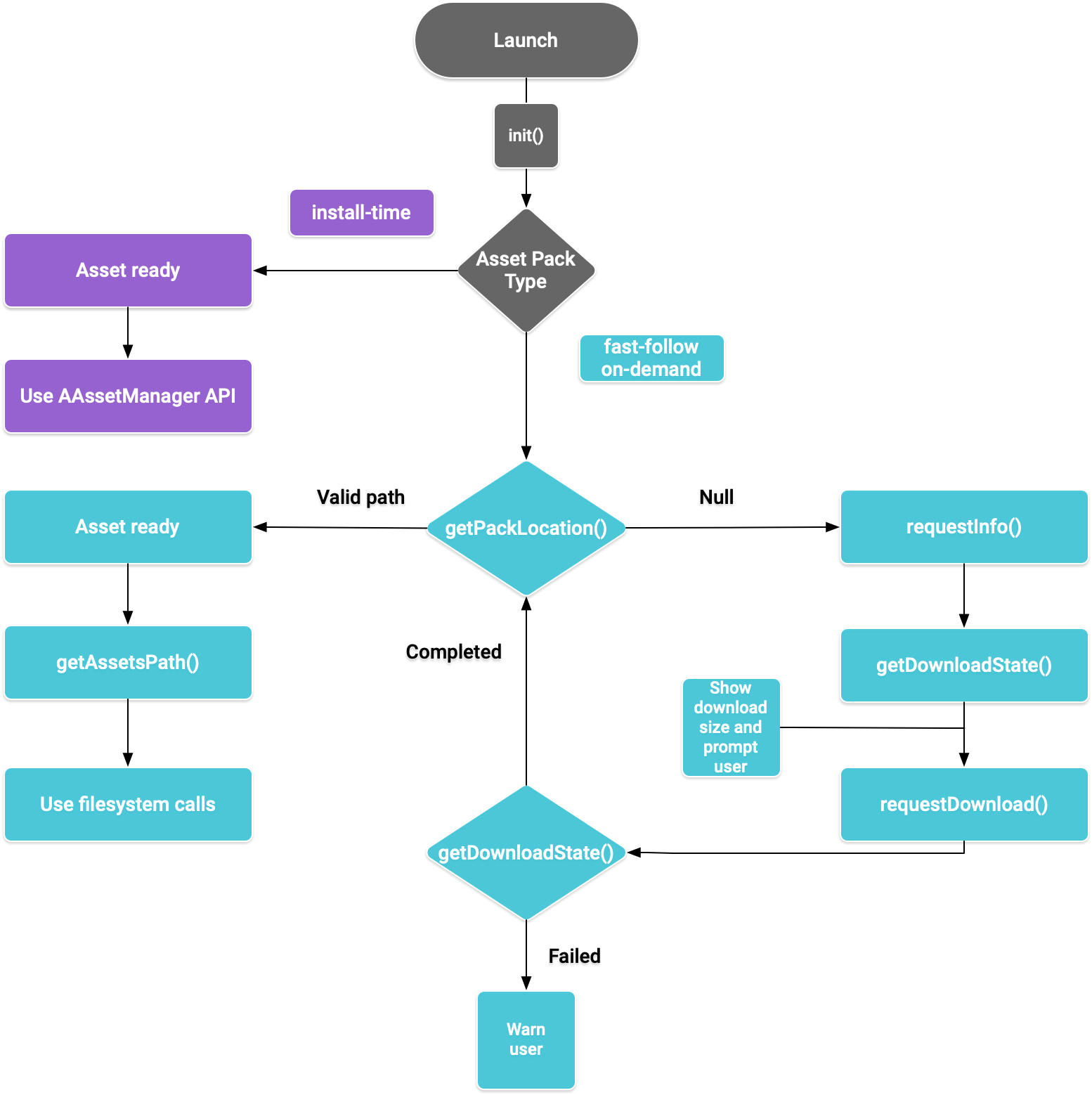
Figure 1. Flow diagram for accessing asset packs
The Play Core Native SDK provides the C header
file play/asset_pack.h for requesting asset packs, managing downloads, and
accessing the assets.
Set up your development environment for Play Core Native SDK
Download Play Core Native SDK
Before downloading, you must agree to the following terms and conditions.
Terms and Conditions
Last modified: September 24, 2020- By using the Play Core Software Development Kit, you agree to these terms in addition to the Google APIs Terms of Service ("API ToS"). If these terms are ever in conflict, these terms will take precedence over the API ToS. Please read these terms and the API ToS carefully.
- For purposes of these terms, "APIs" means Google's APIs, other developer services, and associated software, including any Redistributable Code.
- “Redistributable Code” means Google-provided object code or header files that call the APIs.
- Subject to these terms and the terms of the API ToS, you may copy and distribute Redistributable Code solely for inclusion as part of your API Client. Google and its licensors own all right, title and interest, including any and all intellectual property and other proprietary rights, in and to Redistributable Code. You will not modify, translate, or create derivative works of Redistributable Code.
- Google may make changes to these terms at any time with notice and the opportunity to decline further use of the Play Core Software Development Kit. Google will post notice of modifications to the terms at https://developer.android.com/guide/playcore/license. Changes will not be retroactive.
Do either of the following:
- Install Android Studio version 4.0 or higher. Use the SDK Manager UI to install Android SDK Platform version 10.0 (API level 29).
- Install the Android SDK command-line tools
and use
sdkmanagerto install Android SDK Platform version 10.0 (API level 29).
Prepare Android Studio for native development by using the SDK Manager to install the latest CMake and Android Native Development Kit (NDK). For more information on creating or importing native projects, see Getting Started with the NDK.
Download the zip file and extract it alongside your project.
Download Link Size SHA-256 Checksum 54.8 MiB 008b8fedc6179a6dc6ccc21af75591afc7036f78f3d5559d844f1b923934fef0 Update your app’s
build.gradlefile as shown below:Groovy
// App build.gradle plugins { id 'com.android.application' } // Define a path to the extracted Play Core SDK files. // If using a relative path, wrap it with file() since CMake requires absolute paths. def playcoreDir = file('../path/to/playcore-native-sdk') android { defaultConfig { ... externalNativeBuild { cmake { // Define the PLAYCORE_LOCATION directive. arguments "-DANDROID_STL=c++_static", "-DPLAYCORE_LOCATION=$playcoreDir" } } ndk { // Skip deprecated ABIs. Only required when using NDK 16 or earlier. abiFilters 'armeabi-v7a', 'arm64-v8a', 'x86', 'x86_64' } } buildTypes { release { // Include Play Core Library proguard config files to strip unused code while retaining the Java symbols needed for JNI. proguardFile '$playcoreDir/proguard/common.pgcfg' proguardFile '$playcoreDir/proguard/gms_task.pgcfg' proguardFile '$playcoreDir/proguard/per-feature-proguard-files' ... } debug { ... } } externalNativeBuild { cmake { path 'src/main/CMakeLists.txt' } } } dependencies { // Import these feature-specific AARs for each Google Play Core library. implementation 'com.google.android.play:app-update:2.1.0' implementation 'com.google.android.play:asset-delivery:2.3.0' implementation 'com.google.android.play:integrity:1.6.0' implementation 'com.google.android.play:review:2.0.2' // Import these common dependencies. implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-tasks:18.0.2' implementation files("$playcoreDir/playcore-native-metadata.jar") ... }
Kotlin
// App build.gradle plugins { id("com.android.application") } // Define a path to the extracted Play Core SDK files. // If using a relative path, wrap it with file() since CMake requires absolute paths. val playcoreDir = file("../path/to/playcore-native-sdk") android { defaultConfig { ... externalNativeBuild { cmake { // Define the PLAYCORE_LOCATION directive. arguments += listOf("-DANDROID_STL=c++_static", "-DPLAYCORE_LOCATION=$playcoreDir") } } ndk { // Skip deprecated ABIs. Only required when using NDK 16 or earlier. abiFilters.clear() abiFilters += listOf("armeabi-v7a", "arm64-v8a", "x86", "x86_64") } } buildTypes { release { // Include Play Core Library proguard config files to strip unused code while retaining the Java symbols needed for JNI. proguardFile("$playcoreDir/proguard/common.pgcfg") proguardFile("$playcoreDir/proguard/gms_task.pgcfg") proguardFile("$playcoreDir/proguard/per-feature-proguard-files") ... } debug { ... } } externalNativeBuild { cmake { path = "src/main/CMakeLists.txt" } } } dependencies { // Import these feature-specific AARs for each Google Play Core library. implementation("com.google.android.play:app-update:2.1.0") implementation("com.google.android.play:asset-delivery:2.3.0") implementation("com.google.android.play:integrity:1.6.0") implementation("com.google.android.play:review:2.0.2") // Import these common dependencies. implementation("com.google.android.gms:play-services-tasks:18.0.2") implementation(files("$playcoreDir/playcore-native-metadata.jar")) ... }
Update your app’s
CMakeLists.txtfiles as shown below:cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.6) ... # Add a static library called “playcore” built with the c++_static STL. include(${PLAYCORE_LOCATION}/playcore.cmake) add_playcore_static_library() // In this example “main” is your native code library, i.e. libmain.so. add_library(main SHARED ...) target_include_directories(main PRIVATE ${PLAYCORE_LOCATION}/include ...) target_link_libraries(main android playcore ...)
Data Collection
The Play Core Native SDK may collect version related data to allow Google to improve the product, including:
- App’s package name
- App’s package version
- Play Core Native SDK's version
This data will be collected when you upload your app package
to the Play Console. To opt-out of this data collection process, remove the
$playcoreDir/playcore-native-metadata.jar import in the build.gradle file.
Note, this data collection related to your use of the Play Core Native SDK and Google’s use of the collected data is separate and independent of Google’s collection of library dependencies declared in Gradle when you upload your app package to the Play Console.
Install-time delivery
Asset packs configured as install-time are immediately available at app
launch. Use the NDK AAssetManager API to access
assets served in this mode:
#include <android/asset_manager.h> #include <android_native_app_glue.h> ... AAssetManager* assetManager = app->activity->assetManager; AAsset* asset = AAssetManager_open(assetManager, "asset-name", AASSET_MODE_BUFFER); size_t assetLength = AAsset_getLength(asset); char* buffer = (char*) malloc(assetLength + 1); AAsset_read(asset, buffer, assetLength);
Fast-follow and on-demand delivery
The following sections show how to initialize the API, how to get information
about asset packs before downloading them, how to call the API to start the
download, and how to access the downloaded packs. These sections apply to
fast-follow and on-demand asset packs.
App launch
Always call AssetPackManager_init()
to initialize the asset pack API before calling any other
function. Check for any
asset pack error codes.
#include "play/asset_pack.h" ... AssetPackErrorCode AssetPackManager_init(JavaVM* jvm, jobject android_context);
Also be sure to call the following functions in the onPause() and onResume()
of
ANativeActivityCallbacks:
Get download information about asset packs
Apps are required to disclose the size of the download before fetching the asset
pack. Use the AssetPackManager_requestInfo() function to start an
asynchronous request for the size of the download and
whether the pack is already downloading. Then use
AssetPackManager_getDownloadState() to poll for the download state
(for example, call this function once per frame in your game loop). If a request
fails, check the asset pack error codes.
AssetPackErrorCode AssetPackManager_requestInfo(); // Call once AssetPackErrorCode AssetPackManager_getDownloadState(); // Call once per frame in your game loop
The AssetPackManager_getDownloadState() function returns the opaque type
AssetPackDownloadState
as an output pointer. Use this pointer to call the following functions:
AssetPackDownloadState* state; AssetPackErrorCode error_code = AssetPackManager_getDownloadState(asset-pack-name, &state); AssetPackDownloadStatus status = AssetPackDownloadState_getStatus(state); uint64_t downloadedBytes = AssetPackDownloadState_getBytesDownloaded(state); uint64_t totalBytes = AssetPackDownloadState_getTotalBytesToDownload(state)); AssetPackDownloadState_destroy(state);
Install
Use
AssetPackManager_requestDownload()
to start downloading an asset pack for the first time or to request for an asset
pack update to complete:
AssetPackErrorCode AssetPackManager_requestDownload(); // Call once AssetPackErrorCode AssetPackManager_getDownloadState(); // Call once per frame in your game loop
The AssetPackManager_getDownloadState() function returns the opaque type
AssetPackDownloadState.
For information on how to use this type, see
Get download information.
Large downloads
If the download is larger than 200MB and the user is not on Wi-Fi, the download
does not start until the user explicitly gives their consent to proceed with the
download using a mobile data connection. Similarly, if the download is large and
the user loses Wi-Fi, the download pauses and explicit consent is required to
proceed using a mobile data connection. A paused pack has state
WAITING_FOR_WIFI. To trigger the UI flow to prompt the user for consent, use
the following:
Required user confirmation
If a pack has the REQUIRES_USER_CONFIRMATION status, the download doesn't
proceed until the user accepts the dialog that is shown with
AssetPackManager_showConfirmationDialog(). This status can arise if the
app is not recognized by Play. Note that calling
AssetPackManager_showConfirmationDialog() in this case causes the app to be
updated. After the update, request the assets again.
Access asset packs
You can access an asset pack using file system calls after the download request
reaches the COMPLETED state. Each asset pack is stored in a separate directory
in the app's internal storage. Use
AssetPackManager_getAssetPackLocation()
to get an
AssetPackLocation
for the specified asset pack. Use
AssetPackLocation_getStorageMethod()
on that location to determine the storage method:
ASSET_PACK_STORAGE_APK: The asset pack is installed as an APK. See Install-time delivery to access these assets.ASSET_PACK_STORAGE_FILES: UseAssetPackLocation_getAssetsPath()to get a file path to the directory containing the assets, or null if the assets have not been downloaded. Do not modify downloaded files in this file path.
AssetPackLocation* location; AssetPackErrorCode error_code = AssetPackManager_getAssetPackLocation(asset-pack-name, &location); if (error_code == ASSET_PACK_NO_ERROR) { AssetPackStorageMethod storage_method = AssetPackLocation_getStorageMethod(location); const char* assets_path = AssetPackLocation_getAssetsPath(location); AssetPackLocation_destroy(location); }
Once you locate the assets, use functions like fopen or ifstream to access
the files.
Other Play Core API methods
The following are some additional API methods you may want to use in your app.
Cancel request
Use
AssetPackManager_cancelDownload()
to cancel an active asset pack request. Note that this request is a best-effort
operation.
Request removal
Use
AssetPackManager_requestRemoval()
to schedule the removal of an asset pack.
Next steps
Test Play Asset Delivery locally and from Google Play.
